IJCRR - 13(20), October, 2021
Pages: 129-135
Date of Publication: 24-Oct-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Influence of Thoracic Manipulation on Type I Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Post-Upper Limb Trauma
Author: Manal MH, Amir MS, Hesham HR, Yasser RL
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Complex regional pain syndrome type I (CRPS I) is a chronic condition with disturbances in the sympathetic, somatosensory and motor nervous systems. Objective: To assess the efficacy of combined thoracic manipulation (TM) and traditional physical therapy treatment (TPT) versus TPT treatment alone on pain severity at rest and functional disability in CRPS I patients after upper-limb trauma. Methods: Thirty participants with CRPS I were divided into 2 groups equally at random. The control group (A) consisted of 15 patients with a median (interquartile range [IQR]) age of 53 (13) years. This group received TPT, which consisted of transcutaneous electrical neuromuscular stimulation, mirror therapy, and exercises. The experimental group (B) consisted of 15 patients with a median (IQR) age of 50 (12) years. This group received TPT and TM. The treatment was provided 3 days a week for 12 weeks. Before and after treatment, patients were assessed for pain severity using a visual analogue scale and functional disability using the questionnaire of Disability of Arm, Shoulder, and Hand. Results: As compared with before treatment, all patients showed significant improvement in all measured variables after treatment. Even so, there was a nonsignificant difference in pain severity at rest (p=0.09) , but favoured in group B. In terms of functional disability, there was a significant difference between the groups (p< 0.001) favoured in group B posttreatment. Conclusion: TPT combined with TM is more effective for treating CRPS I after upper-extremity trauma.
Keywords: Complex regional pain syndrome, Function, Manipulation, Traditional treatment, Thoracic, Type I
Full Text:
Introduction
Complex regional pain syndrome(CRPS) is a chronic pain disorder characterised by sensory, motor, vasomotor, and sudomotor manifestations, that is often caused by an injury.1The frequency of CRPS ranged from 3.8–7.0%.[2,3] The highest prevalence occurs among individuals aged 40–60 years.4 It affects the upper extremities more often than the lower extremities and distally, but it can affect an entire limb, such as in shoulder–hand syndrome.5 CRPS has 2 clinical types. CRPS Type II occurs after severe nerve damage, and the rest cases are referred to as CRPS type I. 6
A recent study showed that subjects with CRPS have anti-autonomic antibodies (up to 70%) in their serum, this raises the likelihood that anti-autonomic antibodies are involved in the CRPS pathophysiology. 7,8 The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) involvement in CRPS is debatable. It was considered to be the key driver of CRPS symptoms. In normal circumstances, sympathetic behaviour does not affect nociceptors' discharge; but, in cases of CRPS, the SNS appears to regulate nociceptors. This is referring to as pain-maintained sympathetically.9 There is a close association between pain and the autonomic nervous system. Both the somatic and autonomic nervous systems work together as a single entity, with their functions influenced by one another.10
Conservative treatments for CRPS I have traditionally focused on the management of symptoms in the distal limb. Spinal dysfunction care in CRPS I has not been reported. Manipulation of the spine is a form of manual therapy using “hands-on” treatment techniques causing neurophysiological modifications in the peripheral and central nervous systems. The autonomic nervous system is responsible for preserving normal tissue consistency.11Thus, it's possible that both traditional tissue-specific mechanical techniques and indirect approaches can influence the function of the autonomic nervous system, resulting in good results.10
The sympathetic chain ganglia are located near the thoracic costovertebral and zygapophyseal joints and innervate the upper limb. It might be probable that the sympathetic chain ganglia are affected by thoracic dysfunction that arises from restriction at intraarticular or extraarticular soft tissue and can be related to distal symptoms in CRPS I. So, manipulation can improve joint mobility and reduce the compression on the ganglia.12Thus, thoracic spine manipulation can assist in the overall treatment of patients’ symptoms in CRPS I.
Among the available studies on this topic, none has involved a control group. As are all case studies, even though the results are interesting and encouraging for ongoing studies, the reviews are qualitative, and no concrete conclusions can be drawn.13 However, our study is the first to examine the impact of thoracic spine manipulation in CRPS I patients by comparing a control group and an experimental group. Thus, this study will provide additional care for the management of CRPS I after upper-limb trauma.
