IJCRR - 13(23), December, 2021
Pages: 44-52
Date of Publication: 01-Dec-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Finger Print, Lip Print and Palatal Print as Genetic Markers in the Inheritance of Non-syndromic Cleft Lip and Palate among Bengali Ethnic Group - A Case-control Study
Author: Bera Gopal Chandra, Zahir Shabnam, Bar Shyamal, Saha Rajib, Datta Piyali, Jha Manish
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: CL/CPof neonates may be prevented by identification of genetically susceptible parents through identification of parent's ectodermal markers. Objective/Aim: To identify any specific pattern of Finger Print, Lip Print and Palatal Print among Bengali parents of children with non-syndromic CL&CP which can be considered as a genetic marker in the transmission of CL & CP to their offspring. To determine the predominant finger, lip and palatal print pattern in a healthy Bengali ethnic population. Study Design and Methodology: The present observational, case-control study was performed among 66study subjects, (parents of children with CL&CP), and 66 control subjects, (parents of children without CL&CP) of Bengali ethnicity. Dermato�glyphics, Cheiloscopy and Rugoscopy were performed by ink and paper method, direct photography and impression techniques respectively. Available data were statistically analysed using the Chi-square test and T-test. Result: Study group exhibited increased asymmetry and ulnar loop Fingerprint pattern, higher Type IIa and type O lip print pattern than the control group. Wavy pattern palatal print was the most predominant pattern for both study and control groups. Among the healthy Bengali ethnic population (control group) dominant Finger Print - whorl, Lip Print - Type IIc, Type I and palatal Print - wavy was demonstrated. Conclusion: Increased asymmetry with higher loop patterns in Dermatoglyphics and increased Types IIa, O patterns in Cheilos�copy can be considered as genetic markers for the transmission of CL&CP deformity to offspring in the Bengali populatio
Keywords: Cleft lip and palate, Ectodermal marker, Fingerprint, lip print, Palatal print, Transmission, Cheiloscopy
Full Text:
Introduction
Non-syndromic orofacial clefting is a polygenic, multifactorial disorder. Both genetic and environmental factors contribute to its aetiology.1According to WHO (2001)every 2 minutes a child is born with a cleft somewhere in the world.2In the state of Andhra Pradesh, South India the birth rate of babies with clefts was found to be 1.09 for every 1000 live births.3Children with Cleft lip and palates may be associated with a feeding problem, social stigma, disfigurement, dental malformations, dental caries, speech problems, infections of the middle ear and long term psychological and economical stress for the patient and the family. Thus WHO has included CL & CP in their Global Burden of Disease (GBD) initiatives as it can cause significant infant mortality and childhood morbidity.4
So the ultimate scientific and humanitarian objective must be primary prevention of all craniofacial abnormalities including CL & CP. One of the attempts can be the identification of genetically susceptible parents for having children with cleft lip and palate through the parent’s ectodermal markers such as Finger Print, Lip Print and Palatal Print.
Dermatoglyphics (Finger Print) is a collective term for all the integumentary features, inclusive of the dermal ridge and thick configurational arrangements on the digits, palms and soles excluding flexion creases and other secondary folds. They develop between the 13th to 19th weeks of prenatal life .5Excessive asymmetry between the Dermatoglyphics patterns of the left and right hands may signify relatively unstable genetic control during embryogenesis.6,7
Cheiloscopy(Lip Prints)are also another skin impression, which may be useful in the identification and diagnosis of congenital diseases and anomalies.8,9 L. H. Adamu(2013)concluded that the relationship of Finger Prints and Lip Prints can hold potential promise as a supplementary tool in personal identification as well as genetic markers in many congenital and clinical disorders.10
Rugoscopy (Palatal Print) is the study of palatal rugae which refers to the ridges on the anterior part of the palatal mucosa, each side of the median palatal raphae and behind the incisive papilla. They are being used for forensic personal identification.11,12
Objective-
To record, analyse and compare different patterns of three ectodermal markers namely Finger Print, Lip Print and Palatal Print of healthy parents of children with (study group) or without(control group) non-syndromic CL & CP among Bengaliethnic group of West Bengal, India. To identify if any specific pattern of ectodermal markers of the parent can be considered as a genetic marker in the transmission of CL & CPto their offsprings, thereby helping in primary prevention of CL& CP. To determine the dominant pattern of fingerprint, lip print and palatal print among the control group that is healthy parents with Bengali ethnicity, with healthy children.
