IJCRR - 7(18), September, 2015
Pages: 31-37
Date of Publication: 20-Sep-2015
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
EVALUATION OF PARTIALLY PURIFIED SUBABUL PROTEASE INHIBITORS AS BIO INSECTICIDAL TOOL WITH POTENTIAL FOR THE CONTROL OF SPODOPTERA LITURA
Author: Arti Vasudev, Satwinder K. Sohal
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:The present study investigated the growth inhibitory potential of partially purified protease inhibitors from Subabul (Leucaena leucocephala) on Common cutworm Spodoptera litura (Fabricius) which has attained major pest status in India. Second instar larvae given treated diet (25, 50 100, 200, 400 and 800 \?g/ml) showed a decrease in larval period with increase in concentration when compared with control whereas total developmental period increased at lower concentrations but decreased at 400 and 800\?g/ml in comparison to control. The percentage pupation and emergence of females was inhibited and longevity of adults was reduced with increase in concentration. Percentage of male emergence increased significantly at highest concentration in comparison to control. No egg laying was observed at 400 and 800\?g/ml concentrations. A significant decline in percent hatching upto 200\?g/ml was noticed. The relative growth rate, consumption rate and efficiency of conversion of ingested and digested
food was significantly reduced. The present findings clearly confirmed the potential of the inhibitor for pest control.
Keywords: Leucaena leucocephala, Spodoptera litura, Growth and development, Bioinsecticide, Protease inhibitors
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
All organisms when attacked by their enemies use effective counter measures to defend themselves. Plants have also evolved mechanisms to cope with predatory insects and pathogens. Exploiting these mechanisms will undeniably contribute towards enhancing insect pest resistance. Plants produce different types of proteins to protect themselves from their enemies especially phytophagous insects. There are numerous examples of these proteins like serine and thiol protease inhibitors, amylase inhibitors, lectins and enzymes (Hilder and Boulter 1999). These proteins interrupt pest’s essential amino-acid metabolism by inhibition of protein digestion (Hilder et al., 1992). Many insects particularly those belonging to the order Lepidoptera depend on serine proteases like trypsin, chymotrypsin, and elastase as primary protein digestive enzymes. Much research has focused on exploiting this plant defense mechanism for crop protection. Studies using artificial diets incorporated with plant-derived PIs targeting a particular class of proteinase(s) in the insect gut have established that these proteins retard growth and development in Lepidopteran pests (Boulter, 1993; Pandey et al., 2014). Transforming plant genomes with these proteinaceous PIs provides an ecofriendly and safe approach to pest control (Reckel et al., 1997). However, because of the variability of the insect proteinases and the restricted range of action of the proteinase inhibitors (Ortego et al., 1996), the expression of a particular PI in plants may not yield the desired result and therefore might not be an excellent candidate for biotechnology. Thus there is a continuous search for new inhibitors that are competent to combat pest adaptation via antimetabolic activity. Subabul which belongs to family Leguminoceae, is an ornamental tree used as fodder and firewood. It is reported to exhibit inhibitory activities for plasmin, human plasma kallikrein, trypsin, chymotrypsin and factor XIIa (Oliva et al., 2000). Previous study on STI showed significant reduction in growth and larval development of Helicoverpa armigera by Bhavani et al., 2007. We examined the effects of Subabul protease inhibitors on the growth and development of S. litura larvae. Furthermore, we investigated the effects of this inhibitor on food consumption, absorption and utilization, as well as its effects on the midgut and fecal proteolytic activity of larvae fed on an artificial diet, corroborating novel data on adaptation/resistance of insects to proteinase inhibitors. S. litura is a polyphagous noctuid commonly known as the cluster cater- pillar, tobacco cutworm and tropical armyworm. The larvae have a wide range of host plants of over 40 mostly dicotyledonous plant families, resulting in 69% reduction in yield. It is a polyphagous pest of many forage crops and vegetables in China, Japan and has recently attained the status of a moajor pest on agricultural crops in India (Gokulkrishnan et al., 2012). In India, S. litura is found more in the fields of ground nut, tomato, chilli, bhendi and cotton (Elumalai et al., 2010).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Partial purification of PIs
Mature Subabul seeds were collected from university campus and defatted using acetone (1:10) w/v for 2h then air dried for 15mins. Defatted seed powder (1:20) w/v was stirred for 1h at room temperature with extraction buffer i.e. 0.1M sodium phosphate buffer, pH7.5. This slurry was then centrifuged at 12,000rpm for 30mins at 40 C. Total soluble protein was incubated at 700 C for 10mins followed by centrifugation at 12,000rpm for 30mins at 40 C. Precipitates were dissolved in minimum amount of extraction buffer and were dialyzed against same extraction buffer using a membrane (cutoff Mr 12000-14000 Da) for 24h at 40 C. The dialyzed sample was treated as partially purified PI which was then subjected to further analysis of protein content as well as for trypsin inhibitory activity.