METHODS
Subjects
Initially, 36 participants were reported with CRPS I, based on the standards of the International Association for the Study of Pain.14A total of 30 participants of both genders(21 women, 9 men; age 40–60 years) completed the study. Patients were referred from orthopedists (10–18 weeks’ duration of illness) after sustaining fractures in different upper-limb regions (e.g., shoulder region [clavicle and proximal humerus], elbow region [distal humerus, proximal radius, and ulna], and wrist region [distal radius, ulna, and carpometacarpal bones]), and participants underwent surgical intervention for fixation. Our study was conducted in the clinic of outpatient in South Valley University, Egypt, between July 2018 and June 2020. The study was carried out according to Helsinki’s Declaration and was approved by the institutional review board of the Faculty of Physical Therapy at Cairo University (No. P.T.REC/012\002032). The sample size for the analysis was determined using a power of 80% and a level of confidence of alpha (0.05). Because of the dropout rate in the study, the sample size was increased to 36 patients, even though the sample size was estimated to be 15 patients per study group. Patients underwent spinal X-rays before the intervention. All patients signed a consent form. We excluded patients who had a stroke, any history of autoimmune or peripheral vascular diseases, diabetes, or T4 syndrome (examined by X-rays) as well as patients who had participated in a physical therapy program before the intervention.
Participants were divided into two groups of 15 patients at random. Group A underwent traditional physical therapy treatment (TPT) in the form of transcutaneous electrical neuromuscular stimulation (TENS), mirror therapy, and exercises, whereas group B received TPT plus thoracic manipulation (TM; Maitland screw technique grade V at the T3–T4 level). Treatment was given in 3 days per week for 3 months. All subjects received pharmacological treatment (anti-inflammatory drugs). The study was designed as a randomized, pre–posttest, controlled trial. The primary investigator used concealed envelope randomization, and patients were then offered the allocated therapy. Both patients and assistants were blinded. The first author, who completed a certified course in manual therapy, delivered the intervention for both groups.
Measurement procedures:
Measurement of pain severity using a visual analogue scale.
The patient was asked to draw a mark at the point representing their severity of pain at rest (during 1 day) perpendicular to the visual analogue scale (VAS) line. We measured the score by calculating the distance with millimetres on a 10-cm line between the “non-pain” anchor and the point made by a patient using a ruler, including a selection of scores from 0–100.15 A difference of >12 mm was considered the minimum clinically important difference.16
Measurement of functional disability using a questionnaire of the Disability of Arm, Shoulder, and Hand (DASH).
The DASH score includes a totally of 30 items: 6 for the symptom (1 for stiffness, 1 for weakness, 1 for tingling, 3 for pain) and 24 for function (3 for social function, 21 for physical function). By measuring the mean of at least 27 of 30 items (missing rule), self-assessment and scoring are converted (mean − 1) × 25 into a scale from 0 (no symptoms/full function) to 100 (maximum symptoms/no function). 17 We used the Arabic version, and patients were asked to provide answers based on their conditions during the past week.
Treatment procedures
TPT treatment
transcutaneous electrical neuromuscular stimulation (TENS): Both groups received TENS (Endomed 482, ENRAF, German) at a sensory stimulation level with a pulse width of 150 microseconds, high frequency of 100 Hz, and intensity to evoke a tingling sensation for 30 minutes. 18 Graded current rises and electrode location advancement into areas of increased sensitivity. 13 Only2 points were used for stimulation in a session.
