IJCRR - 13(19), October, 2021
Pages: 142-148
Date of Publication: 11-Oct-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A Cross-Sectional Study to Analyse the Severity of Smoking and its Effects on Copd Patient's Bone Mineral Density
Author: Mani Sathishkumar, Gayathri Ganesh, Giridharan Swetha, Gangadharan Vadivelu
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in adults and currently represents the fourth leading cause of death in world1COPD it is recognized as a multi-component disorder, associated with systemic inflammation and extrapulmonary manifestation. Of which osteoporosis and osteopenia in COPD are a significant extra-pulmonary component which is least considered.3 Objective: The main aim of the study is to access the severity of COPD with Bone Mineral Density(BMD) which defines osteoporosis and osteopenia, along with serum CRP and Serum Calcium levels. We collected about 60 Spirometry proven COPD patient's data and analysed using student t and Pearson chi-square test. Results: Observed majority of the study population was in the moderate to severe COPD group, of the moderate COPD group majority were osteopenic, severe COPD patients were osteoporotic. Conclusion: Lower the BMI the risk of developing low BMD increases, as the study shows patients with low BMI was mostly in the osteoporotic range. Serum calcium, CRP and Smoking status also were correlating with BMD levels.
Keywords: COPD, BMD, Smoking, Spirometry, Serum calcium, Dyspnea
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is defined as a preventable and treatable disease with some significant extrapulmonary effects that may contribute to the severity in individual patients. 2 Its pulmonary component is characterized by airflow limitation that is not fully reversible. The airflow limitation is usually progressive and associated with an abnormal inflammatory response of the lung to noxious particles or gases. 4
COPD has classically been considered to be restricted to pulmonary inflammation and structural remodelling. However, COPD is recognized as a multi-component disorder, associated with systemic inflammation and extrapulmonary manifestation7
The systemic aspects of COPD include oxidative stress and altered circulating levels of inflammatory mediators and acute-phase proteins.5 Local inflammation of the airways and lung parenchyma has always been acknowledged as part of the COPD disease process; however, it is becoming clear that the inflammatory response is systemic.9 In our study we analysed the effect of Systemic inflammation of COPD in the bone mineral density with serum calcium and serum CRP levels to get to know the extent of its impact.
AIMS AND OBJECTIVES
-
To assess the level of BMD in COPD patients using quantitative ultrasound bone densitometer.
-
To correlate the severity of COPD with airway obstruction (GOLD guidelines) and BMD.
-
To assess BMI of COPD patients and its correlation with BMD.
-
To assess serum CRP levels, Serum Calcium levels in COPD patients and their correlation with BMD.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
In the Department of Respiratory Medicine, Saveetha Medical College & Hospital, Chennai, Tamilnadu. Institutional Ethical Committee approval was obtained.
STUDY DESIGN- Prospective, Cross-sectional design
PERIOD OF STUDY September 2019 to April 2020
SAMPLE SIZE Cases: 60
INCLUSION CRITERIA All patients clinically and spirometrically diagnosed with COPD as suggested by GOLD guidelines.
EXCLUSION CRITERIA Spirometry has proven bronchial asthma, COPD with other co-existing lung diseases like Treated Pulmonary Tuberculosis, Bronchiectasis, etc., Patients on long term steroids, Co-morbidities ( DM, SHT, Liver disorders) Cardiac conditions (Recent MI, Unstable Angina, CCF).
STUDY PROTOCOL
A total of 60 patients who were clinically proven COPD, attended to our outpatient department at Saveetha Medical College Hospital were enrolled in the study after getting their written and oral consent.
The patients with the following diagnostic criteria (according to the GOLD guidelines) were defined as having COPD
Presence of cough and sputum production for at least 3 months in each of the two consecutive years, Exertional dyspnoea Clinical& Physical examination showing, Signs of airflow limitation like prolonged expiration and expiratory wheeze which is not fully reversible and with Signs of hyperinflation
Investigations show Chest X-ray showing emphysematous change or chronic bronchitis picture, Spirometry showing post-bronchodilator FEV1/FVC ratio <0.70
For each enrolled patient, detailed history of smoking, personal and family medical histories were obtained Height and weight were measured during the spirometry procedure. Body mass index (BMI) was calculated by the formula.
