IJCRR - 14(6), March, 2022
Pages: 27-32
Date of Publication: 15-Mar-2022
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Effect of Apple Cider Vinegar and Cinnamon (Cinnamomum Cassia) in Combination on Lipid Profile of Mice
Author: Ayesha Aftab, Sohail Ahmad, Muhammad Kashif Munir, Zahid Iqbal, Sana Rehman, Nazish Mazari
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Metabolic syndrome is constituted by hyperlipidemia with presentation of diverse lipid profile including hypertriglyceridemia, hypercholesterolemia and hereditary combined hyperlipidemia.
Objectives: To find the synergistic effect Cinnamomum cassia and apple cider vinegar on combined administration in albino mice.
Methodology: This was an experimental study and conducted at Department of Pharmacology, Al-Nafees Medical College and Hospital Islamabad in collaboration with Animal House of the National Institute of Health, Islamabad-Pakistan. A total of 50 adult albino mice were randomly divided into 5 groups. Hyperlipidemia was induced during the first two weeks of experimentation, and this was followed by treatment period of 6 weeks. Groups were categorized as A (Normal Control), B (Treated Control), C (Treatment Group I), D (Treatment Group II), and E (Treatment Group III). Diet pattern for these groups remained to be high cholesterol, Simvastatin 0.6 mg/Kg BW, ACV upto 15% of animal feed, Cinnamon powder 6mg/Kg BW and Cinnamon with high cholesterol diet respectively. Blood samples to estimate parameters of lipid profile were collected at 0,15th, 30th, 45th and 60th days.
Results: A significant decrease (p< 0.05) was observed in total cholesterol, triglyceride and low-density lipoprotein at 45th and 60th days as compared to normal control group. Serum high-density lipoprotein was low at 15th day among all groups because of induction of hypercholesterolemia, which was then noted to be reversed at 60th day. Highest surge was noted to be in group E and significant increase in all groups (p< 0.05) was noted in all groups as compared to normal control.
Conclusion: Apple Cider Vinegar keeps the anti-hyperlipidemia effect which was found to be significantly high (p< 0.05) in combination with Cinnamomum cassia when consumed by male albino mice.
Keywords: Apple cider vinegar, Cinnamon, Lipid profile, Albino mice, Metabolic syndrome, Lipoprotein
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Hyperlipidemia constitutes a metabolic syndrome with diverse lipid profile including hypertriglyceridemia, hypercholesterolemia and hereditary combined hyperlipidemia leading to various health issues like cardiovascular diseases, atherosclerosis, obesity, diabetes & insulin resistance and is major cause of deaths worldwide.1 For the primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease it is recommended to treat hyperlipidemia along with lifestyle changes. Statins are the first-line drug in treatment of hyperlipidemia associated with cardiovascular disease, but they are reported to be associated with several adverse effects like myopathies, rhabdomyolysis and altered liver function tests.2 Incidence of myopathies and rhabdomyolysis is approximately five in every 1000 patients getting statin therapy. A serious complication of statin-induced myopathy is severe rhabdomyolysis which manifests as high levels of serum creatinine kinase, myoglobinuria and acute renal injury.3 The side effects of drugs result in non-compliance, rendering the treatment ineffective.4
Currently there is growing interest in the use of fruits, vegetables and beverages that contain biologically active phytochemicals and natural antioxidants. Polyphenols are major dietary antioxidant of plant origin present abundantly in fruits, vegetables, legumes and beverages. Apple Cider Vinegar (ACV) is derived from apples that are reported to contain up to 200-300 mg polyphenol per 100-gram fresh weight.5 It was found that as compared to other fruits; apple had the highest portion of free phenolics leading to quick absorption in bloodstream and greater cholesterol-lowering effect.6
Cinnamon is the bark of the Cinnamon tree and being used in traditional and modern medicine and cookery. It is well known for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antidiabetic, anticancer, antimicrobial and lipid-lowering properties.7It contain essential oils and other compounds like cinnamon aldehyde, cinnamic acid, and cinnamate.8 It has been reported that cinnamate is a phenolic compound that inhibit hepatic HMG-Co-A reductase activity leading to lower cholesterol level. It also stimulates antioxidant enzyme activity of liver leading to decrease in lipid peroxidation.9 We hypothesized that the antihyperlipidemic effect of ACV will be increased when given in combination with cinnamon.