Mirror therapy. Both groups received mirror therapy. The affected extremity was positioned behind a mirror and placing the unaffected extremity in front. When the sound limb turns, it appears that the affected limb is behaving normally because of the brain priorities visual feedback over proprioceptive input.19
Physical therapy exercises for the upper limb. Both groups received exercises in the form of gradual weight-bearing using different equipment such as (balls, balloons) at different patient positions 20, range-of-motion, resisting, stretching exercises,21 and fine-motor control training.22
TM
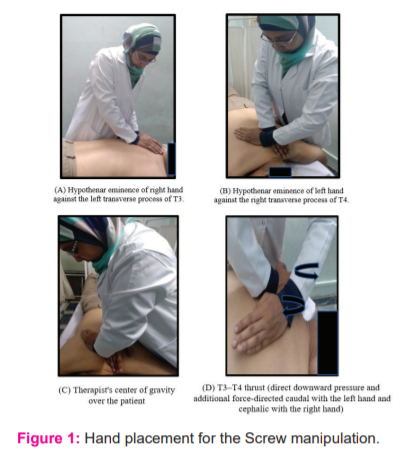
Patients in group B only received TM. A rotation gliding thrust, parallel to the apophyseal joint plane, was used by the screw technique to induce joint cavitation at T3–T4 using the hypothenar eminence of the left and right hands. The patient was asked to lie prone. On the patient’s left side, the therapist stood as upright as possible and resisted crouching, as this would restrict the technique and limit the thrust delivery. The therapist ensured that when applying forces against the transverse processes, good contact was made that did not slide over the skin. By leaning the bodyweight forward onto the arms, the therapist’s centre of gravity was shifted over the patient. Direct downward pressure and additional force-directed caudal with the left hand and cephalic with the right hand on the transverse processes were applied. Pre-Thrust tension was achieved by positioning the T3–T4 segment toward the end range of the available joint gliding. Then applied a downward and cephalic high-velocity, low-amplitude thrust against the transverse process of T3 while simultaneously applying a downward and caudal thrust against the transverse process of T4 23 (Fig. 1).
Statistical analysis
SPSS for Windows, version 24 was conducted to analyze the data (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL). The data were not normally distributed, according to normality tests including normal Q-Q plots, box plots, and the Shapiro–Wilk test. Accordingly, we used nonparametric tests (for within-group difference, Wilcoxon signed-rank test; for between-group difference, Mann–Whitney U test), chi-square test for the site of the fracture, and Z test for sex and side differences. The level of significance was <0.05.
RESULTS
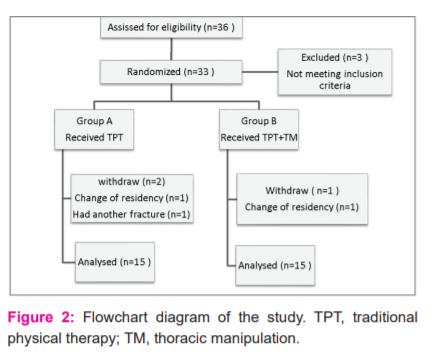
We invited 36 participants with CRPS I to join this study. Six of them were excluded for different causes. Three individuals did not fulfil the criteria for inclusion. Thus, 33 participants were ultimately included and allocated into 2 groups randomly. Group A consisted of 17 participants and group B of 16 participants. During the interventions, 3 participants dropped out; 1 experienced another fracture and declined the treatment interventions and 2 other participants had to change their residential places, which put their dedication to the challenge. The total number of participants was decreased to 30, as shown in Fig. 2.
Demographic characteristics
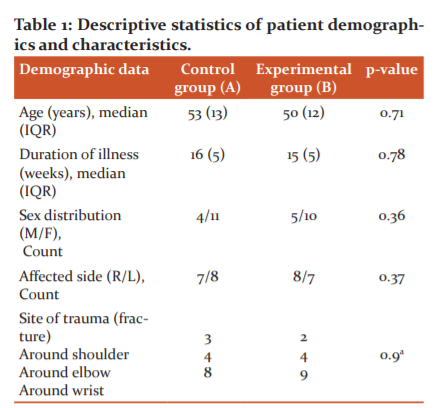
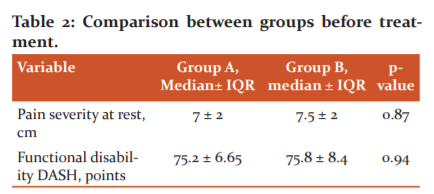
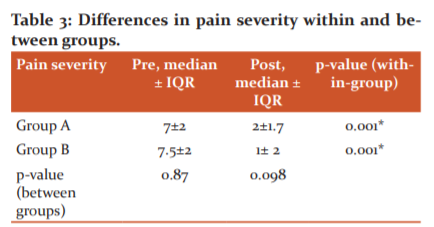
A total of 30 patients completed this study; they were assigned to 2 equal groups at random: the control group (A) and the experimental group (B). Table 1 presents the demographic characteristics of 2 groups. There was a non-significant difference between the 2 groups in median (interquartile range [IQR]) age or duration of illness (p>0.05). The non-significant difference in pretest pain severity or functional disability between the groups was observed (thus revealing homogenous groups), as shown in Table 2.
