IJCRR - 13(19), October, 2021
Pages: 130-136
Date of Publication: 11-Oct-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Correlation of Early Childhood Caries with Maternal Risk Factors among 2-6 Years Old Children in Vijayawada City, Andhra Pradesh, India - A Cross-Sectional Study
Author: M. Sai Divya, S. Srikanth Raju, P. Gowtham
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Maternal risk factors play a vital role in the transmission of infection to the child. Hence this study was undertaken to evaluate the extent of influence of maternal risk factors exert on ECC below 6 -year-old children. Materials and Methods: A single calibrated examiner performed all clinical examinations under natural light using a mouth mirror and probe. The study was conducted in a random sample of 140 mother children pairs. Data related to pregnancy-related issues, feeding methods, oral hygiene measures and dental knowledge & practices was obtained. The data was then tabulated and statistically analyzed. Results: Out of the 140 samples, 103 (73.57%) children had ECC of which 5-6 year children were more prevalent (84%). Children brushing twice daily had significantly less ECC (p< 0.01). Most of the feeding was by breast (57.1%) and 37 children of 80 breastfed mothers had no ECC and the relation was significant statistically (p < 0.01). 82 Children of 89 mothers who woke up during the night for feeding had ECC and this association was significant (p< 0.01). Conclusion: Adverse nighttime feeding habits, sugar additions, oral hygiene measures contribute to ECC. The mother needs to be counselled regarding the risk factors which ultimately help to prevent ECC at the primordial level.
Keywords: Mother, ECC, Children, Risk factors, Feeding methods, Oral hygiene measures
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION:
Dental caries in infants and children has been recognized as a perennial health problem ever since an American physician named Abraham Jacobi first observed and described the problem in 1862 in one of his children.1 Beltrami, in 1932 named it as “Les dentesnoires des tout-petits” implying “black teeth of the very young.1 The term ‘Early Childhood Caries (ECC) was suggested at a workshop held by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and a case definition was proposed using patterns of caries experience as defining criteria at a workshop convened by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) 1999. 2, 3 ECC has a complex, multifactorial aetiology where cariogenic organisms under the influence of fermentable carbohydrates induce caries in a susceptible host over some time. The cariogenic organisms implicated in ECC include mutans streptococci (MS) and Lactobacillus species. Maternal risk factors like infant feeding practices such as frequent exposure to sugar, frequent snacking, taking sweetened drinks during bedtime, and sharing foods with adults, oral hygiene, dietary habits, socioeconomic status and education level also have a bearing on the establishment of high MS counts in children.4,5 Since, maternal risk factors play a vital role in the transmission of infection to the child, the need of the hour is to thoroughly understand and evaluate their role in the disease process. Hence this study was undertaken to evaluate the extent of influence of maternal risk factors exert on ECC below 6 -year-old children.
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
Study design: This is a Randomized clinical trial study approved by the ethical committee of Drs Sudha and Nageswararao Siddhartha Institute of Dental Sciences, Gannavaram Mandal, A.P with an ethical clearance number. O.C.No/IEC/25/2015.
Patient selection: The study was conducted in a random sample of 140 mother children pairs who reported to the Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry, DrsSudha and Nageswararao Siddhartha Institute of Dental Sciences, Gannavaram Mandal, A.P and Department of Paediatrics, Siddhartha Medical College, Vijayawada, A.P. Mothers were explained about the study and written consent was obtained from them
Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
-
Children who belong to the 12 -71 months age group and lost their mothers
-
Children who belong to the 12 -71 months age group whose mothers were not residing with them.
-
Children and mothers with systemic diseases, congenital syndromes & dental developmental disorders
A structured questionnaire by Winter et al., modified according to Indian conditions was used in this study. This questionnaire containing questions related to pregnancy-related issues, feeding methods, oral hygiene measures and dental knowledge & practices was explained by the examiner to the mothers in the language of their understanding and sufficient time was given for answering. The answers were filled in by the examiner only.
The obtained data were tabulated by using Excel (Microsoft). The completed proformas were statistically analyzed to find the correlation between ECC and maternal caries, oral hygiene and risk factors. Descriptive statistical analysis was carried out in the present study. Results were represented as mean ± SD (Min-Max) and categorical measurements were presented as percentages using SPSS- software (version 20). A Chi-square test was used to compare qualitative data.
RESULTS:
Out of the 140 samples, 103 (73.57%) children had ECC of which 5-6 year children were more prevalent (84%).
