IJCRR - 13(18), September, 2021
Pages: 64-71
Date of Publication: 26-Sep-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Efficacy of Cervical Spine Manipulations in Patients Suffering from Migraine
Author: Punia S, Malik M, Singh V, Rastogi V, Kaur J
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Objective: Evaluate the effect of cervical spine manipulation therapy in patients suffering from migraine headaches. Methodology: It was a randomized control trial. Total 62 Subjects suffering from migraine headache and fulfilling the international classification of headache disorders-3 (International headache society) were included in the study. The trial started with 40 participants and in the experimental group, there were 20 participants, with mean age 31.10\?6.54 and 20 participants in the control group, with mean age 25.9\?4.19. Group A received cervical spine manipulation therapy (CSMT) and group B received sham manipulation, thrice per week for 2 weeks. The subjects were asked to fill headache impact test, headache disability index questionnaire, and VAS pre and post-intervention. Descriptive statistics were conducted by means and standard deviations for variables like age, gender, visual analogue scale (VAS), and headache impact test (HIT), and headache disability index (HDI). Paired t-test was used to compare the pre and post-treatment values of the groups for statistical significance. An independent t-test was used to compare both groups. Result: The findings obtained by comparing both groups were, VAS reduced significantly after 2 weeks (MD= -1.27; 95% CI -2.05 to -.48; p=0.002), HIT reduced significantly after 2 weeks (MD= -8.86; 95% CI -11.34 to -6.39; p< 0.001) and also significant reduction seen in HDI variables (MD= -8.48; 95% CI -0.01 to -12.08; p=.003). Conclusion: The study demonstrated that cervical spine manipulation therapy is an effective treatment and could significantly reduce the headache pain intensity in migraine sufferers. There was a statistically significant difference of different variables found between groups.
Keywords: Cervical spine manipulation therapy, Migraine, Manual therapy, Pain, Disability, Spinal manipulative therapy. Evalu�ate the effect of cervical spine manipulation therapy in patients suffering from migraine headaches.
Full Text:
Introduction
Migraine is a usual health problem that causes ensuing physical, psychological, social & financial loss.1 Recently, the global burden of disease survey gave rank to migraine as the 3rd most occurring condition worldwide and has a prevalence of 14.7%. It is thought to be the 2nd most incapacitating disease across the globe.2 Migraine impacts 959 million people across the globe, with the majority being women of childbearing age.3 Researchers have also established that it is the 2nd most usual and incurable primary headache with a prevalence of 11%-14.3% worldwide.4 Out of 69% of primary headaches, migraine affects 15% of the population. Between half and three-quarters of adults have suffered headaches in the past year, and over 10% of this group has suffered a migraine.1
Migraine occurs with a male: female ratio of 3:1.3 The international headache society reported that women are being more affected by migraines i.e. 2 to 4 times than men.5-6 Women of childbearing age are more commonly undergo migraines because of the large underlying hormonal influence.7 Factors such as stress, illness, emotions, or menstrual cycle trigger a severe migraine attack in females.8 Migraine is said to be the 7th leading cause of years lived with disability (YLDs) and is a usual neurological disorder.9
Migraine is usually moderate to severe headache; unilateral & throbbing in nature10 which is intensified by daily physical activity and more often it is accompanied with increased sensitivity to light and sound, nausea, and occasionally vomiting.1, 8, 9
Migraine is characterized by its hemicranial feature recurrence, presence of aura, and sensory symptoms.11 Migraine also affects the ability to perform activities of daily living as well as missed workdays.6, 12
Although Migraine headache is mainly connected with dysfunction of central pathways, many clinical findings are considered peripheral because peripheral nociceptive stimuli can cause the Migraine attack. Nuchal symptoms such as tenderness, stiffness, and weakness are reported by individuals suffering from Migraine.7, 13
About 12% of the world's adult population is affected by migraine as it is a prevalent disease. It is a burdensome disease that affects individuals, their families, and society14. Migraine is thought to be a common cause of public health and socio-economic burden across the globe.15 The ailment is known to be disabling, with more than half of people experiencing a disturbance in daily activities during some of the attacks of the migraine.4
Manual therapy (MT) is one of the most common physical therapy interventions for headache management, which is defined as treatments including 'spinal manipulation (as usually executed by chiropractors, osteopaths, and physical therapists), and spinal mobilization, therapeutic massage, and other manipulation and body-based techniques.11
The mechanism of action of spinal manipulative therapy (SMT) on migraine is not known. It is debated that migraine may arise from the complexity of nociceptive afferent responses associated with the upper cervical spine (C1-C3) leading to a hypersensitivity state of the trigeminal pathology expressing sensory information to the face and head.1
The present randomized controlled trial (RCT) was designed based on previous supporting studies assessing the effect of cervical spine manipulation therapy in the patient suffering from migraine headache. By examining VAS, HIT-6, and HDI assessment scores respectively, therefore study hypothesized that the effectiveness of cervical spine manipulation therapy (CSMT) with superior to that of sham manipulation and pharmacological management for improving the pain and disability caused by a migraine headache.