Study design and Methodology-
The present observational, case-control study was performed with 66study subjects, Group A( parents of children with non-syndromic CL &/ CP, 33father and 33 mothers) and 66 control subjects, Group B (parents of children without CL &/ CP, 33father and 33mother). The study and control subjects were selected from the Department of plastic and reconstructive surgery of a medical college and the Department of Paediatric Dentistry of a Dental college respectively, of Kolkata, West Bengal, India according to their inclusive and exclusive factors (Table 1). Ethical clearance& Informed Written consent were obtained.
Method of recording and analysing fingerprint pattern
Fingerprints were taken using the ink and paper method(Fig- 1a). Each finger of both right and left hand was gently rolled over the ink spread over the glass slab and then placed from left to right on a plain white paper (Royal executive bond) to record the pattern. The finger imprints were labelled by sides of the hand, they belong to (right or left) and each digit was identified by using roman numerals (thumb = I, index finger II, middle finger III, ring finger IV, and little finger = V). The paper with fingerprints was allowed to dry, serially coded and stored in a box with each paper being separated by an OHP sheet.
Fingerprints were analysed into three groups namely arches (Fig- 1b), loops (Fig- 1c) and whorls (Fig- 1d) following classification by Sir Francis Galton (1892).13Asymmetric score was calculated between corresponding fingers of the right and left hand. The score “0” was assigned if the patterns matched between the fingers and a score of “1” was given if the pattern was not similar. For each sample dissimilarity score range from “0” (when all five pairs of digits had identical patterns) to “5” (when five pairs had different patterns).14
.png)
.png)
.png)
Method of recording and analyzing lip print:
The lip prints were recorded by direct photography under natural lighting using a D-SLR camera and colour film, photocopy of lip print was obtained, serially coded and stored in a box. The lip prints were classified into six types (Type I-VI ) (Fig-2a) following Suzuki and Tsuchihashi's (1970) classification.15 Frequency of each pattern was recorded from “6” topographic areas (Fig-2b) assigned on both upper and lower lips as described by Hassan and Fahmy.16
.png)
Method of recording and analysing palatal-rugae pattern:
The impression technique was used for recording palatal print. Palatal rugae pattern were marked on the casts using normal sharp graphite black colour pencil and the shape of rugae on casts were analysed using the classification given by Thomas and Kotze classification 17(straight, wavy, diverging, converging, curved, circular ) (Fig-3 ).
.png)
Statistical analysis:
All the data was recorded and tabulated. Chi-square test and t-test were done with the help of SPSS software (version 16.0) and the level of significance was set at P<0.05.
Result:
Results related to the study of fingerprint patterns:
The predominant pattern in ten fingers in parents (both father and mother) of the study group was ulnar loop pattern {Aa subgroup - digit I-(51.51%), digit II -(57.57%), digit III -(48.48%), digit IV -(48.48%), digit V -(57.57%)},{Ab subgroup - digit I(57.57%), digit II (60.60%), digit III (60.60%), digit IV (66.66%), digit V (72.72%,}whereas that of control group predominant pattern was whorl pattern (Graph 1& 2).
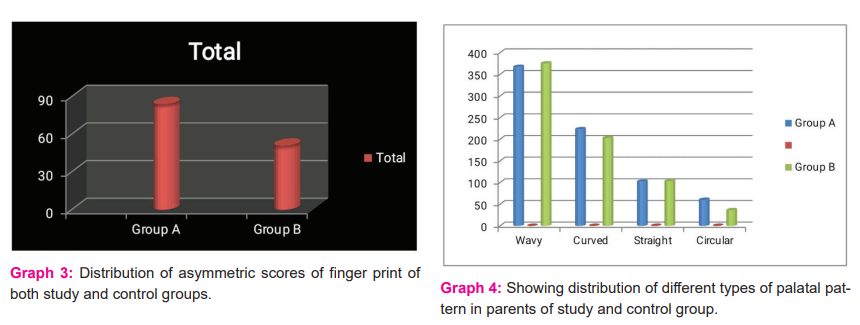
Table 2 shows the asymmetric scores of the Aa group (father of study group) was more (total 41, mean 1.2424, SD1.11) as compared to the Ba group (father of control group) (total 23, mean 0.696, SD0.8472). Table 2 depicts the asymmetric scores of the Aa group (mother of the study group) was more (total 45, mean 1.3636, SD1.0252) as compared to the Ba group (father of control group) (total 27, mean 0.8182, SD 0.8823). Total asymmetric scores were higher in the study group (84, mean 1.2727 ±1.0742) than the control group (51, mean 0.7272±0.8375)(Graph 3).