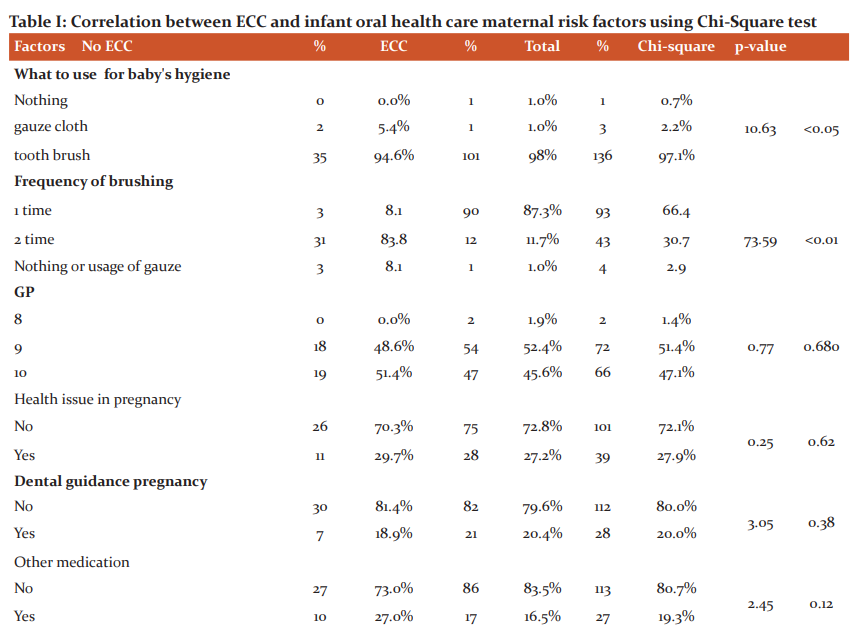
The survey of brushing habits revealed 97% of the sample populations were using toothbrushes and the majority of them (96%) were brushing only ones. Children brushing twice daily had significantly less ECC (p<0.01). One twenty-one members stated not to use any pacifiers for their children and 87 of their children had ECC though it was not significant statistically (p=0.7)
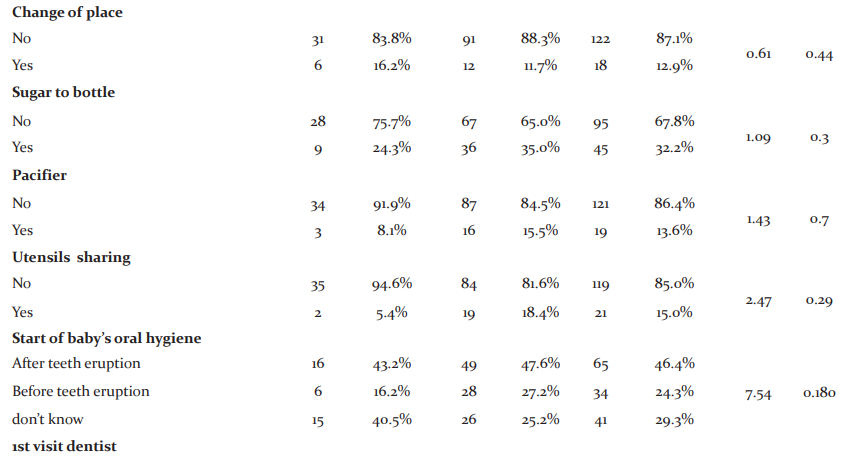
The majority of mothers (72.1%) had no health issues during pregnancy and this factor was not significant with ECC (p=0.62). Eighty per cent of mothers didn’t receive any guidance towards oral health and this factor was not relevant with ECC (p=0.38). Similarly, most of the mothers had not taken any other medication during pregnancy and this also was not having any statistical significance (p=0.12). Other factors like change of place (p=0.44), utensil sharing (p=0.29), initiation of child oral hygiene (p=0.18), 1st dental visit (p=0.560) and 1st tooth eruption (p=0.49) had less influence on ECC (Table I)
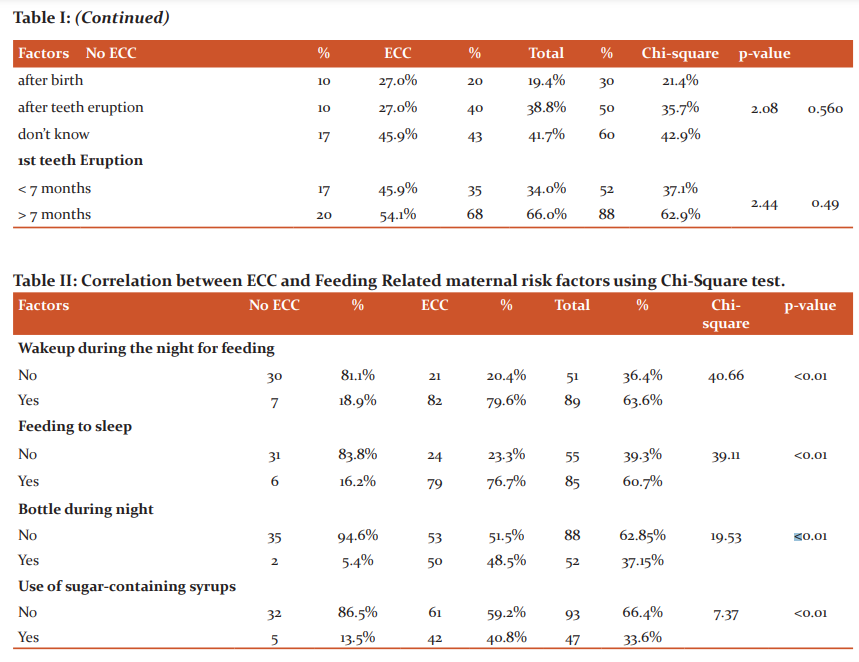
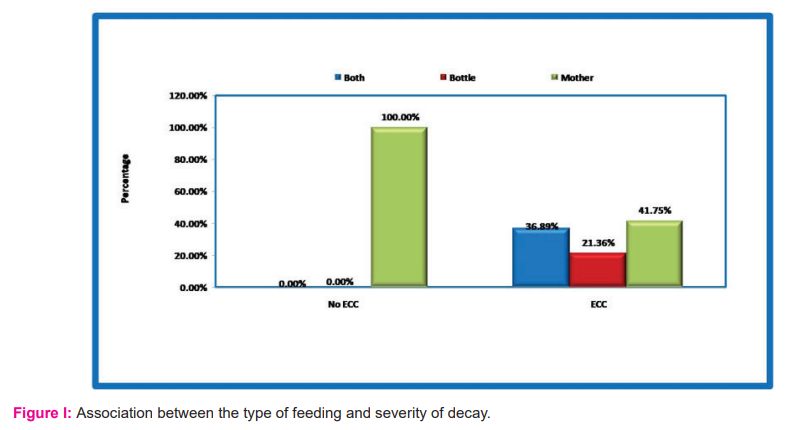
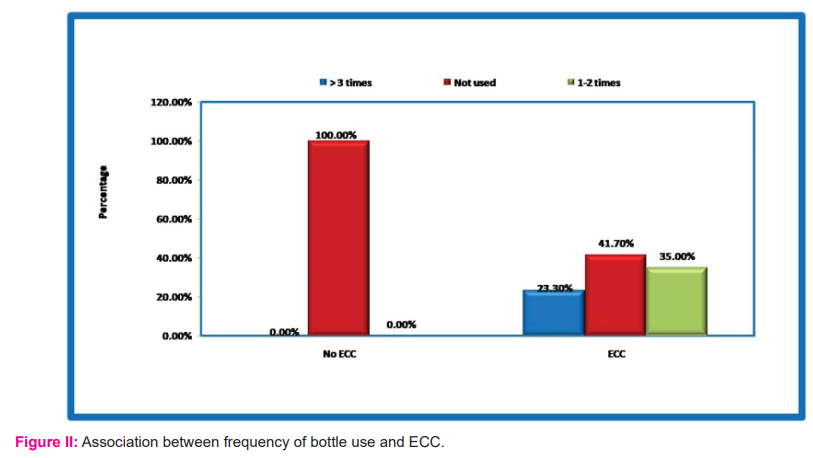
Feeding habits were surveyed in this study. Most of the feeding was by breast (57.1%) and 37 children of 80 breastfed mothers had no ECC and the relation was significant statistically (p <0.01) (Fig I). 82 Children of 89 mothers who woke up during the night for feeding had ECC and this association was significant (p<0.01). Seventy-nine children of 85 mothers who were fed to sleep had ECC and this was significant (p<0.01). Almost all bottle users in the night (50 out of 52) had ECC that was statistically significant(p<0.01) (Table II). All the children who used bottles frequently (more than one time) had ECC and this association was also significant (Fig II)
