IJCRR - 13(20), October, 2021
Pages: 165-169
Date of Publication: 24-Oct-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Drug Sensitivity Pattern in Diabetic and Non Diabetic Patients Suffering from Urinary Tract Infection
Author: Kaila Niyti Vinod, Thorat Sanjay Tukaram
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Urinary tract infection (UTI) is a spectrum of disease caused by microbial invasion of the genitourinary tract that extends from the renal cortex of the kidney to the urethral meatus. The predisposing factors for UTI can be anatomical abnormalities of the urinary tract, Impaired local protective mechanisms, deteriorating immune status, cognitive impairment, comorbid conditions such as diabetes, malignancy, steroid use and chronic debility. Urine serves as an excellent culture medium, to avoid false-positive results transportation should be immediate. Sample should be stored in a refrigerator at 4oC for 48hrs if there is a delay of more than one to two hours. Aim: Here is to study the drug sensitivity pattern in diabetic and non-diabetic patients with urinary tract infections. Method: That we have adopted for our research is carried on patients diagnosed with Urinary tract infection with or without a history of type 2 Diabetes mellitus who were admitted in medical wards in Krishna Hospital and Medical Research Centre, Karad during the study period of 18 months. This study was conducted over 18 months. (October 2018 to March 2020). Ethical clearance from the college and university committee was taken. Result: In the present study, a total of 90 patients diagnosed with urinary tract infections were observed. Among them 45 patients were diabetics and 45 patients were non-diabetics. In the current study, the diabetic group had 26 females (57.78%) and 19 were males (42.22%) and the non-diabetic group had 29 females (64.44%) and 16 males (35.56%) males. Conclusion: Urinary tract infection is one of the common infections requiring hospitalization. In the present study female gender was predominantly affected with urinary tract infection in both groups (i.e. Diabetics and non-diabetics).
Keywords: Diabetic, Urinary tract infection, Cystine lactose electrolyte deficient, Urine, Microbial genitourinary tract, Kidney
Full Text:
Introduction
Urinary tract infection (UTI) is a spectrum of disease caused by microbial invasion of the genitourinary tract that extends from the renal cortex of the kidney to the urethral meatus. The predisposing factors for UTI can be anatomical abnormalities of the urinary tract, Impaired local protective mechanisms, deteriorating immune status, cognitive impairment, comorbid conditions such as diabetes, malignancy, steroid use and chronic debility. Women are more susceptible to UTI because of their urinary tract anatomy and reproductive physiology. The female to male ratio of UTI among geriatrics and younger population shows great variation 50:1 and 2:1 respectively.1
Laboratory diagnosis can be detected by microscopic examination of a fresh sample of urine collected by appropriate methods. Further diagnosis can be confirmed by isolation of the significant number of bacteria on urine culture. Apart from microbiological investigations further work to detect the exact cause, predisposing factors, presence of anomalies and complications can be done by radiological tools and other methods. Sample collection: Clean catch mid-stream urine sample (MSU): This is the most easily and most commonly collected sample. Clean catch mid-stream urine collected in a wide-mouthed, sterile and leak-proof plastic container of 30 ml capacity.2,3 Patient is asked to wash the perineum and the genitalia thoroughly with mild soap and water. Antiseptics for washing or cleaning are not recommended.4
They are particularly used to obtain a sample in elderly men, who don’t have urinary retention problems but have serious functional or mental disabilities, such as dementia. It carries a lower risk of infection than indwelling catheters.5 Invasive methods: Straight catheterization/ In and Out Urinary Catheterization. It yields a sample of the same quality as suprapubic aspirate but carries the risk of the introduction of bacteria to the bladder. It is preferred only when a clean voided sample cannot be obtained and suprapubic sampling is contraindicated.6 Under all aseptic precautions catheter is lubricated and directed in the cleansed urethra initial 15-30 ml is discarded. The mid or low flow urine sample is collected into the vacutainer or a sterile container.
