IJCRR - 13(18), September, 2021
Pages: 16-20
Date of Publication: 26-Sep-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Digit Ratio and Arterial Stiffness in Males: A Novel Observation
Author: Arjun M, Vinita A, Nitin S, Naidu BANM
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Measuring blood pressure is a particularly important vital parameter to assess cardiovascular function. Studies have shown that central aortic pressure is more accurate in predicting Cardiovascular risk & organ damage. Pulse wave velocity is considered to be a gold standard for measuring arterial stiffness. Digit ratio (2D:4D) is a well-established marker for prenatal androgen exposure. It has been associated with many diseases such as CVD, hypertension, autism, personality disorder and even cancer. Objective: Primarily the study was targeted to assess the role of measuring non-invasive aortic blood pressure to determine the vascular status and arterial stiffness and implication of Digit Ratio(2D:4D), Age and Body Mass Index ( BMI) on Central hemo�dynamic parameters. Method: 25 healthy male subjects aged between 23 to 41 years was incorporated in this study. Height & Weight were measured with a calibrated stadiometer. Finger lengths were measured directly from the palmer aspect with a digital calliper. Peripheral blood pressures were recorded from all four limbs (bilateral brachial, bilateral ankle) & Pulse wave analysis was carried out with Periscope vascular analyzer. Statistical analysis was done with Microsoft Excel 365 and statistical package provided by www. stats. blue. Results: Peripheral Systolic Blood Pressure appeared to be significantly more than the Central Aortic systolic Pressure. The same observation was not true for the Diastolic pressure. Central Aortic Pulse pressure was found to be significantly low. Re�regression analysis showed that there is a significant trend) between Carotid to femoral Pulse wave velocity (PWV) and central aortic systolic pressure. Pulse wave velocity was found to be significantly associated with age and left-hand digit ratio. The difference between measured PWV and Normal predicted PWV is significantly associated with the digit ratio of the right hand. Conclusion: Prenatal androgen exposure may play a significant role in arterial health as finger length ratio /digit ratio (2D:4D) was found to be significantly associated with the extent of arterial stiffness in the subjects.
Keywords: Digit Ratio, Arterial Stiffness, Pulse Wave velocity, Central Aortic Pressure, Prenatal androgen Exposure
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Measuring blood pressure is a particularly important vital parameter to assess cardiovascular function. Clinicians routinely record arterial blood pressure non-invasively from the brachial artery and the obtained value of systolic & diastolic blood pressure is commonly assumed as the same throughout the arterial tree. But there is a significant difference in contour & amplitude of pressure waves in ascending aorta and proximal & distal peripheral arteries.1
Measuring systolic BP at various points throughout the arterial tree provides useful information for diagnosing Peripheral arterial disease. A reduced ankle-brachial index, A systolic interarm difference is also associated with peripheral arterial disease, cerebrovascular disease, and increased cardiovascular and all-cause mortality.2 General interventions are based upon peripheral pressure and often central aortic pressure is neglected. Central aortic pressure is a key determinant of coronary perfusion and left ventricular afterload.3 Central Aortic Pressure can be assessed non-invasively by oscillometry or applanation tonometry,4 using specific transfer function from peripheral pulse wave.3 Central Pressures better predict the target organ damage situations. Central Aortic Systolic pressure and or central pulse pressure are strongly affecting vascular damage, cardiovascular events or mortality whenever compared to peripheral blood pressure parameters.5 Hypertension, Diabetes Mellitus atherosclerosis, ageing causes vessel remodelling. Functional and morphological changes to vessels alter the conduction of blood to the peripheral tissues and alteration in shock-absorbing function lead to arterial stiffness (Arteriosclerosis) and thus increase in the Systolic Blood Pressure and Pulse Pressure and decreased Diastolic Pressure. Due to the stiffening of vessels, the reflected wave moves faster through the arterial tree and thereby increase the Left ventricular afterload.6 Pulse wave velocity is the most used measure of arterial stiffness. It is defined as the speed of travelling pressure waves along the aorta and large arteries. Pulse Wave Velocity is calculated by dividing the distance with pressure wave travelling time between two sites of the arterial system. Depending upon the sites of measurement two most commonly used measurements are Carotid to femoral and Brachial to ankle Pulse Wave Velocity.7 In some recent studies digit ratio (2D:4D) as a putative marker of prenatal androgen exposure have been linked with cardiovascular diseases such as myocardial infarction, hypertension etc. Manning & Bernard reported a weak negative relationship between MI and right-hand digit ratio (2D:4D). It was suggested that low prenatal testosterone and high prenatal estrogen may be the reason behind predisposing males to the onset of early MI.8 It has been observed in an Indian study that hypertensive males tend to have a higher digit ratio(2D:4D) for both hands when compared to normal controls.9 In an autopsy-based study it was observed that atherosclerotic plaque formation was found to be more pronounced in Turkish young men with a high digit ratio.10 Present study is aimed to find out the relation of peripheral and central blood pressures in the normal healthy population. The effect of prenatal androgen exposure on arterial stiffness has not been studied earlier. The present study also explores the relation of digit ratio as a proxy marker of prenatal androgen exposure with noninvasive hemodynamic parameters which may point towards the early detection of cardiovascular alterations.
