IJCRR - 13(20), October, 2021
Pages: 95-101
Date of Publication: 24-Oct-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Effect of Drug Abuse Among Persons with Disabilities in South-East Nigeria
Author: Wada Bashir Isiaku, Justina Ifeoma Ofuebe, Chidinma Dede, Benedict Chimezie Nwankwo, Prince Onyemaechi Nweke
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Drug abuse is a universal and social problem with different harms that fluctuate in society. It has become a subject matter of public worry internationally because it adds potentially to deliberate or undeliberate harm. Hence, it is the responsibility of society to facilitate enforcement agencies to eradicate drug abuse in society at large. Objective: The research study examined the effect of drug abuse among persons with disabilities in society at large. Methods: The study adopted a descriptive survey design. The study sampled 688 respondents. The instrument used for data collection was a structured questionnaire. Cronbach Alpha Reliability Coefficient was used to determine the instruments which yielded reliability coefficients of 0.82. The research questions were answered using mean and standard deviation. The scales use for the questionnaire was Strongly Agree (SA), Agree (A), Disagree (D) and Strongly Disagree with the values of 4, 3, 2 and 1 respectively. These responses were based on positively worded items while the reverse was for the negatively worded items. The average score from coded data (4+3+2+1 =10/4) was 2.50. Results: The findings of the study revealed the causes of drugs abuse among persons with disabilities such as earliest influence to smoke, earliest influence to drink alcohol, unemployment, poor academic performance, parental rejection, family abuse, over-controlling by parents, and depression and anxiety among others. The findings of the study revealed preventive strategies to control drug abuse among persons with disabilities and the society at large, which include: dissemination of laws against drug abusers and the establishment of drug law enforcement agencies to monitor drug abuse offenders. Conclusion: Because of the above findings, it was concluded that government should frequently organize educational programs, media broadcasts, advertisements, seminars aimed at enlightening the youths and persons with disabilities on the dangers and consequences of drug abuse.
Keywords: Adolescents, Disabilities, Drug abuse, Drug addiction, Health practitioners, Social problems
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
As Nigeria witnessed a rapid rate of urbanization, some individuals becoming unable to adjust to their changing environment and circumstances. Consequently, such persons become victims of a disordered life and this takes to drugs for relief. Hence, such abusers become of great concern to the family and the society at large, because of the destabilizing effect of anonymity and suffering associated with the use of such drugs.6 During the oil boom days in Nigeria, from the beginning of 1970s dawn to 80s, there were jobs; Nigerians got themselves in the lavishness of materialism and excessive living habits. Hence, nobody thought of an alternative business or what to do to earn a living, lastly after the oil market distorted it bring a tryout of reduction of expenditure as an alternative of employment in the society at large.4It is against this backlash of economic plight that Nigerians had to look beyond the frontier of their nation for quick money-spinning business. However, the general public's underlying hatred was against cannabis use, because of the mental, social and actual impact because of the well-known clamor against the risk of deals and maltreatment of medications in Nigeria.17
Research evidence shows that drugs are also commonly abused among young people,21 such as valium, laxotan, activan, etc.20 Nevertheless, up till the end of seventies, the use of narcotic drugs that essentially relieve pain were used for medical and scientific purposes only and were kept in hard drug cupboards of hospitals to ensure adequate monitoring. Meanwhile, the abuse of narcotic drugs was then a phenomenon of health care workers only. Not until the arrest of a narcotic drug trafficker was made at the Murtala Mohammed International airport, Lagos in 1984, little or no attention was paid to the abuse of narcotic drugs.14 Unfortunately, the rising expectations and unfulfilled dreams have led to depression and experimentation with all kinds of drugs in society. The drug problem has eaten deep into the fabric of the society that some persons with disabilities cannot alter the environment in which they found themselves. Therefore, the public idea of persons that used drugs is severally distorted in a variety of ways, that is why.2 Studies posited that drug addictions are not a hallmark of moral failure or lack of willpower, but a complex disease that deserves long-term, broad therapy, very much like some other persistent condition. Even though individuals who have not battled with substance addiction might think that it is hard to get why individuals engaged in drug abuse.7 Also there are many reasons why some people start abusing drugs, and unfortunately, the consequences can be life-shattering.