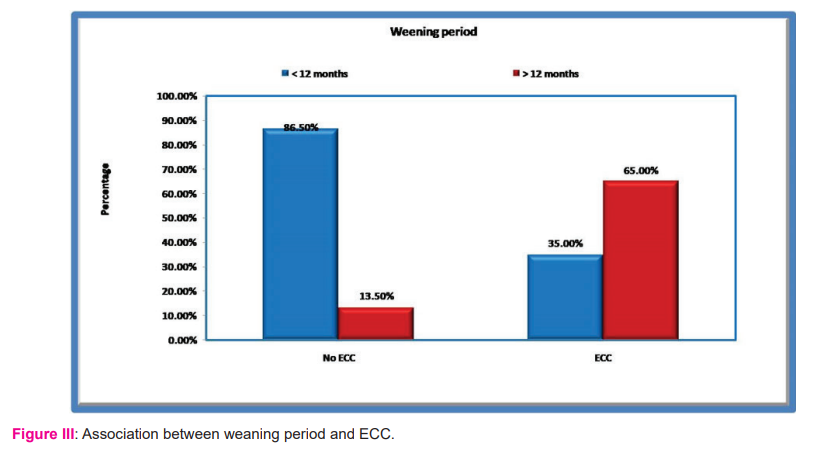
Children with a prolonged weaning period of more than 12 months had a greater proportion (67 out of 72) of ECC (Fig III). Ninety-three (66.4%) children were medicated with sugar-containing syrups and the majority (61) had ECC which was significant. 80% of children fed with sugar in the bottles had ECC though it was not significant statistically.
DISCUSSION:
A significant reduction in the prevalence of tooth decay in children and adults is noticed in the developed world for the past 30 years. However, this decrease has been much less pronounced in primary teeth compared to permanent teeth.6 The dental health of pre-school children in whom nursing caries is evident has largely been ignored in many developing countries like India because of the false notion that primary teeth are not important as permanent teeth.7 Also, drastic change in dietary habits coupled with lack of awareness pertaining prevention of oral diseases has made dental caries a potential threat to the well-being of the child. ECC is a complex disease and several studies had reported that multiple mechanisms like genetic predispositions and environmental factors affect its outcome.8-11 Identifying these risk factors is the focus of contemporary research that might aid in mitigating the onset and progress of ECC. The present study assessed the correlation between ECC and maternal risk factors in terms of past medical history, social behaviour factors, sharing of utensils, their dental knowledge and feeding habits.