ACV and Cinnamon have documented antihyperlipidemic effects but their effect in combination was not reported in literature. Therefore, the present study was aimed to find the synergistic effect Cinnamomum cassia and apple cider vinegar on combined administration in albino mice.
METHODOLOGY
It was an experimental study of one-year duration conducted at the Department of Pharmacology, Al-Nafees Medical College and Hospital, Islamabad in collaboration with Animal House of National Institute of Health, Islamabad, Pakistan. Fifty Balap/c albino male mice, weighing between 20 to 30gms, were used in the study after purchasing them from NIH; Islamabad. The animals were divided into 05 groups, each comprising 10 animals. Before starting the experimentation, the mice were allowed to acclimatize to laboratory conditions i.e. temperature of 22+4 °C for 7 days.
Experiment design
The experimentation period consisted of 8 weeks divided into two phases:
Phase 1: Induction of Hyperlipidemia:
Hyperlipidemia was induced during the first two weeks of experimentation. The mice were given normal routine feed mixed with Cholesterol (Applichem, Darmstadt, Germany. CAT No.A08070100) at the rate of 400mg/kg body weight.10During the whole experimentation period mice had free access to feed and drinking water.
Phase 2: Treatment period
Treatment period consisted of 6 weeks. During this period the mice were given treatment as follows:
Group l: Normal Control
Mice were given high cholesterol diet during the whole experimentation period from day 1 to 60.
Group ll: Treated Control
The mice were given high cholesterol diet for first 15 days after which they were given standard lipid-lowering drug i.e. Simvastatin at a dose of 0.6mg/kg BW10 along with high cholesterol diet for next 45 days.
Group lll: Treated GroupI
The mice were given high cholesterol diet for first 15 days after which they were given Apple Cider Vinegar 15%10 in their diet for the next 45 days.
Group IV: Treated Group II
The mice were kept on high cholesterol diet for first 15 days after which Cinnamon powder was added in diet at a dose of 6mg/kg BW10 for next 45 days.
Group V: Treated Group III
The mice were given high cholesterol diet for first 15 days after which they were given a combination of ACV 15% and Cinnamon powder 6mg/kg BW for next 45 days.
Blood sample collection
Blood samples were collected before start of experimentation and then at 15,30,45,60 days of experimentation. Chloroform was given to anesthetize two mice from each group at the day of sampling. The blood was drawn by direct heart puncturing10 using 3cc disposable syringe and put in vacuum tubes LOT No.1102246. Blood was allowed to clot in a centrifuge tube for 20 minutes and centrifuged for 15 minutes then at 4000rpm, clear supernatant was removed and stored in Eppendorf tubes at -4°C.10
Assessment of lipid profile
Total Cholesterol (TC), Triglycerides (TG) and High-density lipoproteins (HDL) were determined using enzyme-based reagent Kits purchased from Merck (Private)Limited. The samples were then analyzed using Automatic chemistry analyzer. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) was calculated by Friedewald’s formula.11
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was carried out using SPSS version 20. Descriptive statistics were calculated. One way ANOVA (Tukey’s test) was applied. p-value < 0.05 was considered significant.
RESULTS
Hyperlipidemia in mice
Hyperlipidemia was produced in mice as a result of feeding cholesterol powder equivalent to 400mg/kg bodyweight for 0-15 days. In Figures 1, 2, 3 and 4, it is clear from the lipid profile parameters at day 0 and day 15 that Hyperlipidemia has been induced. The serum Cholesterol, Triglycerides and LDL have increased while serum HDL showed a decreasing trend in all the groups.
