IJCRR - 13(18), September, 2021
Pages: 52-58
Date of Publication: 26-Sep-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A Study on Perceived Sources of Stress among Final Year Dental Students During the Covid 19 Pandemic - A Questionnaire Based Survey
Author: Nanda Madhurima, Bagga Dinesh Kumar, Tiwari Sakshi, Singh Aartika, Shahi Prashant Kumar
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: The dental profession can be highly demanding and stressful as practising dentistry requires the acquisition of certain academic, clinical and interpersonal skills. Due to the current situation of the COVID 19 pandemic in the country, dental students especially in the final year are highly susceptible to increased stress and anxiety due to the added factors during these times. The purpose of this survey was to identify the stressors among final year dental students so that various methods can be advocated to minimize the stress level among students. Methods: A cross-sectional study using an online questionnaire was conducted among final year dental undergraduate students of North India. A link was created and distributed to the students. A total of 163 students participated in the survey out of which 161 students responded to all questions. Results: Responses were collated, and average percentages were calculated. The main stressors among students were, the mode of examination (95.7%), insufficient exposure to clinical work (92.5%), lack of preclinical and clinical skills(85.1%), compromised clinical learning (88.8%). 91.9% of students were also stressed about spreading the disease to their family or closed oneswhereas85.1%studentswerestresseddue to the uncertainty regarding their career. Conclusion: The results of our study indicated that the Covid-19 pandemic has significantly impacted dental education resulting in enormous stress among dental students. This study can provide an insight to the faculty and dental schools regarding the problems faced by students and can help in strengthening the current educational system.
Keywords: Covid 19, Pandemic, Stress, Online learning, Clinical skills, Dental students
Full Text:
Introduction
Coronavirus is a highly infectious disease caused by severe acute respiratory distress syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first case of Coronavirus was reported in Wuhan China in December 2019. Since its first case in China, it has now spread to almost every country. World health organization declared it as a “pandemic” on 11th March 2020.1 To curb the spread of Coronavirus, most governments around the world have taken preventive measures such as social distancing and self -isolation leading to closures of all educational institutions like schools, colleges, and universities.
The first case of Coronavirus in India was reported in Kerala on 30th January 2020. The government of India announced its first lockdown on 24h March 2020 as a preventive measure to control the spread of the pandemic. This led to the closure of all educational institutions. The 1st lockdown was announced for 21 days and then it was further extended till 31st May in 4 phases after which the restrictions started to ease in a phased manner.2 However, the educational institutions continued to remain closed resulting in changes in the teaching-learning methods from conventional classroom teaching to online teaching. This also resulted in a halt in the clinical and hands-on training experienced by the dental students
Globally, an increased level of stress is seen among the students pursuing professional courses, especially the medical and dental students.3,4,5 The dental profession can be highly demanding and stressful as practising dentistry requires the acquisition of certain academic, clinical and interpersonal skills. Studies conducted previously have shown increased stress and anxiety levels in dental students especially the final year students.5-9The frequently encountered stressors include factors relating to the fear of failure in examinations, poor grades, not being able to meet the academic and clinical requirements, frequent assignments and examinations, interactions with faculty and support staff, family pressures, personal relationships and financial burdens.7-12These stressors are consistent with most dental students globally. Different factors can affect an individual in different ways but chronic stressors can cause increased anxiety and depression which can further lead to poor academic performance amongst students.
It is also evident from the previous studies that stress levels among the students usually increases as they progress from their initial years of graduation to the final year of studies.6-9In India, the bachelor of dental surgery course is of 4 years duration followed by one year of rotatory internship. The basic sciences and the preclinical courses are taught in the first two years whereas the 3rd and 4th years are mainly focused on clinical education. At the end of the final year, the student has to undergo examinations in 8 subjects and due to the increased academic and clinical load, it is considered to be the toughest year.
Since the start of the pandemic, studies have also been carried out in various parts of the world to assess the impact of Covid -19 on dental education.13-19 The authors have not come across any study identifying the sources of stress among the dental undergraduates during the Covid-19 pandemic in North Indian students. The purpose of this study, therefore, is to identify the perceived sources of stress among final year dental undergraduate students during the COVID 19 pandemic.
Materials & Methods:
Study design: A cross sectional study was conducted among final year dental undergraduate students of North India.
Study Sample: An online survey was conducted using google forms. A Questionnaire was made using google forms and a link was created and distributed to final year dental undergraduate students studying in various government and private colleges in North India. The link was shared via Whatsapp.