Among the healthy Bengali ethnic population (control group) the dominant finger print pattern was whorl pattern {Ba subgroup - digit I(48.48%), digit II (48.48%), digit III (57.57%), digit IV (39.39%), digit V (42.42%,},{Bb subgroup - digit I(48.48%), digit II (48.48%), digit IIIUloop pattern(48.48%), digit IV Uloop (54.54%), digit VUloop(60.06%)}(Graph 1& 2).
There was no statistically significant difference between the fingerprint pattern of father and mother in either of the group (Graph 1& 2).
Results related to study of lip print pattern:
The most dominant pattern for upper and lower lips of the study group was Type IIa pattern ( Aa upper lip- 27.27%, Aa lower lip -21.21%, Ab upper lip- 21.21%, Ab lower lip-27.27%) and type O pattern( Aa upper lip- 18.08%, Aa lower lip -15.15%, Ab upper lip- 24.24%, Ab lower lip-15.15%) which was lower in parents of the control group. Type III pattern was significantly lower (0- 3.03%) in the study group as compared to the control group (3-9%) (Table3, 4, 5, 6).
Among the healthy Bengali ethnic population (control group) the dominant lip pattern was Type IIc (15.15%) in both the upper and lower lip of the father (Ba subgroup)and Type I in both upper (21.21%) and lower lip (24.24%) of the mother (Bb subgroup) (Table 3,4,5,6 ).
Results related to study of palatal print pattern:
Among palatal print patterns, total wavy patterns in parents (mother plus father) were 367(mean 5.47761±1.4705) and 375 (mean 5.56061±1.37179) of the study and control group respectively. There was no statistically significant difference (P value - 0.34832) in the prevalence of wavy patterns in parents of the study & control group (Graph 4).
Among the healthy Bengali ethnic population (control group) the dominant palatal pattern was wavy pattern {375 (mean 5.56061±1.37179)} (Graph 4).
Discussion
The epidermal ridges of the fingers and palm as well as the facial structures like the lip, alveolus and palate are formed from the same embryonic tissues (ectoderm) during the same embryonic period (6-9 weeks). That means that the genetic message contained in the genome-normal or abnormal is deciphered during this period and is also reflected by dermatoglyphics.18Anypeculiarities in the ectodermal patterns of parents may be inherited to their offspring. In this context parents’ ectodermal patterns may be used as a diagnostic tool for ectodermal derived developmental disorders such as neural developmental disorders (Schizophrenia, Down syndromes etc) and cleft lip and or palate. Over the last few decades dermatoglyphics, Cheiloscopy & rugoscopy have been used individually to understand successfully the biology, genetics & evaluation of different congenital diseases and anomalies especially cleft lip and/or palate in addition to their use in personal identification. As of we know, there are very few studies that compared all the three ectodermal markers together among parents of nonsyndromicCL&CP children and parents of healthy children.
Different studies revealed that congenital anomalies especially cleft lip and /or palate have a racial and ethnic predilection.19 Ethnic identity has included a sense of belonging to a group connected by heritage, values, traditions, and languages. The present study has been undertaken among Bengaliethnic groups, whose mother tongue is Bengali and whose permanent residential address for three generations is in West Bengal, India.20 Bengali people are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group native to the Bengal region in South Asia. They speak the Bengali language. Bengalis are the third largest ethnic group in the world.
Nonsyndromic cleft (70% of CL/P cases and 50% of CP cases) accounts for the majority among oral cleft patients, while syndromic cleft accounts for 19% of the cases.21, 22 Thus in the present study parent of children with non-syndromic cleft lip and palate were considered as the study population.