Materials and Methods:
The study was a randomized controlled trial with two parallel groups assessing the efficacy of cervical spine manipulation in the management of migraines. This randomized controlled study was conducted in Hisar, an urban area of Haryana. Total 62 Subjects suffering from migraine headache and fulfilling the international classification of headache disorders-3 (International headache society) were included in the study. Eligible participants were patients suffering from migraines of age 18-65 years with at least one migraine attack per month and were allowed to have a concomitant tension-type headache but no other primary headache. The participants were diagnosed according to the international classification of headache disorders-3 beta version (ICHD-3) of the International headache society.
The participants were excluded if patients having headaches occurred due to spinal radiculopathy, a congenital deformity of the vertebral column, degenerative diseases, recent surgery or fracture of the cervical spine, depression, and patients also excluded if they were un-cooperative patients, osteoporotic, had pregnancy and CSMT within 6 months of intervention.
A total of 62 patients suffering from migraines were approached. Out of which 40 met the inclusion criteria and enrolled in the study as shown in figure 1. The 40 subjects who met all the inclusion criteria were randomly allocated into two groups [cervical spine manipulation therapy (CSMT) and non-CSMT], with 20 patients in each group. A computer-generated random number table was used to allocate the participants in the experimental and control group.
This present trial was approved by GJUS & T (Guru Jambheshwar University of Science & Technology) research ethical committee vide letter no PTY/2019/1014. Each participant of the study gave informed consent after an explanation of the procedure in their local language. This trial has also registered under CTRI (Clinical trial registry-India) via reference number 2019/12/022414.
The participants of group A received CSMT thrice per week for two weeks. CSMT is defined as a passive high-velocity low amplitude thrust applied to a joint complex within its anatomical limits with the intent to restore optimal motion, function, and/or to reduce pain. The use of manipulation of the spine is to treat patients with pain involves a high-velocity thrust that is exerted through either a long or short lever arm.
