IJCRR - 13(13), July, 2021
Pages: 233-239
Date of Publication: 05-Jul-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Health Related Lifestyle Among Students Living in B. Z. University Multan, Pakistan
Author: Alia Hussain, Saima Afzal, Kamran Ishfaq, Allah Daad, Muhammad Ashraf
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Hostel life is a beautiful medley of different cultural backgrounds and ambiences. The study reveals that hostel life affects the standard, ways of living of students, and because of this, they become more punctual, independent, social, realistic, sharp and disciplined. Objective: To find out health-related lifestyles among University students. Methodology: The study was conducted at Bahauddin Zakariya University Multan, Pakistan. To fulfil the purpose of this research work, the researcher tried to approach those students who were living in hostels at BahauddinZakariya University, Multan. A sample of 150 respondents (Umar Hall (25), Abu Bakr Hall (25), Usman Hall (25), Ayesha Hall (25), Amna Hall (25), Hajra Hall (25) were collected by using simple random sampling. Keeping in view the quantitative method, a questionnaire was derived and delivered to 150 male and female hostel dwellers of Bahauddin Zakariya University to find out their health status depending upon their lifestyles. The data were analyzed by using Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS). After it, T-test and ANOVA test were applied. Results: The study reported that unhealthy nutritional behaviour, terrible sleep conduct, physical inactivity, obesity, smoking and use of drugs are a great deal worse. Living alone affected the health-related lifestyle of students living in hostels. Hostels put a negative as well as positive impact on the life of students to make them active, alert, mercurial and lazy. Conclusion: Living in hostels creates individual's issues such as the use of drugs and narcotics etc. Eating habits are based upon the availability of some specific food items thus affecting their health. The study suggests that proper training and awareness of good and bad, beneficial and non-beneficial can help them to prevent themselves from malnutrition and non-communicable diseases.
Keywords: Health-related lifestyle, Students, Hostel, Disease, Self-reliance, Drugs
Full Text:
Introduction:
A hostel is a place where novel ideas are discussed and new perceptions about life are formed. The hostel makes the student ambitious, self-reliant and confident as compared to those who don’t reside in hostels. Hostel prepares them for practical life and they face the situation more confidently and courageously.1,2 It is a matter of discussion that hostel life has a great impact on the health-related lifestyle and pattern of learners living in hostels. Hostel life makes them more social and as a result, their behaviours are modified a lot. Hostel life is a beautiful medley of different cultural backgrounds and ambiences.3 The study reveals that hostel life affects the standard, ways of living of students, and because of this, they become more punctual, independent, social, realistic, sharp and disciplined. Students are independent in hostels. They get chances to handle different situations without the guidance of their parents. Meanwhile, hostel puts a greater impact on the health of students. Students become more lazy and lethargic in hostels. As there is no check, students male or female easily fall prey to many vices. They start using drugs and become much less careless towards their studies. It is a common practice among boarders to take drugs and show laziness.4
Pakistan is a developing country and it is very difficult for parents to afford the expenses of hostels so, students are leftover with a limited amount of money given to them by their parents. Thousands of students reside here and learn how to live with the money they have. Hostel life is a blend of different ambiences, cultures and values.5 Although the hostel is a place with maximum liberty and little bondage, the students are sandwiched in a hostel, university campus and time management. A lot of time is spent to avail the proper and nutritious food proper. Students go to university cafeterias and get food to their satisfaction. Students search for food, beverages and services, and if they are satisfied, they take it.6 The university and college arena are for health and nutritional education for a large number of young adults. Recent research of Kuala Lampur University, Malaysia depicted the results of dietary habits associated with skipping breakfast where a high rate of 29% was found among the respondents. Food is to eat and drink is to sustain life with energy and it promotes growth.6 Regular eating habits promote health education.7
Students who enter hostel life experience homesickness and carelessness resultantly they are sick and their dietary pattern is disturbed because of the change in their lifestyles and eating habits. Diet is a food plan on which a person depends to live. A balanced diet provides all the necessities of life and it makes the body healthy. The human body needs vitamins, fats, and carbohydrates for the general wellbeing of individuals. If there is a lack of abundance, and the stomach is disturbed resulting in diarrhoea, vomiting, stomachache and lost appetite, it becomes necessary to feed the human body with important components of food. The research at Alexandria University lets us know that there are hostels that accommodate a large number of students. The study aimed at identifying health-related lifestyles among students. Smokers were found in abundance in the hostels. To eliminate the prevalence percentage of smoking, daily and weekly smokers were estimated.8 Disturbed eating habits and the availability of food make students obese and overweight causes different diseases and issues among the students in hostels. Obesity is the normal and excessive disposition of adipose tissues that are hazardous for all ages.9