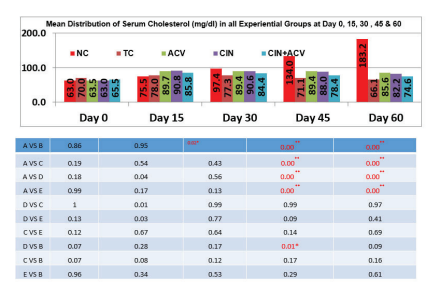
Fig 1: Mean ±SD values of serum Cholesterol (mg/dL) in all experimental groups at day 0, 15,30,45 and 60.
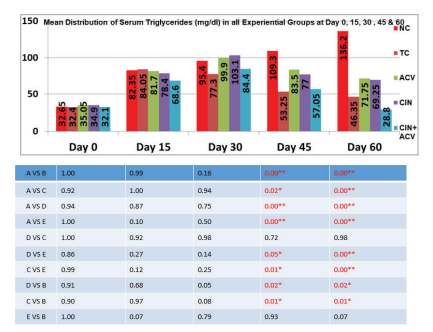
Fig 2: Mean ±SD values of serum Triglycerides (mg/dL) in all experimental groups at day 0, 15, 30, 45 and 60.
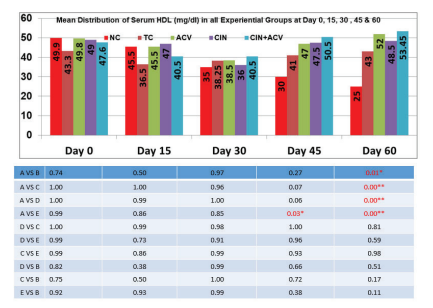
Fig 3: Mean ±SD values of serum HDL-C (mg/dL) in all experimental groups at day 0, 15, 30, 45 and 60.
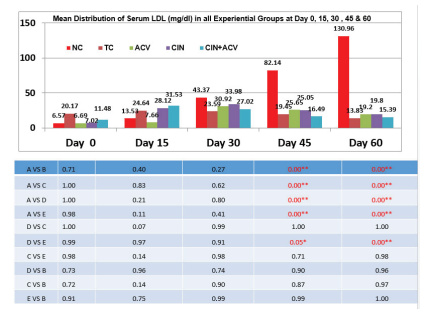
Fig 4: Mean ±SD values of serum LDL-C (mg/dL) in all experimental groups at day 0, 15, 30, 45 and 60.
Effect of treatment on Serum Total Cholesterol in mice(mg/dl)
The effect of treatment with Simvastatin, Apple cider vinegar, Cinnamon and a combination of Apple cider vinegar and Cinnamon on serum total Cholesterol has been given in fig.1. The serum cholesterol level of group A, B, C, D and E has increased at day 15 which is the result of induction of Hyperlipidemia. At day 45 and 60, as per fig.1, the serum cholesterol levels of all the groups except group A were reduced. The anti-hyperlipidemic effect obtained after treatment with a combination of Apple cider vinegar and cinnamon was maximum and also highly significant(p-value <0.05).
Effect of treatment on Serum Triglycerides in mice(mg/dl)
The effect of treatment with Apple cider vinegar, Cinnamon and their combination on serum Triglycerides has been given in fig.2. At day 15 the serum triglycerides level of all the groups were raised which confirmed induction of Hyperlipidemia. At day 45 and 60 the serum triglycerides of group B, C, D and E were decreased significantly as compared to normal control. The mean serum triglycerides level obtained in group E, at day 60 was found to be lowest amongst the groups with p-value <0.05. The reduction in serum triglycerides level observed in group E was also significant as compared to group C and D which proves the synergistic effect of the combination of Apple cider vinegar and Cinnamon in reducing serum Triglycerides. However as compared to group B the result was not significant showing that group B i.e. treated with Simvastatin and E i.e. treated with a combination of Apple cider vinegar and Cinnamon might be equal in efficacy to lower serum Triglycerides.