Feeding habits like breast or bottle, nocturnal feeding, frequency of bottle use and weaning period were surveyed in this study. In the present study bottle-fed and combination of both breast & bottle-fed children showed higher ECC than breastfed children alone. This can be explained by the fact that the bottle contents are constantly in contact with the dental structures, making it an ideal place for acid production and dental caries onset. In this study, only 32% of the sample population was adding sugar to the bottle and the majority of them (80%) had ECC. Thitosomakul et al. stated that there is an association between type of infant feeding and occurrence of ECC.12 The practice of breastfeeding among Indian mothers is almost universal and human milk is the main source of nutrition. However, various aspects of breastfeeding such as children receiving prolonged and nocturnal breastfeeding can be associated with ECC as reported by Rosenblatt et al., Serwint et al., and Ramoz-Gomez et al., 13-15 However, no association was found between the type of feeding and ECC in studies conducted by Du et al 2007., Perera et al.,and Roberts et al.,16
Some of the variables such as wakeup during the night for feeding, feeding to sleep and frequent bottle usage during the night contributed to increasing of ECC in this study. Night- feeding which is considered a dentally non-desirable feeding habit frequently reported for its association with increased risk of enamel demineralization due to reduced flow rate of saliva and prolonged exposure of fermentable carbohydrates to cariogenic bacteria thereby increasing the risk of caries. Febres et al., in their study, found that the incidence of caries was higher in children who slept with the bottle than those who did not.17 It was recommended that infants should not be put to bed with the baby bottle and breastfeeding at night should be avoided after the eruption of the first tooth.