Trypsin inhibition assay
Protienase inhibitory activity was determined according to Paulino da Silva et al., 2001 using BApNA (N-α-benzoylDL-arginine p-nitroanilide) as substrate.
Protein estimation
Protein estimation was done both in defatted and partially purified preparations by the method of Lowry et al., (1951) using bovine serum albumin (BSA) as the standard, for preparing various test concentrations (25, 50, 100, 200, 400, 800µg/ml) for bioassay and nutritional assay studies.
Insect culture
Egg masses and larvae of S. litura were collected from the cauliflower fields around Amritsar (Punjab), India and subsequent generations were reared in the laboratory at 25±20 C temperature, 65±5% relative humidity (RH) and 12:12 (D: L) photoperiod. The rearing was carried out in glass jars (15cm×10cm) on castor leaves. Rearing on artificial diet was done as reported by Koul et al., (1997).
Bioassay studies
All experiments were conducted in B.O.D. incubator maintained at conditions mentioned earlier. Bioassay experiments were conducted as described by Vasudev and Sohal (2013). The various concentrations of partially purified PIs used were 25, 50, 100, 200, 400 and 800µg/ml. There were 6 replications with 5 larvae (n=210) in each replication for each concentration.
Nutritional analysis
Nutritional indices of S. litura were determined by following the procedure of Koul et al., (2005). Dry weights of larvae, diet left and fecal matter were taken by incubating the larvae at the end of experiments at 60°C for 72h inside an incubator. Nutritional indices thus obtained were calculated as proposed by Waldbauer (1968) using dry weights.
Statistical analysis
All the bioassays and nutritional assays were performed in six replicates and the values were represented as mean ± SE. The data were subjected to analysis of variance (ANOVA). Statistical differences were determined by Tukey’s post hoc test.
RESULTS
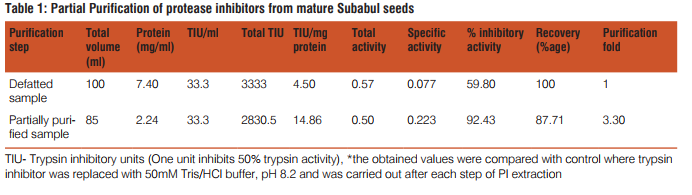
Proteinase inhibitors partially purified from Subabul exhibited 14.86 trypsin inhibitory units (TIU) per mg protein with 92.43% inhibitory activity against bovine trypsin (Table1).
Bioassay studies
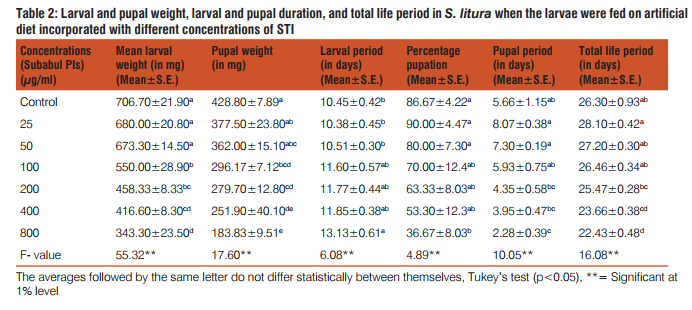
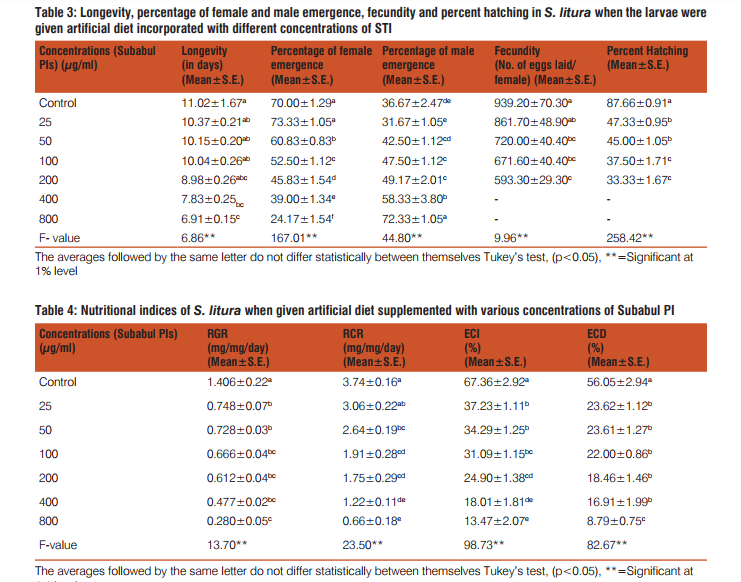
The effect of STI was noticed on developmental physiology of S. litura larvae when they were weighed in their final larval stage after feeding on diet supplemented with different PI concentrations. Larval weight decreased in a dose dependent manner where they weighed 363.4mg less at 800µg/ml in comparison to control (Table 2). Also, an increase was observed in larval period with increase in concentration of STI supplemented diet fed to the second instar larvae. At low concentrations of 25 and 50µg/ml no drastic increase was noticed, whereas at 800µg/ml larval period prolonged significantly by 2.68days in comparison to control larvae (Table 2). Prepupal