IJCRR - 13(8), April, 2021
Pages: 41-47
Date of Publication: 25-Apr-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
The Morphometric Analysis of Human Adrenal Glands of Hanging and Poison Suicidal Death Cases in Different Age Group
Author: K. Manivannan, Kafeel Hussain, H.R. Krishna Rao, R. Sasikumar, D. Rama Manohara Reddy, P. Janaki Raman
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Suicide is complex interactions of mood disorders and which has been around for as long as since the birth of human society and is one of the leading causes of death in India and all around the world. Adrenal glands are a pair of endo�crine glands and target structure of the Hypothalamic Pituitary Adrenal axis and stress system. Stress plays an important role in affecting adrenal gland structure and function which may have a connection with suicidal behaviour in depressed individuals. Objective: To analyze the morphometric changes in length, breadth, thickness and weight of human adrenal glands in hanging and poison death autopsy cases in different age groups. Methods: Sample Size: 186 adrenals from 93 cadavers (52 hanging and 41 poison cases). Study Design: Analytical \?observational Study. Study setting: The samples were collected from Post mortem centre at Sri Venkateswara hospital, Chittoor district and divided into three age groups like 20-30, 30-40, 40-50 years. A study was done at Peoples Education Society Institute of Medical Sci�ences and Research, Kuppam. Chittoor District. The length, breadth, thickness and weight of the samples were measured and results were compared between hanging(sudden death) and poison death(delayed death) autopsy cases. Sampling Technique: Simple random sampling Inclusion Criteria: Both genders of Hanging and poison death cases,3 Age group 20-30 years, 30-40 years and 40-50years and time of autopsy in between 12-24 hours after death were included. Exclusion Criteria: The Adrenal abnormalities, Chronic debilitating illness, Decomposed autopsy cases, Pregnant women, Ac�cident cases, Burns cases, Age group less than 20 and more than 50years, Commence of autopsy less than 12 hrs and more than 24 hrs were excluded. Results: In our study, we found that the length and breadth of right and left adrenal glands were significantly different in the 31- 40 years group when compared to the other two groups. There was a significant difference in thickness of the right adrenal gland when compared with the left adrenal in the group of 31-40 years. When compared to the weight of right adrenals, there was a significant difference in the weight of the left adrenal in the age group of 31-40 years. Conclusion: The length, breadth, thickness and weight of the left and right adrenal glands were significantly different in the 31- 40 years age group and the values of parameters in hanging cases were high compare with poison cases in overall estimation.
Keywords: Adrenal gland, Hanging, Poison, Stress, Suicide
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Suicide is the outcome of complex interactions of biological, psychological, and environmental factors. It is an enormous public health problem in the United States and all around the world. Each year over 30,000 people in the United States and nearly 900,000 people worldwide die by suicide, making it one of the leading causes of death.1,2
It is the leading cause of death among teenagers and adults 15 to 49 years of age ranked among the top 13 causes of death for individuals of all ages worldwide by World Health Organization (WHO)3 and the National Safety Council rates it sixth in the United States.4
Eighty-four per cent of suicides occur only in India and China in the world.5 The World Health Organization reported that about 170,000 people die from suicide in India. However, India’s National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) – which report official suicide rates based on police reports – estimated only 135,000 suicides in the year 2017.5 Worldwide, more than 9 million deaths are annually reported of suicide, 20% are Indians, for 17% of the world population. Suicide is one of the three leading causes of death among people aged between 15–44 years in some countries and the second-leading cause of death aged between 10–24 years; these figures do not include the suicide attempts, which are up to 20 times more frequent than completed suicide.6
Adrenal glands (AG) are a pair of endocrine glands yellowish-brown in colour due to their content of lipids which are important for the sustainability of life to provide the general physiological organization of the organism in the body.AG also being known as adrenals, suprarenal or suprarenal gland is just due to its locations related to the kidneys.7,8