In the present study, children who were breastfed for more than 12 months duration were more likely to have ECC than those who were breastfed for less than 12 months. This finding was supported by Azevedo et al., Dini et al., Hattab et al., and Shantinath et al. 18-21 Human breast milk contains caries protective elements such as maternal immunoglobulins, enzymes, leucocytes and specific antibacterial agents. Beyond 12 months, these elements are progressively reduced thereby negating the caries protective effect of human milk. Conversely, no such association was found in the studies by Feldens et al., and Ollila et al.,.22, 23 However, WHO recommendations state that a child should be breastfed up to the age of 24 months. 24 No specific optimal weaning period or breastfeeding practices have been determined so far specifically to address the risk of dental caries.
The present study revealed that there was a significant association between caries and the use of sugar-containing syrups. Children who require sucrose-containing medications over an extended period are at increased risk for dental caries.25, 26 Other side effects of medications such as xerostomia or sialorrhea may further increase the risk of decay.
Brushing habits surveyed in this study revealed that most of the children were using toothbrushes, however, the majority were brushing once daily. Children brushing twice daily appeared to have lesser ECC, this highlights the importance of motivating and imparting oral health practices early in life to prevent ECC.
In the present study, there was no correlation between pacifier use and ECC. A systematic review did not find any consistent correlation between the use of pacifiers and the development of ECC, regardless of the length of use of pacifiers and the introduction of sweeteners or not. 27, 28 However, the habit of using pacifiers dipped in sugars might cause early colonization of streptococcus mutants in the infant’s oral cavity.
Other factors like health issues during pregnancy, guidance towards oral health, other medications during pregnancy, change of place, utensil sharing, initiation of child oral hygiene, 1st dental visit and 1st tooth eruption had less influence on ECC in this study. The lack of guidance regarding the baby’s oral hygiene was also a predominant factor in this study. In addition to that, they don’t know when to start the baby’s oral hygiene or when to visit the dentist for the 1st time. When the mothers received some type of information, it was from the pediatric physician. The oral health of infants and toddlers is dependent on mothers’ knowledge of oral health and oral hygiene behaviour.
In 2000, the Surgeon General’s Report on Oral Health in America stressed it was necessary for parents to be familiar with the importance and care of children’s primary teeth and to take appropriate actions to prevent ECC. 29 American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry recommended that all infants should be examined at the age of 1 year to identify incipient lesions and also assess feeding and hygiene practices. 30 Besides, improved oral health of the woman during pregnancy might decrease transmission of potentially cariogenic bacteria to infants and reduce children’s future risk of caries.
In the present study, the median age the first tooth emerged was seven months. ECC was more in children whose teeth erupted early (< 7months) though the difference was not statistically significant. This can be due to primary teeth facilitating the initial colonization of MS in the child’s mouth.
CONCLUSION:
It is imperative to counsel, treat, educate and motivate the mothers or caregivers regarding the feeding habits, oral hygiene measures and to mitigate them by their active participation. This highlights the importance of preventive modalities in controlling ECC. This can be best achieved by understanding the risk factors associated with the disease.
Acknowledgement: We would like to thank all study participants for their participation and kindly cooperation.
Source of Funding: No source of funding
Conflict of Interest: No conflict of interest
Ethical Clearance Letter No.: O.C.No/IEC/25/2015
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
-
Dr .M. SAI DIVYA – Conceived the idea and Collected the data
-
Dr. S. Srikanth Raju- Manuscript preparation and collected the data
-
Dr. P. GOWTHAM – Collected and Analyzed the Data
References:
-
Borutta A, Wagner M, Kneist S. Early Childhood caries: A multifactorial disease. OHDMBSC 2010; 9:32-8.
-
Kaste LM, Gift HC. Inappropriate infant bottle-feeding status of the healthy people 2000 objective. Arch PediatrAdolesc Med 1995; 149:786-91.
-
Drury TF, Horowitz AM, Ismail AI, Maertens MP, Rozier RG, Selwitz RH.et al. Diagnosing and reporting Early Childhood Caries for research purposes. A report of a workshop sponsored by the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research, the Health Resources and Services Administration, and the Health Care Financing Administration. J Public Health Dent 1999; 59:192-7.
-
Vadiakas G. Case definition, aetiology and risk assessment of early childhood caries (ECC): a revisited review. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent 2008; 9:115-25.
-
Kawashita Y. Dental caries in 3-year-old children are associated more with Child Rearing Behaviors than Mother-Related Health Behaviors. J Public Health Dent 2009; 69:104-10.