Drug abuse is a universal physical condition and social problem with different conditions and harms that fluctuate in society at large. The use of psychoactive substances among adolescents, youths and persons with disabilities has become a subject matter of public worry internationally because it adds potentially to deliberate or undeliberate harm. Drug abuse can be defined as an emotional problem mainly influenced by current social factors in any given society. It refers to a condition where the drug is used to produce an effect that the drug is not designed to produce.15Drug abuse is defined as non-medical, self-administration of a substance to induce psychoactive effects, intoxication or altered body image, despite the knowledge of its potential adverse effects while drug misuse implies that a drug has a proper medical use and prescription and is being employed for an incorrect purpose. Drug abuse, according to Food and Drug Administration is an intentional therapeutic use of a drug product in an inappropriate way.9 Studies carried out by scholars reported that despite the efforts of Nigerian National Drug Law Enforcement Agency and other governmental agencies to stem the tide of substance abuse in Nigeria, there has been a consistent rapid rise in the number of cases of drug abuse among young people (ages 10- 24) in Nigeria.1
Operationally, drug abuse is defined as a patterned use of a drug in which the abuser devours the substance in amounts that are destructive or dangerous to their health. Therefore, when an individual perseveres in utilize of drugs despite the harms related to the use of the substance, substance dependence may be diagnosed. Consequently, uncontrollable and cyclical use may result in forbearance to the consequence of the drug and results in withdrawals symptoms when use is reduced. On the other hand, a disability is when an individual’s body or mind is impaired in such a way that they are unable to engage in one or more major activities in their life. Importantly, some people are born with a disability, while other disabilities may be a result of injury.11 Disabilities may increasingly get worse over time, remain unchanged, or even come and go depending on the specific disability, the harshness of symptoms, treatment, and the person.
Conversely, the causes of drug abuse and well predictive risk factors among persons with disabilities.10 The author further explains that the earliest influences to smoke, drink alcohol, or use drugs may come from the family, while factors related to drug use during adolescence include poor self-image, low religiosity, poor school performance, parental rejection, family dysfunction, abuse, under-or over-controlling by parents, and divorce. Similarly, common risk factors for teen drug abuse, include a family history of substance abuse; a mental or behavioural health condition, such as depression, anxiety or attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder; and impulsive among others.13Other causes or risk factors associated with drug abuse among persons with learning disabilities include poor socioeconomic status, peer-group pressure influence, family problems and poor academic performance, unemployment, and broken home.12 Importantly, for any society or government to eradicate drug abuse must be ready to organize media broadcasts, advertisements and seminars aimed at enlightening the youths and persons with disabilities on the dangers and consequences of drug abuse.