AG are triangular-shaped endocrine glands located on the posterior wall of the abdomen on the antero-superior aspect of the upper end of each kidney at the L1 vertebrae level. Each gland measures 5 cm in length, 3 cm in breadth, 1 cm in thickness and 5 gm weight.9-11 Right adrenal gland (RAG) is a pyramid-shaped gland that is located close to the inferior vena cava (IVC) which connected by the right adrenal vein and is in strong contact with the uncovered area of the liver. The left adrenal gland (LAG) is semilunar shaped and slightly longer and wider compared to the right one. It is neighbored by the abdominal aorta and the cardiac end of the stomach. The anterior surface of the gland is related to the pancreas, splenic artery and with spleen partially in the Lower part
The shape and structure of the glands can change due to many diseases. Clinical studies have shown that stress plays an important role in affecting adrenal gland structure and function. In particular, adrenal gland size is partially regulated by adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulation12, which is known to regulate stress corticosterone levels during the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis activation due to acute physical or mental stress.13 Elevation of plasma cortisol level and enlargement of adrenals have been found in those who suffer from chronic stress and in depressed patients14, and increases in adrenal weight have been found in individuals who have committed suicide.15
The present study aims to analyze the morphometric changes in the dimensions of adrenal glands such as length, breadth, thickness and weight in hanging which belongs to chronic stress sudden death and poison which belongs to chronic stress and delayed death after intake of poison. This study will be useful for forensic surgeons, Forensic Pathologist and the Medico-legal fraternity to determine the changes in adrenals.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The analytical comparative study was done after approval by the institutional human ethical committee at PES institute of medical sciences and research, Kuppam, Chittoor district. A total of 186 suprarenal glands obtained from 93 autopsy cadavers those belongs to hanging (52 cases) and poison (41 cases) and age between 20 to 50 years were included in this study and divided into three age groups such as 20-30 yrs (43 cases), 31-40 yrs (26cases) and 41-50 yrs (24 cases) when undergone postmortem examination in Sri Venkateswara hospital, Tirupati, Chittoor district, Andhra Pradesh in the years 2018 and 2019. The usual dissection kit was used to clean and dissect the adrenal gland specimens after stored in 10% formalin for preservation and fixation for up to twelve to twenty-four hours to prevent autolysis, to reduce the shrinkage and distortion (IHEC no-21).
The length, breadth, thickness of the right and left adrenal glands were measured with Vernier calliper and the weight of the glands were checked with a digital weighing machine with an accuracy of 0.1mg(ShimadzuAY220 Analytical balancer max 220gm min 10mg, Mettler-Toledo India Private Limited Mumbai e=1mg d=0.1mg)after dissecting the suprarenal glands meticulously by removing the surrounding fat and fascia. The lengths of both right and left adrenal glands were measured at the base of the gland (Figure 1), the part which is related to kidneys. The breadth of the right adrenal gland was measured from apex to base (Figure 2). The breadth of the left adrenal gland was measured at the level of the middle of the gland. The thickness of the glands was measured at the level of the hilum of both glands to maintain the uniformity where the suprarenal vein is coming out of the glands (Figure 3). The weight was measured with the digital weighing machine with an accuracy of 0.1mg (Figure 4).


Inclusion Criteria
Both genders of suicidal (Hanging and poison) death cases
3 Age group 20-30 years, 30-40 years and 40-50years
Time of autopsy in between 12-24 hours after death
Exclusion Criteria
Adrenal abnormalities
Chronic debilitating illness
Decomposed autopsy cases
Pregnant women
Accident cases
Burns
Age group less than 20 and more than 50
Commence of autopsy less than 12 hrs and more than 24 hrs.
Statistical Analysis
An Independent t-test was performed using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) for Window version 21.0 software. Values of p<0.05 was considered to be significant.