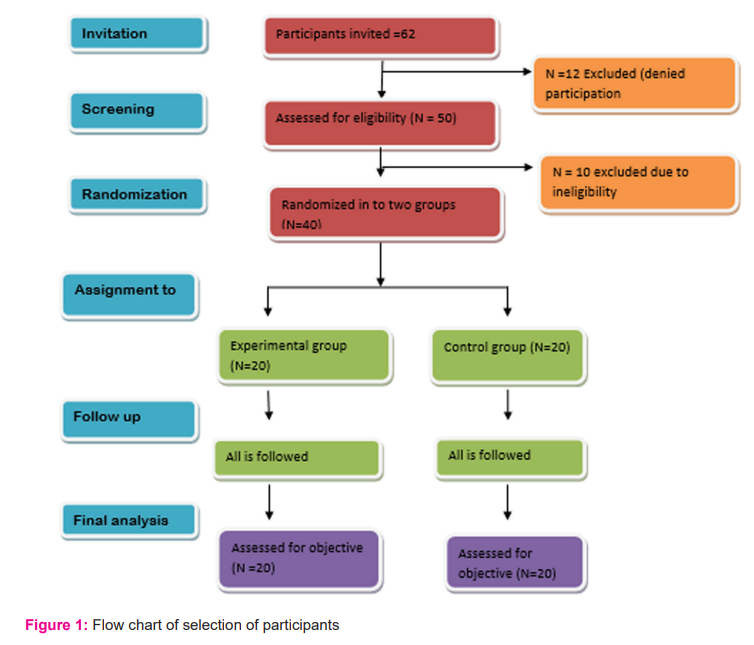
40 participants suffering from migraine headache and fulfilling the international classification of headache disorders-3 (International headache society) were included in the study. The subjects were randomly allocated into 2 groups i.e. group A (experimental group) and group B (control group). The subjects were asked to fill headache impact test (HIT), headache disability index (HDI) questionnaire, and VAS before the start of the intervention. The subjects were also asked to keep a headache diary in which they noted down the details of migraine headaches (i.e frequency, duration, and intensity of pain) experienced by them. Baseline reading of all outcomes measures was noted before the start of the intervention.
The long lever technique moves many vertebral articulations simultaneously whereas the short lever technique involves a low amplitude thrust that is directed at a specific level of the vertebral column. The patient lies in the supine position and the thrust is applied in a short lever arm to restore the mal-alignment of the cervical spine which is thought to be the culprit causing the headache.
The participants of group B received a placebo effect i.e sham manipulation and continue their pharmacological drugs for 2 weeks. Sham manipulation is termed as a broad non-specific contact low velocity, low amplitude sham pushover manoeuvre in a non-intention and non-therapeutic direction line of the lateral edge of the scapula or the gluteal region.
The subject was in a sitting or side-lying position. Lateral push manoeuvre to the lateral edge of the scapula is done for both sides. In the side-lying position, the patient's with the bottom leg straight and the top leg flexed with the top leg ankle resting on the bottom leg's flexed knee and a pushover manoeuvre was delivered in the gluteal region.
Utilizing an established and reliable pain measuring tool is a cornerstone for achieving a sufficiently precise assessment.VAS is a powerful research tool in the field of pain research due to its practicability, reproducibility, sensitivity to treatment effects, and ease of analysis. We used VAS to quantify the pain from baseline to after intervention and later analyzed it for statistical significance.
The HIT-6 questionnaire is a simple, easy-to-administer assessment that can be used as a clinical evaluation of the impact of headaches on a patient's quality of life. We used HIT-6 to measure the intensity and frequency of headaches caused to the sufferers, from baseline and post-intervention. Later the values are statistically analyzed.
The HDI questionnaire is useful in assessing the impact of headache, and its treatment on daily living. We used HDI to assess the disability caused by migraine headaches from baseline to post-intervention.
Statistical Methods
Data were analyzed using the SPSS software (version 21). Descriptive statistics were conducted by means and standard deviations for variables like age, gender, VAS, HIT-6, and HDI. Normality was checked done for all the variables using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Significance was set at a p-value of >0.05. Paired t-test was used to compare the pre and post-treatment values of the groups for statistical significance. An independent t-test was used to compare both groups.
Results
All patients in a different group of this trial had done almost all exercise sessions. The trial started with 40 participants and in the experimental group, there were 20 participants, with a mean age of 31.10±6.54 years and 20 participants in the control group, with a mean age of 25.9±4.19 years. All participants had given their outcome reading (100% Compliance rate). 16 males and 23 females were included in the study. There were 20 participants (Males: 6; Females: 13) in the experimental group and 20 (Males: 10; Females: 10) in the control group as shown in table 1. The outcome measures i.e VAS, HIT-6, and HI were analyzed pre and post-treatment.
Females showed a more significant reduction in post value of VAS, HIT, and HDI than males in both groups.