Studies carried out by scholars mentioned various consequences of drug abuse that are so devastating and very shameful to the extent that both the national and international organizations across the globe are also worried about the spread of this scourge among the youths and persons with disabilities, which include mental disorder, social violence, gang formation, cultism, armed robbery, internet frauds, social miscreants, lawlessness among youths, lack of respect for elders, rape, loss of senses, instant death and wasting of precious and innocent lives and many more.15 Interestingly, the impact created by smoking tobacco relies upon the nicotine that is ingested from the smoke. While, a large number of the understudies move on from tobacco smoking to Marijuana smoking, which they trust could be all the more remarkable on them or make them hyperactive. The author further opined that drug habit is not only expensive; but difficult to sustain.5 Similarly, the symptoms of codeine overuse include: loss of joy in most loved exercises and diversions, absence of will in doing basic things throughout everyday life, detachment toward family, occasions, or friends and family, diminished interest in sex and fondness, loss of expert or individual drive, ignorance of how to conduct and passionate pain. Moreso, additional signs of clinical depression include itching, rash, lack of sexual drive, nausea, vomiting, pinpoint pupils, sweating, and urinary retention. However, drug abuse affects aspects of a person’s life beyond their physical health.18 The study further explained that drug abuse, especially over an extended period, could have numerous long-term health or psychological effects, such as depression, anxiety, panic disorders, increased aggression, loss of memory, Kidney damage, Liver disease, inability to learning, and lack of concentration.18
Similarly, one of the major consequences of drug abuse is dependence and addiction, characterized by compulsive drug cravings seeking behaviours and use that persist even in the face of negative consequences.15 The results of chronic drug use, help crime percentages, cultism, psychological sickness, low confidence and sense of pride, wounds to one's wellbeing, and turning into an oddball and carrying disgrace to their kinfolk.5 The result of biting kola-nut taking boring espresso and different substances that improve one to remain alert around evening time-could prompt compulsion and substance misuse which may result in negative health implications and adversely affect performance in examination contrary to the expectation of the students.16 Interestingly, major consequences as reported by some scholars opined that since the consequences of drug abuse are full of the negative impact that means there is a need to provide strategies to prevent or control such abuse among persons with disabilities since there are major indicators of the study.15
Studies have posited that the drug abuse problem is a global phenomenon despite intensive efforts directed at controlling it, the problem seems intractable.8 Nigeria and other African countries have in the past adopted measures aimed at controlling drug abuse among Nigerian youth and persons with disabilities, such as follows: pretrial detention of persons accused of serious drug abuse; severe trial and sentence penalties against drug offenders; mandatory prison sentences for large scale distributors of marijuana; establishment of drug law enforcement agency monitors drug abuse and persecute offenders among others. Other preventive strategies as measures for drug abuse are as follows: teaching and awareness programmes for persons with disabilities; resist peer pressure; manage stress and anxiety; increase taxes on addictive materials like cigarettes; campaigns to appeal to youth against drug abuse; control on OTC medication; and role of parents is imperative.13 Similarly, studies also suggested some effective strategies combat drug abuse, which includes: drug users with post-traumatic stress disorder to seek the help of a trained professional for treatment before it leads to substance use; parental monitoring to slow the expansion of drugs in the family situations; schools to introduce drug prevention programs; schools to introduce strict compliance rules and counselling support to reduce usage; schools based drug abuse prevention programmes; enforcement agencies to focus mainly on tracking the network deeply and prosecuting producers and suppliers; investigation of illegal drug trafficking is a specialized task; and creating awareness among citizens.18 Interestingly, studies also posited that early identification of the factors related to substance use can improve scopes for planning and preventive approaches for the vulnerable group before the problems get serious after which interventions become difficult.19
Statement of the Problem
Drug abuse is a global predicament and has become a social problem especially in Nigeria; it is common among the youths both within and outside the school system. The consumption of illicit drugs among youth especially among individuals with disabilities is considered as an immoral effect on their life. Importantly, sociologists, psychologists, special education professionals, health practitioners and other medical personnel have tried to find out remedies and to make possible suggestions on how to cut short this serious social problem in society. Undoubtedly, the abusers derive control from the act but such comfort is only temporary. There is no doubt to say that drug abuse is more constant among youth. It is against this backdrop that the study becomes helpful to society at large. Hence, this could draw the attention of the government to imported social habits, pornographic films and dealers of these illicit drugs in Nigeria. Importantly, the significance of this study attempt to provide a blueprint for checking the indiscriminate causes of drug abuse which are adversative to the ideals of this desired ethical revolution. Furthermore, the attempt could be made to find out the overall consequences of drug abuse both on the abuser's life and the society at large. It is also believed that with minor variations, the findings could be the same in any other area in the country.
Purpose of the Study
The general purpose of the study was to examine the effect of drug abuse on persons with disabilities in South-East, Nigeria. Specifically, the study sought to:
-
examined the causes of drug abuse among persons with disabilities.
-
ascertain the consequences of drug abuse among persons with disabilities.
-
determine strategies to control drug abuse among persons with disabilities.