MATERIALS & METHODS
Study population:
The study was conducted in the Department of Physiology Mayo Institute of Medical Sciences, Barabanki and was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee vide approval letter number MIMS/Ex2019/198. This is a cross-sectional study comprised of 32 healthy volunteers who responded to be part of the study. Informed consent was taken, and the volunteers were screened as per study protocol. 25 subjects were found to be fit for inclusion in the study. Though invitation was open for both sexes only male candidates responded.
Exclusion Criteria:
Any kind of arthropathy, History of Cardiac disease, Hyper/hypothyroidism, Diabetes, hypertension, tuberculosis, any kind of restrictive or obstructive disease of lung, present history of liver disease, viral myositis, and other muscular diseases. Female subjects with hormonal disorders including polycystic ovarian disease and adrenal hyperplasia. Subjects, who are a smoker or using tobacco in any form, were excluded from the study.
Body Mass Index (BMI) Estimation:
Height and weight were measured for each subject using a standard calibrated stadiometer and Body Mass Index (BMI) was calculated using formula 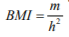 where m is mass in Kgs and h is height in meters.
where m is mass in Kgs and h is height in meters.
Digit Ratio Calculation:
The lengths of the 2nd digit (index finger-2D) and 4th digit (ring finger-4D) of both hands were measured with a digital Vernier calliper (accuracy 0.01mm) from the palmer aspect. The length of each finger was defined as the distance between the Proximal crease of the digit to the tip of the digit in millimetres. The ratio was calculated as Length of 2D/Length of 4D for both hands.
Pulse wave Analysis:
Periscope, Arterial health & Cardiovascular analysis system by Genesis Medical Systems Pvt. Ltd. India, was used for simultaneous recording of all 4 limbs noninvasive blood pressure and ECG, Pulse wave analysis was done with dedicated PeriscopeTM (Version 3.0) software. Subjects were instructed to restrict themselves from use of caffeine products for 24 hrs before participating in the study.
Statistical Analysis:
Data were analyzed using Microsoft Excel 365 Statistical plugin software & statistical package provided by www.stats.blue. Results are expressed as Mean, Standard deviation. T-test and regression analysis were performed with data obtained. Results were considered statistically significant whenever P < 0.05.
RESULTS
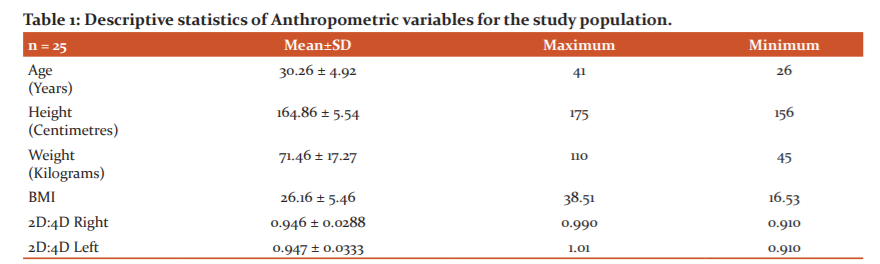
Descriptive statistics of Anthropometric variables and age is explained in Table 1. Details of various blood pressures are depicted in Table 2.