Transportation: Urine serves as an excellent culture medium, to avoid false-positive results transportation should be immediate. Sample should be stored in a refrigerator at 4oC for 48hrs if there is a delay of more than one to two hours.7 Transportation in a container with boric acid at a final bacteriostatic concentration of 1.8% is another alternative to refrigeration. Dip-slide method: Urine is collected in a dip slide container that has different media seeded on a small tray. Extra urine is drained out and charged dip slides are then incubated. Limitations of this technique are microscopic analysis and quantification of bacteria cannot be done. It is useful for screening a large number of patients, geriatric nursing homes and for use in clinics remote from the laboratory.4 Microscopic examination is a standard technique for examining urine specimens microscopically has not been established. An uncentrifuged sample of urine is examined for the presence of polymorphs or pus cells and bacteria.
Wet mount: The presence of an increased number of pus cells (normal excretion of leukocytes is about 106 in 24 hours) in urine indicates pyuria. This is an indication of infection in the urinary tract when culture fails to show significant growth either due to antibiotic effect or if the bacteria require special media. One leukocyte per seven high power fields corresponds with 104 leukocytes per ml. Anything more than this is considered significant. Contamination is suspected when there is the presence of squamous epithelial cells (from perineum and vagina) on microscopy.4 Gram’s stain is an inexpensive method to detect bacteriuria. The presence of even one organism per oil immersion field in uncentrifuged urine has a sensitivity of 94% and specificity of 90% for detecting colony counts of 105 CFU/ml. It can provide a quick detection of gram-positive or Gram-negative bacteria before culture reports come where pyuria has been observed on a wet film to start an empirical treatment.8
Culture Quantitative culture: Urinary pathogens grow well on simple as well as selective media with an overnight incubation at 37oC. Blood agar, MacConkey agar and Cystine lactose electrolyte deficient (CLED) agar are the preferred media used. MacConkey and CLED agar have an added advantage as they can distinguish lactose fermenters from non-lactose fermenters. They also inhibit Proteus spp. from swarming and CLED agar is less inhibitory to Staphylococcus saprophyticus. Blood agar is recommended for nutritionally exact in organisms. In the standard loop method, a sterile loop, nichrome or platinum wire of SWG 28 is used which delivers a volume of 0.004 ml volume which yields around 400 colonies, the count then will be 105. Alternatively, since this may produce confluent growth making it difficult to obtain isolated colonies, a sterile loop holding 0.001ml is ideal. The growth of about 100 colonies by this method indicates the presence of 105 bacteria/ml of urine.2,4 Filter paper method: Standard filter paper strip of L shape (12 x 6 mm), sterilized at 160oC for one hour is used. Angulated end and foot is dipped into a well-mixed, uncentrifuged sample of urine and pressed on selected media and is kept for incubation. This method is quite rapid and economical because eight to ten samples can be tested at the same time on a single plate. Growths are noted as semi-confluent and confluent depending on the number of colonies. Approximately 25 colonies of bacilli or 30 colonies of cocci correspond to105CFU/ml.4
Identification: The Gram staining of the growth on the plate is done. The preliminary tests like motility, catalase and oxidase are performed. The biochemical reactions like Hugh Leifson’s oxidation fermentation, nitrate reduction, indole, methyl red, Voges- Proskauer, citrate, triple sugar iron agar, sugar fermentation, urease, lysine decarboxylation, arginine dehydrogenation, ornithine decarboxylation and phenylalanine deaminase (PPA) tests to differentiate bacilli. Staphylococcus aureus can be differentiated from coagulase-negative Staphylococcus spp. based on tube coagulase test. The Novobiocin test can further differentiate Staphylococcus saprophyticus from other species of Staphylococcus. Catalase test can differentiate Streptococcus spp. from Staphylococcus spp. Enterococcus spp. can easily be identified based on bile esculin and sugar fermentation tests.
Aim:
To study the drug sensitivity pattern in diabetic and non-diabetic patients with urinary tract infection.