The food consumption pattern of university students is of particular concern because they tend to skip meals frequently and eat fast foods and snacks. This may be understood because students are habitual of junk foods. Fresh fruits are rarely available at university canteens. Students reported mental and physical health issues because of tension and the non-availability of proper foodstuff.10 The students living in hostels have their physicians and youth counsellors. Health services centres have been established to ensure special attention and treatment according to age and need. Here, counselling, training, information, diagnosis and treatment are provided. A study was conducted in Ameer-ud-din Medical College, Lahore where 50% were females and the canteen was also in the college arena. Many food outlets were also there. Students ate there and got tensed as well.11
The present study hypothesized that the effect of food will be about the quality of life where day scholars enjoy good health as compared to those not living with their families. Health professionals should also develop the style, attitudes and approaches to cope with the professional liabilities to play their role in the betterment of health and quality of life. Health professionals should be conscious enough to inform and educate the learners.12 Who focuses on poverty as a fundamental cause of poor health in hostels barely meet the expenses of studies and thus are compelled to have low priced unhealthy eateries.13 The study reported that unhealthy nutritional behaviour, terrible sleep conduct, physical inactivity, obesity, smoking and drug use are a great deal worse. Living alone affected the health-related lifestyle of students living in hostels. Hostel put negative as well as positive impact on the life of students making them active, alert, mercurial and lazy.
University life is accompanied by emotions that have an impact on their mental and physical health. Today there are many health care models which focus on attitudes that improve, protect, sustain and enhances the health of individuals, families and communities. It has been noted that by some authors that women’s health is more influenced by structural and psychological factors such as stress and lower levels of self-esteem, while men’s health was more affected by health behaviour such as smoking and physical activity.14 Health care workers have an effective role as a guide to provide services. They should be equipped with the latest knowledge and technology to practice healthy lifestyle behaviours.15 Health is a resource of everyday life, not the object of life and living. It is a basic fundamental human right that is pivotal for personal development. Keeping in view the nation’s economic growth and internal security.16University borders face unique problems and have unique basic needs as they are away from home. Students living in hostels face multi problems because of physical, social and economic characteristics. The hostel is a shelter for all those who live here and learn differently. They try to live within means and face health issues. Good health is essential to achieve educational goals. The result of the study will help them to maintain balance in their lives. That’s why the researchers choose the topic, “Health-related lifestyle among students living in Bahauddin Zakariya University, Multan”.
Objectives of the study:
-
To know student’s points of view about hostel life.
-
To examine the health-related lifestyle of university students.
-
To assess the impact of academic life on health status.
Research Methodology:
The present study was conducted at Bahauddin Zakariya University Multan, Pakistan. Students who were living in main university hostels, three for males and three for females, (the academic year 2018-2019) were the target population. The sample comprised 150 students from Bahauddin Zakariya University. A sample of 150 respondents (Umar Hall (25), Abu Bakr Hall (25), Usman Hall (25), Ayesha Hall (25), Amna Hall (25), Hajra Hall (25) were selected by using simple random sampling. A self-administrated questionnaire was developed by the researcher and completed by the students living in above mention hostels in 20-30 minutes. The questionnaires were dispensed to the hostel students with the hostel supervisor’s help. The questionnaire was explained to the students. The response rate was 94%. The population of the study were all the students living in hostels. The target population was 150 students living in hostels (Umar hall, Usman hall, Qasim hall, Ayesha hall, Amna hall, Hajra hall). The data was collected through purposive sampling (Non-probability sampling). Pre-testing was done to check the validity and accuracy of the questionnaire. Therefore 10 questionnaires had been used for pre-testing. After pre-testing a few hurdles have been noticed consequently a few modifications have been made to the questionnaire. The coding procedure turned into made to have statistical analysis. The data were analyzed by using SPSS (statistical package deal for social sciences) for the inferential statistics ANOVA test was applied.