Effect of treatment on Serum HDL-Cholesterol in mice(mg/dl)
The effect of treatment with Apple cider vinegar, Cinnamon and their combination on serum HDL has been given in fig.3. At Day 15 the serum HDL- cholesterol of all the groups was decreased from their respective value at day 0 which is the result of Hyperlipidemia with cholesterol powder. At day 45 of treatment, the serum HDL of all the treated groups including the treated control was increased but the result was only significant with group E when compared to normal control. The serum HDL of all the treated groups was increased at day 60 and the result was significant when compared to normal control. The highest mean value of serum HDL was obtained in group E. When compared to group B i.e. treated control the P-values of group C, D and E at day 60 were not significant showing equal efficacy to elevate the serum HDL cholesterol in hyperlipidemic mice.
Effect of treatment on Serum LDL-Cholesterol in mice(mg/dl)
The effect of treatment with Apple cider vinegar, Cinnamon and combination of Apple cider vinegar and Cinnamon on serum LDL has been given in fig.4. At day 15 LDL levels were raised showing induction of Hyperlipidemia. At day 45 and 60 the serum LDL-cholesterol of all the groups except the normal control was decreased. Group E showed the lowest mean value of LDL-cholesterol as compared to group C and D. The comparison with normal control showed significant result with p-value <0.05. As compared to treated control, group C, D and E showed non-significant changes in LDL-cholesterol level proving equal efficacy.
DISCUSSION
The present study investigated the effect of Cinnamon and apple cider vinegar in combination and alone on lipid profile including total cholesterol, triglycerides, HDL-cholesterol and LDL-cholesterol in male balap/c albino male mice. This study showed significant changes in lipid profile levels by Apple cider vinegar and Cinnamon which were in agreement with literature. The mice were fed with cholesterol powder for the first fifteen days of experimentation which resulted in Hyperlipidemia with an increase in serum Cholesterol, Triglycerides, LDL-C and decrease in HDL-C. At day 15 total cholesterol levels were increased compared with the Control group receiving normal rat feed.In another study performed by Abdelgadir et al., hyperlipidemia was induced in male albino rats after feeding high cholesterol diet for 08 days. The serum lipid profile showed elevated levels of TC, TG and LDL while HDL values were decreased.12
Overfeeding of fat causes an increased production of Chylomicrons, which enter liver by pinocytosis hence level of Triglycerides in liver is enhanced. In addition, the free fatty acids (FFA) generated by hydrolysis of TG of Chylomicrons, leads to the increased influx of FFA in liver and the synthesis of TG and Very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL) is increased. Enhanced VLDL levels in plasma in turn lead to an increase in LDL level.13 Composition of HDL is altered VLDL by the effects of cholesteryl ester transfer protein and hepatic lipase that directs the development of minute dense HDL and enhances the catabolism of these entities. An inverse correlation between liver fat and HDL has also been noticed.14
The present study showed a significant decrease in serum cholesterol level after 6 weeks of treatment with ACV and CIN. The reduction in serum Cholesterol level of Group E was greater when compared to Group C and D, which confirmed the synergistic effect of ACV and CIN.