mortality was noticed at 400 and 800µg/ ml (Fig. 4a). Rearing of larvae on diet amended with STI adversely affected %pupation as only 36.67% larvae pupated at the highest concentration in comparison to 86.67% pupation observed in the larvae reared on control diet (Table 2). Pupal duration showed no particular trend as it increased at lower concentrations (25-100µg/ml) but with increase in PI amount in diet (200-800µg/ml), it decreased significantly when compared with control (Table 2). Pupal weight decreased effectively at all the concentrations when compared with control (Table 2). The pupa formed at 400 and 800µg/ ml concentrations were small in size (Fig. 4b). The adverse effect of STI in its partially purified form was also observed on male and female emergence along with their performance. While the female emergence decreased to 34.52% of the control, the percentage of males emerged from treated larvae was 1.97 times more than control at highest concentration (Table 3). Longevity of adults declined significantly by 4.11days at 800µg/ml when compared with control group. The number of eggs laid by adult females emerged from treated larvae was 593.30/female at 200µg/ml in comparison to control where 939.20eggs/female were laid. At high concentrations, no egg laying was seen by emerged females. Also the eggs laid by emerged females from treated larvae were not much viable as only 33.33% eggs hatched at 200µg/ml (Table 3). Aberrations in adults were more pronounced at 400 and 800µg/ml concentrations where adult half emerged from pupa or adults with deformity in wings were more often seen (Fig. 4c andd).
Nutritional indices
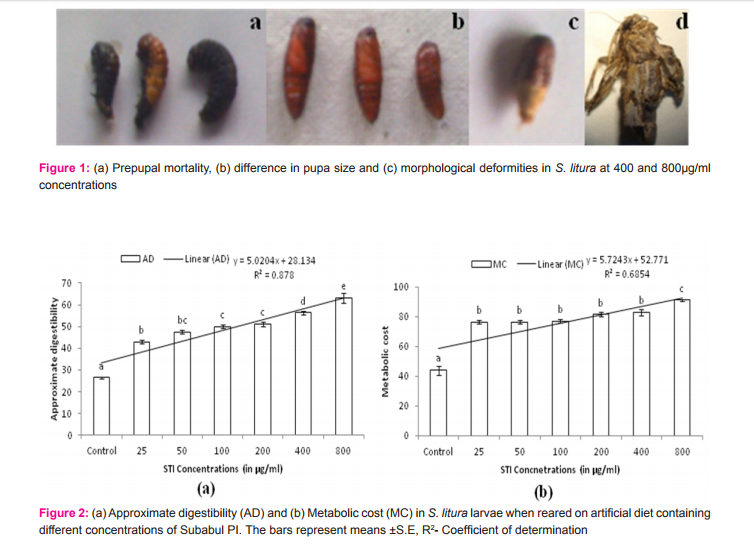
Nutritional analysis indicates considerable effect of partially purified protease inhibitors from Subabul on food utilization by S. litura. As is apparent from Table 4, there was noteworthy decline in relative growth and consumption rate of S. litura larvae as well as efficiency of conversion of ingested and digested food after ingestion of PI treated diet. Amended diet resulted in 47-80% reduction in RGR over the control. With the increasing concentration of STI, the RGR reduced significantly in comparison to control. Similarly, significant reduction in food consumption rate was recorded where it showed negative correlation with concentration. The concentrations of 400 and 800µg/ml caused 67.38 and 82.36% reduction in RCR over control. Adverse effects of partially purified PI were also recorded on ECI and ECD parameters. Both decreased significantly as concentration of PI increased in diet. Approximate digestibility (AD) increased in a dose response manner in all the treatments when compared with control (Fig. 5A). Metabolic cost to metabolize the ingested PI increased as the amount of PI in diet increased and was maximum (91.20%) at 800µg/ml in comparison to control (43.97%) (Fig.5B).