Research Questions
The following research questions guided the study.
-
What are the causes of drug abuse among persons with disabilities?
-
What are the consequences of drug abuse among persons with disabilities?
-
What are the strategies to control drug abuse among persons with disabilities?
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The study adopted a descriptive survey design. The population of the study was 688 respondents drawn from South-East (Abia State, Anambra State, Ebonyi State, Enugu State and Imo State), Nigeria. There was no sampling since the population was manageable. The instrument for data collection was a structured questionnaire developed by the researchers titled: “Effect of Drug Abuse Persons DisabilitiesQuestionnaire (EDAPDQ)”. The instrument was validated by three experts, one from the Special Education Unit, Department of Educational Foundations; one from the Department of Human Kinetics and Health Education, and one from the Department of Science Education (Measurement and Evaluation Unit), Faculty of Education, University of Nigeria, Nsukka. The internal consistency of the instrument was determined using Cronbach Alpha for reliability analysis with the coefficient of 0.82 obtained. This indicates that the instrument was reliable. The research questions were answered using mean and standard deviation. The scales use for the questionnaire was Strongly Agree (SA), Agree (A), Disagree (D) and Strongly Disagree with the values of 4, 3, 2 and 1 respectively. The arithmetic mean of the scale of the items is 2.50, which means any item with a weighted mean value of 2.50 and above was considered acceptable, while any weighted mean of less than 2.50 was considered rejected or not accepted.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Research Question One: What are the causes of drug abuse among persons with disabilities?
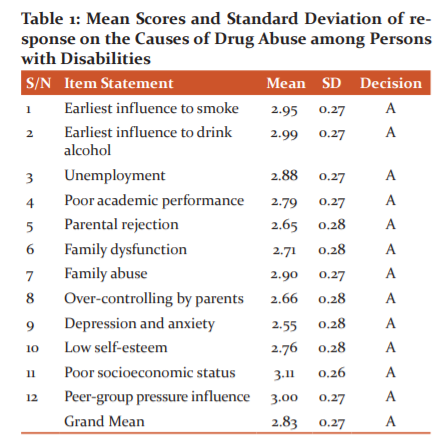
Table 1 showed the mean scores and standard deviation on causes of drug abuse among persons with disabilities. The respondents agreed on all the items in the table with mean scores above the mean standard of 2.50. The grand mean score of 2.83 with a standard deviation of 0.27 indicated that the items were agreed upon as the factors that lead to the drug among persons with disabilities which include: earliest influence to smoke, earliest influence to drink alcohol, and poor self-image, poor academic performance, parental rejection, family dysfunction, family abuse, over-controlling by parents, divorce, depression among others.
Research Question Two: What are the consequences of drug abuse among persons with disabilities?
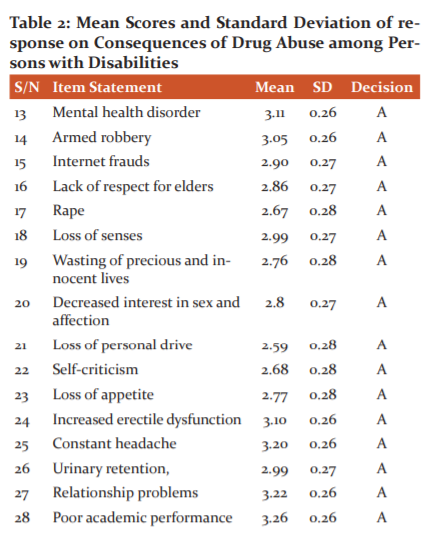
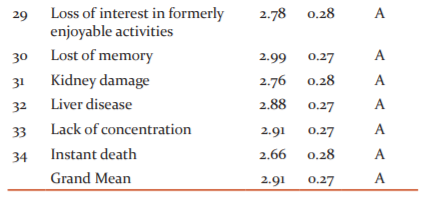
Table 2 revealed the consequences of drug abuse among persons with disabilities. The items 13 – 34 were agreed by respondents with mean scores above the mean criterion of 2.50 with a grand mean score of 2.91 with a standard deviation of 0.27 correspondingly, which implies that the items mentioned above were agreed upon as the consequences of drug abuse among youth. Therefore the consequences of drug abuse among youth include the following: mental disorder, social violence, cultism, armed robbery, 419 syndrome, internet frauds, social miscreants, lack of respect for elders, rape, loss of senses, instant death, wasting of precious and innocent lives, loss of pleasure in favourite activities, and lack of will in doing simple things in life among others.