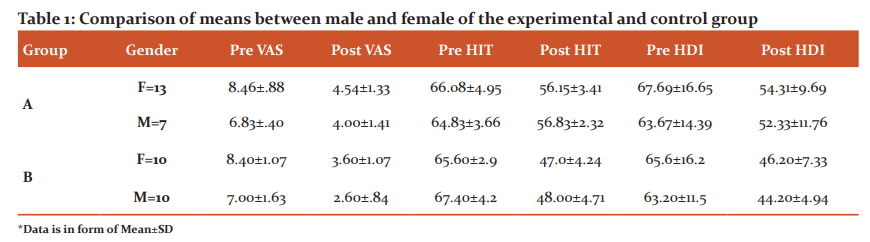
Effect of experimental group exercise on VAS, HIT AND HDI
Paired t-test was used to determine the effectiveness of CSMT and pharmacological treatment on VAS, HIT-6, and HDI variables after 2 weeks. As shown in table 2 & figure 2, a statistically significant difference was found in all outcome variables. VAS reduced significantly after 2 weeks (MD= -4.6; 95% CI -4.16 to -5.04; p<0.001), HIT reduced significantly after 2 weeks (MD= -19.00; 95% CI -16.49 to -21.50; p<0.001) and also significant reduction seen in HDI variables (MD= -19.20; 95% CI -14.11 to -24.28; p<0.001).
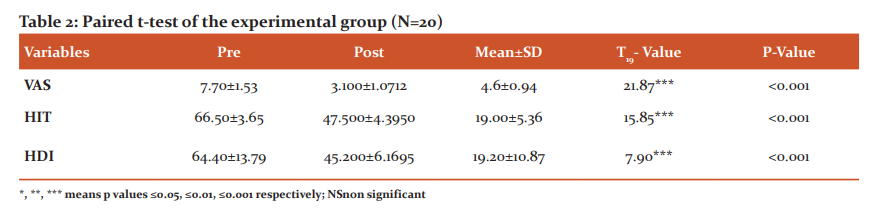 Effect of control group exercise on VAS, HIT and HDI
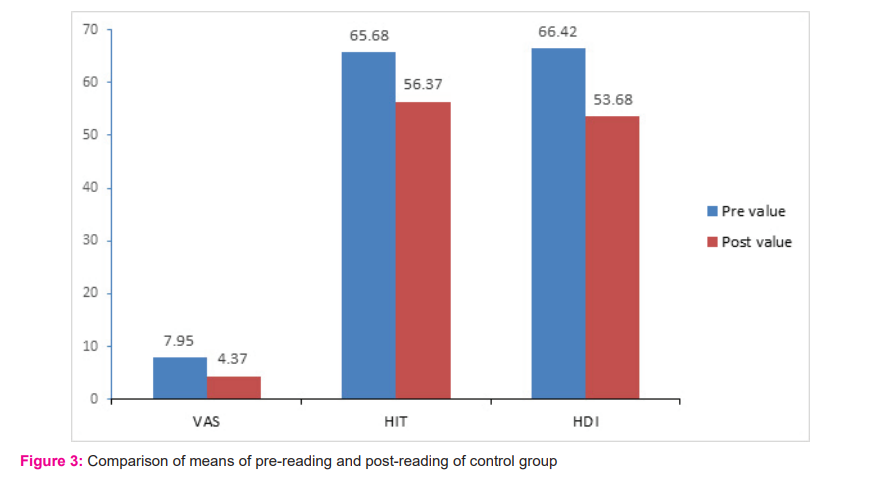
Effect of control group exercise on VAS, HIT and HDI
Paired t-test was used to determine the effectiveness of sham manipulation and pharmacological treatment on VAS, HIT, and HDI variables after 2 weeks. As shown in table 3 & figure 3, a statistically significant difference was found in all outcome variables. VAS reduced significantly after 2 weeks (MD= -3.58; 95% CI -2.99 to -4.16; p<0.001), HIT-6 reduced significantly after 2 weeks (MD= -9.32; 95% CI -7.39 to -8.42; p<0.001) and also significant reduction seen in HDI variables (MD= -12.74; 95% CI -8.42 to -17.05; p<0.001).
