IJCRR - 7(4), February, 2015
Pages: 48-53
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
EFFECT OF INCREASED ADIPOSITY ON OCULAR PERFUSION PRESSURE IN YOUNG ADULTS
Author: Rajalakshmi R., Gowd Aruna R.
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: The objective of this study was to study the effect of increased adiposity on Ocular Perfusion Pressure (OPP) and its relation with obesity indices. Methods: The study included 82 subjects grouped into two based on their Body Mass Index (BMI) as obese group (n=41) and Normal group (n=41). Blood Pressure was measured using sphygmomanometer. Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) was calculated. Intraocular Pressure (IOP) was recorded using Schiotz indentation tonometer after anaesthetizing the cornea with 2% paracaine solution. OPP was calculated as 2/3 the MAP minus IOP, Systolic Ocular Perfusion Pressure (SOPP) was calculated by Systolic Blood Pressure minus IOP and Diastolic Ocular Perfusion Pressure (DOPP) was calculated by Diastolic Blood Pressure minus IOP. Statistical analysis was performed using the SPSS version 19.
Results: Resting mean SBP, DBP, MAP, IOP, OPP, SOPP & DOPP were significantly higher (p< 0.05) in the obese group. IOP, OPP, SOPP & DOPP were significantly positively correlated with all the obesity indices. BMI was the most important individual parameter in prediction of IOP where as WHR & WC was the major predictors for OPP, SOPP and DOPP. Conclusions: The study thus shows that Ocular perfusion pressures were significantly affected by the increase in adiposity inyoung adults
Keywords: Obesity, Ocular perfusion pressure, Obesity indices
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Obesity is characterized by the accumulation of excess adipose tissue and can occur as a result of white adipose tissue enlargement, caused by adipocytes hyperplasia and/or hypertrophy1 . Obesity is a complex condition resulting from the interplay among genetics, environment, and lifestyle2 . The prevalence of obesity has increased dramatically as a result of our modern lifestyle and is one of the most important targets of public health programs and its associated pathological conditions3 . The normal functioning of tissues depends on the maintenance of an adequate perfusion, with sufficient blood flow. Presence of ample perfusion pressure is necessary to meet tissue needs and this requires a balance between arterial and venous blood pressure4 . Ocular Perfusion Pressure (OPP) is expressed as the difference between the arterial BP and the intraocular pressure (IOP), which is considered a substitute for the venous pressure. The perfusion pressure equals 2/3 the Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) minus IOP 5 . Alterations in ocular perfusion could cause ischemia and thus reduced perfusion of tissues in the optic nerve can have deleterious effects4 . The relationship between obesity and hypertension is well established both in adults and children6, 7. Obese individuals exhibit higher blood pressure levels than non obese individuals even in the normotensive range. Thus the combination of obesity and hypertension increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases 8 . Obesity is characterized by increase intraorbital fat and episcleral venous pressure which may contribute to increase in IOP9, 10. High IOP is a major risk factor for glaucoma and is related to optic nerve damage even in case of normal pressure glaucoma 11. Hence we hypothesize that variation in MAP & IOP can lead to variation in OPP in obese persons. Thus this study was undertaken to know the effect of obesity on OPP and to evaluate the independent association of obesity indices with OPP in healthy young adults of Indian population.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This is a comparative study done on the first year medical students (n = 150). Subjects were screened using a questionnaire which included inclusion and exclusion criteria’s and by physical examination for their age, history of hypertension, cardiac or pulmonary diseases, eye disorders, other factors affecting IOP, smoking and consumption of alcohols. The weight, height Waist Circumference (WC) and Hip Circumference were measured for each subject. BMI was calculated as weight (kg) / height (mt)2 and Waist Hip Ratio (WHR) was computed. Subjects fitting the inclusion and exclusion criteria’s (n = 115) were considered for the study. Overweight subjects (n=15) and subjects with refractive errors (n=20) were excluded. Subjects were divided into two groups depending on BMI cut off for Indian population. Study group was formed by obese subjects with BMI ≥ 25 Kg.m2 (n = 41) and Control group was formed by normal weight subjects with BMI 18.5 to 22.9 Kg.m2 ( n=41). Out of 74 normal weight subjects 41 were selected randomly by using random number table. Thus the study consisted of two group’s namely Normal Weight (NW) and obese groups. This sample size was estimated to be enough to detect a clinically relevant difference of 10% in the parameters under study at 5% level of significance with 80% power. The study was approved by the Ethical committee of Institution. Subjects were informed about the purpose of the study, the study protocol and the informed consent was obtained. Study was carried out in the research laboratory in the department between 3 to 5 PM by a single observer in a quiet room. Subjects were briefed again about the experiment protocol and were allowed to relax for 10 minutes. Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure were measured in sitting posture with a standard mercury sphygmomanometer. Pulse Pressure (PP) and Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) were calculated. IOP was recorded using Schiotz indentation tonometer after anaesthetizing the cornea with 2% paracaine solution. OPP was calculated 2/3 the MAP minus IOP, Systolic Ocular Perfusion Pressure (SOPP) was calculated by SBP minus IOP and Diastolic Ocular Perfusion Pressure (DOPP) was calculated by DBP minus IOP. Descriptive statistics with mean and Standard Deviation (SD) were calculated. Inferential statistical analysis Independent sample t-test, Pearson’s correlation and regression analysis were performed using the SPSS version 19. p Value < 0.05 are considered to be significant.