Ethical Considerations: The participation was voluntary. Informed consent was obtained and only those students who agreed to participate were included in the study. A total of 163 students participated in the survey out of which 161 students responded to all questions.
Questionnaire
A detailed structured questionnaire was created using google forms consisting of 3 sections. The first section introduced the research to the participants and collected the informed consent of the participants. The forms were created so that only the participants who gave informed consent could participate in the study. The second section collected the demographic and academic details of the participants including gender, age, year of study, name and type of the institution. The third section comprised of a modified DES (Dental Environmental stress)4with 20 items under 4 different headings including Mode of Teaching, Academics and Performance Pressure, Preclinical and Lab work and Professional training. A 3 point Likert scale (agree, neutral, disagree) was used to assess the responses. At the end, there was an open-ended question where students were asked to specify the reasons for stress during this period other than mentioned in the questions.
Results
Responses were collated, and average percentages were calculated.
Demographic details: Out of the 163 total respondents, 98.8% (161) who gave informed consent were included in the study.Out of the 161 respondents, 78.9%(n=124) were females and 21.1% (n=34) were males.The mean age of the students was 22.72 years with a range from18-29 years.85.7% (n=135)students were studying in private institutions whereas 14.3% (n=23) were in government institutions.
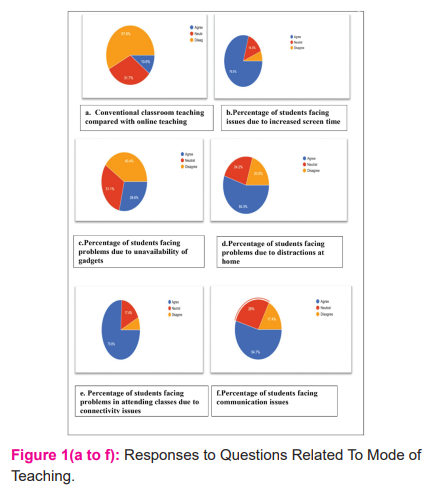
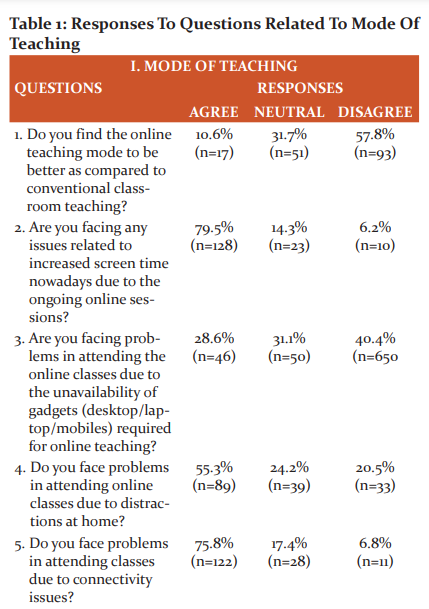
Mode of Teaching (Figure1, Table 1)
When asked about the mode of teaching, 57.8% (n=93) of the students found conventional classroom teaching better as compared to the online teaching mode (Figure1a). Issues with increased screen time were faced by 79.5%(n=128) of the students (Figure 1b ). 28.6% (46) students faced problems due to the unavailability of gadgets(Figure 1c). Almost half of the students (55.3%;n=89) faced problems in attending classes due to distractions at home (Figure1d ).75.8% (n=122) students faced problems due to connectivity issues (Figure 1e). 54.7%(n=88) students felt that there is a lack of two-way communication in the online mode (Figure1f).