M, male; F, female; R: right side; L: left side. IQR, interquartile range. a Chi-square test.
Pain severity
In both groups, we found significant differences between pre-and post-treatment (p=0.001) VAS scores at rest, with a significant reduction of pain observed after treatment. There were nonsignificant post-treatment differences between the groups (p=0.09), but group B had reduced pain post-treatment as compared with group A (see Table 3).
Functional disability (DASH)
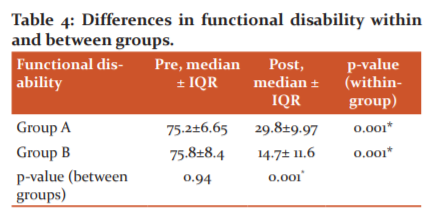
We found asignificant difference in DASH scores between pre- and posttreatment in both groups (p=0.001), with a significant reduction of disability posttreatment. There was significant difference (p<0.001) between groups after treatment which was favored in the experimental group B (see Table 4).
DISCUSSION
We conducted our study to examine the effect of combined TM and TPT versus TPT alone on pain severity at rest and functional disability in patients with CRPS I after upper-limb trauma. According to the results of the VAS and DASH questionnaire at the end of treatment, we found that both treatment interventions were beneficial in treating pain and function. However, there was a non-significant difference between groups in pain severity at rest post-treatment (p=0.09), but in favour of group B., There was a significant difference between groups in posttreatment functional disability (p<0.001) favoured in group B. The greatest improvement in findings was observed in the group that received TM and TPT treatment together. There were no harms detected during or after the TM intervention.
Patients with arm CRPS I show postural deviations related to the arm’s defensive role. Thoracic hypomobility can be exacerbated by the arm's immobility and poor posture. Furthermore, since the sympathetic chain is anatomically close to the defective dorsal joints, the ganglions are vulnerable to mechanical stress.12 According to McNair and Maitland 24, among the dorsal spine pain syndromes, joint hypomobility is the most prominent feature. In addition, Gonzalez-Darder 25 identified the pressure of the T4 nerve (posterior ramus) by a spur from the inferior T4 facet joint. Surgically decompression reduced autonomic dysfunction as well as the pain of the patient’s arm, neck, and thoracic region. Therefore, it was necessary to treat the areas close to the symptoms.
A study conducted by Yip Menck et al. 12 demonstrated a significant improvement in the range of motion of the shoulder joint immediately after TM and decreased pain. The authors thus concluded that management of the dorsal spine in patients with upper-limb CRPS I should be considered.
Plausible reasons for decreasing pain intensity and improving function after TM include neurogenic enhancement to the SNS, reduction of mechanical compression to the sympathetic trunk, decreasing of referred pain from thoracic zygapophyseal, reflexive suppression of muscle spasm, and it could be a placebo effect. 12
Pain is a product of the activity of the posterior horn interneuron 26 that defines the accumulative effect of the efferent input. Although this behaviour of the interneuron is not yet completely understood 10, several neurochemicals, such as endorphins, substance P, serotonin, and gamma-aminobutyric acid, might influence the activity of these interneurons. The inhibition or promotion effect on segmental interneurons can be the product of descending pathways from cranial structures. 27
Spinal manipulation has been shown to influence interneural activity in the level of the spinal segments that affect the central descending pathways as well as have an impact at the cortical level. 28 Our findings are agreed with those reported by Savva et al.29, who indicated that activation of periaqueductal grey modulates spinal cord nociception, providing an analgesic effect on musculoskeletal pain. There are distinct descending mechanisms within the neural pathways of the periaqueductal grey to the spinal cord, including the nonadrenergic and serotonergic control systems. To suppress mechanical stimuli, the noradrenergic system uses noradrenaline, whereas the serotonergic system uses serotonin to induce sympathoinhibition. The activation of the descending inhibitory pain mechanism, which uses noradrenaline and serotonin, then causes the mechanical hypoalgesia that accompanies the remote-site application of manual therapy.