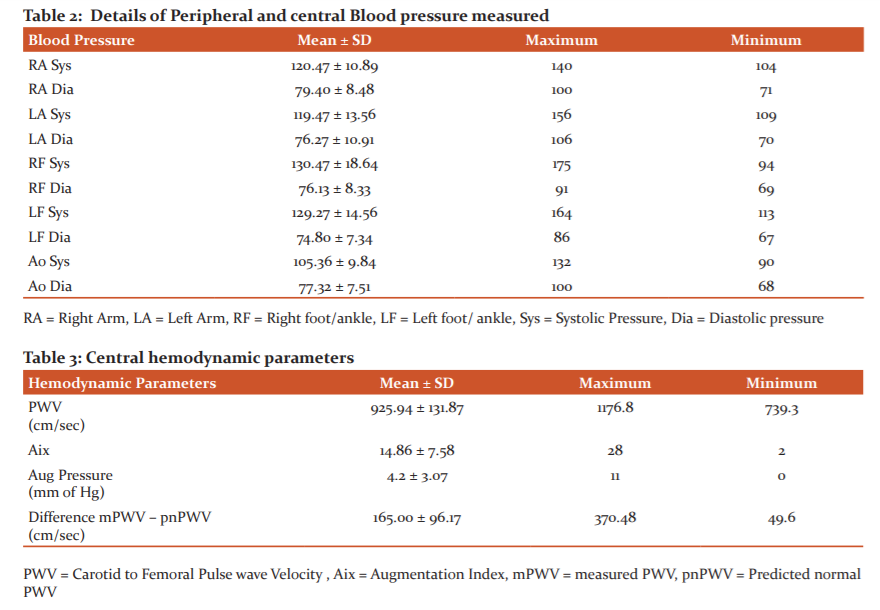
Peripheral Systolic Blood Pressure appeared to be significantly more (p=0) than the Central Aortic systolic Pressure. The same observation was not true for the Diastolic pressure (p=0.42). Central Aortic Pulse pressure was found to be significantly low (p=0.02) compared to Peripheral Pulse Pressure. There was no significant difference observed between Right & Left ABI (Ankle to Brachial index) (p=0.829) supportive to the observation of the absence of any Peripheral Arterial Disease among the study subjects. Descriptive data regarding hemodynamic parameters are depicted in Table 3. Regression analysis showed that there is a significant trend (p=0.037) between Carotid to femoral Pulse wave velocity (PWV) and central aortic systolic pressure and no significant trend (p=0.097) observed with Peripheral Systolic pressure. Pulse wave velocity was found to be significantly associated with age (r = 0.58, p=0.022) but not with BMI. Left hand Digit ratio was significantly associated PWV (r = 0.63, p = 0.01). Correlation for right hand also shown a moderate association but was not significant (r = 0.44, 0.09) Table 3.
Difference of measured PWV and predicted normal PWV was found to have significant moderate association (r = 0.45, p = 0.021) with right hand digit ratio and similar association also established for left hand digit ratio (r = 0.44, p = 0.024)
DISCUSSION
This study shows that the peripheral Systolic Blood Pressure is significantly higher than the Central Aortic Blood Pressure. No significant difference in Diastolic blood pressure was observed for peripheral and central sites. Systolic pressure and diastolic pressure represent dynamic and tonic components of the pulsatile pressure component respectively. Being the dynamic component as the distance from the aortic root increase systolic pressure also increases at the peripheral site whereas the diastolic pressure change is minimal.11 Peripheral Pulse pressure also found to be significantly higher than the central pulse pressure. Pulse wave velocity which is a marker for arterial stiffness positively correlates with age in our study. PWV is inversely linked with arterial distensibility,12 with aging the arterial walls become rigid due to continuous fatigue fracture of elastic elements and collagen cross-linking.13 Obesity is one of the conditions that envelopes the complete spectrum of cardiovascular diseases. BMI is considered as a common tool to assess obesity in common practice, despite studies, has proved that BMI is not always associated with adiposity.14 Most of the studies showed inverse relationships between PWV & Obesity.15 In our study we did not observe any relationship between BMI and arterial stiffness.
We did observe a significant association between PWV with left-hand digit ratio, but no significant association was observed for the right-hand digit ratio. Interestingly significant association observed with the right-hand digit ratio and the difference of measured PWV and predicted normal PWV. The difference between predicted and measured PWV is suggestive of the extent of increase in arterial stiffness in the individual. Several indirect studies explored the relationship with neck circumference, Waist Hip Ratio, BMI and Digit ratio and concluded that digit ratio may correlate with Cardio Vascular Disease. Manning and Bundred observed the age of onset of MI and Digit ratio maintains a negative relationship.8 In a Greek study it was observed that digit ratio may be a biomarker for predisposition to MI in men, but not in women.16 A recent study showed that Digit ratio (2D:4Dratio) is uncorrelated with CVD or CVD risk factors in menopausal women.17 Digit ratio and circulating Testosterone have shown controversial relationships18,19 and majorly one does not correlate with other. Circulating high Testosterone has been reported with low arterial stiffness in males.20 Manning et al, had shown digit ratio is strongly predictive of performance in endurance running and speculated that prenatal Testosterone may have some organizational effect on the vascular system.21 It has been well appreciated that receptors for androgens, estrogen and progesterone are expressed on the vascular tissues. Though the exact molecular mechanism behind the effect of prenatal androgen on adult body function and disease predisposition is still unknown it can be hypothesized that Prenatal androgen may alter the receptor sensitivity towards the androgen resulting in a modification in the body systems. These initial findings are interesting and our study probably for the first time reporting the significant moderate relationship between digit ratio and arterial stiffness to the scientific community. Our study extends support with observable data to the speculation that digit ratio may correlate with vascular function and thereby may be used as a marker of predisposition to CVD in males.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors acknowledge the immense help received from the Mayo Institute of Medical Sciences and Nims University for the conduction of this research. The authors also acknowledge the help from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
None
SOURCE OF FUNDING
Self-financed research project
AUTHOR’S CONTRIBUTION
All the authors contributed to this article significantly
Author 1: Designing, data collection, data analysis, article writing
Author 2: Designing, data verification, article editing
Author 3: Data collection, article writing
Author 4: Data collection, article editing.