BMI = Weight in Kgs / (Height in Meters)2
Spirometry was performed using the ‘KOKO legend’ desktop spirometer, model no. 314000. This equipment met the American Thoracic Society performance criteria. Spirometry was performed after 20 minutes following the administration of Salbutamol (2.5mg) nebulisation for reversibility. The following parameters were noted
-
FVC, FEV1,FEV1/FVC,FEF25-75%,PEFR
The procedure was repeated on 3 occasions and the average value was taken.
Serum CRP was estimated in the Department of Microbiology lab, Saveetha Medical College Hospital. The test was performed using the latex agglutination method. The positive result was expressed when the agglutination occurred.
Serum calcium was estimated in the Department of Biochemistry lab, Saveetha Medical College & Hospital. The test was performed using Arsenazo III Method.
Bone mineral density was assessed using ACHILLES quantitative ultrasound bone densitometer produced by GE HEALTH CARE. The left heel bone (calcaneus) of the patients after applying gel was placed in the machine and the bone density is measured T- score -1 to+1 is taken as normal and -1 to -2. 5 is considered to be osteopenic and <-2.5 is considered to be osteoporotic.
Statistical analysis was carried out in all 60 patients. Baseline data were collected from patients and classified into mild, moderate and severe COPD. Age, body mass index, CRP, Serum calcium and BMD were all collected from all the patients and the parameters were analyzed.
The statistical analysis was carried out using windows Excel and SPSS version 13 software. The student ‘t' test was used to find out the difference. Pearson Chi-Square test was used to find out the statistical significance.
RESULTS
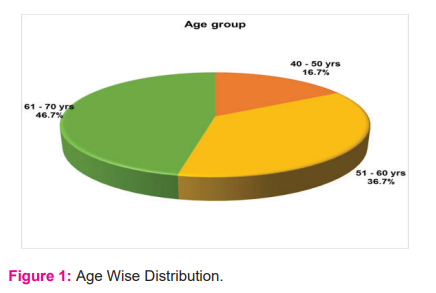
In our study majority of patients were in the age group of 61 years and above (58.33%), followed by 26.6% of patients who were seen in the age group of 51 to 60 years (Figure- 1). Only 7 patients (11.6%) were in the age group of 40 to 50 years. No patients were in the age group of fewer than 40 years.
The majority of our study population was male with 51 patients (85%) when compared to the female population with only 9 patients (15%). (Table-1)
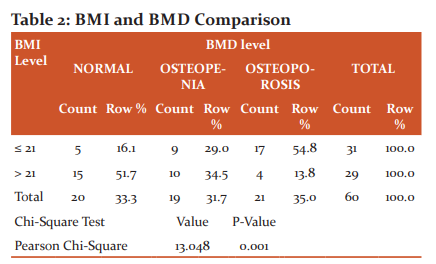
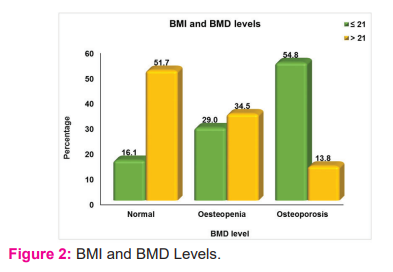
In the study population, Body Mass Index showed a significant correlation with Bone Mineral Density levels. In (Figure-2) 17(54.8%) osteoporosis patients have BMI <21, 4(13.8%) osteoporosis patients have BMI>21, 10(34.5%) osteopenic patients are with BMI>21, and 9 (29%) osteopenic patients are with BMI <21. BMI and BMD show a positive correlation with a p-value <0.01(Table-2).