Objectives:
• To assess the prevalence of urinary tract infection in diabetic and non-diabetic patients
• To assess the yield of urine culture in diabetic and non-diabetic patients suffering from urinary tract infection and the common causative organisms
• To study the comparison of drug sensitivity patterns in diabetic and non-diabetic patients suffering from urinary tract infection
Methods
This was a Cross-Sectional and observational Study. The study was carried on patients diagnosed with Urinary tract infection with or without a history of type 2 Diabetes mellitus who were admitted to medical wards in Krishna Hospital and Medical Research Centre, Karad during the study period of 18 months. This study was conducted over 18 months. (October 2018 to March 2020). Ethical clearance from the college and university committee was taken. After ethical clearance, permission was taken from the head of departments. (Protocol Number 0258/2018-2019). According to a study conducted by S M Aswani et al.,[9] the prevalence of bacteriuria in diabetic and non-diabetic patients in their study was found as 30.5%,
So, p 30.5%
Using formula for sample size (n) calculation, 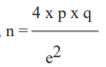
Where, p = 30.5% = 0.305 q = 1 - p = 0.695
Taking e, absolute error of 10%, e = 0.1 So, n = 4 x 0.305 x 0.695
0.1 x 0.1
n = 84.79 ≈ 85
A minimum of 85 patients will be included in the study, rounding it off to 90 for better yield and statistical results. n= 90. A total of 90 patients were enrolled for the present Cross-Sectional and observational study, 45 each from diabetic and non-diabetic groups.
Inclusion criteria: All patients aged >18 years presenting at tertiary care centre at Krishna hospital Karad. The first episode of symptomatic and asymptomatic bacteria, in both diabetic and non-diabetic patients. Patients with or without symptoms of UTI with significant Pyuria. Significant Pyuria is defined as more than 5 WBC per high power field in males and more than 8 WBC per high power field in females. Patients with fasting blood glucose levels of 126mg/dl or higher or random blood glucose levels of 200mg/dl or higher or patients with glycosylated HbA1C levels of 6.5% or higher will be in included as patients with diabetes mellitus.
Exclusion criteria: Age less than 18 years. Gestational diabetes mellitus, Immunocompromised states-HIV, patients on steroids, malignancy, transplant recipients, Reproductive tract infection Investigations. Blood sugar levels (Fasting, Postprandial, Random), Glycosylated haemoglobin (HbA1c), Urine routine microscopy, Urine culture and sensitivity.
For estimation of fasting blood glucose levels, early morning venous blood samples with 8 hours of no-calorie intake were taken with the aseptic precautions in an Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) sodium fluoride vacutainer (1ml). Similarly, samples were collected for 2 hours postprandial and random blood glucose estimation. Blood sugar levels (fasting, postprandial and random) were calculated by Trinder‘s method (Glucose Oxidase-Peroxidase Method) automatically on the EM360 Transasia machine. For estimation of blood HbA1c levels, venous blood samples were collected in EDTA vacutainer (2ml) with the aseptic precautions and were tested by latex immunoturbidimetric test (automatically) on EM360 Transasia machine. It reflects blood sugar levels over the past 8 to 12 weeks.
Results
In the present study, a total of 90 patients diagnosed with urinary tract infections were observed. Among them 45 patients were diabetics and 45 patients were non-diabetics. In the current study, the diabetic group had 26 females (57.78%) and 19 were males (42.22%) and the non-diabetic group had 29 females (64.44%) and 16 males (35.56%) males. The Female: Male ratio in this study was 1.57:1. The mean age group found in this study was about 55.02 years with the majority of subjects falling in the age group of 41 to 50 years and 51 to 60 years.