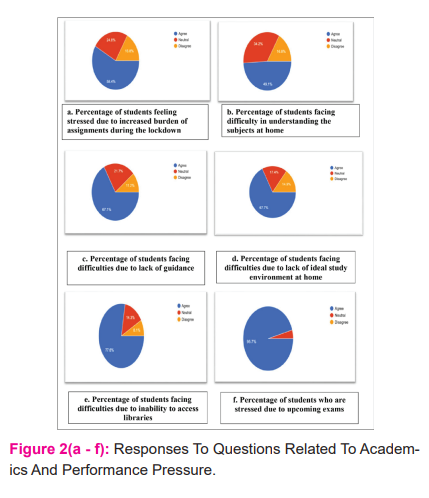
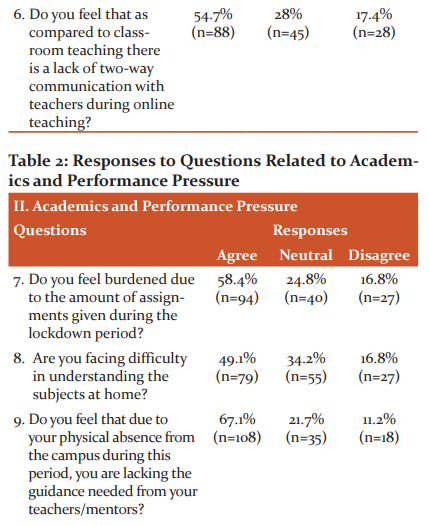
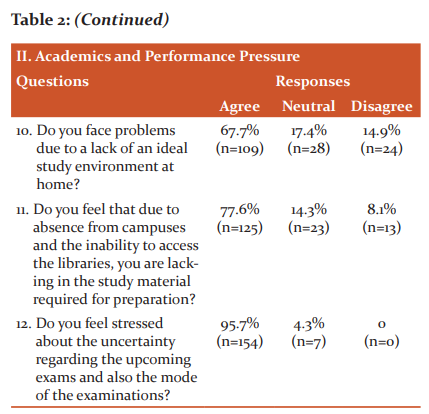
Academics and Performance Pressure(Figure2, Table 2)
58.4% felt the increased burden of assignments during this period(n =94) (Figure 2a), whereas 49.1% (n=79)faced difficulty in understanding the subjects at home (Figure 2b).67.1% (n=108) students felt that due to the lockdown,they are lacking the guidance required from teachers and mentors(Figure 2c).
67.7% (n=109) students faced problems due to a lack of an ideal study environment at home (Figure 2d). 77.6% (n=125 ) students felt that due to absence from campuses and inability to access the libraries, they lacked the study material for preparation (Figure 2e). Another important stressor was uncertainty regarding the mode of exams which was felt by 95.7% (n=154)of the students(Figure 2f).
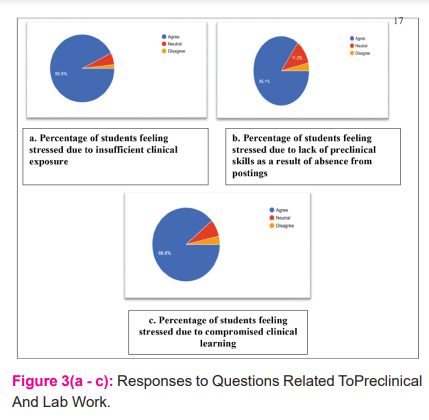
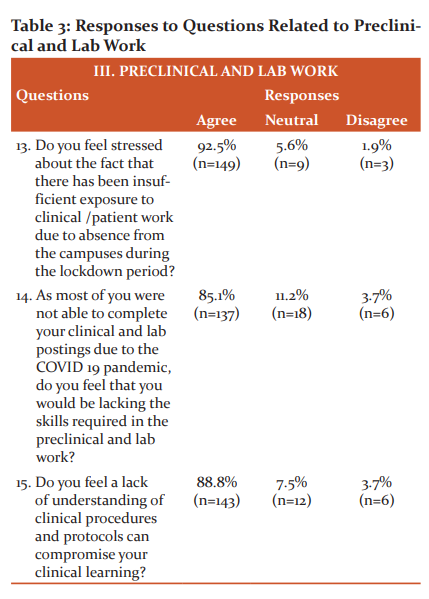
Pre -Clinical and Lab work(Figure3, Table 3)
Out of 161 respondents,92.5% (n=154) students felt that there has been insufficient exposure to clinical/patient work due to absence from the campuses during the lockdown period (Figure 3a). Also, 85.1% (n=137) students felt that they would be lacking the skills required in the preclinical and clinical work as they were unable to complete their clinical and lab postings due to the Covid 19(Figure 3b). 88.8% ( n=143) of the respondents felt that due to the lack of understanding of clinical procedures and protocols, their clinical learning would be compromised (Figure 3c).