The different method of recording fingerprints is the ink and paper method and the Live Scan method. Either Rolled impressions, Flat impressions of fingers are taken for the ink and paper method.23Lip prints can be recorded by Photographing the lips, lipstick and paper or cellophane tape method, using a fingerprinter, by taking an impression of the lip with a Magna brush and magnetic powder.24Photographs or oral impressions are routinely used in Palatal rugoscopy.25Present study utilized ink and paper method with rolled impression technique, the photograph of lip and impression of the palate for recording fingerprint, lip print and palatal print respectively as they are easy, adequate method with the requirement of few and simple armamentaria.
Similar to the present study Naveen Reddy Admalaet al.(2014) and K Saujanya et al. (2016)also concluded that increased dermatoglyphic asymmetry with higher loop patterns was seen in the parents with cleft children and increased whorl patterns in parents with normal children.26,27 Asymmetry reflects the influence of the environment on developing structures, and as a result, it can serve as an indicator of environmental stress and the general co-adaptation of the genome. 28-31
Similar to the Bengali population Georgia’s Asian population have more whorl pattern than other ethnicities.32 Unlike Bengali population the most commonly occurring patterns are Loops among two major ethnic groups of North India, Rajput and Brahmin ancestry of Districts Shimla and Solan of Himachal Pradesh state of north India33, Loops and arches are dominant fingerprint pattern among the Black population of Georgia32 and ulnar loop was dominant among the Itsekiri females and Urhobo males while the whorl and arch patterns were frequent in the Itsekiri males and the Urhobo females of Southern Nigeria. 34
Wael M Saad et al. (2005) concluded that there was an increased frequency of lip print patterns II (branched grooves ) in parents of CLP subjects with an increase in pattern III(intersected lines) in normal children’s parents which were similar to the result of this study .35
The most common lip print pattern in the Bengali population was Type I, which is in agreement with the study done by Vahanvala and ParekhandTsuchihashi et al.36, 37 While in a study conducted on the Indo-Dravidian population, Sivapathasundharam et al. found that Type III pattern was predominant.38Verghese et al. in their study on Kerala population, found that Type IV pattern was predominant.39
In the present study, there was no statistically significant difference in the prevalence of different palatal Print patterns between study and control groups. As per the authors’ knowledge, there is no documented previous study analysing palatal print as a genetic marker for the inheritance of cleft lip and palate in the immediate generation.
Regarding rugoscopy of healthy parents (control group) of Bengali ethnicity, the wavy pattern was the most common predominant pattern. Abdellatif AM et al. (2011)40 in Egyptians and Saudi pediatric population groups, Nayak P et al. (2007),41Kotrashetti et al. (2011),42Satish KN et al. (2012),43in Indian population andKapali et al. (1997)44in Australian Aborigines and Caucasian population, also found the wavy pattern of palatal rugae to be the most common shape. In contrast, Shetty SK et al. (2005)45 revealed that Indian males had the more curved pattern and Tibetan females had wavier patterns than their counterparts.
Conclusion: Increased asymmetry with higher loop patterns in Dermatoglyphics and increased Types IIa and O patterns in Cheiloscopy can be considered as genetic markers for the transmission of CL&CP deformity to offspring in the Bengali population. Among the healthy Bengali ethnic population dominant fingerprint, lip print and palatal print pattern are whorl pattern, Type IIc, Type I pattern and wavy pattern respectively.
Acknowledgement-
Faculty members of Guru Nanak Institute of Dental Sciences & Research, for all the support during this project.
Ethical Clearance- Letter No. GENDER/15-30
Source of Funding-Nil
Conflict of Interest -Nil
Authors’ Contribution
Conception- ShabnamZahir, Gopal Chandra Bera,
Data collection- Gopal Chandra Bera, Shyamal Bar, Piyali Datta, RajibSaha
Data analysis - Gopal Chandra Bera, Shabnam Zahir, Shyamal Bar, Manish Jha
Drafting the article- Gopal Chandra Bera, Shabnam Zahir, Shyamal Bar,
Piyali Datta, Rajib Saha
Final approval of the version to be published - Gopal Chandra Bera,
Shabnam Zahir, Shyamal Bar,Piyali Datta, Rajib Saha, Manish Jha
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
References:
1. Dixon MJ, Marazita ML, Beaty TH, Murray JC. Cleft lip and palate: understanding genetic and environmental influences. Nat Rev Genet. 2011 Mar;12(3):167-78.