Research Question Three: What are the strategies to control drug abuse among persons with disabilities?
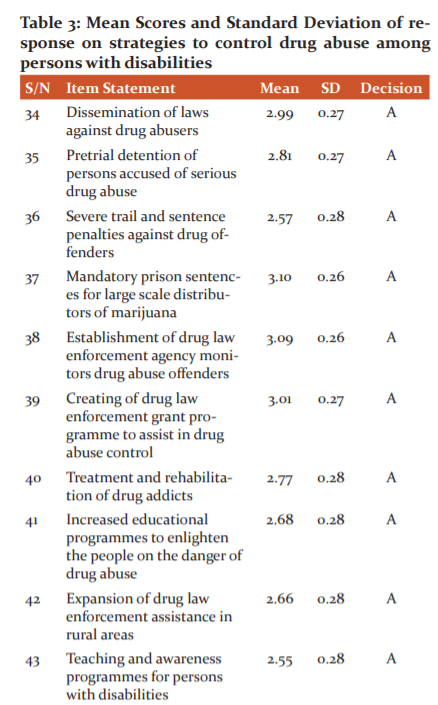

Table 3 shows the strategies to control drug abuse among persons with disabilities. The table indicated that items 34 – 45 have mean scores above the criterion mean of 2.50 which showed that they are accepted as the strategies to control drug abuse. The respondents accepted the items to be the strategies with a grand mean score of 2.82 and 0.27 standard deviation respectively. This entails that the strategies to control drug abuse among persons with disabilities include: dissemination of laws against drug abusers; pretrial detention of persons accused of serious drug abuse; severe trial and sentence penalties against drug offenders; and mandatory prison sentences for large scale distributors of marijuana among others.
DISCUSSION
The findings of the study revealed the causes of drugs abuse among persons with disabilities such as earliest influence to smoke, earliest influence to drink alcohol, poor self-image, poor academic performance, parental rejection, family dysfunction, family abuse, over-controlling by parents, divorce, depression, anxiety, low self-esteem, poor socioeconomic status, peer-group pressure influence, family problems, unemployment, and broken home. The findings of the study are inconsonant with the results which posited causes of drug abuse and well predictive risk factors of drugs abuse among persons with disabilities.10 The results further explains that the earliest influences to smoke, drink alcohol, or use drugs may come from the family, while factors related to drug use during adolescence include poor self-image, parental rejection, under-or over-controlling by parents, and divorce. The findings of the study are also in line with the results which posited common risk factors for teen drug abuse, which include: a family history of substance abuse; a mental or behavioural health condition, such as depression, anxiety or attention-deficit disorder; impulsive or risk-taking behaviour.13
The findings of the study revealed the consequences of drug abuse which include anger, irritability, sadness, self-criticism, loss of appetite, irregular sleep, increased erectile dysfunction, constant headache, urinary retention, relationship problems, poor academic performance; noticeable changes in appearance, loss of interest in formerly enjoyable activities; loss of memory, kidney damage, liver disease, inability to learning and lack of concentration. The findings of the study are line with the results which mentioned various consequences of drug abuse that are so devastating and very shameful to the extent that both the national and international organizations across the globe are also worried about the spread of this scourge among the youths and persons with disabilities, which include mental disorder, social violence, gang formation, cultism, internet frauds, social miscreants, lawlessness among youths, lack of respect for elders, rape, loss of senses, instant death and wasting of precious and innocent lives and many more.15
The findings of the study revealed preventive strategies to control drug abuse among persons with disabilities and the society at large, which include: teaching and awareness programmes for persons with disabilities; manage stress and anxiety; and increase taxes on addictive materials like cigarettes among others. The findings are inconsonant with the results which posited that the drug abuse problem is a worldwide phenomenon despite intensive efforts directed at controlling it, the problem seems intractable.8 Therefore, Nigeria and other African countries have in the past adopted measures aimed at controlling drug abuse among Nigerian youth and persons with disabilities as follows: dissemination of laws against drug abusers and pretrial detention of persons accused of serious drug abuse. The findings of the study are also in line with the results that suggested some effective strategies to combat drug abuse, which include: drug users with post-traumatic stress disorder to seek the help of a trained professional for treatment before it leads to substance use; parental monitoring to slow the expansion of drugs in family situations; schools to introduce drug prevention programs; schools to introduce strict compliance rules and counselling support to reduce usage; and schools based drug abuse prevention programmes among others.18
