IJCRR - 13(18), September, 2021
Pages: 79-86
Date of Publication: 26-Sep-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
The Micrometric Analysis of Zone Wise Proportion of Human Adrenal Glands in Hanging and Poison Death Autopsy Cases in Different Age Groups
Author: Manivannan K, Kafeel Hussain, Krishna Rao H.R, Sasikumar R, Rama Manohara Reddy D, Janaki Raman P
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Stress plays a vital role in alterations in the structure and function of suprarenal glands which may have related to suicidal behaviour. Suicide is the complex interaction of biological, psychological, socio-economic and environmental factors in India and all around the world. The adrenal glands are a pair of life-saving endocrine glands of the human body composed of two parts, the cortex and the medulla. The cortex consists of three zones which are zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata and zona reticularis. The secretions of these zones are corticosteroids which are responsible for sustaining life against stress and fear. Aims and Objectives: The present study aims to analyze the micrometric changes of zone wise proportion of suprarenal glands such as the zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, zona reticularis and medulla in hanging and poison death autopsy cases in different age groups. Methodology: Study Design: Analytical -observational Study. Study setting: The samples were collected from Post mortem centre at Sri Venkateswara hospital, Chittoor district and divided into three age groups as 20-30, 30-40, 40-50 years. A study was done at Peoples Education Society Institute of Medical Scienc�es and Research, Kuppam. Chittoor District. The thickness of zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, zona reticularis and medulla of the adrenal samples were measured with stage and ocular micrometre by calibration and results were compared between hanging(sudden death) and poison death(delayed death) autopsy cases. Sample Size: 186 adrenals from 93 cases (52 hanging and 41 poison cases). Sampling Technique: Simple random sampling Inclusion Criteria: Both genders of hanging and poison death autopsy cases, three age groups 20-30 years, 30-40 years and 40-50 years and time of autopsy in between 12-24 hours after death were included. Exclusion Criteria: The adrenal abnormalities, burns cases, chronic debilitating illness, Accident cases, decomposed autopsy cases, pregnant women, age group less than 20 and more than 50years, commence of autopsy less than 12 hrs and more than 24 hrs were excluded. Results: In the present study we found that the volume of zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, zona reticulars and medulla of right and left adrenal gland were significantly high in poison suicidal case in the age group of 41-50 years, when compared to other two groups. There was no significant difference in zona reticular and medullary volume of both right and left adrenal glands in the age group of 31-40 years. Measurement of zona glomerulosa in the age group 31-40 years right gland show significantly decreased in poison suicidal cases when compared to hanging case but left gland statistically not significant. Conclusion: The left and right adrenal gland volume of zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, zona reticular and medulla were significantly high in poison suicidal cases in the age group of 41-50 years and the measurement of zona glomerulosa in the age group 31-40 years right gland show significantly decreased in poison suicidal cases.
Keywords: Manivannan K, Assistant Professor, Department of Anatomy, PES Institute of Medical Sciences and Research, Kuppam Pin-517425, Chittoor District, Andhra Pradesh, India
Full Text:
Introduction
Suicide is the complex interaction of biological, psychological, socio-economic and environmental factors in India and all around the world. National Crime Records Bureau of India has reported official suicide rates based on police reports – estimated only 1,35,000 suicides in the year 2017 due to frustration, sudden emotional outbursts, unemployment, poverty, failure to cope with stress at times of unexpected circumstances.2 Worldwide, more than 9, 00, 000 deaths are annually reported of suicide, of which 20% are Indians. Suicide is one of the three leading causes of death among people aged 15–44 years in some countries and the second-leading cause of death among those aged 10–24 years; these figures do not include the suicide attempts, which are up to 20 times more than complete suicide.3
Stress is common in the people of the united states and one in ten, age 12 and more and one in four among women in their age 40 and 50 are using antidepressant drugs due to modern lifestyle, multitasking and overburden in their work.4,5 Suicide is a leading cause of death among teenagers and adults 15 to 49 years of age and is graded among the top thirteen causes of death for human individuals of all ages worldwide by the World Health Organization (WHO).6
Stress plays a vital role in alterations in the structure and function of suprarenal glands which may have been related to depression and suicidal behaviour. The human adrenal gland is composed of two parts, the cortex(87%) and the medulla(13%). Both parts differ from each other by structure, function and development. The cortex consists of three zones; Zona Glomerulosa (ZG-15%), Zona Fasiculata ZF-65%) and Zona Reticularis(ZR-7%).7-10 Adrenal glands are a pair of endocrine glands and target structure of Hypothalamo Pituitary Adrenal(HPA) axis and stress system. Depression, anxiety, nervousness and fear plays an important role in affecting the structure and function of the adrenal gland, which may have a connection with suicidal behaviour in depressed individuals.