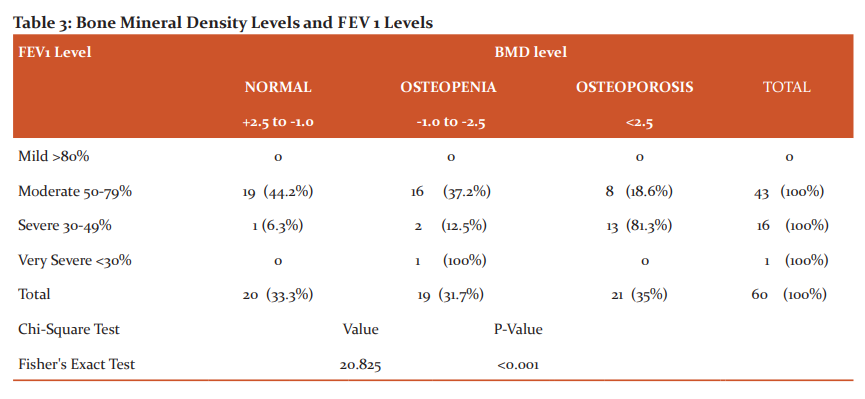
Among 60 cases enrolled in our study 43(71.6%) cases are with moderate obstruction, 16(26.7%) cases are with severe obstruction, and 1(1.7%) cases with very severe obstruction. The majority of our study is in the moderate COPD group. In the study population, 21(35%) patients were osteoporotic out of which 13(81.3%) were with severe obstruction, and 8(18.6%) were with moderate obstruction. Totally 19(31.7%) patients were osteopenic out of which 2(12.5%) patients were with severe obstruction and 16(37.2%) were with moderate COPD. The study showed a statistical significance of p<0.001. (Table-3)
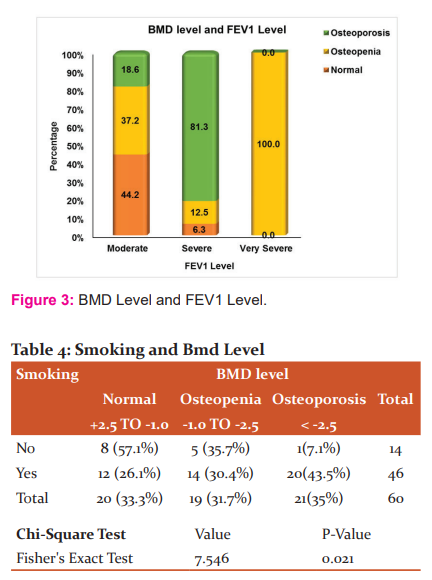
In our study out of 60 cases, 14(23.33%) were non-smokers, 46(76.67%) cases were smokers. The mean smoke years for normal BMD patients is 16.45, for osteopenic patients is 21.87 and for 28.15 for osteoporosis patients. (Table-4)
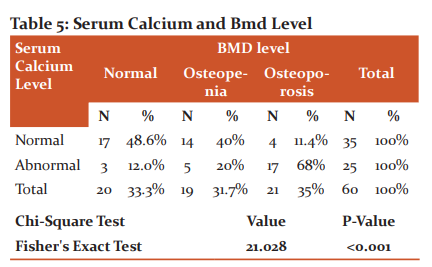
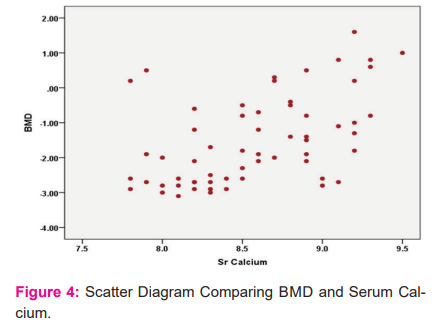
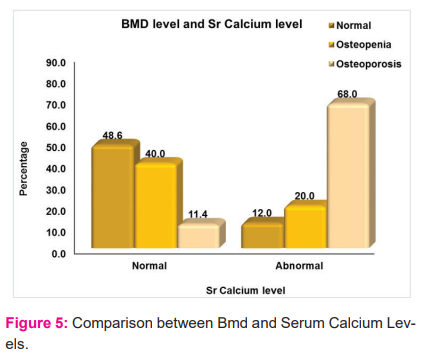
Serum calcium normal level is 8.5-9.5 mg/dl. In our study population all the cases are with values < 9.5mg/dl. Patients with values less than < 8.5 is taken abnormal and > 8.5 is taken as normal. In Patients with normal sr.calcium levels 17(48.6%) patients are with normal BMD, 14(40%) with osteopenia status and 4(11.4%) are in osteoporotic state(Figure-3). In patients with abnormal sr.calcium levels i.e<8.5mg/dl , 3(12%) patients are with normal BMD(Figure-4). 5(20%) patients are in osteopenic state and 17(68%) patients were in osteoporotic state. Study shows abnormal the sr.calcium level more the patients are osteoporotic (p<0.001).(Table-5),(Figure-5).