Ngozi et al. 2019 also reported a decrease in serum TC after 4 weeks of feeding with ACV, and showed that ACV has a significant cholesterol-lowering effect.15 It was proposed that the hypocholesterolemic effect of ACV might be due to polyphenolic compounds.16 A study on the hypocholesterolemic effect of different types of vinegar showed a significant decrease in serum Cholesterol by ACV. It is also emphasized that the serum Cholesterol is reduced by acetic acid components in vinegar which inhibit hepatic lipogenesis and promote excretion bile acid in feces.17These results were in line with Naz?ro?lu et al. 2014 who observed in their study that triglycerides and cholesterol were lesser among mice treated with ACV and fed high cholesterol.18
Cinnamon also has hypocholesterolemic properties which were proven by a study conducted by Alsoodeeri et al. on hypercholesterolemic rats. It was found in the study that cinnamon extract given as a daily dose of 4g/kg presented an anti-hyperlipidemic effect among hypercholesterolemic rats. A reduction in serum LDL-C, triglyceride and total cholesterol levels and a rise in serum HDL-C were noted by them on day 30 of their experiment.19 It is said that Cinnamon treatment might have a direct role in lipid metabolism. Marean et al. reported that supplementation with cinnamon significantly decreased serum triglycerides and cholesterol concentrations though showed no effects on blood concentrations of HDL-C and LDL-C.20
Feeding ACV and CIN has caused a significant reduction in TG level. Effect of treatment was greatest in group E which was given a combination of ACV and CIN. This was in agreement with study of Ousaaid et al. in which they concluded that a moderate reduction in concentrations of total cholesterol (TC) were seen by apple vinegar in female rats while LDL-C and triglycerides among rats of both genders.21 Another study examined the effect of ACV in diabetic mice. After 4 weeks of treatment with apple cider vinegar a significant decrease in serum total cholesterol (TC), LDL-C, and TG levels was noted.22 This lipid-lowering effect was attributed to acetic acid in ACV which suppresses the accumulation of body fat and hepatic lipids by upregulation of genes for fatty acid oxidation and soluble apple fiber pectin which increases fecal bile acid excretion leading to a decrease in plasma TC and TG.23 However, research evidence that ingestion of apple cider vinegar can decrease triglycerides and total cholesterol in plasma only once consumed normal levels of dietary lipids24 and is not in agreement with present findings.
In the present study ACV and CIN showed a significant effect on serum HDL-C and LDL-C level. The serum LDL-C levels in group E showed a decreasing trend while HDL-C levels were raised. This was in agreement with the study conducted by Halima et al who concluded that an increase in levels of blood HDL after consumption of apple cider vinegar among study subjects with a statistically significant difference (p<0.05).25However Panetta et al. performed a randomized clinical trial to evaluate the impact of vinegar on HDL-C and proved that consuming 30ml Apple cider vinegar daily for 8 weeks had no beneficial effect on HDL-C and LDL-C levels.26 Beheshti et al. observed an increase in serum HDL-C and a decrease in LDL-C after intake of ACV in human subjects but the difference was not statistically significant for rise in HDL-C.27 It has been suggested that this effect of ACV may be due to its influence on the glycemic index(GI). The acidic food e.g. pickled food or those containing vinegar or lemon juice have low GI and may result in lower LDL cholesterol and enhanced HDL cholesterol levels.24
It was noted in this study that cinnamon also showed a positive effect on HDL-C and LDL-C. This hypolipidemic effect was more pronounced in combination with ACV which proved their synergistic effect. In a study done by Jain SG et al, involving 129 metabolic syndrome patients, the cinnamon intervention resulted in a significant decrease in total cholesterol, serum triglycerides, LDL-C, whereas a significant increase in HDL-C as compared to the placebo group was noted.7 This was somewhat in agreement with a study performed on diabetic patients who were given cinnamon supplementation in the form of 250 mg water extract of cinnamon twice per day for two months. The serum lipids showed a decrease in TC and LDL levels however there was no significant change in HDL-C of the subjects.28
In this work, a comparison of the efficacy of cinnamon, ACV, cinnamon, and ACV combination, was made with simvastatin. Nikolic T et al reported that when statins such as atorvastatin and simvastatin were administered to hypercholesterolemic rats they induce inhibition of cholesterol production in rat liver by blocking HMG-CoA reductase-C levels at the end of 4 weeks.29 We found that the synergistic effect of ACV plus cinnamon was more as compared to the effect of simvastatin in achieving decreased total cholesterol, triglycerides, LDH and increased HDL.
CONCLUSION
Apple Cider Vinegar keeps the anti-hyperlipidemia effect which was found to be significantly high (p<0.05) in combination with Cinnamomum cassia when consumed by male albino mice.