DISCUSSION
Partially purified Subabul PIs affected negatively growth and development of S. litura. Similar findings have been reported by Pompermayer et al., 2001 where soybean inhibitor in its partially purified form significantly affected the growth as well as development of Diaterea saccharalis larvae when given in artificial diet. Also trypsin inhibitor partially purified from Theobroma cacao seeds at 0.25% increased the larval and pupal period resulting in morphological abnormalities in adults of D. saccharalis and Anticarsia gemmatalis whereas in Heliothis virescens it caused a significant decline in pupal weight (Paulillo et al., 2012). The larval stage in Lepidoptera is an actively feeding stage whereby they accumulate efficiently all the nutrients present in the food. Any disturbance in essential nutrient accumulation efficiency will directly affect the larval weight and size which clearly accounts for the negative impact of PI on later life stages of S. liura as has been observed in the present study. Since achieving a critical weight is essential for pupation, the delayed larval period observed in the present work could be due to less consumption of diet by the larvae of S. litura indicating the antifeedant nature of the extract. The decrease in the weight of the pupae formed from larvae of S. litura fed on STI diet seems to have adversely affected the reproductive capacity of the emerged females. Achieving high pupal mass is significant as there exists a strong association between adult body weight and its reproductive potential (Tammaru et al. 1996a). Negative effect on fecundity and fertility has previously been documented on S. litura with partially purified PIs from B. oleracea (Vasudev and Sohal, 2013). Any interference in the protein assimilation at larval stage subsequently affects the egg laying capacity of female moths and morphological deformities in adults. Less fecundity at higher concentrations, less number of female adults at all treatments, absence of egg hatching at high concentrations in present study could be accounted for by the less bioavailability of protein or amino acids in food or inability on part of the insect to assimilate the digested food. Similar impact of PIs on nutritional indices of lepidopteran larvae has been reported by several researchers (Da Silva et al., 2012; Mittal et al., 2014; Singh et al., 2014). Nutritional indices and its analysis can form the basis to understand the behavioral and physiological aspects of insect-plant interactions (Lazarevic and Peric-Mataruga, 2003). Our data showed that S. litura larvae fed on STI diet had a low relative consumption as well as growth rate which indicated that less food was utilized by the larvae. This index shows that the feeding rate is directly connected to larval weight (Srinivasan and Uthamasamy, 2005). Our findings also demonstrated a dose dependent decrease in mean larval weight which correlates with the decrease in RCR. Consecutively the larvae took a longer time to pupate and were smaller in size, weighing much less than control which was evident from the low RGR, ECI and ECD. As a result the fecundity and longevity of the adult moths was also severely affected. ECI which is generally a measure of an insect’s capacity to utilize the food ingested for growth and development (Koul et al., 2004) was highest for control and lowest for high-est treatment. This indicated a sign of poor availability of proteins in diet supplemented with PI. Change in ECD also points towards the overall increase or decrease of the proportion of digested food metabolized for energy (Koul et al., 2004). In the current study, the larvae fed on the PI amended diet had reduced value of ECD which suggests that these larvae were actually not as competent in turning digested food into biomass. Approximate digestibility indicates ability of an insect to absorb food through the stomach wall. Increase in AD is an indicative of attempts made by insect to make up for inferior nutritive value of the food and to accomplish the desired growth rate.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, partially purified Subabul proteinase inhibitors showed strong anti metabolic and growth inhibitory activity against major pest S. litura. Dietary utilization experiments clearly revealed the growth deterrent impact of the PI; thereby signifying its possible importance to control insect pest populations. These results indicate that future finding of PI from non host plant can be of great importance in environment safe pest management programmes.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors acknowledge the Department of Botanical and Environmental Sciences, Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar for identifying the seeds. The authors would also like to thank University Grants Commission for providing University with Potential for Excellence research fellowship under the PhD programme of Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar. Also authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited in the manuscript. The authors are grateful to author/ editors/ publishers of all those articles, journal and books from where the literature for this manuscript has been reviewed and discussed.
