IJCRR - 13(19), October, 2021
Pages: 27-32
Date of Publication: 11-Oct-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Potential Antibacterial Activity of Green Synthesized Copper Nanoparticles and its Characterization
Author: Keerthika E, Ishwarya K, Jayashree L, Maripandian S, Nivetha, Irivichetty Sai Chandana
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction and Objective: Copper oxide (CuO) nanoparticles are one of the most significant transition metal oxides in the burgeoning area of nanotechnology due to their intriguing features. Because of its simplicity, eco-friendliness, and potential as next-generation antibiotics, its synthesis using green chemistry principles is gaining traction. Cost-effectiveness, lower toxicity, and remarkable broad-spectrum antibacterial activity against a range of bacteria through the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and release of copper ions. Materials and Methods: For CuO Nanoparticles synthesis Copper sulfate was used as starting material and its reduction was carried by Coriander Leaf Extract from Cu2+ to Cu0 The synthesized Cu nanoparticles were characterized by UV-Visible, FTIR and XRD methods. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) demonstrated particle sizes in the range of 10\?15 nm. CuO nanoparticles demonstrated antimicrobial activity against a range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, including MRSA. Time kill determination assay was done. Results: According to TEM energy dispersive spectroscopy, the copper to oxygen element ratio is 54.18 per cent to 45.26 per cent. Most resistant human pathogenic strains, including Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, showed significant inhibitory action (p0.0001). With a 31.66 mm zone of inhibition, the maximum effectiveness was recorded against Bacillus cereus. The addition of a sub-MIC concentration [broth dilution technique] of nano CuO reduced all populations to zero by 4 h. Conclusion: Studies of CuO nanoparticles suggest the release of ions may be required for optimum killing
Keywords: Copper oxide nanoparticle, X-ray diffraction, Transmission electron microscope, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), broth dilution technique and Fourier transform Infra-red spectroscopy
Full Text:
Introduction:
Copper oxide nanomaterials have been given a wide scope of their applications in various fields from the wellbeing and climate area. 1
Additionally, the antimicrobial action of CuO nanomaterial has made them the solid possibility to be utilized as helpful agents.2 as of now, analysts are confronting a significant test in the medical care area to battle drug opposition. In such manner, step by step a few improved blend procedures are building up that incorporates physical, compound and natural processes.3
Anyway, the utilization of vegetables for the union of nanoparticles is extremely restricted. Here, we use Coriander leaf separate for the blend of Cu NP. Coriander (CoriandrumsativumL.) is a flavour crop that has a place with the family Apiaceae (Umbelliferae) is primarily developed from its seeds over time. 4 Constituent of Coriander is phenolic corrosive including caffeic and chlorogenic corrosive. The flavonoids incorporate quercetin, kaempferol, rhamnetin, apigenin and the majority of these mixes are known to hinder free extremists created in the cell when they are gotten through the eating routine.5 Coriander has been accounted for to have numerous pharmacological exercises like cell reinforcement and antimicrobial.
Restricted data on the conceivable antimicrobial movement of nano CuO is accessible. CuO is less expensive than silver, effectively blended in with polymers and generally stable as far as both compound and actual properties. Exceptionally ionic nanoparticulate metal oxides, for example, CuO, might be especially significant antimicrobial specialists as they can be set up with amazingly high surface territories and abnormal gem morphologies.6 The points of this examination were to portray truly, what's more, synthetically nano CuO and to explore this compound concerning its expected antimicrobial applications.
Materials and Methods:
Material
All of the chemicals and reagents used in this experiment were bought from Sisco Research Laboratory in Chennai and were of analytical quality. Coriander leaves were cleaned well and dried in the shade. To make the plant broth solution, combine all of the ingredients in a large mixing bowl. 20 gm dried leaves of coriander was cut into small pieces and washed with distilled water. This was taken in a 250ml beaker with 100ml of distilled water and then boiled the mixture for 20 minutes at 80°C.
Synthesis of Cu nanoparticles using Coriander leaf extract:
10 ml of coriander leaf extract was added to 100ml 0f 1mM aqueous copper sulphate solution in a 250ml conical flask. Kept this flask at room temperature overnight and Cu nanoparticles were separated and settle at the bottom of this solution. The Cu nanoparticle thus obtained was purified by repeated centrifugation method at 5000 rpm for 15minute followed by redispersion of the pellet in deionized water. Then the Cu nanoparticles were dried in the oven at 80°C.