Comparison of outcome variables between both groups
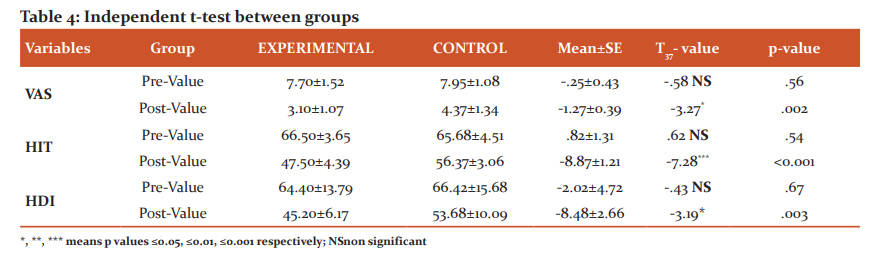
All three variables were non-significant at the start of the intervention. Post interventions reading of primary variables after the intervention were compared between the two groups using an independent t-test. The outcome measure shows a significant reduction in all three variables in as shown in table 4.
When we compared both group, VAS reduced significantly 2 weeks (MD= -1.27; 95% CI -2.05 to -.48; p=0.002), HIT reduced significantly 2 weeks (MD= -8.86; 95% CI -11.34 to -6.39; p<0.001) and also significant reduction seen in HDI variables (MD= -8.48; 95% CI -0.01 to -12.08; p=.003).
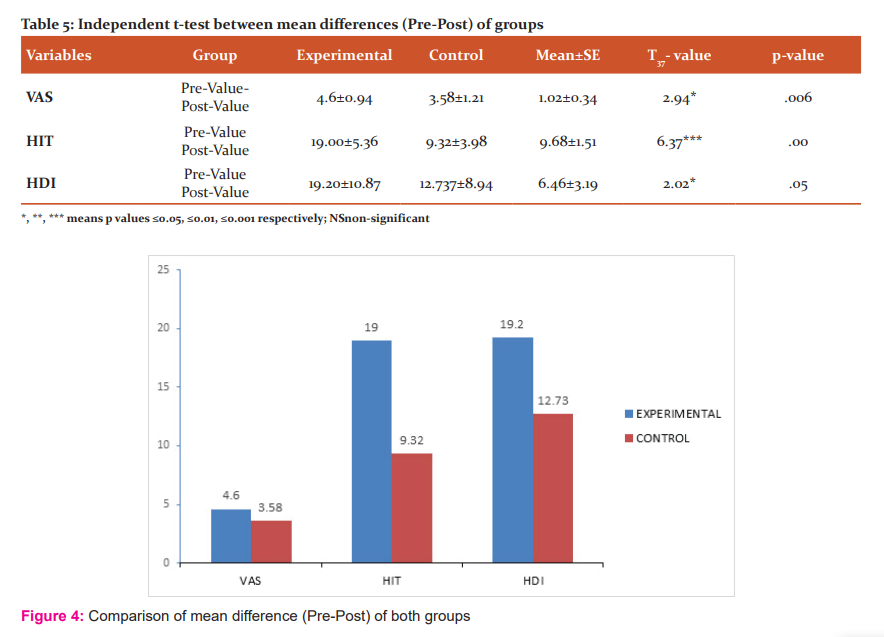
When we compared mean difference of all outcome variables of both group, VAS reduced significantly after 2 weeks (MD= 1.02; 95% CI .32 to 1.72; t37=2.94; p=0.006), HIT-6 reduced significantly after 2 weeks (MD= 9.68; 95% CI 6.60 to 12.76; t37=6.37; p<0.001) and also significant reduction seen in HDI variables after 2 weeks (MD= 6.46; 95% CI -.014 to 12.94; t37=2.02; p=.05) as shown in table 5 & figure 4.