RESULTS
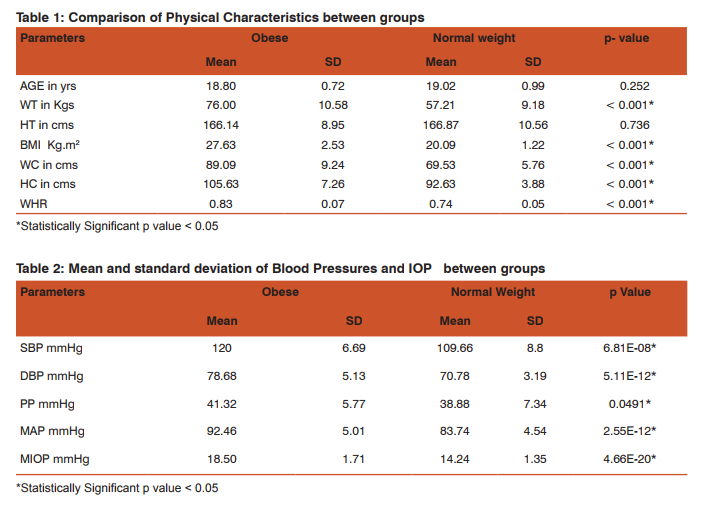
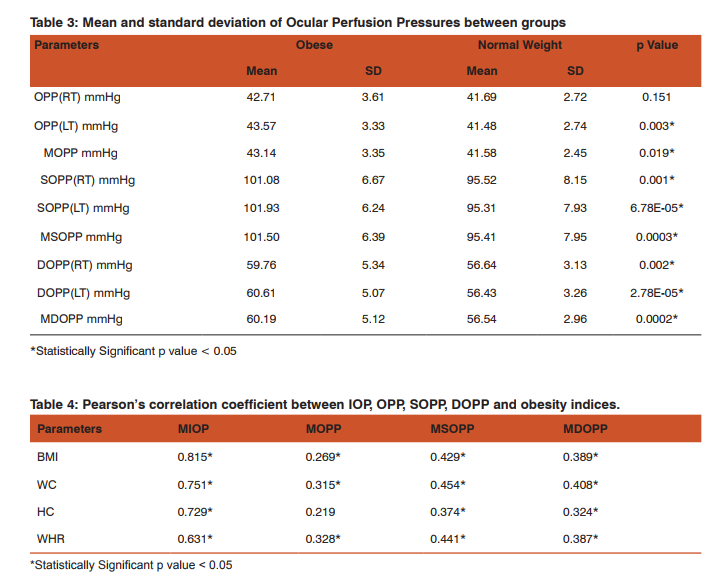
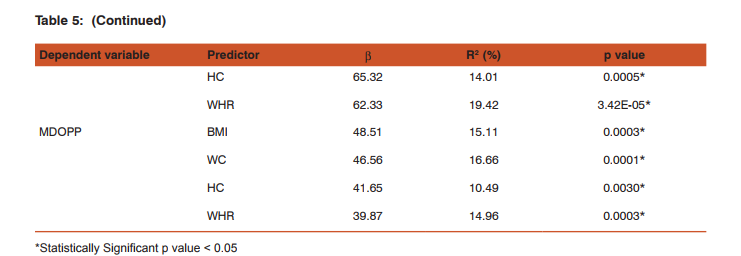
The study included 82 young adults in the age group of 18 to 21 yrs (obese group n=41 & NW group n=41). The physical characteristics of the two groups are represented in Table 1. There was significant difference in Weight, BMI, WC, HC & WHR between the two groups. Age and Height showed no significant difference between the two groups. Resting mean level of SBP, DBP & MAP among obese young adults was significantly higher (p<0.05) as compared to the normal weight group (Table 2). MIOP, MOPP, MSOPP & MDOPP were significantly higher in the obese group when compared to normal weight group (Table 3). Pearson’s correlation analysis (Table 4) showed that MIOP, MSOPP & MDOPP were significantly positively correlated with all the obesity indices whereas MOPP was significantly positively correlated with BMI, WC & WHR. Table 5 shows results of simple linear regression analysis for MIOP, MOPP, MSOPP & MDOPP which was significantly correlated with obesity indices. BMI was the most important individual parameter in prediction of MIOP where as WHR & WC was the major predictors for MOPP, MSOPP and MDOPP. On multiple regression analysis it was found that the significant obesity indices taken together were responsible for 69.95% of variation of MIOP, 11.46% of variation of MOPP, 23.84% of variation of MSOPP and 18.41% of variation of MDOPP.