Elevated fasting blood sugar levels were found in 45.55% of cases and postprandial blood sugar levels in 31.11% of cases. A significant difference was seen between the urine sugar values of the participants. The most common organism isolated was E Coli in 66.7% cases followed by Klebsiella spp.14.4% cases, Enterobacter spp. In 6.7% cases, Coagulase Positive Staphylococcus in 6.7% cases and Pseudomonas aerogenosa in 5.6% cases. The most common organism isolated in both diabetics and non-diabetics was E Coli amounting to 46.7% and 53.3% cases respectively. This was followed by Klebsiella spp. for both diabetics and non-diabetics amounting to 61.5% and 38.5% cases respectively. Among Coagulase Positive Staphylococcus isolates 33.3% cases were diabetics and 66.7% cases were non-diabetics. Also Enterobacter spp. isolates were seen in 33.3% cases of diabetics and 66.7% cases of non-diabetics. Pseudomonas aerogenosa were all seen in diabetics (100%).
There was a significant difference between the diabetics and non-diabetics with regards to Trimethoprim + Sulfamethoxazole resistance with 57.1% cases seen in diabetics and 42.9% cases in non-diabetics. There was a significant difference between the diabetics and non-diabetics with regards to Ampicillin resistance, with diabetic patients showing more resistance. There was a significant difference between the diabetics and non-diabetics with regards to Amoxicillin resistance, with diabetic patients showing more resistance. There was a significant difference between the diabetics and non-diabetics with regards to 1st generation Cephalosporins resistance, with diabetic patients showing more resistance.
There was a significant difference between the diabetics and non-diabetics with regards to Nitrofurantoin resistance, with diabetic patients showing more resistance. There was no significant difference between the diabetics and non-diabetics with regards to Fluoroquinolones resistance. Comparison based on the number of drugs resistant in diabetic and non-diabetic groups was found to be significant where overall the diabetic group had more number of drug resistance. Their a significant association between the number of drugs an organism is sensitive or resistant to with the presence of diabetes.
Discussion
Demographic profile and frequency distribution of age of study population
Out of all 90 cases, 55(61.1%) were females and 35(38.9%) were males. The Female: Male ratio in the present study was 1.57:1 According to Akbar daad et al. who conducted a hospital-based study of a total of 182 patients and found 114 (62.63%) were females and 68 (37.36%) were males.10 The female: male ratio was 1.6:1 which was similar to the present study. In another study done by Ramrakhia S, Raja K, Dev K, et al.. who conducted a hospital-based study found that female: male ratio was 1.28 :1 which had 288 (56.25%) females and 224 (43.75%)11 males and the study of Christy VR et al.. conducted an epidemiological study on urinary tract infections found female: male ratio 1.29:1 which had 1029(56.41%) females and 795 (43.58%) males12 which was lower than the present study but however it was still found that the prevalence of urinary tract infection was higher in females as compared to males. The study from Kumar R, Kumar R, Perswani P, et al.. had 256 patients in the diabetic group with a female: male ratio of 1.28:1, there were 112 (43.7%) males and 144 (56.3%) females.13 Considering non-diabetic group there were more women (n = 156; 62.4%) than men (n = 94; 37.6%) which was similar to the present study.
The majority of the patients were from the age group of 51 to 60 years, 33 patients (36.7%) followed by 41 to 50 years with 23 patients (25.6%), 61 to 70 years with 17 cases (18.9%), 9 cases less than 40 years (10%) and 8 cases in the age group of 71 to 80 years (8.9%). The mean age of our study was 55.02 years. According to Magliano et al.. the study reported that 58% of subjects were in the age group of 60 years and above while comparing to the present study there were 45.55% of patients in the same age group.14 According to the study from Aswani SM et al.. the mean age among diabetic and non-diabetic patients was 60.2 ± 13.76 years and 53.47 ± 18.56 years.9
Maharjan, Narayani & Thapa et al.. study has shown average age of subjects affected with urinary tract infection was 51 to 70 years (45.9%)15 which was similar to the present study. The study of Christy VR et al.. has shown patients affected with urinary tract infection fallen in the age group of 50 years and above where 38.92% which was lower than the present study.12 The study from Kumar R, Kumar R, Perswani P, et al.. mean age group affected was 56 +/- 11years which is found to be similar to the present study.13 In the present study, fasting blood sugar level was raised in 41 cases (45.55%) suffering from urinary tract infection and postprandial blood sugar was raised in 28 cases (31.11%) According to the study done by Hamdan HZ et al.. it was found that 54.2% cases of urinary tract infections had elevated fasting blood sugar levels16 being similar to present study. The study done by Sharma S, Govind B, Naidu SK, Kinjarapu S, Rasool M et al.. had found 96% cases with elevated fasting sugar levels.17 which is higher than the present study. The most common organism isolated in the present study was E Coli in 60 cases (66.7%) followed by Klebsiella spp. in 13 cases (14.4%), Enterobacter spp. in 6 cases (6.7%), Coagulase Positive Staphylococcus in 6 cases (6.7%) and Pseudomonas aerogenosa in 5 cases (5.6%). The study done by Kumar R, Kumar R, Perswani P, et al. also showed most common organisms isolated as E Coli in 21 cases (60%) followed by Klebsiella spp. in 6 cases (17.1%), Enterobacter spp. in 3 cases (8.6%), Coagulase Positive Staphylococcus in 2 cases (5.7%) and Pseudomonas aerogenosa in 5 cases (14.3%)13, results being similar to the present study.