CONCLUSION
The abuse of drugs is a dilemma that is making true anxiety for individuals universally. However, the issue is predominant among young people and persons with disabilities who much of the time are uninformed about the dangers of inherited in medicating abuse. Furthermore, a large number of young people and individuals with disabilities occupied drug abuse out of frustration, poverty, absence of parental management, peer impact and pleasure. Notwithstanding, with a feasible guiding system, the issues can be handled. The efforts of the government to eliminate drug abuse in society at large have been severely constrained by factors such as unemployment, idleness, peer group pressures influence, bad parental upbringing etc. The consequences of drug abuse have been so appalling in society that it has wasted lives, caused various crimes, broken homes, caused accidents etc. However, this situation can take a turn for the better if all the recommendations recommended in the research study are used and strictly applied by the government and individuals in society.
RECOMMENDATIONS
Based on the findings of the study, the following recommendations are made:
-
Qualified health practitioners, special educationists and counsellors should be employed in helping drug addicts or those dependent on drugs by giving them special advice on the consequences of drug abuse.
-
Federal and State Ministry of Education should as matters of urgency add to the curricula, drug education at all levels of education
-
Government should organize educational programmes, media broadcasts, advertisements, seminars aimed at enlightening the youths and persons with disabilities on the dangers and consequences of drug abuse.
-
Parents should educate their children early enough on the risks associated with drug abuse.
-
Governments should ban joints or selling points for illicit substances and ensure that uncompleted buildings that are hide-out for the consumption and sale of illicit substances are completed by the owners or risk demolition.
Acknowledgement:
The researchers acknowledge the support received from the Special Education Unit, Department of Educational Foundations, University of Nigeria, Nsukka. The researchers also acknowledge all academic staff in the special education unit for their support in engaging participants for the study.
Conflict of Interest:
The authors declare that the research was conducted in absence of any conflict of interest.
Ethical Clearance: Not Required
Source of Funding: This research received no specific grant from any funding agencies.
Author’s Information:
Dr. Isiaku, Wada Bashir: Lecturer, Department of Psychology, Aminu Kano College of Islamic and Legal Studies, Kano state
Dr. Ofuebe, Justina Ifeoma: Lecturer, Department of Human Kinetics and Health Education, University of Nigeria, Nsukka (Corresponding Author)
Dede Chidinma: Postgraduate Student, Department of Educational Foundations, University of Nigeria, Nsukka
Dr Nwankwo, Benedict Chimezie: Lecturer, Department of Psychology, Ebonyi State University, Abakaliki
Nweke, Prince Onyemaechi: Research Fellow, Institute of Education, University of Nigeria, Nsukka
References:
REFERENCES
-
Abdu-Raheem BO. Sociological factors to drug abuse and the effects on secondary school students’ academic performance in Ekiti and Ondo States, Nigeria. Contemporary Issues in Education Research. 2019; 6(2): 233-240. Available from: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1073210.pdf
-
Alta M. The causes and effects of drug addiction. 2020. Available from: https://www.altamirarecovery.com/causes-effects-drug-addiction/
-
Ajayi, IA, Ekundayo HT. Contemporary Issues in Educational Management. 2010; Lagos, Nigeria: Bolabay Publications
-
Aribisala F. Planning for a Nigerian future without oil. 2013; Available from: https://www.vanguardngr.com/2013/10/planning-nigerian-future-without-oil/
-
Dankani IM. Abuse of cough syrups: A new trend in drug abuse in the Northwestern Nigeria States of Kano. Sokoto, Katsina, Zamfara and Kebbi. International J Physical Sciences. 2012; 2, 101-115.