The cortisol level is increased in blood circulation due to sudden fear and severe pain at the time of sudden death and failure of long loop negative feedback mechanism leads unable to balance the cortisol level by the HPA axis11&12 and leads changes takes place in dimensions and volumes of adrenal glands.
The effect of trauma through nociceptor pathways, afferents from Nucleus tractus solitaries(NTS), Emotion via the Limbic system and drive for circadian rhythm are initiatives for stimulation of the Hypothalamus to release Corticotrophin Releasing hormone(CRH), which passing through the hypothalamic hypophyseal portal circulation to stimulate the pituitary gland to secrete and release ACTH in turn which control and regulate the secretions from the adrenal cortex(only ZF and ZR) to release the glucocorticoids (Fig-3). The Zona glomerulosa is controlled by the renin-angiotensin -aldosterone mechanism. The adrenal medulla is sympathetic in origin, which regulates increased heart rate, cardiac output by secreting adrenalin and noradrenalin at the time of stress and fear.11
This study was carried out to find the Micrometric changes of human adrenal glands of hanging and poison death cases in different age groups within a limited period after death. This study will be useful for forensic surgeons, medical-legal fraternity, forensic pathologists and entire medical faculty to determine the alterations in suprarenal glands between hanging and poison death autopsy cases.
Aims/objectives
To analyze the micrometric changes in thickness and zone-wise proportion of adrenal glands in hanging and poison death autopsy cases in different age groups.
Materials
The analytical study was done in the department of Anatomy after approval from the institutional human ethical committee at PES Institute of medical sciences and research, kuppam(IHEC Number-021). A total of 186 suprarenal glands was collected from 93 cadavers aged 20 to 50 years and both genders belong to hanging (52) and poison(41) death cases with due consent from close blood relatives of the deceased when undergone postmortem examination at Sri Venkateswara hospital, Chittoor district, Andhra Pradesh in the years 2018 and 2019.
Inclusion Criteria: Both genders of hanging and poison death autopsy cases, three age groups 20-30 years, 30-40 years and 40-50 years and time of autopsy in between 12-24 hours after death were included.
Exclusion Criteria: The adrenal abnormalities, burns cases, chronic debilitating illness, Accident cases, decomposed autopsy cases, pregnant women, age group less than 20 and more than 50years, commence of autopsy less than 12 hrs and more than 24 hrs were excluded.
(Institutional Human Ethical Clearance Number-21)
Methods
The samples of adrenals were divided into three age groups as 20-30 yrs (43 cases), 30-40yrs (26cases) and 40-50yrs (24 cases). The specimens were stored at 10% formalin immediately after collection for the preservation of tissues and fixation up to 12 to 24 hours to prevent distortion, autolysis and to reduce the shrinkage. The dissection kit was used to clean the adipose tissue and fascia around the glands. The cut section was made at the level of the hilum of adrenal glands ( fig- 1) to maintain the uniformity then fixed again in 10 % formal saline up to 12-24 hours duration for infiltration of the tissue in formalin. The histological slides were prepared after the processing, embedding, sectioning, staining with haematoxylin and eosin stains.
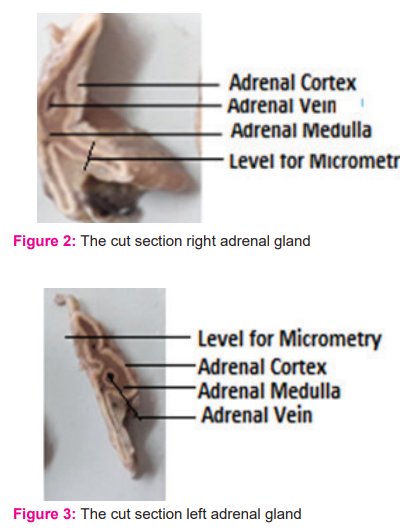
Micrometric Analysis
The term micrometry means the measurement of macroscopic objects. The standard unit of measurement of structures as accepted in the histological study is called a micron or micrometry.