Results
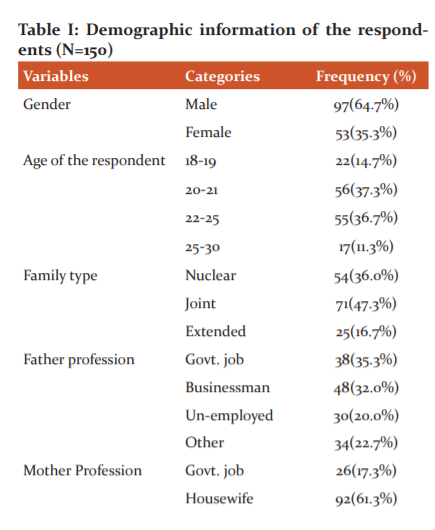
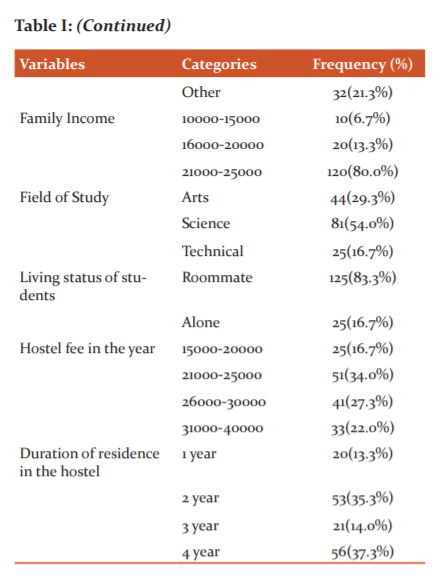
Table I represents that the variables of gender, age, family type, the profession of father and mother, their income, the field of study, the living status of students in hostels with fee payable and the period spent in the hostels by the borders of the university. This table showed that the age of hostlers ranges from 18-19, 20-21, 25-30 years whereas a smart percentage of 64.7% of boys of universities prefer to line in a hostel while almost half of this 35.3% of the female abode in hostels. While talking about their age group 14.7% of boys and 37.3% of girls ranging the age of 20-21 live in hostels. About 36.0% of boys line in nuclear families, while 47.3% are from joint families whereas a good number of 16.7% is from extended families while talking about the profession or job status of the hostlers, the result depicted that a goodly number of parents do government job, fathers 35.3% and mothers ration is 17.3% in the government job. About 32.0% of fathers prefer their own business and 61.3% of mothers are housewives while among in 20.0% of fathers of students are jobless, while 21.3% of mothers belong to other jobs. Hostel fee also ranges from 15000-30000 per year and 16.7% of learners spend 15-20 thousand per month while 34.0% ranges from 21 to 35 thousand whereas 27.3% spend lavishly from 26000-30000 per month. In the end, the duration of living hostels ranges from 1-4 years according to their need and requirement of the subject of study.