Discussion
Migraine headaches are common nowadays and the pain associated with them is incapacitating and causes major concern to many patients. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of cervical spine manipulation in the treatment of migraine over sham manipulation. The patients were grouped under the experimental group who received CSMT and the control group who underwent sham manipulation and resumed their consumption of pharmacological medication. The intervention was given thrice per week for 2 weeks. The present study result supports our hypothesis that CSMT is more effective in migraines. The findings obtained by comparing both groups were, VAS reduced significantly after 2 weeks (MD= -1.27; 95% CI -2.05 to -.48; p=0.002), HIT reduced significantly after 2 weeks (MD= -8.86; 95% CI -11.34 to -6.39; p<0.001) and also significant reduction seen in HDI variables (MD= -8.48; 95% CI -0.01 to -12.08; p=.003).There was a statistically significant difference of different variables found between groups. The post values of VAS, HIT-6, and HDI were decreased significantly in the experimental group when compared with the control group.
Some patients do not tolerate medicine because of the adverse effects caused by them or due to the co-morbidity of another disease. Hence, these patients can be treated with CSMT5. The earlier proofs of the patient disappointment with prophylactic headache medicinal management suggested that it should be a crucial predictor for the headache patient to visit manual therapy providers.16 The drug treatment used to eliminate migraine headaches accounts for a huge part of the medical cost, hence the implementation of medication-free physiotherapeutic modalities might reduce the cost of treatment of migraine headaches.16 The utilization of massage therapy already has been evaluated with some potential results as the preventive treatment for headaches occur due to migraine. Various clinical trials show that spinal manipulation therapy might be helpful in the management of migraine cephalgia.16
Migraine is a substantial community health issue and there is a strong interest among both patients and healthcare providers to use non-pharmaceutical treatment options to cure migraine.10
There have been several studies demonstrating significant improvements in headaches or migraines after chiropractic SMT. Stress is the major factor for migraines reported by the high percentage of participants (>80%). Thus, present study findings appear to support previous results indicating that some people report significant improvement in migraines after chiropractic SMT. The average response of the treatment group (N=83) showed statistically significant improvement in migraine frequency (p<0.005) duration (p<0.01) disability (p<0.001) when compared to the control group17. In another study proposed by Chaibi et al., 2017 presented the findings that the patients assigned to CSMT had depletion from threshold to after treatment in migraine duration (p=0.003), intensity (p=0.002), headache index (p<0.001), as did patients assigned to the sham procedure. These effects continued at all three follow-up time points. However, at 12 months follow-up patients assigned to CSMT had a significant reduction in consumption of paracetamol correlated with placebo (p=0.04) and the control groups (p=0.03). Overall adverse events were few, mild, and transient. The findings of the study suggest that cervical spine manipulation therapy is more effective in the treatment of migraine than sham manipulation.
Conclusion
Cervical spine manipulations followed by postural correction exercises are effective in decreasing headache pain and disability associated with migraines. Future researches can be performed to investigate the possible physiological mechanism resulting in improvement in migraineurs after correction of cervical spine misalignment through manipulation followed by postural correction exercises.
Acknowledgement
The authors acknowledged the patients who participated in the study. The authors are also grateful to the institution from where we collected our data and authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals, and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Conflict of interest
None is declared.
Financial support
The study did not get any financial support.
Authors Contribution
All the authors contributed to every segment of the manuscript like content, collection of data, writing, and analysis of data, and formatting of data.
Punia S: Conceptualization; Formal analysis; Investigation; Methodology; Project administration; Resources; Software; Supervision; Validation; Visualization; Writing - review & editing.
Malik M: Conceptualization; Data collection; Formal analysis; Investigation; Methodology; Project administration; Resources; Software; Supervision; Validation; Visualization; Roles/Writing - original draft.
Singh V: Conceptualization; Data collection; Formal analysis; Investigation; Methodology; Project administration; Resources; Software; Supervision; Validation; Visualization; Roles/Writing - original draft
Rastogi V: Conceptualization; Data collection; Formal analysis; Investigation; Methodology; Roles/Writing - original draft; Writing - review & editing.
Kaur J: Conceptualization; Data collection; Formal analysis; Investigation; Methodology; Roles/Writing - original draft; Writing - review & editing.