Source of funding Authors acknowledge the funds received from University Grants Commission, Delhi under University with potential for excellence (UPE).
Conflict of Interest Authors declare that there is conflict of interest.
References:
1. Bhavani, P., Bhattacharjee, C., Prasad, D.T. (2007). Bioevaluation of partially purified subabul proteinase inhibitors on Helicoverpa armigera. Arthropod Plant Interaction, 1: 255-261.
2. Bhavani, P., Prasad, D.T. (2012). Effect of partially purified Subabul (Leucaena leucocephala) proteinase inhibitors on Helicoverpa armigera and different fungal species. Trends in Biosciences, 5: 312-314.
3. Boulter, D. (1993). Insect pest control by copying nature using genetically engineered crops. Phytochemistry, 34: 1453-1466.
4. Bown, D.P., Wilkinson, H.S., Gatehouse, J.A. (1997). Differentially regulated inhibitor-sensitive and insensitive protease genes from the phytophagous insect pest, Helicoverpa armigera, are members of complex multigene families. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 27: 625-638.
5. Broadway, R.M. (1995). Are insects resistant to plant proteinase inhibitors? Journal of Insect Physiology, 41: 107–116.
6. Broadway, R.M. (1997). Dietary regulation of serine proteinases that are resistant to serine proteinase inhibitors. Journal of Insect Physiology, 43: 847-858.
7. Broadway, R.M., Duffey, S.S. (1986). The effect of dietary protein on the growth and digestive physiology of larval Heliothis zea and Spodoptera exigua. Journal of Insect Physiology, 32: 673–680.
8. Burgess, E.P.J., Steven, P.S., Keen, G.K., Laing, W.A., Christeller, J.T. (1991). Effects of protease inhibitors and dietary protein level on the black field cricket Teleogryllus commodus. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata, 61: 123-130.
9. Da Silva, W., Freire, M.G.M., Parra, J.R.P., Marangoni, S., Macedo, M.L.R. (2012). Evaluation of the Adenanthera pavonina seed proteinase inhibitor (ApTI) as a bio insecticidal tool with potential for the control of Diatraea saccharalis. Process Biochemistry, 47: 257-263.
10. Elumalai, K., Krishnappa, K., Anandan, A., Govindarajan, M., Mathivanam, T. (2010). Certain essential oil against the field pest army worm, Spodoptera litura (Lepidopetra: noctuidae). International Journal of Recent Scientific Research, 2: 56-62.
11. Gokulkrishnan, J., Krishnappa, K., Elumalai, K. (2012). Effect of plant oil formulations against armyworm, Spodoptera litura (Fab.), Cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Hub.) and fruit borer, Earias vitella (Fab.) (Lepidopetra:Noctuidae). International Journal of Current Life Sciences, 2: 1-4.
12. Hilder, V.A., Boulter, D. (1999). Genetic engineering of crop plants for insect resistance a critical review. Crop Protection, 18, 177-191.
13. Hilder, V.A., Gatehouse, A.M.R., Boulter, D. (1992). Transgenic plants conferring insect tolerance: protease inhibitor approach. In: Kung, S., Wu, R., editors. Transgenic plants. New York (NY): Academic Press, pp. 310-338.
14. Koul, O., Shankar, J.S., Mehta, N., Taneja, S.C., Tripathi, A.K., Dhar, K.L. (1997). Bioefficacy of crude extracts of Aglaia species (Meliaceae) and some active fractions against lepidopteran larvae. Journal of Applied Entomology, 121: 245–248.
15. Koul, O., Singh, G., Singh, R., Multani, J. (2005). Bioefficacy and mode of action of aglaroxin A from Aglaia elaeagnoidea (syn. A. roxburghiana) against Helicoverpa armigera and Spodoptera litura, Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata, 114: 197–204.
16. Koul, O., Singh, G., Singh, R., Singh, J., Daniewski, W., Berlozecki, S. (2004). Bioefficacy and mode-of-action of some limonoids of salannin group from Azadirachta indica A. Juss and their role in a multi component system against lepidopteran larvae. Journal of Biosciences, 29: 409–416.
17. Lazarevic, J., Peric-Mataruga, V. (2003). Nutritive stress effects on growth and digestive physiology of Lymantria dispar larvae. Yugoslav Medical Biochemistry, 22: 53–59.
18. Lowry, O.H., Rosenbrough, N.J., Farr, A.L., Randall, R.J. (1951). Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 193: 265–275.