Acknowledgment:
Authors acknowledge the supporting staff for providing their sincere efforts and services to carry out this work. Authors also acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Source of funding:
None
Conflict of Interest:
None
Authors’ Contribution:
AA Conceptualized the work and participated in writing: SA did data collection: MKM analyzed the data and wrote the results:ZI did drafting and revision: SR did data management, entry and verification: NM did a literature search and data collection.
Ethical Clearance:
Ethical clearance was obtained from the institutional review board of ISRA University Islamabad Campus through letter no. F.2/IUIC-ANMC/EC-63/2015.
References:
-
Wang H, Naghavi M, Allen C, Barber RM, Bhutta ZA, Carter A et al., Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study2015. The Lancet. 2016;388(10053):1459–44.
-
Gheorghe G, Toth PP, Bungau S, Behl T, Ilie M, Pantea Stoian A et al. Cardiovascular risk and statin therapy considerations in women. Diagnostics. 2020;10(7):483.
-
Karr S. Epidemiology and management of hyperlipidemia. Am J Managed Care. 2017 Jun 1;23(9 Suppl): S139-48.
-
Jacobson TA, Cheeley MK, Jones PH, La Forge R, Maki KC, López JA et al. The Statin Adverse Treatment Experience Survey: Experience of patients reporting side effects of statin therapy. J Clin Lipidol. 2019 May 1;13(3):415-24.
-
Tripathi S, Mazumder PM. Apple cider vinegar (ACV) and their pharmacological approach towards Alzheimer’s disease (AD): A review. Indian J Pharm Educ Res. 2020;54:s67-74.
-
Patocka J, Bhardwaj K, Klimova B, Nepovimova E, Wu Q, Landi M et al. Malus domestica: A Review on Nutritional Features, Chemical Composition, Traditional and Medicinal Value. Plants. 2020 Nov;9(11):1408.
-
Jain SG, Puri S, Misra A, Gulati S, Mani K. Effect of oral cinnamon intervention on metabolic profile and body composition of Asian Indians with metabolic syndrome: a randomized double-blind control trial. Lip Health Dis. 2017 Dec;16(1):1-1.
-
Lucas K, Fröhlich-Nowoisky J, Oppitz N, Ackermann M. Cinnamon and hop extracts as potential immunomodulators for severe COVID-19 cases. Front Plant Sci. 2021 Feb 26;12:263.
-
KGC D, Liyanage RP, Ranasinghe RH. Traditional Sri Lankan Spices for Dyslipidemia.
-
Iqbal Z, Ashraf T, Khan AA, Hussain R, Mudassar M. Antihyperlipidemic efficacy of cinnamon in albino rats. Asian J Agri Biol. 2016;4(1):8-16.
-
Friendewald WT. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma without use of the preparative ultra-centrifuge. Clin Chem.1972; 8: 499-502.
-
Abdelgadir AA, Hassan HM, Eltaher AM, Khnsaa Mohammed GA, Lamya Mohammed AA, Hago TB. Hypolipidemic effect of cinnamon (Cinnamomum zeylanicum) bark ethanolic extract on triton X-100 induced hyperlipidemia in albino rats. Med Aromat Plants (Los Angeles). 2020;9(351):2167-0412.
-
Packard CJ, Boren J, Taskinen MR. Causes and consequences of hypertriglyceridemia. Front Endocrinol. 2020 May 14;11:252.
-
Ference BA, Ginsberg HN, Graham I, Ray KK, Packard CJ, Bruckert E et al. Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Evidence from genetic, epidemiologic, and clinical studies. A consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel. Eu Heart J. 2017 Aug 21;38(32):2459-72.
-
Okoye NF, Porolo SB. The Effect of Apple Cider Vinegar on the Lipid Profile and Electrolytes of Wistar Rats. J Adv Biol Biotechnol. 2019 May 14:1-1.