2. Global strategies to reduce the health care burden of craniofacial anomalies: report of WHO meetings on international collaborative research on craniofacial anomalies. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2004 May;41(3):238-43
3. Reddy SG, Reddy RR, Bronkhorst EM, Prasad R, Ettema AM, Sailer HF, Bergé SJ et al. Incidence of cleft lip and palate in the state of Andhra Pradesh, South India. Indian J Plast Surg. 2010 Jul;43(2):184-9.
4. Mossey P, Little J. Addressing the challenges of cleft lip and palate research in India. Indian J Plast Surg. 2009 Oct; 42Suppl (Suppl)
5. Cummins H, Midlo C. Palmar and plantar epidermal ridge configuration (Dermatoglyphics) in Europeans - Americans. Am J Phy Anthrop.1926;9(4):471-502
6. Woolf CM, Gianas AD. A study of fluctuating dermatoglyphic asymmetry in the sibs and parents of cleft lip propositi.Am J Hum Genet. 1977 Sep;29(5):503-7
7. Neiswanger K, Cooper ME, Weinberg SM, Flodman P, BundensKeglovits A, Liu Y, Hu D?N, Melnick M, Spence MA, Marazita ML et al. Cleft lip with or without cleft palate and dermatoglyphics asymmetry: evaluation of Chinese population. OrthodCraniofac Res. 2002 ; 5 (3) : 140- 146.
8. Synder LM. Personal identification using lip prints. Quoted from Suzuki K and Tsuchihashi Y. J Forensic Med 1970;7:52.
9. Gondivkar SM, Indurkar A, Degwekar S, Bhowate R. Cheiloscopy for sex determination. J Forensic Dent Sci . 2009;1:56-60
10. Adamu LH, Taura M G, Hamman W O, Ojo S A, Dahiru A U, Sadeeq A A, Umar KB et al. Relationship of thumbprints and lip prints among Nigerians. J Med Dent Sci.2013; 9(2) :12-17
11. Alshihri AM, Kruger E, Tennant M. Western Saudi adolescent age estimation utilizing third molar development. Eur J Dent 2014;8:296-301
12. Manjunath S, Bakkannavar SM, Pradeep Kumar G, Bhat VJ, Prabhu N, Kamath A, et al. Palatal rugae patterns among the Indians at Manipal, India. J Pharm Biomed Sci 2012;20:1-5.
13. Galton F.( 1892).Fingerprint.Macmillan, London;78
14. Shadrina E, Vol’pert Y. Functional asymmetry and fingerprint features of left-handed and right-handed young Yakuts (Mongoloid race, North-Eastern Siberia). Symmetry2018; 10:728.
15. Jaishankar S, Jaishankar N, Shanmugam S. Lip prints in personal identification. J Indian Acad Dent Spec 2010; 1:23-6.
16. Hassan FZ, Fahmy SM. The pattern of lip prints in upper Egyptian. Assiut Medical J 1977; 1(4) : 477- 486
17. Thomas CJ, KotzeTW, Van Der Merwe CA.An improved statistical method for the racial classification of man employing palatal rugae.Archives of Oral Biology.1987;32(4):315-317
18. Mathew L, Hegde A M, Raik: Dermatoglyphic peculiarities in children with oral cleft .J Indian SocPedodPrev Dent 2005; 23(4):179-182.
19. Arosarena OA. Cleft lip and palate.OtolaryngolClin North Am. 2007 Feb; 40(1):27-60
20. Phinney JS, Ong A.Conceptualization and measurement of ethnic identity: Current status and future directions. Journal of Counselling Psychology.2007;54:271-281
21. Jugessur A, Farlie PG, Kilpatrick N. The genetics of isolated orofacial clefts: from genotypes to subphenotypes. Oral Dis. 2009 Oct;15(7):437-53
22. Hadadi AI, Wahhabi DA, Amtrak N, Aljahdali N, Meshal OA, Badri M. Congenital anomalies associated with syndromic and non-syndromic cleft lip and palate.JPRAS Open.2017;14:5-15
23. FBI. Recording Legible Fingerprints; cited on 22.9.20: Retrieved from <https://www.fbi.gov/services/cjis/fingerprints-and-other-biometrics/recording-legible-fingerprints>
24. Dinesh Shankar J, Ganapathi N, Yoithapprabhunath TR, Maheswaran T, Kumar MS, Aravindhan R. Lip prints: Role in forensic odontology. J Pharm Bio allied Sci. 2013; 5(Suppl 1)
25. Bansode SC, Kulkarni MM. Importance of palatal rugae in individual identification. J Forensic Dent Sci [serial online] 2009;1:77-81.