References:
-
Chaibi A, Šaltyt Benth J, Tuchin PJ, Russel MB. Chiropractic spinal manipulative therapy for migraine: a study protocol of a single-blinded placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial. Eur J Neurol. 2015;5(11):e008095.
-
Viana M, Khaliq F, Zecca C, et al. Poor patient awareness and frequent misdiagnosis of migraine: findings from a large transcontinental cohort. Eur J Neurol. 2019; 27(3): 536-541.
-
Afridi SK. Migraine: navigating the hormonal minefield. Pract Neurol. 2020;20(2):115-121.
-
Harris S, Rasyid A. Objective diagnosis of migraine without aura with migraine vascular index: A novel formula to assess vasomotor reactivity. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2020;46(6):1359-1364.
-
Chaibi A, ŠaltytBenth J, Tuchin PJ, Russel MB. Chiropractic spinal manipulative therapy for migraine: a three-armed, single-blinded, placebo randomized controlled trial. Eur J Neurol. 2017;24(1):143–153.
-
Hubbard TA, Kane JD. Chiropractic management of essential tremor and migraine: A case report. J Chiropr Med. 2012;11(2):121-126.
-
Espi´-Lopez GV, Ruescas-Nicolau MA, Nova-Redondo C, Benitez-Martinez JC, Dugailly PM, Falla D. Effect of Soft Tissue Techniques on Headache Impact, Disability, and Quality of Life in Migraine Sufferers: A Pilot Study. J Altern Complement Med. 2018;24(11):1099-1107.
-
Voigt K, Liebnitzky J, Burmeister U, Sihvonen-Riemenschneider H, Beck M, Voigt R et al. Efficacy of Osteopathic Manipulative Treatment of Female Patients with Migraine: Results of a Randomized Controlled Trial. J Altern Complement Med. 2001;17:225–230.
-
Davidson I, Crooks K, Newington L, Pilling M, Todd C. Assessing the feasibility of mobilisation of C0-C3 cervical segment to reduce headache in migraineurs. Int J Ther Rehab. 2018;25:8.
-
Wayne PM, Bernstein C, Kowalski M, Connor JP, Osypiuk K, Long CR, et al. The Integrative Migraine Pain Alleviation through Chiropractic Therapy (IMPACT) trial: Study rationale, design and intervention validation. Contemp Clin Trials Commun. 2020 Mar 1;17:100531.
-
Moore C, Adams J, Leaver A, Lauche R, Sibbritt D. The treatment of migraine patients within chiropractic: analysis of a nationally representative survey of 1869 chiropractors. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017;17(1):519.
-
Rist PM, Hernandez A, Bernstein C, Kowalski M, Osypiuk K, Vining R, et al. The impact of spinal manipulation on migraine pain and disability: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Headach. 2019;59(4):532-542.
-
Ferracini GN, Dach F, Chaves TC, Pinheiro FC, Grossi DB, Fernandez-de-las-penas C, et al. Cervico-occipital Posture in Women With Migraine: A Case-Control Study. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2016;46(4):251-257.
-
Bevilaqua-Grossi D, Carvalho GF, Dach F, Bigal ME. Additional Effects of a Physical Therapy Protocol on Headache Frequency, Pressure Pain Threshold, and Improvement Perception in Patients with Migraine and Associated Neck Pain: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2016;97(6):866-874.
-
Woldeamanuel YW, Cowan RP. Migraine affects 1 in 10 people worldwide featuring recent rise: a systematic review and meta-analysis of community-based studies involving 6 million participants. J Neurol Sci. 2017;372:307-315.
-
Moore C, Leaver A, Sibbritt D, Adams J. The management of common recurrent headaches by chiropractors: a descriptive analysis of a nationally representative survey. BMC Neurol. 2018;18(1):171.
-
Tuchin PJ, Pollard H, Bonello R. A randomized controlled trial of chiropractic spinal manipulative therapy for migraine. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2003;23(2):91-95.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License