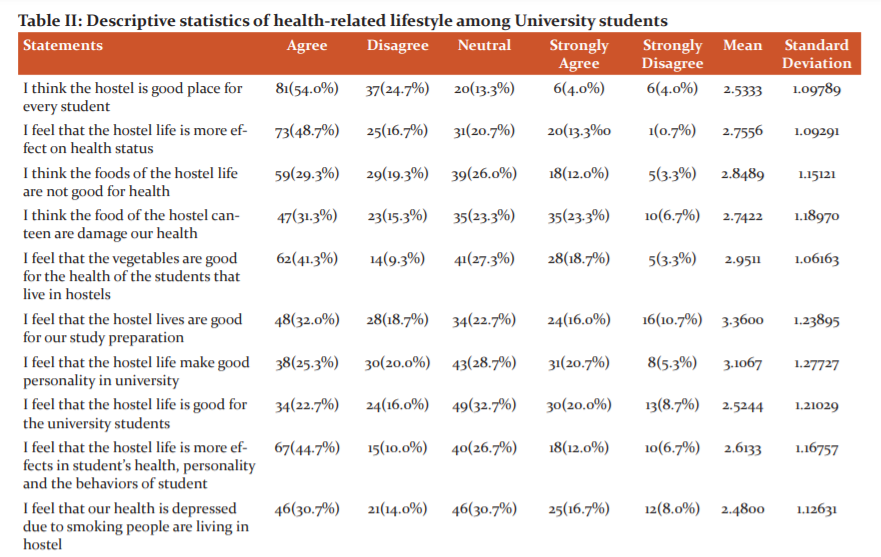

Table II showed different statements about the health-related lifestyle that affect university students, and the result shows that most of the public is affected by university lifestyle. A great no of respondents 78.7% agreed with the statement that hostels are a great place for students to live and 65.4% agreed that hostel life affects the health of students. 48.6% were of the view that food available in hostels is not good and almost 46.6% claimed their health to be damaged by the food. 50.6% of the boarders liked me of vegetable for good health. 50.7% of students like to live in hostels better for study preparation and very interestingly 45.3% of the hostlers think that it’s good for personality grooming and 38.7% loved to be in the hostel as it is good for university students. Almost 50.7% of the respondents were of the view that hostel life affects the health personality and behaviour of students here we find the equal status of those who rejected the statement and their ratio is almost 46%. Due to smokers, almost 44.7% of the boarders depict that smoking is injurious to health and as a result and as a result of the presence of smokers their health is depressed, 45.3% of the students claimed that drugs are daily used in hostels that depress the mental health of non-smokers while a great number of 22.7% damn care for the issue. Here almost 29.4% of the students agreed that the use of the drug is useless for the students living in the hostel and it is just a wastage of time and many 46% of students claimed that the use of narcotics/drugs damage the health status of students and change their lifestyle very badly. 46% of the students claimed that due to the unhealthy atmosphere in hostels many diseases attack the learners and affect their health very badly thus making their life miserable. 44% of the respondents were very alarming about the disease like hepatitis, aids, cancer, obesity and diabetes and they claimed that unhealthy atmosphere of the hostel is responsible for the prevalence of these diseases in society.
Testing of Hypothesis
Hypothesis 1
Hostel life effects more on male health than female health
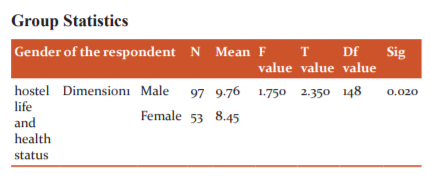
In this research, researcher used an independent sample t-test to find out the relationship between gender and hostel life effects on health. According to the null hypothesis, it is stated that there is no relationship between gender and hostel life effects on health and according to the alternative hypothesis, there is a relationship between gender and hostel life effects on health. The mean of the male towards hostel life effects on health is high than female. These results accept the alternative hypothesis, which states that there is a relationship between gender and hostel life effects on health. And reject the null hypothesis which states that there is a relationship between gender and hostel life effects on health. So it is concluded that males are more effects on health aware than female
Hypothesis 2
Hostel life affects the health more of the nuclear family’s students as compared to joint family.
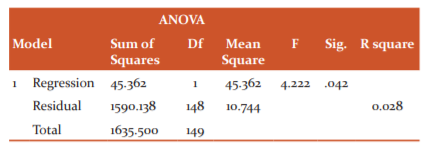
In this research, researcher used the ANOVA test to find out the relationship between family type and hostel life effects. According to the null hypothesis, it is stated that there is no relationship between family type and hostel life effects on health. According to the alternative hypothesis, there is a relationship between family type and hostel life effects on health. These results accept the null hypothesis, which states that there is no relationship between family type and hostel life effects on health and rejected the alternative hypothesis which states that there is a relationship between family type and hostel life effects on health. So it is concluded that family type is not associated with duration of hostel life effects on health.