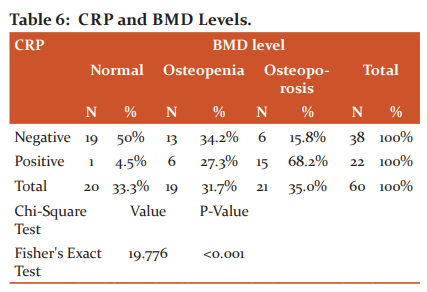
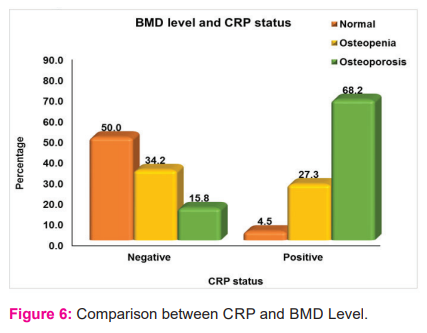
In the study population, CRP was positive in 22(36.7%) patients out of which 15(68.2%) patients were osteoporotic and 6(27.3%) were osteopenic(Figure-6). CRP showed a positive correlation with BMD with statistical significance p<0.001. (Table-6)
DISCUSSION
COPD is a systemic disease as incorporated in the definition of COPD according to GOLD guidelines.4 Systemic effects, however, are direct consequences of the disease itself with a definite cause-and-effect relationship.33 Nevertheless, disorders like osteoporosis in COPD could be a co-morbidity due to shared risk factors or a systemic consequence due to a cause-and-effect relationship. In addition, a co-morbidity can contribute to a systemic consequence in COPD that may trigger the production of systemic inflammatory mediators in other parts of the body like bone marrow and skeletal muscles.
A. Vriezeet et al4 and Bhattacharyya et al15 found the prevalence of osteopenia and osteoporosis in COPD patients using ultrasound bone densitometer and a positive correlation between BMI and CRP levels.
To our knowledge, there is no Indian study comparing BMD with CRP, serum calcium, smoking and BMI. In our study, we compared everything with BMD levels.
In the study, the population showed that the majority are in the age group of >60 years (46.7%), followed by 51 to 60 years (36.7%) and 40-50 years(16.7%). In our study, we found the majority of our patients were males 51(85%) and 9(15%) were females.
According to WHO, the normal value for T- score in measuring BMD is within 1SD of the mean value for young adults i.e-1 to+1 is taken as normal and -1 to -2.5 is considered to be osteopenic and <-2.5 is considered to be osteoporotic.
Then BMI is compared with BMD, BMI is divided into two groups <21 and >21. 31 patients had BMI<21 out of which 5(16.1%) were normal, 9(29%) were osteopenic and 17(54.8%) were osteoporotic. 29 patients had BMI > 21 out of which 15(51.7%) were normal, 10(34.5%) were osteopenic and 4(13.8%) are osteoporotic. This shows that patients with low BMI are at risk of developing low Bone Mineral Density and thereby suggesting that there is underlying systemic inflammation. Similar studies have been done by A.Vriezeet et al4 and jyotihariholi et al68 who described the depletion of fat-free mass and thereby a reduction in BMI in patients with severe COPD.
Malnutrition is the result of an imbalance between energy expenditure and intake, a situation that will favour muscle protein breakdown to provide amino acids to maintain whole-body homeostasis.