Physiochemical Characterization of CuNPs:
Spectroscopy in the UV-Visible Range
Visualization of peaks acquired from a UV-Vis spectral scan from 200 nm to 800 nm in a UV-Visible spectrophotometer was used to examine optical characteristics (Motras Scientific; UV Plus).
Infrared Spectroscopy using Fourier Transform
The sample was grounded with a KBr pellet and examined on a Perkin Elmer (Model: Spectrum Two) with a spectrum recorded in the 400–4000 cm1 band for the Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) study.
Diffraction of X-Rays
With Cu-K radiations (= 0.154 nm) in 2 ranges from 20o to 80o, an X-ray diffractometer (XRD, Model: Mini Flex II; Make: Rigaku) was used to assess the crystallite size, structure, and crystallinity of nanoparticles, followed by data analysis in PowderX software. According to the JCPDS (Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards) database and the International Centre for Diffraction Data, the mean size of nanocrystals for the particle was estimated from the diffraction peaks corresponding to the most intense reflections (ICCD).
TRANSMISSION ELECTRON MICROSCOPE
The size of the produced particles was determined by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) using a 200kV JEOL transmission electron microscope (JEOL Ltd.). The sample was prepared for TEM investigation by pouring 20 litres of CuO nanomaterial solution onto a Cu grid, drying it at room temperature, and then examining it under the microscope at various magnifications. CuONP Biological Screening.
In vitro Antimicrobial Activity of CuONPsagainst Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial Strains
According to CLSI (Clinical Laboratory Standard Institute) guidelines, the susceptibility of CuONPs to multidrug-resistant bacterial strains was tested using Kirby-disk Bauer's diffusion and agar well diffusion methods (2009). 24,25,26 The researchers utilised seven Gram-positive (Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus mutans, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus viridans, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Corynebacteriumxerosis, and Bacillus cereus) and four Gram-negative (Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumonia, Pseudomonas an Each strain was tested with around 50L of the test sample (concentration of CuONPs 1.25 mg/50L DMSO). Kept for 37 0C. DMSO was used as negative control while 50μL aqueous extract of Coriandrumsativum was used as positive control and 10μg Streptomycin disk for Gram-positive and 10μg Norfloxacin disk for Gram-negative strains were used as standard: positive control.
Antibacterial activity was assessed using a zone of inhibition (ZoI) measured after the incubation period against each tested micro-organisms.
Time–kill determination
To investigate possible antibacterial activity and thus minimise potential toxicity and resistance problems, mixtures of nanoparticles were also tested. CuO at sub-MBC concentrations was used in killing assays against the following strains: S. aureus strains – MRSA and S. aureusOxford (NCTC 6571); S. epidermidisSE-51; E. coli NCTC 9001; P. aeruginosaPAOI; and Proteus spp. All nanoparticles were prepared in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) with sonication as described above.
At time zero, ca. 5×107 CFU/mL of each microorganism was added to the nanoparticle suspension at a dilution of 1 in 80. Incubation was then carried out in a shaking incubator (200rpm at 37 ?C in air for up to 4 h). Inoculated nano particle-free suspensions in PBS were used as negative controls. Growth was assessed by plating serial dilutions of each nanoparticle/bacterial suspension at different time points onto tryptone soya agar plates. Plates were then incubated at 37 ?C in the air with CO2 for 24 h.
Statistical Analysis
The experiment was repeated three times, and the mean SEM (S.D) was compared to the standard and statistically analysed using graph-paid instant Dataset1.One way ANOVA.
RESULTS
The Coriander leaves were purchased from the Local vegetable market in Madurai, India. The extract was filtered through Whatman filter no. 1 and then was stored at 5°C and used within a week. The colour of the solution changes from blue to pale yellow and stirred the solution of coriander leaf extract and copper sulphate solution for homogeneous mixing. [figure: 1a,b,c,d,e]


The synthesized Cu nanoparticles were characterized by pH of the solution, UV-Visible, FTIR, and XRD.
pH of solution
the pH of the copper sulphate solution was 2.16, when we added coriander leaf extract to this solution, pH changes from 2.16 to 2.64. the pH of coriander leaf extract was 6.78. From this, we confirmed that the capping between Cu and coriander leaf extract was taken place.