Antimicrobial drug sensitivity and resistance pattern among diabetics and non-diabetics. Trimethoprim + Sulfamethoxazole sensitivity & resistance in Diabetics and non-diabetics. Total 70 cases (77.8%) were resistant to Trimethoprim + Sulfamethoxazole & 20 cases were sensitive (22.2%) in the present study out of the resistant cases,40 cases were diabetic (57.1%) and rest 30 were non-diabetic (42.9%). The study from Akbar daad et al. showed Trimethoprim + Sulfamethoxazole resistance in 50% diabetic cases and 27% non-diabetic cases 10 which is similar to our study. According to the study from Aswani SM et al. showed Trimethoprim + Sulfamethoxazole resistance in 38.9% diabetic cases and 30.2% non-diabetic cases.9 Ampicillin sensitivity & resistance in Diabetics and non-diabetics. Total 57 cases (63.3%) were resistant to Ampicillin & 33 cases were sensitive (36.7%) in the present study. Out of a total of 57 cases resistant to Ampicillin, 36 cases were diabetic (63.2%) and the rest 21 were non-diabetic (36.8%). According to the study from Aswani SM et al. showed Ampicillin resistance in 16.7% diabetic cases and 17% non-diabetic cases.9 Akbar daad et al. showed Ampicillin resistance in 8% diabetic cases and 15% non-diabetic cases.10
Conclusion
Urinary tract infection is one of the common infections requiring hospitalization. The presence of diabetes mellitus increases the susceptibility to urinary tract infection. In the present study female gender was predominantly affected with urinary tract infection in both groups (i.e. Diabetics and non-diabetics). In the present study, the predominant isolates were E.coli and Klepsiella spp. for both diabetic and non-diabetic groups. Most of the isolates showed intermediate to low levels of resistance to one or more antimicrobials tested. Diabetic subjects showed resistance to multiple antimicrobial drugs as compared to non-diabetic subjects. This indicates that regular surveillance is required to establish reliable information about the sensitivity and resistance pattern of urinary tract infective pathogen for empirical therapy of diabetic patients with urinary tract infection. According to the results of the present study, Nitrofurantoin, Fluoroquinolones and first-generation Cephalosporins (Cephalexin and Cefadroxil) can be used empirically till culture and sensitivity reports are awaited.
Acknowledgement: We acknowledge the contribution of our university and department for the unending support.
Conflict of Interest: There is no conflict of Interest
Source of Funding: No Source of Funding
Authors Contribution: This is a collaborative work among both authors. Niyti Vinod Kaila, Sanjay Tukaram Thorat performed the statistical analysis, wrote the protocol, and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. Niyti Vinod Kaila managed the literature searches. Both the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
References:
1. Venkatesh RK, Prabhu MM, Nandakumar K, Sreedhara K, Pai R. Urinary tract infection treatment pattern of elderly patients in a tertiary hospital setup in south India: a prospective study. J Young Pharm 2016;8(2):108-13.