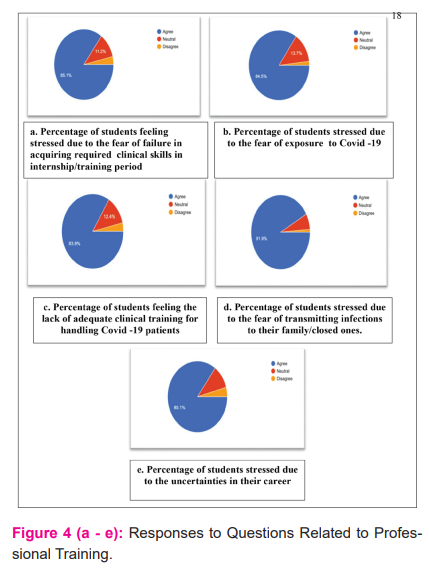
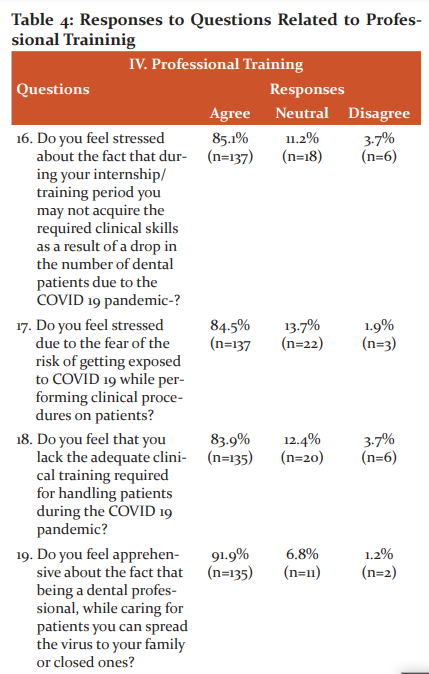
Professional Training (Figure4, Table 4)
85.1%(n=137) respondents were stressed about the fact that during the internship period they may not be able to acquire the required clinical skills because of the drop in dental patients due to the ongoing pandemic(Figure 4a). Many of the students (84.5%;n=136) feared getting exposed while performing clinical procedures in patients (Figure 4b). Another reason for stress during the pandemic among 83.9% (n=135)students was the lack of clinical training required for handling patients during the pandemic (Figure 4c).
The majority of the students (91.9%;n=148) were also apprehensive of the fact that being a dental professional while caring for patients they may spread the disease to their family or closed ones. (Figure 4d). Regarding the career placement, 85.1% (n=137) students were stressed due to the uncertainty regarding their career/ placement because of the current situation(Figure 4e).
In the open-ended question where the students had to mention the reason for stress, many students were stressed for not being able to practice their laboratory or clinical skills for a long time which in turn could greatly affect their manual dexterity skills.
Discussion
Dentistry is considered a stressful and demanding profession. Previous studies have identified the main stressors among dental students like workload, peer competition, examination and grades, patient care responsibilities, difficulty in learning clinical procedures, reconsideration of dentistry as a proper choice, fear of failure, faculty relations and financial responsibilities.19-22 The present study was carried out to identify the perceived sources of stress amongst the final year dental undergraduate students of North India during the Covid-19 pandemic so that targeted interventions can be suggested and implemented.
The modified DES (dental environmental stress ) scale used in our study has also been used previously by many authors to assess the stress level among dental students.
Assessing the current mode of teaching, students have adapted to the new online mode but still more than half of the students find the conventional classroom teaching to be better as compared to the online mode. Most of the students also faced issues due to the increased screen time, connectivity issues at home, distractions at home. Similar findings have been reported from other studies23, 24questioning the blended mode of teaching suggested in upcoming times.
In the survey conducted, academics and performance pressure was also a reason for stress for many of the students. Almost half of the students felt burdened due to the increased number of assignments being given during this period and also faced difficulty in understanding the subjects at home. Many of the students were anxious as they felt the lack of guidance from their teachers and mentors due to absence from the schools /colleges during this period and also felt that they do not have the required study materials as they were unable to access the libraries. Students also felt that at home, they lacked an ideal study environment required for professional studies. However, the major stressor among the students was fear related to the examinations 95.7%. Most of the students felt quite apprehensive about their upcoming exams. The findings are similar to the other studies conducted in different parts of the world.14,15
Clinical and professional training seemed to concern the majority of the students as most of the students agreed that due to their physical absence from the campuses during this period, they are going to lack the manual dexterity skills required for the dental profession. Similar results were reported in other studies20-25 suggesting that the majority of students expressed deep concerns regarding graduating without gaining practical experience in certain clinical procedures. A significant concern among the students due to the clinical care education emphasizes the need for consideration of strategies like a demonstration, simulated clinical learning. Also, prolonged suspension of clinical training is likely to have an impact on the clinical confidence and competence of dental students. Another major stressor among dental students was the fear of acquiring and transmitting infections to their families and loved ones. This has also been reported in previous studies.22-30Most of the students were also found to be anxious regarding their career and future placements.