This compensatory phenomenon will eventually compromise the maintenance of muscle mass. Calorie intake may be diminished in patients with COPD, particularly in advanced disease and during episodes of exacerbation. Subsequently, basal and activity related metabolic rates are often amplified, creating metabolic imbalance.40
Smoking and the development of COPD is well proven beyond any doubt by numerous studies. Smokers experience an accelerated rate of decline in lung function.33 Quitting smoking can slow the progressive loss of lung function19 and can reduce symptoms18 at any point in time. Nearly all patients with clinically significant emphysema are smokers. Smoking is also a major risk factor for chronic bronchitis. Heavy smokers are at greater risk of developing COPD than moderate smokers. Low exposures to cigarette smoke as encountered during passive smoking also seem to be harmful.
Fletcher and Peto27 showed that smoking was associated with irreversible obstructive changes in airways in some subjects while not in others. Marcus et al21 described that smoking causes a decline in pulmonary function in a dose-dependent manner and cessation of smoking improves the obstructive pattern.
On average, the rate of expiratory airflow in smokers decrease twice as fast in smokers (40 - 69 ml per year) as in non-smokers (20 ml per year).2,39 Nonetheless, most smokers do not develop symptomatic COPD, probably because of the large physiological reserve of the lung. However, some smokers (15%) do experience accelerated loss of lung function and develop symptomatic disease.
In our study majority, 76.7% were smokers out of which 30.4% were osteopenic and 43.5% were osteoporotic. Mean the number of smoking pack-years for osteopenic patients is 21.87 and 28.15 for osteoporotic patients. This shows that when smoking pack years increases the bone mineral density decreases hence smoking is a major risk factor for a decrease in bone density.
According to GOLD guidelines COPD is classified into four stages as mild, moderate, severe and very severe. Patients are categorized into these groups and bone density is measured. The majority of our study was with moderate COPD (71.7%) of those 19(44.2%) were with normal BMD, 16(37.2%) were osteopenic and 8(18.6%) were osteoporotic level. Only one patient was in the very severe group who is in the osteopenic range. This proves that as the severity of the BMD increases there is a decline in the FEV1 level majority of the patients in the moderate COPD group are osteopenic and the severe COPD group are osteoporotic.
We took C Reactive Protein (CRP) a marker of systemic inflammation since it has been shown to upregulate the production of proinflammatory cytokines and tissue factors by monocytes, increase the uptake of LDL by macrophages and directly induce expression of adhesion molecules by the human endothelial cells.
Additionally, CRP may deposit directly into the arterial wall during atherogenesis, interacting with other inflammatory mediators to create foam cells, which serve as building blocks to atherosclerotic plaques,30 Karadag F36 and Cirilloet al37 showed an increasing CRP
value with worsening airflow obstruction.
In our study, CRP was positive in 22(36.7%) patients out of 60 patients. Out of which 15(68.2%) patients were in osteoporotic level, 6(27.3%) patients were osteopenic and 1(4.5%) patient were in the normal range. This implies that there is underlying chronic inflammation seen in severe COPD patients. To our knowledge, this is the first study correlating the CRP levels and bone mineral density.
This study showed that serum calcium was significantly decreased in moderate to severe COPD group patients. The normal range of serum calcium is 8.5 to 9.5mg/dl. In our study group, all 60 cases had serum calcium levels <9.5mg/dl. Out of which 25 cases (41.7%) had serum calcium level < 8.5mg/dl. In that 17 (68%) patients were in the osteoporotic state, 5(20%) patients were in the osteopenic level. This describes that as the COPD patients severity increases serum calcium level in the circulating blood decreases. This shows the statistical significance of P-value <0.001. this was also correlating with other study’s such as Hans D et al.34
CONCLUSION
Our study concludes that as BMD decreases as the age, airway obstruction, smoking pack increases. There is a decline in serum calcium levels and body mass index (BMI)as the BMD decreases. Since ultrasound bone densitometer is an easy and reliable tool for assessing the BMD can be used as a screening tool. CRP and Serum calcium levels are also useful methods for assessing early bone destruction. Hence COPD is a systemic disease with various systemic manifestations and bone mineral destruction is an important and life-threatening feature of COPD.