Discussion:
As per a study carried out in the Bahauddin Zakariya University’s hostel Multan, the Majority of the scholars are affected negatively because of the eateries available for them in the variety of hostels. No doubt, their health is badly affected. This study aimed at finding out the magnitude of eating habits among them. Most of the hostel dwellers fall victim to drug addiction.4 It is also observed that girl students adjust themselves easily to the new horizon of the hostel while boys feel much difficulty here. Hostel life puts negative as well as positive impact on the life of students making them active, alert and mercurial and lazy, careless as well. The personality of students is groomed here as they are to face different issues from diet to proper health care and they are to solve all these by themselves. They face the hardships of life more bravely and courageously.17 A direct as the close relationship among social help and wellbeing among hostel students become additionally found. They were found active in all the activities during their stay in the hostel. It is also assumed that the attitudes and behaviour of the learners are also bettered as they were habitual to select eateries during their stay at home but now they adjusted themselves with what was available in hostel canteen or cafeteria.
The study shows the age of hostellers ranges of 18-19, 20-21, 25-30 years were as a smart percentage of 64.7% of boys of universities prefer to line in the hostel while almost half of this 35.3% of the female abode in hostels. The data reveals that 39.3% agreed, 19.3% disagreed, 26.0% were neutral, 12.0% strongly agree and 3.3% strongly disagreed. Most students are participating in bad things with friends. Drugs and smoking are badly affected student’s health. Young adults inside the age organization of 18 – 25 years are regularly the unnoticed group in any health or nutrition schooling in comparison to kids and adults. When these teens leave home and modify to impartial living, true dietary habits received from domestic decline.18 Some students live alone and do not talk with others and live alone in the room they are affected in student’s health. In a hostel mostly students use the internet and all the time use Facebook, Twitter and WhatsApp that are badly affected in student’s health and students behaviour. They see the bad movies and bad dramas in the hostel.
Raised degrees of stress can put a toll on our framework however we can create approaches to adapt to pressure or make endeavours in our lives to evade it. Students, particularly fresher, are a gathering especially inclined to worry because of the transitional idea of school life. The strain to gain great imprints (grades) and to win a diploma is exceptionally excessive. Winning excessive evaluations isn't always the primary wellspring of worry for understudies. Other potential wellsprings of stress incorporate over the top schoolwork, unclear assignments and awkward study halls. Notwithstanding scholarly necessities, associations with employees and time weight may likewise be wellsprings of stress. Associations with loved ones, eating and dozing propensities and forlornness may influence a few understudies on a normal.19
The findings of the present examination regarding unhealthy nutritional behaviour, terrible sleep conduct, physical inactivity, obesity and smoking and drug use are a great deal worse.3,20 This method that university college students inside the BahauddinZakariya University hostels appear to be initiating health-risk behaviour earlier, and in most instances before they are developmentally ready to deal with the potential outcomes. The findings of our take a look at the display that almost a quarter of the students reported horrific perceived fitness; decrease proportions suffered from health conditions.10 This may explain why the majority of the students had been disenchanted with residence within the hostels, mainly those with horrific perceived health and excessive perceived symptoms. However, females were more likely than male students to be upset with residence within the hostels, and much more likely to have more issues, in all likelihood due to the fact they generally came from higher social class households and there was a higher share of disillusioned college students among the ones of excessive social class households.
Conclusion:
The study explored the health-related lifestyle of the hostel, college students. It highlighted the experiences, behavioural changes, and character characteristics of hostel college students. It also researches the gender differences of some of the roommates. While they're living in university hostels, the student’s fitness is inappropriately affected. The use of medicine smoking, small quarrels, use of excessive net affects the fitness of college students. It becomes also look at that maximum of the boarder’s opted to smoke due to the fact their dad and mom were smokers. Skipping morning meals is very not unusual for many of the students of the hostel, consequently, this results in mental misery and incorrect attention towards their research and other activities as well. The study also discovered that the major cause in the back of skipping breakfast is the negative status of meals available for breakfast and other meals for eating, this puts stress and stress. As a result of this, the students prefer fast food to fill their urge for food and on occasion, they do it for flavour which is never a very good chance to healthy meals.
Recommendation
• Attached washrooms have to be provided.
• Hygienic and healthy meals ought to be given to hostel students.
• Health schooling messages should be disseminated via formal or informal programmers’ to bring about behavioural adjustments in terms of smoking, bodily activity, healthy dietary habits, and sleep behaviour.