References:
1. Karamanoglu M, O’Rourke MF, Avolio AP, Kelly RP. An analysis of the relationship between central aortic and peripheral upper limb pressure waves in man. Eur Heart J. 1993;14(2):160 – 167.
2. Clark CE. Four-limb blood pressure measurement: a research tool looking for clinical use. Hypertens. 2013;61(6):1146–1147.
3. Scolletta S, Herpain A, Romano SM, Taccone FS, Donadello K, et al. Estimation of central arterial pressure from the radial artery in patients undergoing invasive neuroradiological procedures. Bri Med J Anesthesiol. 2019;19(1):173.
4. Millasseau S, Agnoletti D. Non-invasive estimation of aortic blood pressures: A close look at current devices and methods. Curr Pharm Des. 2014;21(6):709 – 718.
5. Wang K-L, Cheng H-M, Chuang S-Y, Spurgeon HA, Ting C-T, et al. Central or peripheral systolic or pulse pressure: which best relates to target organs and future mortality? J Hypertens. 2009;27(3):461 –467.
6. Ageenkova O, Ageenkova O, Purygina. Central aortic blood pressure, augmentation index, and reflected wave transit time: reproducibility and repeatability of data obtained by oscillometry. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2011;649.
7. Kim H-L, Kim S-H. Pulse wave velocity in atherosclerosis. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2019;6:41.
8. Manning JT, Bundred PE. The ratio of second to fourth digit length and age at first myocardial infarction in men: A link with testosterone? Brit J Card. 2001;8(12):720 –723.
9. Yadav RK, Bala M. A study of 2nd to 4th digit ratio (2D: 4D) concerning hypertension in north Indian males and its implications for risk factors in coronary heart disease. Indian J Clin Anat Physiol. 2016;3(1):24.
10. Ozdogmus O, CakmakYO, Coskun M, Verimli U, Cavdar S, et al. The high 2D:4D finger length ratio effects on atherosclerotic plaque development. Atheroscl. 2010;209(1):195 –196.
11. Williams B, Lacy PS. Central aortic pressure and clinical outcomes. J Hypertens. 009;27(6):1123–1125.
12. Millasseau SC, Kelly RP, Ritter JM, Chowienczyk PJ. Determination of age-related increases in large artery stiffness by digital pulse contour analysis. Clin Sci (Lond). 2002;103(4):371 – 377.
13. McEniery CM, Wilkinson IB, Avolio AP. Age, hypertension and arterial function. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2007;34(7):665 – 671.
14. Mukherjee D, Ojha C. Obesity paradox in contemporary cardiology practice. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2017;10(13):1293–1294.
15. Shah NR, Braverman ER. Measuring adiposity in patients: the utility of body mass index (BMI), per cent body fat, and leptin. PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e33308.
16. Kyriakidis I, Papaioannidou P, Pantelidou V, Kalles V, Gemitzis K. Digit ratios and relation to myocardial infarction in Greek men and women. Gend Med. 2010;7(6):628 –636.
17. Fischer Pedersen JK, Klimek M, Galbarczyk A, Nenko I, Sobocki J, et al. Digit ratio (2D:4D) is not related to cardiovascular diseases or their risk factors in menopausal women. Am J Hum Biol. 2020;e23505.
18. Crewther B, Cook C, Kilduff L, Manning J. Digit ratio (2D:4D) and salivary testosterone, oestradiol and cortisol levels under challenge: Evidence for prenatal effects on adult endocrine responses. Early Hum Dev. 2015;91(8):451 – 456.
19. Kowal M, Sorokowski P, ?ela?niewicz A, Nowak J, Orzechowski S, et al. No relationship between the digit ratios (2D:4D) and salivary testosterone change: Study on men under an acute exercise. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):10068.
20. Hougaku H, FlegJL, Najjar SS, LakattaEG, Harman SM, et al. Relationship between androgenic hormones and arterial stiffness, based on longitudinal hormone measurements. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2006;290(2): E 234–242.
21. Manning JT, Morris L, Caswell N. Endurance running and digit ratio (2D:4D): implications for fetal testosterone effects on running speed and vascular health. Am J Hum Biol. 2007;19(3):416 –421.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License