Acknowledgement: I thank the department and my colleagues and the authors who contributed to the work and special mention to all the patients who have participated in the study without hesitance and I also thank our management and the Journal committee for accepting and publishing the study.
Author’s Contribution: Data collection, statistical work and article write-up.
Source of Funding: None
Conflict of Interest: None
IEC Letter No: SMC/IEC/2020/02/158
References:
-
Agusti AG, Noguera A, Sauleda J. Systemic effects of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur Respir J. 2003;21(2):347- 60.
-
Al-Fayez SF, Salleh M, Ardawi M, AZahran FM. Effects of sheesha and cigarette smoking on pulmonary function of Saudi males and females. Trop Geogr Med. 1988;40(2):115-23.
-
American Thoracic Society. Chronic bronchitis, asthma and pulmonary emphysema: a statement by the Committee on Diagnostic Standards for Nontuberculous Respiratory Diseases. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1962; 85: 762–768.
-
American Thoracic Society and European Thoracic Society. Skeletal muscle dysfunction in chronic obstructive disease. Am J RespirCrit Care Med. 1999; 159: Suppl. 4, 1–40
-
Anthonisen NR, Wright EC, Hodgkin JE. Prognosis in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986;133: 14-20.
-
Anto JM, Vermeire P, Vestbo J, Sunyer J. Epidemiology of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur Respir J. 2001; 17: 982–994.
-
Badham C. An essay on bronchitis: with a supplement containing remarks on the simple pulmonary abscess. 2nd ed. London: J Callow. 1814.
-
Balmes J, Becklake M, Blanc P, Henneberger P, Kreiss K, Mapp C, et al.American Thoracic Society Statement: Occupational contribution to the burden of airway disease. Am J RespirCrit Care Med. 2003;167(5):787-97.
-
Barker DJ, Godfrey KM, Fall C, Osmond C, Winter PD, Shaheen SO et al. Relation of birth weight and childhood respiratory infection to adult lung function and death from chronic obstructive airways disease. Bri Med J. 1991;303(6804):671-5.
-
Biernacki W, Flenley DC, Muir AL, MacNee W. Pulmonary hypertension and right ventricular function in patients with COPD. Chest. 1988; 94: 1169–1175.
-
Bikle DD, Halloran B, Fong L, Steinbach L, Shellito J. Elevated 1,25- dihydroxy vitamin D levels in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease treated with prednisone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993; 76(2):456-461.
-
Blanco I, de Serres FJ, Fernandez-Bustillo E, Lara B, Miravitlles M. Estimated numbers and prevalence of PI*S and PI*Z alleles of alpha1 antitrypsin deficiency in European countries. Eur Respir J. 2006; 27(1):77.
-
Bon JM, Zhang Y, Duncan SR, Pilewski JM, Zaldonis D, Zeevi A et al. Plasma inflammatory mediators associated with bone metabolism in COPD. J Cron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2010; 7:186-191.
-
. Bolton CE, Ionescu AA, Shiels KM, Pettit RJ, Edwards PH, Stone MD et al. Associated loss of fat-free mass and bone mineral density in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004; 170(12):1286-1293.
-
B. Parthasarathi, Pl. Rantu, G. Malabika, et al, Prevalence of osteoporosis and osteopenia in advanced chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients, Lung India. 28 (3) (2011) 184–186
-
Bonet T. Geneva. Sepulchretumsive anatoniapructica ex CadaveribusMorbodenatis, proponensHistoa’s Observations omniumpenéhumanicorporisaffectuum, ipsarcomoueCausasrecorditasrevelans.
-
British Thoracic Society. Guidelines for the management of the chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax 1997;52(suppl 5).
-
Buist AS, Sexton GJ, Nagy JM, Ross BB. The effect of smoking cessation and modification on lung function. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976; 114: 115–122.