UV-Visible
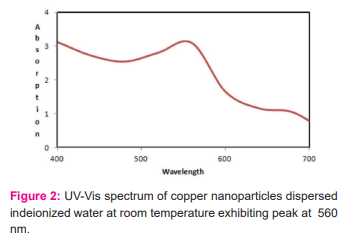
The reduction of copper sulphate to pure Cu nanoparticles was monitored by using an ultraviolet visible spectrophotometer. UV-Vis spectral analysis was done by using a double beam spectrophotometer 2203 Systronics range of 400-700. The absorption spectrum of pale yellow nanoparticle solution prepared with the proposed method showed a plasmon absorption band with a maximum of 560nm. [figure:2]
FTIR
FTIR spectra of biosynthesized copper nanoparticles were recorded to identify the capping
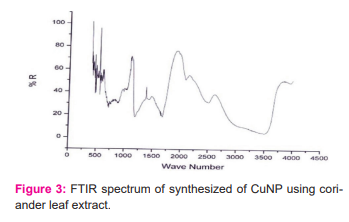
and efficient stabilization of the metal nanoparticles by biomolecules present in the coriander leaf extract. The FTIR spectrum of synthesized Cu nanoparticles using coriander leaf extract was shown in Figure 3. The band at 3500 cm-1 corresponds to the O-H stretching of alcohols and phenols.
The band at 1575 cm-1 corresponds to the N-H bend of primary amines. The peak at 1418 cm-1corresponds to C-Nstretching of the aromatic amino group. The band corresponds to 2670 cm-1 corresponds to the carbonyl group of flavonoids, phenolic acids etc. The band at 3225 cm-1corresponds to C-O linkages of phenol, acid, flavonoids. The band below 600 cm-1 corresponds to copper. Therefore, the synthesized copper nanoparticles were surrounded by proteins and metabolites such as phenolic acid, carboxylic acid, flavonoids. From the analysis of FTIR studies, we confirmed that phenolic compounds have the stronger ability to bind metal indicating that the phenols could form the metal nanoparticles to prevent agglomeration and thereby stabilized the medium. This suggests that the biological molecules could perform dual functions of formation and stabilization of Cu nanoparticles in the aqueous medium.
XRD
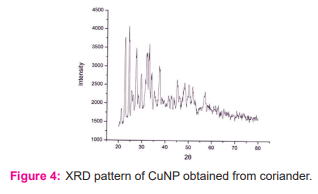
XRD pattern of synthesized Cu nanoparticles using Coriander leaf borth extract is shown in Figure 3. The sample demonstrated a high crystallinity level with diffraction angles of 22.74°, 27.55°, 29.63°, and 33.12° [figure: 4] which correspond to the characteristic of face-centered cubic of copper lines indexed at (1111), (2211), (2100) and (2200). The diffraction angle observed at 21.3° which is related to the Coriander leaf extract. The average size of the copper NPs was found to be 13.88nm. The size of copper nanoparticle was found in the range of 21.66nmto 41.65nm.
TEM analysis:
TEM analysis demonstrated that nano CuO particles exhibited an approximate equi-axes shape with no sharp edges observed (figure: 5). The particle size was determined to be in the range 22.4–94.8 nm.

Minimum bactericidal concentration and time-kill determinations
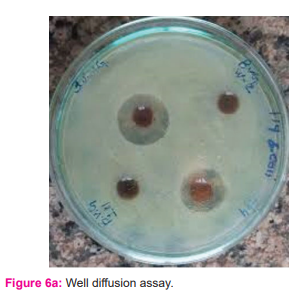
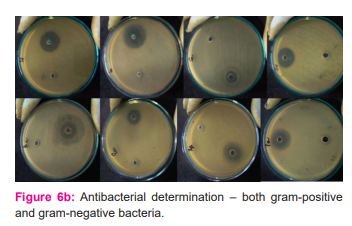
Using time-kill assays, populations of Gram-positive (×4 strains) and Gram-negative (×3 strains) organisms tested were reduced by 68% and 65%, respectively, in the presence of 1000µg/mL nano CuO within 2 h. This was increased to 88% (p<0.05; Student’s independent t-tests). Populations of P. aeruginosa, S. aureus(Oxford), MRSA-16 and S. epidermidis SE-51 were reduced to zero by 4 h in the presence of 1000µg/mL nano CuO. Except for MRSA-15, the addition of a sub-MBC concentration of nano Cu reduced all populations to zero by 4 h. (figure: 6a and 6b)
Discussion:
Identification of the exact essential arrangement, molecule size reach and surface morphology of nanoparticulate CuOis an essential to a full comprehension of its potential application abilities. TEM-EDS examination showed that the nuclear creation of the Cu and O components was 54.18% and 45.26%, separately. The mean proportion of Cu and O was subsequently 54.18:45.