-
Abdulrauf RA, Dawud FA, Emmanuel NS, Muhammad HD, Dange AS, David BA et al. Lipid peroxidation and some antioxidant enzymes evaluation in Apple Cider Vinegar (ACV) treated male and female wistar rats exposed to chronic restraint stress. Adv Enz Res. 2018 Sep 14;6(03):21.
-
Launholt TL, Kristiansen CB, Hjorth P. Safety and side effects of apple vinegar intake and its effect on metabolic parameters and body weight: a systematic review. Eu J Nutr. 2020;13(3):1-7.
-
Naz?ro?lu M, Güler M, Özgül C, Saydam G, Küçükayaz M, Sözbir E. Apple cider vinegar modulates serum lipid profile, erythrocyte, kidney, and liver membrane oxidative stress in ovariectomized mice fed high cholesterol. J Memb Biol. 2014Aug;247(8):667-73.
-
Alsoodeeri FN, Alqabbani HM, Aldossari NM. Effects of Cinnamon (Cinnamomum cassia) Consumption on Serum Lipid Profiles in Albino Rats. J Lipids. 2020 Jan 23;2020.
-
Maierean S, Serban MC, Sahebkar A, Ursoniu S, Serban A, Penson P et al. The Effects of Cinnamon Supplementation on Plasma Lipid Concentrations: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Clin Lipidol. 2017 Nov 1;11(6):1393-406.
-
Ousaaid D, Laaroussi H, Bakour M, ElGhouizi A, Aboulghazi A, Lyoussi B et al. Beneficial effects of apple vinegar on hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia in hypercaloric-fed rats. J Diab Res. 2020 Jul 13;2020.
-
Halima BH, Sarra K, Houda BJ, Sonia G, Anis B, Abdallah A. Benefic Effect of Apple Vinegar Cider on Lipid Profile in Streptozotocin-Diabetic Rats. Life Sci J. 2017;14(7).
-
Mateos-Aparicio I, De la Peña Armada R, Pérez-Cózar ML, Rupérez P, Redondo-Cuenca A, Villanueva-Suárez MJ. Apple by-product dietary fibre exhibits potential prebiotic and hypolipidemic effectsin high-fat fed Wistar rats. Bioactive Carbohyd Diet Fibre. 2020 Jul 1;23(1):100219.
-
Petsiou EI, Mitrou PI, Raptis SA, Dimitriadis GD. Effect and mechanisms of action of vinegar on glucose metabolism, lipid profile, and body weight. Nutr Rev. 2014 Oct 1;72(10):651-61.
-
Halima BH, Sarra K, Mohamed S, Louay T, Fethi BS, Houda BJ et al. Apple cider vinegar ameliorates hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia in Tunisian type 2 diabetic patients. Int J Multidisciplinary Current Res. 2017 Nov;5(2321-3124):1453-9.
-
Panetta CJ, Menk JS, Jonk YC, Brown AJ, Powers MA, Shapiro AC. Prospective randomized clinical trial evaluating the impact of vinegar on high-density lipoprotein. J Am Dietetic Assoc. 2010 Sep 1;110(9):A87.
-
Beheshti Z, Chan YH, Nia HS, Hajihosseini F, Nazari R, Shaabani M et al. Influence of apple cider vinegar on blood lipids. Life Sci J-Acta Zhengzhou University Overseas Edition. 2012;9(4):2431-40.
-
Anderson RA, Zhan Z, Luo R, Guo X, Guo Q, Zhou J et al. Cinnamon extract lowers glucose, insulin and cholesterol in people with elevated serum glucose. J Trad Complement Med. 2016 Oct 1;6(4):332-6.
-
Nikolic T, Zivkovic V, Srejovic I, Stojic I, Jeremic N, Jeremic J et al. Effects of atorvastatin and simvastatin on oxidative stress in diet-induced hyperhomocysteinemia in Wistar albino rats: a comparative study. Mol Cell Biochem. 2018 Jan;437(1):109-18.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License