The Micrometric changes in the thickness of Zona Glomerulosa(ZG), zona fasciculata (ZF), Zona Reticularis(ZR) and adrenal medulla were measured with the use of stage micrometre (SM) and ocular micrometre (OM) after preparing the histological slides.
Calibration under 4x objective
The thickness of zone wise adrenal cortex was measured (as in Fig-4) after calibration with stage and ocular micrometre under the 4 x objective. The scale in stage micrometre (SM) is 1 mm and divided into 100 units which are equal to 1000 micron
The scale in ocular Micrometer(OM) is divided into 100 equal units(Fig-4). The SM was placed in the stage of the microscope and the OM was placed in the diaphragm of the eyepiece. The units of SM overlapped by units of OM were counted under the 4 x objective. The 100 units of SM were equal to 40 units of OM in the count.12 The distance between the two units of OM was 25 micrometres in calculation by using the formula
40 ocular units =1000 micron
1 ocular unit = 25 micron.
The SM was removed from the stage and a measurable histological slide was placed. The thickness of each layer of the adrenal cortex was measured by OM (Fig-3), multiplied by 25 and divided by 1000 to convert into millimetres. All the 186 slides belong to hanging and suicidal cases were measured in the same method.13 ,14
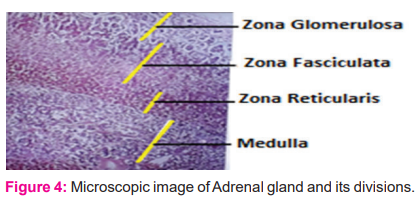
The thickness in mm was converted into percentage by calculating the thickness of the individual zone divided by the total thickness of the medulla and 3 zones of cortex multiplied by 100.
Statistical Analysis
The data was analysed by an Independent t-test using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) and Window version 21.0 software. Values of p <0.05 was considered to be significant.
Results
Data depicted in Table-1 represent the age and gender distribution of hanging and poisoning cases. Among the 93 cases, in the age of 20-30 years 29 were hanging (male-12 & female-17) and 14 were poison (male-5 & female-9) accounting for 46% total. In the age group 31-40 ,15 were hanging (male-12 & female-3) and 11 were poison (male-8 & female-3) accounting for 28% total. in the age of 41-50 years 8 were hanging (male-4 & female-4) and 16 were poison (male-11 & female-5) accounting for 26% total.

Table 2 shows, the measurements of right zonaglomerulosa (ZG) volume significantly reduced in poison suicidal cases when compared to hanging cases but no significant difference in left zonaglomerulosa (ZG) volume. The volume of zona fasciculate (ZF) and zonareticularis (Z) in both right and left glands significantly decreased in poison suicidal cases when compared to hanging cases. there is no significant difference in the right and left medulla in both cases.

The volume of ZG in the age group 20-30 years of right and left gland significantly reduced (P<0.001) in poison suicidal cases when compared to hanging cases. Measurement of ZG in the age group 31-40 years right gland shows significantly decreased (P<0.01) in poison suicidal cases when compared to hanging case but left gland statistically not significant. In the age group 41-50 years volume of ZG in both right and left gland was significantly high (right P<0.03 & left P<0.001) in poison suicidal cases when compared to hanging cases. (Table3)
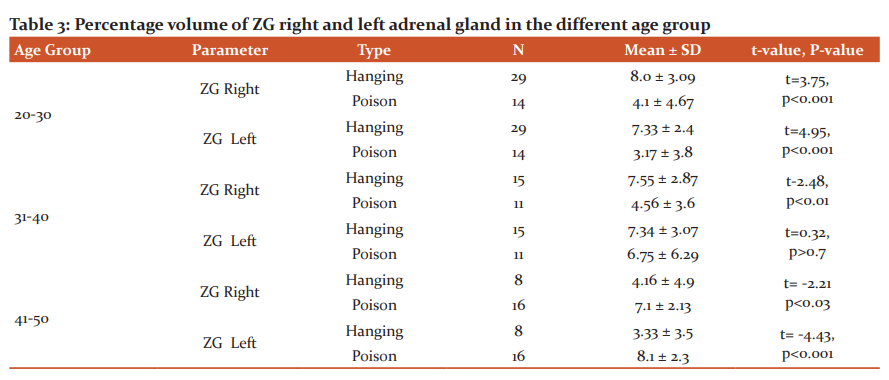
Table 4 shows, the measurement of ZF in the age group 20-30 years and 31-40 years of right and left gland significantly reduced in poison suicidal cases when compared to hanging cases. But in the age group 41-50 years volume of ZF in both right and left gland was significantly high (right P<0.001 & left P<0.02) in poison suicidal cases when compared to hanging cases.