26. Admala NR, Arjun S, Adusumili G, Thirumala JR, Devanna R, Pichai S. Dermatoglyphics and Cheiloscopy in the inheritance of cleft lip and palate: Unravelling the mystery. J Indian Orthod Soc. 2014; 48:175-9.
27. Saujanya K, Prasad MG, Sushma B, Kumar JR, Reddy YS, Niranjani K. Cheiloscopy and dermatoglyphics as genetic markers in the transmission of cleft lip and palate: A case-control study. J Indian SocPedodPrev Dent. 2016 Jan-Mar;34(1):48-54.
28. Zakharov VM, Zhdanova NP, Kirik EF, Shakil FN. Ontogenesis and population: Evaluation of developmental stability in natural populations. Russ J Dev Biol. 2001;32:336–351
29. Leary RF, Allendorf FW. Fluctuating asymmetry as an indicator of stress: Implications for conservation biology. Trends Ecol Evol. 1989 Jul;4(7):214-7.
30. Parsons PA. Fluctuating asymmetry: an epigenetic measure of stress. Biol Rev CambPhilos Soc. 1990 May;65(2):131-45
31. Parsons PA. Fluctuating asymmetry: a biological monitor of environmental and genomic stress. Heredity (Edinb). 1992 Apr;68 ( Pt 4):361-4.
32. Swofford H J.Fingerprint patterns: A study on the finger and ethnicity prioritized order of occurrence.J. Forensic Identif.2005; 55 (4):480-488
33. Baryah N, Krishan K. Exploration of digital dermatoglyphics of two ethnicities of North India- forensic and anthropological aspects.Forensic Science International: Reports.2020;2:100055
34. Ojigho E J J, Odokuma I E, &Igbigbi P S. Comparative study of fingerprint patterns of two ethnic groups: A Nigerian study. J College of Med Sci Nepal. 2019;15(4):270-275
35. SaadWM, Kamel AH, Hassan FZ, Elotiefy MA. Genetic studies on the inheritance of lip prints in-cleft lip and palate. Egypt J PlastReconstr Surg. 2005; 29:9-12
36. Vahanwala SP, Parekh BK. Study of lip prints as an aid to forensic methodology. J Indian Dent Assoc. 2000;71:268–71.
37. Tsuchihashi Y. Studies on personal identification using lip prints. Forensic Sci. 1974; 3: 233-48
38. Sivapathasundaram B, Prakash PA, SivakumarG.Lip prints(rhinoscopy). Indian J Dent Res.2001;12:234–7.
39. Varghese A J, Somesekar M, Babu UR. A study on lip prints types among the people of Kerala. J Indian Acad Forensic Med. 2010;32:6–7.
40. Abdellatif AM, Awad SM, Hammad SM. Comparative study of palatal rugae shapes in two samples of Egyptian and Saudi children. Pediatric Dent J. 2011;21:123–8.
41. Nayak P, Acharya AB, Padmini AT, Kaveri H. Difference in the palatal rugae shape in two populations of India. Arch Oral Biol. 2007; 52:977–82.
42. Kotrashetti VS, Hollikatti K, Mallapur MD, Hallikeremath SR, Kale AD. Determination of palatal rugae patterns among two ethnic populations of India by logistic regression analysis. J Forensic Leg Med.2011;18:360–5.
43. Kumar S, Vezhavendhan N, Shanthi V, Balaji N, Sumathi MK, Vendhan P. Palatal rugoscopy among Puducherry population. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2012; 13:401–4.
44. Kapali S, Townsend G, Richards L, Parish T. Aust. Dent. J. 1997; 42:(2):129-33
45. Reddy LV. Lip prints: An overview in forensic dentistry. J Adv Dent Res 2011; 2:17-20.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License