19. Macedo, M.L.R., Freire, M.D.G.M., Cabrini, E.C., Toyama, M.H., Novello, J.C., Marangoni, S. (2003). A trypsin inhibitor from Peltophorum dubium seeds active against pest protease and its effect on the survival of Anagasta kuehniella (Lepidoptera:Pyralidae). Biochimica Biophysica Acta, 1621: 170-182.
20. Macedo, M.L.R., Mello, G.C., Freire, M.G.M., Novello, J.C., Marangoni, S., Matos, D.G.G. (2002). Effect of a trypsin inhibitor from Dimorphandra mollis seeds on the development of Callosobruchus maculatus. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 40: 891-898.
21. Mittal, A., Kansal, R., Kalia, V., Tripathi, M., Gupta, V.K. (2014). A kidney bean trypsin inhibitor with an insecticidal potential against Helicoverpa armigera and Spodoptera litura, Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 36: 525-539.
22. Nandeesha, P., Prasad, D.T. (2001). Characterization of serine proteinase inhibitor from subabul (Leucaena leucocephala, L.) sedds. Journal of Plant Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 10: 75- 78.
23. Oliva, M.L., Souza-pinto, J.C., Batista, I.F., araujo, M.s., Silveria, V.F., Aureswald, E.A., mantele, R., Eckerskorn, C., Sampaio, M.U., Sampaio, C.A. (2000). Leucaena leucocephala serine proteinase inhibitor: primary structure and action on blood coagulation kinin release and rat paw edema. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1477: 64-74.
24. Ortego, F., Novillo, C., Castafiera, P. (1996). Characterization and distribution of digestive proteases of the stalk com borer Sesamia nonagrioides Lef. (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 33: 163–180.
25. Pandey, P. K., Singh, D., Singh, S., Khan, M.Y., Jamal, F. (2014). A nonhost peptidase inhibitor of 14 kDa from Butea monosperma (Lam.) Taub. seeds affects negatively the growth and developmental physiology of Helicoverpa armigera. Biochemistry Research International, http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/361821
26. Paulillo, L.C.M.S., Sebbenn, A.M., Derbyshire, M.T.V.C., GoesNeto, A., Brotto, M.A.P., Figueira, A. (2012). Evaluation of in vitro and in vivo effects of semipurified proteinase inhibitors from Theobroma seeds on midgut protease activity of lepidopteran pest insects. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 81: 34-52.
27. Paulino da Silva, L., Leite, J.R.S.A., Bloch, C. Jr., Maria de Freitas, S. (2001). Stability of a black eyed pea trypsin/chymotrypsin inhibitor (BTCI). Protein and Peptide Letters, 8: 33–38.
28. Pompermayer, P., Lopes, A.R., Terra, W.R., Parra, J.R.P., Falco, M.C., Silva-Filho, M.C. (2001). Effects of soybean proteinase inhibitor on development, survival and reproductive potential of the sugarcane borer, Diatrea sachharalis, Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata, 99: 79-85.
29. Reckel, G.R.K., Kramer, K.J., Baker, J.E., Kanost, M.R., Fabrick, J.A., Behnke, G. A., 1997. Proteinase inhibitors and resistance of transgenic plants to insects, in: N. Carozzi, M. Koziel (Eds.), Advances in Insect Control. The Role of Transgenic Plants. Taylor and Francis, London, pp. 157– 183.
30. Singh, D., Jamal, F., Pandey, P.K. (2014). Kinetic assessment and effect on developmental physiology of a trypsin inhibitor from Eugenia jambolana (Jambul) seeds on Helicoverpa armigera (HÜBNER), Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 85: 94-113.
31. Srinivasan, R., Uthamasamy, S. (2005). Studies to elucidate antibiosis resistance in selected tomato accessions against fruitworm, Helicoverpa armigera Hubner Resistant Pest Management Newsletter, 14: 24–26.
32. Tammaru, T., Kaitaniemi, P., Ruohomäki, K. (1996). Realized fecundity in Epirrita autumnata (Lepidoptera: Geometridae): relation to body size and consequences to population dynamics. Oikos, 77: 407–416.
33. Vasudev, A., Sohal, S.K. (2013). Bioinsecticidal potential of partially purified proteinase inhibitors from Brassica oleracea (L.) against Spodoptera litura (Fab.) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), Efflatounia,. 13: 1-7.
34. Waldbauer, G.P. (1968). The consumption and utilization of food by insects, Advances in Insect Physiology, 5: 229–288.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License