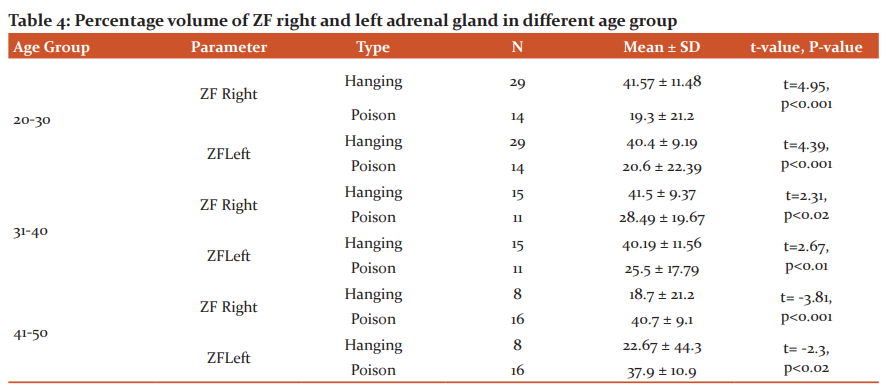
Table 5 shows, the volume of ZR in the age group 20-30 years of right and left gland significantly reduced in poison suicidal cases when compared to hanging cases. But in the age group 41-50 years volume of ZF in both right and left gland was significantly high (right P<0.005 & left P<0.01) in poison suicidal cases when compared to hanging cases. There was no significant difference in the 31-40 years age group.
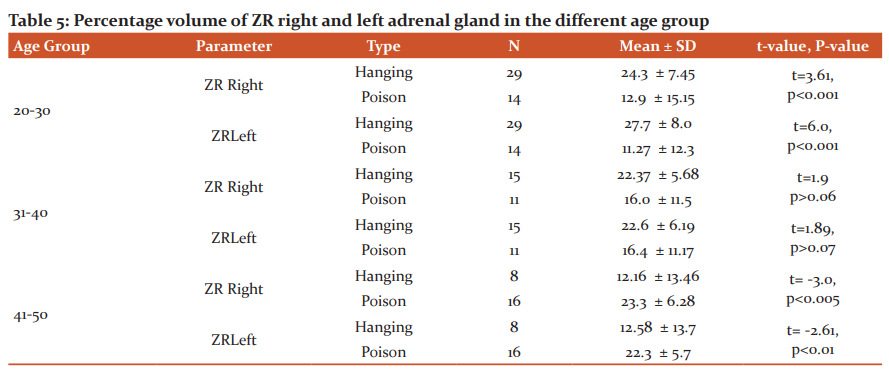
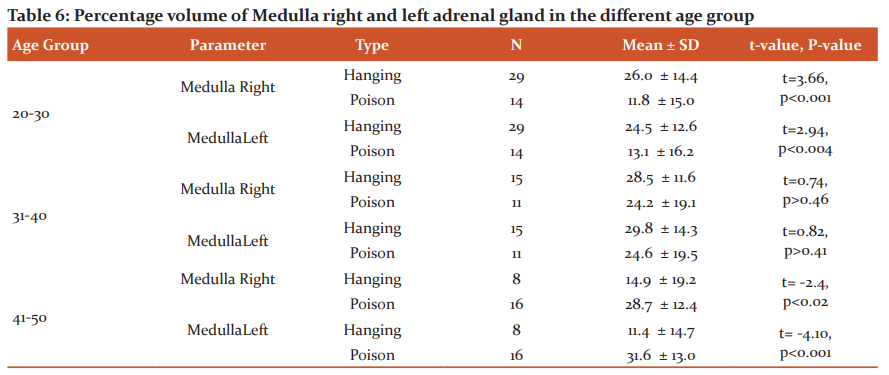
The percentage volume of the medulla in the age group 20-30 years of right and left gland significantly reduced in poison suicidal cases when compared to hanging cases. But in the age group 41-50 years measurement of the medulla in both right and left gland was significantly high (right P<0.02 & left P<0.001) in poison suicidal cases when compared to hanging cases. There was no significant difference in the age group of 31-40 years. (Table 6)
Discussion
In the present study, we found that the mean volume of ZG, ZF, ZR and medulla of the right adrenal gland is 7.93%, 40.93%, 23.76% and 27.35% respectively. The mean volume of ZG, ZF, ZR and medulla of the Left adrenal gland is 7.23%, 40.10%, 26.87% and 25.78% respectively in hanging cases. The mean volume of ZG, ZF, ZR and medulla of the right adrenal gland is 7.37%, 40.01%, 24.16% and 28.44% respectively. The mean volume of ZG, ZF, ZR and medulla of the Left adrenal gland are 7.88%,38.74%, 22.69% and 30.67% respectively in poison cases. The values of this study are slightly different from the values of standard anatomical textbooks due to the level of a section of glands at the hilum level.
In the present study, we found that the volume of ZG, ZF, ZR and medulla of right and left adrenal glands were significantly high in poison suicidal cases in the age group of 41-50 years when compared to the other two groups. There was no significant difference in ZR and medullary volume of both right and left adrenal glands in the age group of 31-40 years. Measurement of ZG in the age group 31-40 years of right gland shows significantly decreased volume in poison cases when compared to hanging cases but left gland statistically not significant. The ZF is significantly high in poison suicidal cases in the age group of 41-50 years when compared to the other two groups.