DISCUSSION
The present study reports the mean ocular perfusion pressures in obese young adults and its association with different obesity indices. Ocular perfusion pressure is a delicate balance between IOP and blood pressure. Lower ocular perfusion pressure is associated with an increased risk of the development of open-angle glaucoma as well as its progression 5, 12, 13. High systemic blood pressure is also related to an increased risk of glaucoma 4, 14, 15. Obesity is a risk factor for systemic hypertension as well as ocular hypertension 5, 7,9,10. While there have been a large number of studies that have examined the effect of obesity on IOP and on blood pressure, the two components of OPP, the present study is first of its kind to show the relationship between obesity and OPP in Indian population. The present study shows that obese young adults have higher ocular perfusion pressures, IOP and blood pressure than the normal weight young adults. MDOPP was more significantly increased when compared to MSOPP. Even though there was increase IOP which reduces the ocular perfusion pressure, the MOPP was higher in obese young adults. This increase in MOPP could be due to increase in mean arterial pressure in obese persons and this is also supported by the fact in our study that MOPP. was more significantly positively correlated with MAP (r = 0.80) than with MIOP (r = 0.16). Our findings are consisted with an earlier population based studies which showed a correlation between higher body mass index and a reduced incidence of Open Angle Glaucoma (OAG) due to increase in ocular perfusion pressures in these persons 16, 17. In a study by L. Y Yip et al, women and people with lower BMI had low perfusion pressure and this was consistent with a vascular dysregulation mechanism 18. But a study by Kardaq et al have reported that subjects with higher BMI have decreased Ocular perfusion amplitude values indicating decrease in choroidal perfusion and ocular blood flow. But in their study, there was no difference in systolic and diastolic blood pressures between the groups 19. One study by Zheng He et al have shown that the susceptibility of retinal perfusion to IOP challenge can be partially ameliorated by acute high Blood pressure, and exacerbated by low Blood pressure 20. This study also analyzed the relationship between ocular perfusion pressures and different obesity indices. BMI indicates the overall obesity where as WC, HC & WHR indicates central obesity. In the present study MOPP was significantly positively correlated with BMI, WC & WHR but the association was more significant with central obesity parameters. MSOPP and MDOPP was significantly associated with all the obesity indices including hip circumference, again the association was better with central obesity. Regression analysis showed that BMI was the most important individual parameter in prediction of MIOP where as WC, HC & WHR were the major predictors for MOPP, MSOPP and MDOPP. Thus the study shows that increase in adiposity affects the ocular perfusion pressures by both, influencing the IOP and BP. Clinical implementation of this study is that, in obesity elevated IOP is a risk factor for glaucoma and may reduce nutrient availability by decreasing ocular perfusion pressure. However, higher OPP in obese persons due to increase in systemic blood pressure may provide protection against IOP elevation and decrease the risk of Glaucoma. On the other hand, systemic hypertension may be complicated by vascular dysfunction which might reduce the ocular perfusion and counteract any protective effect afforded by high BP, thus increasing the risk of OAG. Regular monitoring of OPP in obese individuals will be helpful in early diagnosis of glaucoma and its progression.