In their study, Budgell and Polus30 examined the impact of TM on the autonomic nervous system and showed that, despite the lack of a statistically significant effect, TM can partially affect the autonomic nervous system. Our study is consistent with this view, although there we showed no statistically significant reduction in pain severity between groups post-treatment; however, group B had a greater reduction in pain than group A did, indicating that TM can affect the autonomic nervous system.
In addition, the reflexogenic mechanism, which is an inappropriate biomechanical association between the neighbouring vertebrae, can press the roots of the nerve, resulting in an effect on the associated segmental muscle function, such as muscle spasms, which could explain the relationship between the thoracic spine and upper-extremity CRPS I pain and functional impairment. This can cause abnormal patterns of upper-limb movement.31 The reported improvements in treatment outcomes in patients handled with TM and TPT could be related to the restoration of joint functions and associated local or far symptoms due to TM,32 as the efficient use of this regional treatment technique to achieve effective functional results for subjects with different musculoskeletal disorders has also been demonstrated and shown regional interdependence. 33In addition, Melzack 34 developed the gate theory, which notes that the afferent transmission of pain pathways would be blocked by any raise in sensory feedback, such as visual, auditory, cutaneous, articular, or muscular. The manipulation may have provided sensory feedback that either blocked pain or hindered the muscle.
In the medical community, the psychological influence of the hand’s laying of the clinician is also well accepted and couldn’t be dismissed as a cause affecting the response of the patient to TM. The placebo factor is understood to be unequivocally strong after a procedure. 35 In their study, Hoehler and Tobis 36performed a study of manipulation versus sham and reported that the group of manipulation indicated substantially superior relief relative to subjects who experienced “hand’s laying on.”
CRPS a difficult condition to be managed successfully. It is often involving psychological and social elements that are additional primary diagnostic characteristics. The variety of possible patient manifestations, as well as the fact that the manifestations often change over time, make effective identification and management difficult. 37
Conclusion:
The current study proved that a combined program of TM and TPT had a superior effect when compared with TPT for the treatment of pain and functional disability and can be immediately applied in the clinic for patients with CRPS I so that the physiological responses of manual therapy should continue to be recorded and registered in patients with CRPS I.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS: All the authors want to thank all individuals who participated in this study.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST:
No conflicts of interest were reported for this study.
FUNDING SOURCES:
No funding sources.
Authors Contribution:
Manal MH, design of the work, data collection, analysis, interpretation of data, drafting, and revising the work.
Amir MS, revising the work, accountable for all aspects of the work related to accuracy or integrity.
Hesham HR, revising the work for intellectual content and providing final approval of the version to be published.
Yasser RL, analysis, interpretation of data, and revising the work.
References:
1- Marinus J, Moseley GL, Birklein F, Baron R, Maihöfner C, Kingery WS, et al. Clinical features and pathophysiology of complex regional pain syndrome. Lancet Neurol. 2011;10(7):637-48. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21683929/
2- Beerthuizen A, Stronks DL, Vant A, Yaksh A, Hanraets BM, Klein J, et al. Demographic and medical parameters in the development of complex regional pain syndrome type 1 (CRPS1): a prospective study on 596 patients with a fracture. J Pain. 2012;153(6):1187-92. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/28127572
3- Moseley GL, Herbert RD, Parsons T, Lucas S, Van Hilten JJ, Marinus J. Intense pain soon after wrist fracture strongly predicts who will develop complex regional pain syndrome: prospective cohort study. J Pain. 2014;15(1):16-23. https://pubmed.ncbinlm.nih. gov/ 24268113/.