Conclusion:
The findings of the present study indicate that Covid -19 pandemic has resulted in a significant amount of stress among dental students. Many stressors were identified during this period, the important ones being related to the examination fear, clinical training and career placements. Stress due to any reason can result in diminished efficiency and learning among students. It can also lead to emotional exhaustion and substance misuse. This suggests the need for counselling and behavioural support for students and also the implementation of various strategies by the dental schools and professional councils. The impact of lockdown on education has also been carried out in other areas of education other than dental and significant stress levels has been seen among the students and strategies has been advised by the experts.
Limitations & Future Recommendations
The present study was a cross-sectional study limited to fewer participants. The findings of the study might not apply to other dental schools. Also, the study was conducted considering the current pandemic situation, at the time of publication of the article, the situation might be different as pandemics can change their course resulting in changes in guidelines and recommendations.
Future studies with larger sample size and assessing the pandemic situation at that time should be conducted so that professional schools and councils can come up with strategies that will help in reducing the stress level among dental students. Based on the current study following recommendations are provided :
-
Considering the constantly changing situation of the pandemic, dental schools and councils after discussion with the faculty and students, should improvise the teaching-learning methods and implement policies and protocols to protect the students, staff and the patients.
-
Institutions should make the necessary changes in the clinical settings to ensure a safe and infection-free environment for the stakeholders(students and patients). This will ensure a sense of security and confidence among the students, patients and also the faculty.
-
A reform in educational systems is required so as overcome the current pandemic scenario and also to be prepared for similar future events.
Acknowledgement: Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed. We would also like to thank the students for their participation in the study.
Conflict of interest: NIL
Source of funding: NIL
ORCHID
Madhurima Nanda: http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9035-2971
Authors ‘contributions
Conceptualization: Madhurima Nanda
Data curation: Sakshi Tiwari, Aartika Singh, Prashant Kumar Shahi
Formal analysis: Dinesh Kumar Bagga
Methodology: Madhurima Nanda
Project administration: Sakshi Tiwari, Aartika Singh, Prashant Kumar Shahi
Visualization: Madhurima Nanda
Writing – original draft: Madhurima Nanda
Writing – review & editing: Madhurima Nanda, Dinesh Kumar Bagga

References:
-
Jebril N. World Health Organization declared a pandemic public health menace: A systematic review of the coronavirus disease 2019 “COVID-19”, up to 26th March 2020. Available at SSRN 3566298. 2020 Apr 1
-
BBC News. Coronavirus: India Enters ‘Total Lockdown’ after Spike in Cases. Accessed Mar. 2020;31:2020
-
Jiménez-Ortiz JL, Islas-Valle RM, Jiménez-Ortiz JD, Pérez-Lizárraga E, Hernández-García ME, González-Salazar F. Emotional exhaustion, burnout, and perceived stress in dental students. J Int Med Res. 2019 Sep;47(9):4251-9.
-
Garbee WH, Zucker SB, Selby GR. Perceived Sources of Stress Among Dental Students. J Am Dent Assoc. 1980 Jun;100(6):853–7.
-
Basudan S, Binanzan N, Alhassan A. Depression, anxiety, and stress in dental students. Int J Med Educ. 2017 May 24; 8:179–86.
-
Tangade PS, Mathur A, Gupta R, Chaudhary S. Assessment of stress level among dental school students: an Indian outlook. Den Res J. 2011;8(2):95.
-
Polychronopoulou A, Divaris K. A longitudinal study of Greek dental students’ perceived sources of stress. J Dent Educ. 2010 May;74(5):524–30.
-
Sangiorgio J, Araujo P, Navarro C, Zen I, Costa S, Ribeiro P, et al. Dental Environment Stress: Findings among Lusophone Dental Students. Pesqui Bras Em Odontopediatria E Clínica Integrada. 2016;16(1):411–24.
-
Abu-Ghazaleh SB, Sonbol HN, Rajab LD. A longitudinal study of psychological stress among undergraduate dental students at the University of Jordan. BMC Med Educ. 2016 Dec;16(1):1-6.