RESULTS
Data depicted in Table-1 represent the age-wise distribution of suicidal and accidental hanging and poisoning cases. Among the 93 cases, 43 were 20-30 years, -26 were 31-40 years and 24 were 41-50 years. The age Grade representing (20-30 years) has the highest incidence of suicidal cases (Hanging 31% and Poison 15%) accounting for (46%) in the younger age group, the 2nd highest incidence of suicidal cases (Hanging 16 % and Poison 12%) accounting to (28%) in the age group 31-40 years and least incidence of suicidal cases in older age group i.e. 41 to 50 years.
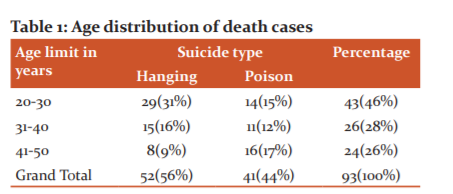
Table 2 and graph 1shows the length, breadth, thickness and weight of right and left adrenal glands of both hanging and poison suicidal cases. It is evident that the number of hanging suicidal case is high, maximum in the younger age group and the 2nd highest incidence in poison suicidal case, maximum in the older age group
Table 2: The comparison of length, breadth, thickness and weight of right and left adrenal glands of hanging and poison suicidal cases in 20-50 years and 12-24hours after death, values are expressed as Mean±SD in CMs and weight in gms
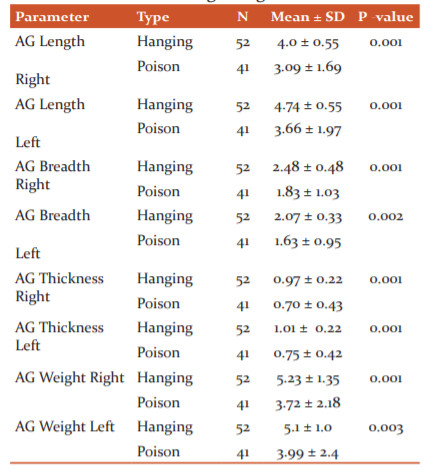
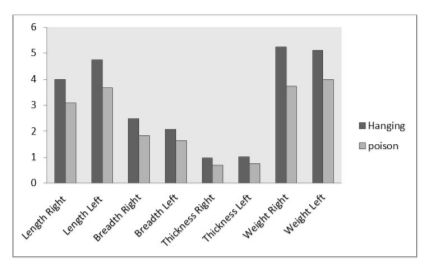
Graph 1: The comparison of length, breadth, thickness and weight of right and left adrenal glands of hanging and poison suicidal cases in 20-50 years. Y axis represents values in cm.
Table 3shows the length of the right and left adrenal gland in different age group, the young age groups (20-30 years) show a higher length than the other two age groups. The right and left adrenal length of suicidal death cases were compared age-wise. There was a significant difference in the 20-30 years age group (P < 0.001) and 41-50 years age group (P < 0.001) of both hanging and poison suicidal cases. There was no significant difference in the 31-40 years age group.
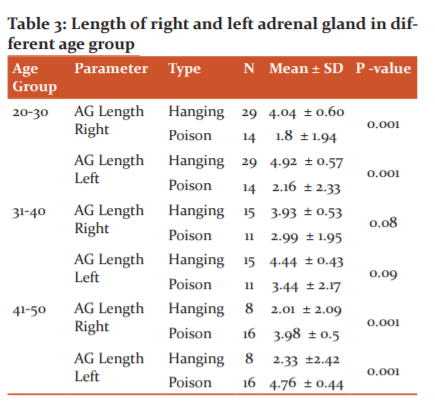
Table 4 shows the breadth of the right and left adrenal gland in different age group, the middle age groups (20-30 years) of the right adrenal show a higher breadth than the other two age groups. The right and left adrenal breadth of suicidal death cases were compared age-wise. There was a significant difference in both right and left adrenal in the 20-30 years age group (P < 0.001) and 41-50 years age group (P< 0.004 & P< 0.001) respectively, of both hanging and poison suicidal cases. But there was no significant difference in the 31-40 years age group.