CONCLUSION
Obesity which is an independent risk factors for both increase in IOP and BP that affects the Ocular Perfusion Pressures. Increase in OPP can reduce the risk of glaucoma in obese young adults. But long term effects of hypertension on blood vessels can increase the risk of glaucoma. Thus regular monitoring of OPP in obese persons can become an important tool in early diagnosis and management of open angle glaucoma.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Conflict of interest: There is no conflict of interest to declare.

References:
1. Hid kuni Inadera.The usefulness of circulating adipokine levels for the assessment of obesity related health problems. Int J Med Sci 2008; 5(5): 248-262.
2. Jana V. van Vliet-Ostaptchouk, Harold Snieder, Vasiliki Lagou. Gene–Lifestyle Interactions in Obesity. Current Nutrition Reports. 2012; 1(3) : 184-196.
3. Mello MM, Studdert DM, Brennan TA. Obesity- the new frontier of public health law. New England Journal of medicine. 2006 ; 354 :2601-10.
4. Leske MC. Ocular perfusion pressure and glaucoma: clinical trial and epidemiologic findings. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2009 March; 20(2): 73–78.
5. Leske MC, Wu SY, Hennis A, Honkanen R, Nemesure B; BESs Study Group. Risk factors for incident open-angle glaucoma: the Barbados Eye Studies. Ophthalmology 2008;115(1):85–93.
6. Kotsis V, Stabouli S, Bouldin M, Low A, Toumanidis S, Zakopoulos N. Impact of obesity on 24-h ambulatory blood pressure and hypertension. Hypertension 2005; 45: 602– 607.
7. Stabouli S, Kotsis V, Papamichael C, Constantopoulos A, Zakopoulos N. Adolescent obesity is associated with high ambulatory blood pressure and increased carotid intimal medial thickness. Journal of Pediatrics 2005; 147: 651–656.
8. Mancia G, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, Cifkova R, Fagard R, Germano G et al. Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension; European Society of Cardiology. Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). J Hypertens 2007; 25: 1105–1187.
9. K Mori, F Ando, H Nomura, Y Sato, H Shimokata. Relationship between intraocular pressure and obesity in Japan. International Journal of Epidemiology. 2000; 29(4):661-666.
10. Akinci A, Cetinkaya E, Aycan Z, Oner O. Relationship between intraocular pressure and obesity in children. J Glaucoma. 2007 ; 16(7):627-630.
11. Douglas R Anderson. Normal-tension glaucoma (Low-tension glaucoma). Indian J Ophthalmol. 2011; 59(Suppl1): S97–S101.
12. Bonomi L, Marchini G, Marraffa M, et al. Vascular risk factors for primary open angle glaucoma: the Egna-Neumarkt Study. Ophthalmology. 2000;107:1287–1293.
13. Quigley HA, West SK, Rodriguez J, et al. The prevalence of glaucoma in a population-based study of Hispanic subjects: Proyecto VER. Arch Ophthalmol. 2001;119:1819–1826.
14. Leske MC, Connell AM, Wu SY, Hyman LG, Schachat AP. Risk factors for open-angle glaucoma. The Barbados Eye Study. Arch Ophthalmol. 1995 Jul; 113(7):918-924.
15. Mitchell P, Lee AJ, Rochtchina E, Wang JJ. Open-angle glaucoma and systemic hypertension: the blue mountains eye study. J Glaucoma. 2004 Aug;13(4):319-26.
16. Gasser P, Stumpfig D, Schotzau A, Ackermann-Liebrich U, Flammer J. Body mass index in glaucoma. J Glaucoma. 1999;8:8–11.
17. Pasquale LR, Willett WC, Rosner BA, Kang JH. Anthropometric measures and their relation to incident primary open-angle glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 2010;117:1521– 1529.
18. Yip JLY, Broadway DC, Luben R, Garway-Heath DF, Hayat S, Dalzell N. Physical activity and ocular perfusion pressure: the EPIC-Norfolk Eye Study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2011;52:8186–92.
19. Remzi Karadag, Zeynel Arslanyilmaz, Bahri Aydin, Ibrahim F. Hepsen. Effects of body mass index on intraocular pressure and ocular pulse amplitude Int J Ophthalmol. 2012; 5(5): 605–608.
20. Zheng He, Christine T. O. Nguyen, James A. Armitage, Algis J. Vingrys, Bang V. Bui. Blood Pressure Modifies Retinal Susceptibility to Intraocular Pressure Elevation. PLoS One. 2012; 7(2): e31104. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0031104.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License