2. Forbes BA, Sahm DF, Weissfeld AS. Diagnostic microbiology. St Louis: Mosby; 2007. p. 842-543.
3. Tawab KA, Gheith O, Al Otaibi T, Nampoory N, Mansour H, Halim MA, Nair P, Said T, Abdelmonem M, El-Sayed A, Awadain W. Recurrent urinary tract infection among renal transplant recipients: risk factors and long-term outcome. Exp Clin Transplant. 2017 Apr 1;15(2):157-63.
4. Collee JG, Duguid JP, Fraser AG, Marmion BP, Simmons A. Laboratory strategy in the diagnosis of infective syndromes. Mackie and McCartney practical medical microbiology. 1996;14: 53-94.
5. Holroyd S. Indwelling urinary catheterisation: evidence-based practice. J. Community Health Nurs. 2019 Oct 1;33(5).
6. Hinkel A, Finke W, Bötel U, Gatermann SG, Pannek J. Increasing resistance against antibiotics in bacteria isolated from the lower urinary tract of an outpatient population of spinal cord injury patients. Urol. Int. 2004;73(2):143-8.
7. Porter IA, Brodie J. Boric Acid Preservation of Urine Samples. Br Med J 1969;2(5653):353-55.
8. Wilson ML, Gaido L. Laboratory diagnosis of urinary tract infections in adult patients. Clin Infect Dis 2004;38(8):1150–8.
9. Maharjan, Narayani, Thapa, Niresh,Maharjan, Muna, Sharma, Vijay, Maharjan, Nabina, Paudyal, Rabin. The pattern of bacteria causing urinary tract infection and their antibiotic susceptibility profile in diabetic and non-diabetic patients in Lalitpur, Nepal-a hospital-based study. 20187; 7. 1248-5348.
10. Ramrakhia S, Raja K, Dev K, Kumar A, Kumar V, Kumar B. (September 17, 2020) Comparison of Incidence of Urinary Tract Infection in Diabetic vs Non-Diabetic and Associated Pathogens. Cureus 12(9): e10500. doi:10.7759/cureus.10500
11. Christy VR, Athinarayanan G, Mariselvam R, Dhasarathan P, Singh RAJA (2019) Epidemiology of urinary tract infection in south India. Biomed Res Clin Prac 4:
12. Kumar R, Kumar R, Perswani P, Taimur M, Shah A, Shaukat F. (August 22, 2019) Clinical and Microbiological Profile of Urinary Tract Infections in Diabetic versus Non- Diabetic Individuals. Cureus 11(8): e5464 doi:10.7759/cureus.5464
13. Magliano, Enrico, Grazioli, Vittorio, Deflorio, Loredana, Leuci, Antonia, Mattina, Roberto, Romano, Paolo,Cocuzza, Clementina. (2012). Gender and Age-Dependent Etiology of Community-Acquired Urinary Tract Infections. Sci World J. 2012. 349597.
14. Aswani SM, Chandrashekar U, Shivashankara K, Pruthvi B. Clinical profile of urinary tract infections in diabetics and non-diabetics. Australas Med J. 2014 Jan 31;7(1):29-34.
15. Hamdan HZ, Kubbara E, Adam AM, Hassan OS, Suliman SO, Adam I. Urinary tract infections and antimicrobial sensitivity among diabetic patients at Khartoum, Sudan. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob.. 2015 Dec 1;14(1):26.
16. Sharma S, Govind B, Naidu SK, Kinjarapu S, Rasool M. Clinical and Laboratory Profile of Urinary Tract Infections in Type 2 Diabetics Aged over 60 Years. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017 Apr;11(4):OC25.
17. KU, Shah AH, Fawwad A, Sabir R, Butt A. Frequency of urinary tract infection and antibiotic sensitivity of uropathogenic in patients with diabetes. Pak J Med Sci. 2019;35(6):1664-1668.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License