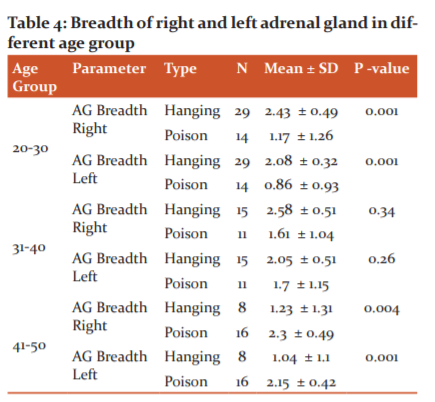
Table 5 shows the thickness of the right and left adrenal gland in different age group, the younger age groups (20-30 years) shows a higher thickness than the other two age groups. The right and left adrenal thickness of suicidal death cases were compared age-wise. There was a significant difference in both right and left adrenal in the 20-30 years age group (P < 0.001) and the 41-50 years age group (P < 0.001) of both hanging and poison suicidal cases. But there was no significant difference in the right adrenal glands when compared to the left adrenal in the 31-40 years age group.
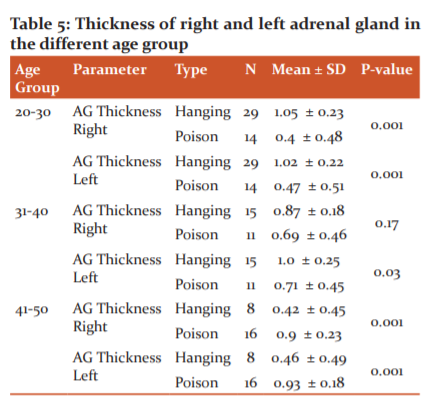
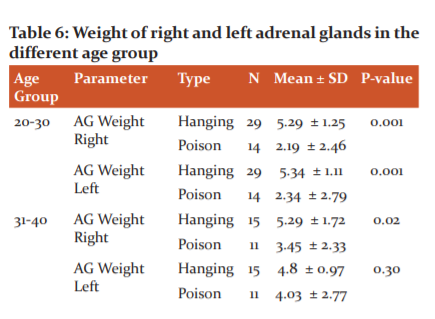
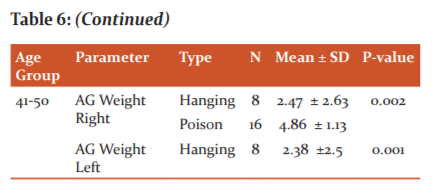
Table 6 shows the weight of right and left adrenal gland in different age group, the older age groups (40-50 years) shows a lower weight than the other two age groups. The right and left adrenal weight of suicidal death cases were compared age-wise. There was a significant difference in both right and left adrenal in the 20-30 years age group (P < 0.001) and the 41-50 years age group (P < 0.001) of both hanging and poison suicidal cases. But there was no significant difference in the left adrenal glands when compared to the right adrenal in the 31-40 years age group.
DISCUSSION
In our study, we found that the right and left adrenal length and breadth have significantly differed in the 31-40 years group when compared to the other two groups. There was a significant difference in thickness of the right adrenal gland when compared with the left adrenal in the group of 31-40 years. When compared to the right weight of the adrenal, there was a significant difference in the left weight of adrenalin in the age group of 31-40 years.
Probably, the reason or maximum sufferers in the age group of 31-40 years is due to a sudden emotional outburst, early marriage, frustration, failure to cope with stress and strain of life at middle age, poverty, unemployment etc. HPA and sympathetic adrenomedullary axis are the systems mainly involved in maintaining homeostasis during the stress response, and the adrenal is essential to the stress responding organ common to both systems.