Fawcett16 suggested that zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata and zona reticularis consists of 15%, 78% and7% respectively of the total volume of the cortex in humans.
According to Maitra17, the outer zona glomerulosa is approximately 10-15%, zona fasciculata is about 80% and zona reticularis is about 5-10% of the total cortical volume. Barrett et al.15 reported that the zona glomerulosa makes up 15% of the mass of the adrenal gland; the zona fasciculata 50%; and the zonareticularis 7%. Hall16 stated that the zona glomerulosa constitutes about 15% of the adrenal cortex, the middle widest portion, zona fasciculata, is about 75% and zona reticularis, the deep layer is about 10% of the adrenal cortex.
According to Ross & Pawlina18, the outer zona glomerulosa constitutes 15%, while the middle zona fasciculata is 80%, and inner zona reticularis is only 5-7% of the total cortical volume. Mescher19 reported that the outer zona glomerulosa is about 15%, middle zona fasciculata is 65% and inner zona reticularis is 7% of the total thickness of the adrenal gland. Gartner & Hiatt20 mentioned that the outer zona glomerulosa constitutes about13%, zona fasciculata is approximately 80% and zona reticularis is 7% of the total cortical volume.
Deepti Gautam et al21 suggested in their study that epithelium of clusters in zona glomerulosa was retracted from the basement membrane and most of the nuclei were completely hyperchromatic while pyknotic and vesicular nuclei were hardly seen. In zona, fasciculata sinusoids were slightly dilated with prominent endothelial cells and some cells with edematous changes. In zona reticularis, sinusoids were slightly dilated and most of the nuclei were hyperchromatic at the periphery. Cell outline was not clear in some places of the medulla and most of the nuclei were completely hyperchromatic.
Sarkar et al22 in their study found similar results that the adrenal weight, width of zona fasciculata, total cortical width was significantly higher for the suicide group than the accidental group. The mean width of zona fasciculata of the adrenal gland on the right side for the suicide group was 0.74 mm. and in the control group was 0.57 mm. and, that of the adrenal gland on the left side for the suicide group was 0.77 mm. and in the control group was 0.61 mm. The mean and standard deviation of the width of zona fasciculata of right and left, adrenal glands were significantly higher for the suicide group than the accidental group. These results correlate findings of our study.