-
Macentee M, Harrison R, Wyatt C. Strategies to Enhance the Oral Health of British Columbians, specifically Aboriginal Peoples, Tobacco-Users, and those of Low Socioeconomic Background. 2001; 8-14.
-
Holm A-K. Caries in the preschool-child - international trends. J Dent 1990; 18:291-5.
-
Conry JP, Messer LB, Boraas JC, Aeppli DP, Bouchard TJ Jr. Dental caries and treatment characteristics in human twins reared apart. Arch Oral Biol 1993; 38:937-43.
-
Watt R G. Emerging theories into the social determinants of the health: implications for oral health promotion. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 2002; 30:241-7.
-
Finlayson TL, Siefert K, Ismail AI, Sohn W. Psychosocial factors and early childhood caries among low-income African-American children in Detroit. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 2007; 35:439-48.
-
Shearer DM, Thomson WM. Intergenerational continuity in oral health: a review. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 2010; 38:479-86.
-
ThitasomakulS, Piwat S, Thearmontree A, Chankanka O, Pithpornchaiyakul W, Madyusoh S.et al. Risks for early childhood caries analyzed by negative binomial models. J Dent Res. 2009; 88:137-41.
-
Rosenblatt A, Zarzar P. Breast-feeding and early childhood caries: an assessment among Brazilian infants. Int J Pediatr Dent. 2004; 14:439–45.
-
Serwing JR, Mungo R, Negrete VF, Duggan AK, Korsch BM. Child-rearing practices and nursing caries. Paediatrics. 1993; 92:233-237.
-
Ramos-Gomez FJ, Tomar SL, Ellison J, Artiga N, Sintes J, Vicuna G.et al. Assessment of Early Childhood Caries and dietary habits in a population of migrant Hispanic children in Stockton, California. J Dent Child. 1999; 66:395-403.
-
Avila WM, Pordeus IA, Paiva SM, Martins CC. Breast and Bottle Feeding as Risk Factors for Dental Caries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0142922.
-
Febres C, Echeverri EA, Keene HJ. Parental awareness, habits, and social factors and their relationship to baby bottle tooth decay. Pediatr Dent. 1997; 19:22-27.
-
Azevedo TD, Bezerra AC, de Toledo OA. Feeding Habits and Severe Early Childhood Caries (S-ECC) in Brazilian Preschool Children. Pediatr Dent. 2005; 27(1):28-33.
-
Dini EL, Holt RD, Bedi R. Caries and its association with infant feeding and oral health-related behaviours in 3–4-year-old Brazilian children. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 2000; 28:241-8.
-
Hattab FN, AI-Omari MA, Angmar-Mansson B, Daoud N. The Prevalence of Nursing Caries in One-to-Four-Year-Old Children in Jordan. ASDC J Dent Child 1999; 66:53-8.
-
Shantinath SD, Breiger D, Williams BJ. The relationship of sleep problems and sleep-associated feeding to nursing caries. Pediatr Dent 1996; 18:375-8.
-
Feldens CA, Giugliani ER, Vigo A, Vitolo MR. Early feeding practices and severe early childhood caries in four-year-old children from southern Brazil: A birth cohort study. Caries Res 2010; 44:445-52.
-
Ollila P,Lamas M. A seven-year survival analysis of caries onset in primary second molars and permanent first molars in different caries risk groups determined at age two years. ActaOdontologicaScandinavica 2007; 65:29-35.
-
World Health Organisation (WHO). Global strategy for infant and young child feeding. Geneva: WHO 2003.
-
De Menezes VA, Cavalcanti G, Mora C, Garcia AFG, Leal RB. Pediatric medicines and their relationship to dental caries. Braz J Pharm Sci. 2010; 46:157-64.
-
Marrs JA, Trumbley S, Malik G. early childhood caries: determining the risk factors and assessing the prevention strategies for nursing intervention. Pediatr Nurs. 2011; 37:9-15.
-
Winter GB, Rule DC, Mailer GP, James PM, Gordon PH. The prevalence of dental caries in pre-school children aged 1 to 4 years. Br Dent J. 1971; 130:434-6.
-
Ribeiro NM, Ribeiro MA. Breastfeeding and early childhood caries: a critical review. J Pediatr. 2004; 80:199-210
-
Oral health in America: a report of the Surgeon General. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research. 2000
-
American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry, Reference manual. Pediatr Dent. 2003; 25:1-150.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License