Dorovini-Zis K and Zis AP had done an investigation on the expanded adrenal gland in casualties of suicide among the Canadian population, and adrenal gland weight was significantly higher in victims of violent suicide than those who died suddenly from an accidental cause. The mean±SD joined weight of both adrenal glands was fundamentally higher for the suicidal group (9.77±1.74 g) than for the accidental group (7.74±0.82g).16 These results have a resemblance with our study results which analyzed individually.
Szigethy E et al. had examined 'Adrenal weight and morphology in victims of suicide’ and their outcomes demonstrated a positive relationship like our study between's adrenal weight and total cortical thickness in both left and right glands, giving direct proof that expanded adrenal weight in suicide victims is because of cortical hypertrophy.17 Previous studies have shown that more patients with depression had increased plasma cortisol level and enlargement of adrenals.18-20 Depression is a stress-related disorder and it is one of the common cause of suicide. Many depressed patients have altered Hypothalamic Pituitary Adrenal (HPA) axis physiology that is characterized by increased HPA axis functional activity21 and enlargement of adrenal glands.22
Many studies showed that this increase in adrenal weight is associated with the increased size of the adrenal cortex23, and many depressed patients have exaggerated cortisol responses after ACTH administration. Furthermore, the level of glucocorticoids has been connected with the severity of depression which indicating that alterations in structure and function of the HPA axis may also be relevant and these alterations have a connection with depression and suicidal thoughts.24 Arpita Sarkar et al found in their study that the adrenal glands on the right side had a mean weight for suicide group 9.57 grams and accidental group 6.64 grams, and adrenal gland of left side had mean weight for suicide group of 10.06 grams and in the accidental group was 7.13 grams. The mean and the standard deviation for the weight of right and left adrenal glands were significantly higher for the suicide group than the control group which corroborates with the findings of this study.25
CONCLUSION
Considering the basic role of adrenalin coping up with stress, the human model of morphological study of the adrenal gland has been taken up to correlate the morphological (Adrenal length, breadth, thickness and weight) features in the confirmed suicidal cases. There was a significant difference in right and left adrenal length and breadth in the 31-40 years group. There was a significant difference in the right thickness of the adrenal gland when compared with the left adrenal in the group of 31-40 years. When compared to the right weight of the adrenal, there was a significant difference in the left weight of the adrenal in the age group of 31-40 years. Further works in this regard are needed in showing more light on the medico-legal problems occurring from time to time. Thus this present study concludes that there was a difference in length, breadth, thickness and weight in the age from 31-40 years.
Ethical approval and consent to participate: The ethical approval obtained from the institutional human ethical committee at PES institute of medical sciences and research and consent from blood relatives of deceased during the autopsies (IHEC no-21)
Consent to publish: Applicable
Author’s contribution: Project development, data collection and management, data analysis and manuscript writing1 data analysis, manuscript editing and overall supervision2., Data analysis and manuscript editing3., Data analysis and manuscript editing4., Collection of samples, data analysis, manuscript editing5., Statistical analysis.6 All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Availability of Data and materials
Please contact the author for data request ( Manivannan- e-mail Address: maniroopaa@gmail.com)
Declaration of Competing Interest: The authors have declared that they have no competing interests.
Conflict of interest: No Conflict of interest
Acknowledgements:
"Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed."
Financial support:
This Research project did not receive any grants from any specific funding agency or third party.
References:
-
World Health Organization. Prevention of suicide: guidelines for the formulation and implementation of national strategies. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 1996.
-
US Public Health Service. The Surgeon General’s call to action to prevent suicide. Washington, DC: US Public Health Service; 1999.
-
Meier RF, Clinard MB. Sociology of deviant behaviour. 14th ed. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Cengage Learning; 2008:169.
-
Bertolote JM, Fleischmann A. Suicide and psychiatric diagnosis: a worldwide perspective. World Psychiatry 2002;1(3):181–185.
-
National Crime Records Bureau. Accidental Deaths and Suicides in India. New Delhi: Government of India; 2008.