Conclusion
The mean volume of ZG, ZF, ZR of right and left adrenal glands were significantly high in hanging suicidal cases when compared to poison suicidal cases and vice versa there is the minimum difference when comparing the medulla of hanging and poison cases in overall estimation. The reason assumed was that failure of long loop negative feedback mechanism to HPA axis in hanging due to sudden death and positive feedback mechanism in poison due to delayed death. Further studies will be recommended with a limited age group and more samples.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
The ethical approval obtained from the institutional human ethical committee at PES institute of medical sciences and research and consent from blood relatives of deceased during the autopsies (Institutional Human Ethical Clearance Number-21)
Consent to publish: Applicable
Author’s contribution
Project development, data collection and management, data analysis and manuscript writing1 data analysis, manuscript editing and overall supervision2., Data analysis and manuscript editing3., Data analysis and manuscript editing4., Collection of samples, data analysis, manuscript editing5., Statistical analysis6. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Statement of Data Availability
Please contact the author for data (Manivannan- e-mail Address: maniroopaa@gmail.com)
Conflict of interest: No Conflict of interest
Acknowledgements:
"Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed."
Financial support:
This Research project did not receive any grants from any specific funding agency or third party.
References:
1. World Health Organization. Prevention of suicide: guidelines for the formulation and implementation of national strategies. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization, 1996.
2. National Crime Records Bureau. Accidental Deaths and Suicides in India. New Delhi: Government of India; 2008.
3.World Health Organization Report. Suicide prevention. ; 2009 accessed 13.08.19.
4.US Public Health Service. The Surgeon General’s call to action to prevent suicide. Washington, DC: US Public Health Service, 1999.
5. Laurie Mueller. The science of stress. The American chiropractor, Nov-2017;27.
www.The American Chiropractor.com
6. Meier RF, Clinard MB. Sociology of deviant behaviour. 14th ed. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Cengage Learning; 2008. p169.
7. Datta AK. Essentials of Human Anatomy: Thorax and Abdomen. 4th ed. Kolkata(India): Current Books International; 2005;147-49.
8. Susan standring. Gray‘s Anatomy-the Anatomical basis for clinical practice. 41st international ed. Elsevier Ltd; 2016;1194.
9. BD Chaurasia. Textbook of Human Anatomy: Volume (2) Lower limb, Abdomen and pelvis. 4th ed. Bengaluru(India): CBS Publishers and distributors; 2004;305.
10. T.S. Ranganathan. A Textbook of Human Anatomy. 6th ed. New Delhi(India): S.Chand & Company Ltd; 2006;343-6.
11. Guyton AC and Hall JE. The adrenocortical hormones In Textbook of medical physiology. 11th ed. New Delhi: Elsevier; 2006; 869-83.
12. Sembulingam K and PremaSembulingam. Essentials of Medical Physiology. 4th ed. New Delhi(India): Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers P(Ltd); 2006;393-408.
13. Singh D R. principles and techniques in histology microscopy and photomicrography. 1st ed. CBS publishers and distributers; 2003: p153.
14. Gilles bolduc. Calibration of the microscopic ocular micrometre. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HaqgCtA-ioI (Last cited on 2018 December 21)
15. Smita P, Rath S, Dutta BK. Morphological study of the adrenal gland in case of suicidal deaths. Indian J Applied Res 2015;5:333–7.
16. Fawcett DW. Bloom & Fawcett-a textbook of histology. 12th ed. New York: Chapman & Hall; 1994;503.
17. Maitra A. The endocrine system. Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease. 8th ed. New Delhi: Elsevier Saunders. 2010. p1148.
18. Ross MH, Pawlina W. Histology: a text and atlas with correlated cell and molecular biology. 6th ed. Baltimore: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2011. p762.
19. Mescher AL. Junqueira’s basic histology: text and atlas. 13th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2013. p414.
20. Gartner LP, Hiatt JL. Colour atlas and text of histology. 6th ed. Baltimore: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2014. p246.
21. Deepti G, Meena G, Bichitrananda R. Sequential Postmortem histological changes in human adrenal gland up to thirteen hours and thirty minutes post mortem interval. Int J Advanced Res .2015;3(7):1138-55.
22. Sarkar A, Chatterjee M, Batabyal S. A post mortem study on the weight and morphology of adrenal glands in victims of suicide. Int J Cur Res Rev. 2014; 6(1):21-27.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License