-
Dietz E, O'Connell D, Scarpitti F. Therapeutic communities and prison management: an examination of the effects of operating an in-prison therapeutic community on levels of institutional disorder. International J of Offender Therapy and Comparative Criminology. 2003; 47, 210-23. Dol: 10.1177/0306624X03251088.
-
Egbochuku EO, Aluede O, Oizimende P. Analysis of the use, dependence and source of knowledge of stimulants among Nigerian university undergraduates. Kamla-Raj Anthropologist. 2009;11(3): 213-218.
-
Eric P. Penalties and sentencing for drug abuse, selling, and smuggling in the United States America. 2021; Available from: https://drugabuse.com/addiction/drug-abuse/penalties/
-
Food and Drug Administration. Abuse-deterrent opioids: Evaluation and labelling guidance for industry. 2015; Available from: https://www.fda.gov/media/84819/download
-
Harolyn MEB, Harold E. Substance abuse in children prediction, protection, and prevention. Arch Pediatric Adolescent Medicine. 2020; 152(10):952-960. Available from:https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapediatrics/fullarticle/189961 Doi:10.1001/archpedi.152.10.952.
-
Ikenna DM, Oluwakemi OO.The prevalence of drug use and illicit trafficking: A descriptive cross-sectional study of irregular migrant returnees in Nigeria. J of Migration and Health.2021; 3: 100034. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmh.2021.100034
-
Jatau AI,. The burden of drug abuse in Nigeria: a scoping review of epidemiological studies and drug laws. Public Health Review. 2021;42:1603960. Available from: https://www.ssph-journal.org/articles/10.3389/phrs.2021.1603960/full Doi: 10.3389/phrs.2021.1603960
-
Mayo CS. Teen drug abuse: Help your teen avoid drugs. 2021; Available from: https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/tween-and-teen-health/in-depth/teen-drug-abuse/art-20045921
-
National Drug Law Enforcement Agency. NDLEA arrest Nigerian drug lord with N8 billion worth of cocaine. 2021; Available from: https://www.bbc.com/pidgin/tori-57232374
-
Ogunsola SO, Fajemisin EA, Aiyenuro AE, Tunde AA. Experiences and projections for drug abuse sensitization and eradication among youths in South West, Nigeria. J of Alcoholism Drug Abuse & Substance Dependence. 2020; 6:018-24. Available from: https://www.heraldopenaccess.us/openaccess/experiences-and-projections-for-drug-abuse-sensitization-and-eradication-among-youths-in-south-west-nigeria
-
Ojikutu RK. The desire to remain awake at night among students of tertiary institutions in Lagos State, Nigeria: The health implications.Int. J. Acad. Res. 2010; 2(2): 29-33.
-
Roxanne D, Melissa CS. Facts you should know about marijuana (cannabis). 2021; Available from: https://www.medicinenet.com/marijuana/article.htm
-
Sirisha Y.What are the effects of drug abuse? 2020; Available from: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/effects-of-drug-abuse
-
Syed, (2013). Socio-demographic characteristics of substance abusers among school children in northern India.Int. j. curr.. 2013;5(9): 76-84
-
Weaver MF. Prescription sedative misuse and abuse. Yale J of Biological Medicine, 2015; 88(3): 247–256. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4553644/
-
United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. Drug use in Nigeria. 2018; Available from:https://www.unodc.org/documents/data-andanalysis/statistics/drugs/drug_use_survey_Nigeria_2019_book.pdf
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License