-
World Health Organization Report. Suicide prevention. <http:// www.who.int/mental_health/prevention/suicide/suicideprevents/ en/>; 2009 accessed 13.08.10.
-
Moore KL, Persaud TVN. The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology. 5th ed. Philadelphia W. B. Saunders; 1993.
-
Anand LN, Vijayan. Studies on the effect of intratesticular administration of opioid peptides, naloxone or N-acetyl beta-endorphin antiserum on some testicular parameters in rats. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 1998;42(1):107-12.
-
Datta AK. Essentials of Human Anatomy: Thorax and Abdomen.4th edition. Kolkata(India): Current Books International; 2005, p147-149.
-
Chaurasia BD. Textbook of Human Anatomy. Volume (2) Lower limb Abdomen and pelvis. 4th edition. Bengaluru(India): CBS Publishers and distributors;2004, p305.
-
Ranganathan TS. A Textbook of Human Anatomy. 6th edition. New Delhi (India):S.Chand & Company Ltd; 2006. p343-6.
-
Edwin D, Bransome JR. Regulation of adrenal growth. Differences in the effects of ACTH in normal and dexamethasone-suppressed guinea pigs. Endocrinology1968; 83(5): 956-64.
-
Solberg LC, Baum AE, Ahmadiyeh N, Shimomura K, Li R, Fred W, et al. Genetic analysis of the stress-responsive adrenocortical axis. Physiol Genom 2006;27:362-369.
-
Gelfman NA. Morphological change of adrenal cortex in disease. Yale J Bio Med 1964; 37(1):31-54.
-
Dumser T, Barocka A, Schuber Et. Weight of Adrenal Glands May Be Increased in Persons Who Commit Suicide. Am J Forens Med Pathol 1998;19(1):72-76.
-
Dorovini-Zis K, Zis AP. Increased adrenal weight in victims of violent suicide. Am J Psychiatry 1987;144:1214-15.
-
Szigethy E, Conwell Y, Forbes NT, Cox C, Caine ED. Adrenal weight and morphology in victims of completed suicide. Biol Psychiatry 1994;36(6):374-80.
-
Amsterdam JD, Marinelli DL, Arger P, Winokur A. Assessment of adrenal gland volume by computed tomography in depressed patients and healthy volunteers: a pilot study. Psychiatry Res 1987; 21(3):189-97.
-
Caroll BJ, Curtis GC, Mendels J. Neuroendocrine regulation in depression II. Discrimination of depressed from non depressed patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1976; 33(9):1051-58.
-
Dorovini-Zis K, Barocka A, Schubert E. Weight of adrenal glands may be increased in persons who commit suicide. Am J Forens Med Pathol 1998;19:72-76.
-
Sachar EJ, Hellman L, Roffwarg HP, Halpern FS, Fukushima DK, Gallagher TF. Disrupted 24-hour patterns of cortisol secretion in psychotic depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1973; 28(1):19-24.
-
Siddiqua D, Ara S, NurunnabiASM, Ahmed R, Hosne AP. A postmortem study on the weight of the human adrenal glands. Bangla J Med Sci 2010;9(4):204-207.
-
Willenberg HS, Bornstein SR, Dumser T, Bornstein ME, barocka A, Chrousos GP, et al. Morphological changes in adrenals from victims of suicide about altered apoptosis. Endocrine Res 1998;24(34):963-967.
-
Yvonne M Ulrich-Lai, Helmer F Figueiredo, Michelle M Ostrander, Dennis C Choi, Wiiliam C Engeland, James P Herman. Chronic stress induces adrenal hyperplasia and hypertrophy in a subregion-specific manner. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2006; 291:965-73.
-
Sarkar A, Chatterjee M, Batabyal S. A post mortem study on the weight and morphology of adrenal glands in victims of suicide. Int J Curr Res Rev 2014; 6(1):21-27.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License