• Focus organization interviews with college students have to be performed to elicit in-depth statistics approximately students’ problems as well as their suggestions for improvement.
Acknowledgement:
The services of the data collection team are highly appreciated. The cooperation of the head of departments to allow the data collection was really helpful.
Conflict of Interest:
There is no conflict of interest regarding this study. This research was not funded by any organization.
References:
-
Abolfotouh MA, Bassiouni FA, Mounir GM, Fayyad R. Health-related lifestyles and risk behaviours among students living in Alexandria University Hostels.2007.
-
Akhtar N, Zareen H, Sarmad R. Eating habits and nutritional status of female students of a medical college of Lahore. Annals of King Edward Medical University.2018; 24(1).
-
Ahmad U. Zindge Gulzar Hay. Pakistan: Elm-o-Irfan publisher.2006.
-
Ceylantekin Y, Öcalan D. Evaluation of University Students' Healthy Lifestyle Behaviors: Afyon Example. 2015.
-
Chhaya S, Jadav P. Dietary and lifestyle pattern concerning overweight and obesity among the medical and nursing students. Nurs. 2012; 53: 21-9.
-
Güzel A, Y?lmaz Y. Erdem, Healthy lifestyles of university students, K.U. Medical Fac J. 2012;14: 1-7.
-
Ghani, F. A., Zahari, M. S. M., Ramli, N., Jusoff, K., Zaini, Z. M. M., Hamid, M., ... & Rahmat, N. (2011). Service at UITM Residential Hostel Cafeterias—Is It Satisfactory. World Appl Sci J. 2016;12, 8-13.
-
Harris KM, Gordon-Larsen P, Chantala K & Udry JR. Longitudinal trends in race/ethnic disparities in leading health indicators from adolescence to young adulthood. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med.2015;160(1): 74-81.
-
Iftikhar A, Ajmal A. A qualitative study investigating the impact of hostel life. Int J Emerg Ment Health Hum Resil, 2015;17(2): 511-5.
-
Kozaei F, Ayub N, Hassan AS, Kozaei Z. The factors predicting students satisfaction with university hostels, case study, university Sains Malaysia. Asian Culture and History, 2010;2(2):148-158. of information and Communication, Gundhinagar. http://www. coolage.in/2012/06/02/diary-of-a-fresher-2/
-
Mishra AN.Students and Hostel Life. New Delhi: Mittal Publications.2019.
-
Ritsatakis A. Equity and social determinants of health at a city level. Health Promotion International, 2017; 24(1), i81-i90.
-
Shah AI. Ethnographic Report of Medical Colleges of Pakistan. Unpublished thesis. http://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/id/eprint/24135.
-
Shah C, Trivedi RS, Diwan J, Dixit R, Anand AK. Common stressors and coping of stress by medical students. J Clin Diag Res.2017; 3(4), 1621-1626.
-
Wu H, Wu S, Wu H, Xia Q, Li N. Living arrangements and health-related quality of life in Chinese adolescents who migrate from rural to urban schools: mediating effect of social support. Int J Env Res Pub Health. 2017;14(10): 1249.
-
WHO. Global recommendations on physical activity for health. WHO, Geneva.2010.
-
Yahia N. Abdallah A. Physical activity and smoking habits concerning weight status among Lebanese university students. Int J Health Res. 2010; 3(1): 21-27.
-
Afzal S, Yasin G. Demographic and Socio-Economic Effects of Delays in Health Services with Special Reference to Infant Mortality in Multan City-Pakistan. Pak J Life Soc Sci.2008; 6(1): 118-24
-
Khan SN, Sani U, Ullah S. The Merits and Positive Effects of Exercise on Teenagers, Who Feel Depression. J Sports Sci Phys Edu.2017; 2(2): 29-36.
-
Ilyas I, Muhammad A, Afzal R, Qamar T, Alariqi M, Ali Raza. Analysis of the Factors Faced by Female Teachers in Implementing Effective Styles of Teaching in Faisalabad, Punjab, Pakistan. Int J Sci Tech Res.2021;10(6): 238–243.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License