Therefore, it is assessed that a large portion of the nanoparticulate test, produced by warm plasma innovation, was to be sure CuO. CuO nanoparticles were compelling in murdering a scope of bacterial microorganisms associated with medical clinic procured diseases. Higher convergences of nano CuO were needed to accomplish a bactericidal impact. It has been recommended that the decreased sum (somewhere in the range of 3-and 20-fold) of contrarily charged peptidoglycans would make Gram-negative microbes less vulnerable to such emphatically charged antimicrobials.7 This is upheld by the MBC discoveries with nano CuO in this examination for P. aeruginosa and Proteus spp. Notwithstanding, in the time-kill tries the Gram-negative strains tried indicated a more noteworthy vulnerability to nano CuO.
Studies to survey the capability of nano CuO implanted inside the scope of polymer materials have demonstrated a lower contact-murdering capacity in examination with discharge slaughtering capacity against MRSA strains (Allaker, Vargas-Reus and Ren, unpublished perceptions), which would recommend an arrival of particles into the nearby climate is needed for ideal antimicrobial action.
TEM is a helpful method to explore the adjustments in microscopic organisms upon openness to antimicrobials. TEM gives a direct representation of any morphological changes in the microbial cell .8 Studies utilizing TEM with 'aerogel'- produced nano copper oxide and Escherichia coli have demonstrated that the cell mass of this bacterium is widely harmed, permitting the substance to spill out and nanoparticles to acquire passage.9
In like manner, Cu nanoparticles have been appeared to join to the microbial cell surface and enter inside, where intracellular targets, including respiratory catalysts, are disturbed.10The exact instrument of activity of nano CuO is the subject of progressing examinations.
Conclusion:
Clinics and transport are two specific regions that offer chances for the utilization of nano particulate metals and metal oxides to forestall the spread of contamination. With the expansion in air travel and more prominent versatility all in all of the individuals, the airborne, vector-borne and zoonotic spread of irresistible specialists is a significant general medical problem. Inside the medical clinic climate, divider covers, gear, dress and bedding are altogether potential danger zones for the spread of disease. In this manner, as far as likely use, the joining of nanoparticulate metals and metal oxides, including nano CuO, into surfaces and different items could be visualized.
Acknowledgement: We thank the microbiology department of Saveetha medical college, Chennai.
Authors contribution: Keerthika and Iswarya made substantial contributions to conception, acquisition of data, took part in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content, Jayashree Lakshmi, Maripandian and Nivetha made FTIR, XRD, UV SPEC and TEM analysis [Graphical data] and final approval of the version to be published, and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work
Source of funding: None declared.
Conflict of interests: None declared.
Ethical approval: Not required.
References:
[1] Morones JR, Elechiguerra JL, Camacho A, Holt K, Kouri JB, The bactericidaleffect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology. 2005;16:2346–53.
[2] Sondi I, Salopek-Sondi B. Silver nanoparticles as an antimicrobial agent: a case study on E. coli as a model for gram-negative bacteria. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2004;275:177–82.
[3] Cioffi N, Torsi L, Ditaranto N, Tantillo G. Copper nanoparticle/polymer composites with antifungal and bacteriostatic properties. Chem Mater. 2005;17:5255–62.
[4] Li Z, Lee D, Sheng X, Cohen RE, Rubner MF. Two-level antibacterial coating with both release-killing and contact-killing capabilities. Langmuir. 2006;33:9820–3.
[5] Cava RJ. Structural chemistry and the local charge picture of copper oxide superconductors.
Science. 1990;247:656–62.
[6] Tranquada JM, Sternlieb BJ, Axe JD, Nakamura Y, Uchida S. Evidence for stripe correlations of spins and holes in copper oxide superconductors. Nature.1995;375:561.
[7] Kwak K, Kim C. Viscosity and thermal conductivity of copper oxide nanofluid dispersed in ethylene glycol. Korea–Australia Rheol J. 2005;17:35–40.
[8] Xu JF,JiW, Shen ZX, Tang SH, Ye XR, Jia DZ. Preparation and characterization of CuO nanocrystals. J Solid State Chem. 1999;147:516–19.
[9] Stoimenov PK, Klinger RL, Marchin GL, Klabunde KJ. Metal oxide nanoparticles as bactericidal agents. Langmuir. 2002;18:6679–86.
[10] Kawahara K, Tsuruda K, Morishita M, Uhida M. Antibacterial effect of silverzeoliteon oral bacteria under anaerobic conditions. Dent Mater. 2000;16:452–5.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License