-
Burrows B, Knudson RJ, Cline MG, Lebowitz MD. Quantitative relationships between cigarette smoking and ventilatory function. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977; 115: 195–205.
-
Burrows B. Predictors of loss of lung function and mortality in obstructive lung diseases. Eur Respir Rev. 1991;1:340-5.
-
Cosio M, Ghezzo H, Hogg JC, et al.CBO RichtlijnOsteoporoseenFractuurPreventie. Derdeherziening (2011). http://www.cbo.nl/Downloads/1318/Definitieve%20richtlijn%20osteoporose%20 28-04-201 The relations between structural changes in small airways and pulmonary-function tests. N Engl J Med. 1978; 298:1277–1281.
-
Definitions, epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and staging. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995;152:supply:s78-s83.
-
Dekhuijzen PN, Aben KK, Dekker I, et al. Increased exhalation of hydrogen peroxide in patients with stable and unstable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J RespirCrit Care Med. 1996; 154: 813–816.
-
Dimai HP, Domej W, Leb G, Lau KH. Bone loss in patients with untreated chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is mediated by an increase in bone resorption associated with hypercapnia. J Bone Miner Res. 2001; 16(11):2132- 2141.
-
Domingo-Salvany A, Lamarca R, Ferrer M, et al. Health-related quality of life and mortality in male patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J RespirCrit Care Med 2002;166:680-685.
-
Ezzati M. Indoor air pollution and health in developing countries. Lancet. 2005;366(9480):104-6.
-
Fletcher CM, Tinker CM, Peto R, Speizer FE. The natural history of chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Oxford, Oxford University Press, 1976.
-
Frost ML, Blake GM, Fogelman I (2002) A comparison of fracture discrimination using calcaneal quantitative ultrasound and dual X-ray absorptiometry in women with a history of fracture at sites other than the spine and hip. Calcif Tissue Int. 71(3):207–211.
-
Gan WQ, Man SF, Senthilselvan A, Sin DD. Association between chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and systemic inflammation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Thorax. 2004;59(7):574- 80.
-
Global initiative for chronic obstructive lung disease. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. 2007; available from www.goldcopd.com: accessed Oct 5, 2008.
-
Gluck O, Colice G. Recognizing and treating glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis in patients with pulmonary diseases. Chest. 2004; 125(5):1859- 1876.
-
Gold DR, Wang X, Wipyj D, Speizer FE, Ware JH, Dockery DW. Effects of cigarette smoking on lung function in adolescent boys and girls. N Engl J Med. 1996; 335: 931–937.
-
Hansson GK. Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352(16):1685-95.
-
Hans D, Dargent-Molina P, Schott AM, Sebert JL, Cormier C, Kotzki PO et al (1996) Ultrasonographic heel measurements to predict hip fracture in elderly women: the EPIDOS prospective study. Lancet.. 348(9026):511–514
-
Hofbauer LC, Schoppet M. Clinical implications of the osteoprotegerin/RANKL/RANK system for bone and vascular diseases. J Am Med Ass. 2004; 292(4):490-495.
-
Incalzi RA, Caradonna P, Ranieri P, Basso S, Fuso L, Pagano F et al. Correlates of osteoporosis in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir Med. 2000; 94(11):1079-1084
-
Ito K, Ito M, Elliott M, Cosio MG, Caramori G, Kon O et al. Decreased histone deacetylase activity in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Relationship to severity. N Engl J Med.
-
Jindal SK, Agarwal AN, Gupta D. A review of population studies from India to estimate the national burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and its association with smoking. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci. 2001; 43(3):139-47.
-
Jindal SK, Aggarwal AN, Chaudhry K, Chhabra SK, D'Souza GA, Gupta D, et al. A multicentric study on the epidemiology of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and its relationship with tobacco smoking and environmental tobacco smoke exposure. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci. 2006;48(1):23-9.
-
Karadag F, kirdar S, Karul AB. The value of C- reactive protein as a marker of systemic inflammation in stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur J Int Med. 2008; 19(2):104-8.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License