-
Kumar S, Dagli RJ, Mathur A, Jain M, Prabu D, Kulkarni S. Perceived sources of stress amongst Indian dental students. Eur J Dent Educ. 2009 Feb;13(1):39–45.
-
Telang LA, Nerali JT, Telang A, Chakravarthy PV. Perceived sources of stress among Malaysian dental students. Eurp J Gen Dent. 2013 Sep 1;2(3):300.
-
Alzahem AM, van der Molen HT, Alaujan AH, Schmidt HG, Zamakhshary MH. Stress amongst dental students: a systematic review. Eur J Dent Educ. 2011 Feb;15(1):8-18.
-
AlAteeq DA, Aljhani S, AlEesa D. Perceived stress among students in virtual classrooms during the COVID-19 outbreak in KSA. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2020 Oct;15(5):398–403.
-
Agius AM, Gatt G, Vento Zahra E, Busuttil A, Gainza?Cirauqui ML, Cortes AR, et al. Self?reported dental student stressors and experiences during the COVID?19 pandemic. J Den Edu. 2021 Feb;85(2):208-15.
-
Van Doren EJ, Lee JE, Breitman LS, Chutinan S, Ohyama H. Students’ perceptions on dental education in the wake of the COVID?19 pandemic. J Den Educ. 2020 Jul 5.
-
Loch C, Kuan IB, Elsalem L, Schwass D, Brunton PA, Jum'ah A. COVID?19 and dental clinical practice: Students and clinical staff perceptions of health risks and educational impact. J Den Educ. 2021 Jan;85(1):44-52.
-
Jum’ah AA, Elsalem L, Loch C, Schwass D, Brunton PA. Perception of health and educational risks amongst dental students and educators in the era of COVID?19. Eur J Den Educ. 2020 Nov 14.
-
Doughty F, Moshkun C. The Impact of COVID-19 on dental education and training. Dent Update. 2020 Jun 2;47(6):527–8.
-
Desai BK. Clinical implications of the COVID-19 pandemic on dental education. J Dent Educ. 2020 May;84(5):512.
-
Bennardo F, Buffone C, Fortunato L, Giudice A. COVID?19 is a challenge for dental education—A commentary. Eur J Dent Educ. 2020 Nov;24(4):822–4.
-
Chang TY, Hong G, Paganelli C, Phantumvanit P, Chang WJ, Shieh YS, et al.Innovation of dental education during COVID-19 pandemic. J Dent Sci. 2021 Jan 1;16(1):15-20.
-
Galibourg A, Maret D, Monsarrat P, Nasr K. Impact of COVID?19 on dental education: How could pre?clinical training be done at home? J Dent Educ. 2020 Sep;84(9):949–949.
-
Hakami Z, Khanagar SB, Vishwanathaiah S, Hakami A, Bokhari AM, Jabali AH, et al. Psychological impact of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID?19) pandemic on dental students: A nationwide study. J Dent Educ. 2020 Oct 31.
-
Iyer P, Aziz K, Ojcius DM. Impact of COVID-19 on dental education in the United States. J Dent Educ. 2020 Jun;84(6):718–22.
-
Lingawi HS, Afifi IK. COVID-19 Associated Stress Among Dental Students. Open Dent J. 2020 Nov 13;14(1):554–62.
-
Quinn B, Field J, Gorter R, Akota I, Manzanares M, Paganelli C, et al. COVID?19: The immediate response of European academic dental institutions and future implications for dental education. Eur J Dent Educ. 2020 Nov;24(4):811–4.
-
Schlenz MA, Schmidt A, Wöstmann B, Krämer N, Schulz-Weidner N. Students’ and lecturers’ perspective on the implementation of online learning in dental education due to SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19): a cross-sectional study. BMC Med Educ. 2020 Dec;20(1):1-7.
-
Özdede M, Sahin S. Views and anxiety levels of Turkish dental students during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Stomatol. 2020;73(3):123–8.
-
Hung M, Licari FW, Hon ES, Lauren E, Su S, Birmingham WC, et al. In an era of uncertainty: Impact of COVID?19 on dental education. J Dent Educ. 2020 Feb;85(2).148-156.
-
Kapasia N, Paul P, Roy A, Saha J, Zaveri A, Mallick R, Barman B, Das P, Chouhan P et al. Impact of lockdown on learning status of undergraduate and postgraduate students during COVID-19 pandemic in West Bengal, India. Children and Youth Services Review. 2020 Sep 1;116:105194.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License