4- Sterling G. West. Rheumatology Secrets. 3rd ed. p. 384; Philadelphia: Elsevier 2015. Available from: https://yalesmn.org/624751/rheumatology-secrets-3e.pdf.
5- Adebajo A, Dunkley L. ABC of rheumatology. 5th ed. p. 137; USA: John Wiley & Sons. 2018 Available from: https://b-ok.lat/book/3493686/fb0eb6.
6- Bruehl S, Maihöfner C, Stanton M, Perez RS, Vatine JJ, Brunner F, et al. Complex regional pain syndrome: evidence for warm and cold subtypes in a large prospective clinical sample. J Pain. 2016;157(8):1674-81. https://link.springer.com/article/ 10.1007/s10286-019-00612-0
7- Kohr D, Singh P, Tschernatsch M, Kaps M, Pouokam E, Diener M, et al. Autoimmunity against the β2 adrenergic receptor and muscarinic-2 receptor in the complex regional pain syndrome. J Pain .2011;152(12):2690-700. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007 /s 40264-017-0593-3.
8- Dubuis E, Thompson V, Leite MI, Blaes F, Maihöfner C, Greensmith D, et al. Longstanding complex regional pain syndrome is associated with activating autoantibodies against alpha-1A adrenoceptors. J Pain. 2014;155(11):2408-17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11916-018-0667-7.
9- Raja SN, Meyer RA, Ringkamp M, Campbell JN. Peripheral neural mechanisms of nociception. In: The Textbook of Pain Wall PD, London MR, editors.; 2011. p. 11-57. Available from: https://journals.physiology.org/doi/full/10.1152/jn.01293.2005.4thed Churchill Livingstone
10- Sillevis R. Cleaned J., Hellman M. immediate effects of thoracic spine thrust manipulation on the autonomic nervous system: a randomized clinical trial. J Man Manip Ther. 2010;18:181-90. https://doi.org/10.1179/106698 110 X12804993.
11- Maguire AM, Craig ME, Craighead A, Chan AK, CusumanoJM, Hing SJ. Autonomic nerve testing predicts the development of complications. Diabetes Care 2007; 30: 77–82. https://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/31/6/1201.
12- Menck JY, Requejo SM, Kulig K. Thoracic spine dysfunction in upper extremity complex regional pain syndrome; Type I. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2000;30(7):401-09. https://www.jospt.org/doi/ 10.2519/jospt.2000.30.7.401.
13- Thacker M, Gifford L. A review of the physiotherapy management of complex regional pain syndrome Corpus.ID 45488344; 2013:130-4. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009416 .pub2.
14-International Association for the Study of Pain. Classification of
chronic pain. 2nd edition (revised). https://www.iasp-pain.org/PublicationsNews /Content.aspx?ItemNumber=1673.
15- Hawker GA, Mian S, Kendzerska T, French M. Measures of adult pain: visual analogue scale for pain. Arthritis Care Res. 2011;63; Suppl 11:S240-52. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/333294066.
16- Bijur PE, Silver W, Gallagher EJ. Reliability of the visual analogue scale for the measurement of acute pain. Acad Emerg Med. 2001;8(12):1153-57. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1553-2712.2001.tb01132.x.
17- Angst F, Goldhahn J, Drerup S, Flury M, Schwyzer HK, Simmen BR. How sharp is the short Quick DASH? A refined content and validity analysis of the short form of the disabilities of the shoulder, arm and hand questionnaire in the strata of symptoms and function and specific joint conditions. Qual Life Res. 2009;18(8):1043-51. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19707887.
18- Anandkumar S, Manivasagam M. Multimodal physical therapy management of a 48-year-old female with post-stroke complex regional pain syndrome. Physiother Theor Pract. 2014;30(1):38-48. https://doi.org/10.3109/09593985.2013.814186.
19- Pollard C. Physiotherapy management of complex regional pain syndrome. N Z J Physiother.2013;41(2):65-72.https://rsds.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/ICCPollard .pdf.
20- Galve M, Rittig B, Moeller L, Groendahl A. Complex regional pain syndrome. Man Ther.2016;26:223-30.http://www.elsevier. com/math.
21- Kisner C, Colby LA. Therapeutic exercise foundations and technique. 5th ed. P43-6(68), p. 82-4, 165,167-68.; Philadelphia: F. A. Davis Company. 2007. ISBN-10: 0-8036-1584-1. Available from: http://www.fadavis.com.
22- Carlson AG, Rowe E, Curby TW. Disentangling fine motor skills’ relations to academic achievement: the relative contributions of visual-spatial integration and visual-motor coordination. J Genet Psychol. 2013;174(5-6):514-33.https://doi.org/10.1080/00221 325 .2012.717122.
23- Gibbons P, Tehan P. Manipulation of the spine, thorax and pelvis. 4th ed. p. 219-21. 2016 USA: Elsevier; ISBN-13: 978-0702059216, ISBN-10.0702059218. Available from: Http://WwwSpinethoraxpelvis.com
24- McNair J, Maitland G. Manipulative therapy techniques in the management of some thoracic syndromes. In: Grant R, editor. Clinics in physical therapy: physical therapy of the cervical and thoracic spine. New York: Churchill Livingstone; 1988.p.243-69. Available from:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S00049514146033 05.
25- González JM. Thoracic dorsal ramus entrapment. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1989;70(1):124-25. https://iaom-us.com/thoracic-four-syndrome-case.
26- Rhudy JL, Williams AE, McCabe KM, Rambo PL, Russell JL. Emotional modulation of spinal nociception and pain: the impact of predictable noxious stimulation. J Pain. 2006;126(1-3):221-33. http://europepmc.org/articles/PMC3113268.
27- Fernández C, Pérez M, Brea M, Miangolarra JC. Immediate effects on pressure pain threshold following a single cervical spine manipulation in healthy subjects. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2007;37(6):325-29. https://www.jospt.org/doi/10.2519/jospt.2011.
28- Haavik H, Murphy B. Cervical spine manipulation alters sensorimotor integration: a somatosensory evoked potential study. Clin Neurophysiol. 2007;118(2):391-402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2006.09.014
29- Savva C, Giakas G, Efstathiou M. The role of the descending inhibitory pain mechanism in musculoskeletal pain following high-velocity, low amplitude thrust manipulation. A review of the literature. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2014;27(4):377-82. https://doi.org/10.3233/BMR-140472.
30- Budgell B, Polus B. The effects of thoracic manipulation on heart rate variability: a controlled crossover trial. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2006;29(8):603-10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmpt.2006.08.011.
31- Walser RF, Meseve BB, Boucher TR. The effectiveness of thoracic spine manipulation for the management of musculoskeletal conditions: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Man Manip Ther. 2009;17(4):237-46. https://doi.org/10.1179/106698109 791352085.
32- Chitroda H. Effect of thoracic and rib manipulation in the frozen shoulder - an RCT. Indian J Health Sci Biomed Res (KLEU). 2014;7(2):92. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/273168809.
33- Walker MJ, Boyles RE, Young BA, Strunce JB, Garber MB, Whitman JM. The effectiveness of manual physical therapy and exercise for mechanical neck pain: A randomized clinical trial. Spine. 2008;33(22):2371-78. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e318183391e.
34- Melzack R. The puzzle of pain. London: penguins 1973; 49 (9). Dent Surv;28-32. PMID PubMed.
35- Lopez A, Alonso JL, González JL, La Touche R, Lerma S, Izquierdo H. Mobilization versus manipulation versus sustain apophyseal natural glide techniques and interaction with psychological factors for patients with chronic neck pain: RCT. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2015;51(2):121-32. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25296741.
36- Hoehler FK, Tobis JS, Buerger AA. Spinal manipulation for low back pain. IAMA. 1981;245(18):1835-38. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01765777.
37- Harden RN, Oaklander AL, Burton AW, Perez RS, Richardson K, Swan M. Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy Syndrome Association. Complex regional pain syndrome: practical diagnostic and treatment guidelines, 4th edition. Pain Med. 2013;14(2):180-229. https://doi.org/10.1111/pme.12033.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License