IJCRR - 13(17), September, 2021
Pages: 179-185
Date of Publication: 12-Sep-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Study of Cardiac Biomarkers in Patients with Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock
Author: Ashwathi V, Virendra CP
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Sepsis is having a rapid advancement as a disease process requiring immediate adjustments in therapy. Corrrect identification of disease severity is absolutely important for treatment, reducing and preventing complications, envisaging prognosis and mortality. Objective: The objective of the present study is to study clinical and laboratory parameters of patients with severe sepsis and septic shock. We have also planned to calculate Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation-II score (APACHE-II). We have undertaken an Echocardiographic evaluation of cardiac functions. Assessment of cardiac biomarkers like Troponin-T and creatine phosphokinase myocardial band (CPK-MB) have also been attempted in this study. Methodology: This was a prospective, observational descriptive cohort study. The Sample size was calculated based on the Prevalence of Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock. Result: In the present study, it was observed that higher CPK-MB levels and positive Troponin-T were associated with significant mortality. Raised CPK-MB levels were associated with sepsis and septic shock. Positive Troponin-T and raised CPK-MB levels also indicate myocardial injury leading to coronary insufficiency in patients with the diagnosis of sepsis and septic shock. Conclusion: Troponin is frequently elevated in critically ill patients; more research is desirable on the diagnostic and prognostic significance and its possible implication in patients with sepsis septic shock.
Keywords: Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation-II, Troponin-T, Creatine phosphokinase myocardial band, Septic shock
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Sepsis is having a rapid advancement as a disease process requiring immediate adjustments in therapy. Correct identification of disease severity is absolutely important for treatment, reducing and preventing complications, envisaging prognosis and mortality.1 Mortality rates depend on the severity of the disease and the depreciation of the health status of critically ill patients. It is crucial to determine the cause for the underlying infection and the manifestation of organ dysfunction. The presence of predisposing conditions increase the morbidity and mortality rates as the severity of the disease process intensifies, extremes of age, diabetes mellitus, trauma, surgery, history of organ transplantation should be ascertained. Florence Nightingale in 1863, first noticed that the evaluation of outcomes in severely ill patients was an issue.2 The prognostication of outcome in severely ill patients was based on the insight and adjudication of the physician, since the beginning of time. The drastic expansion of the intensive care units, in modern times, has commanded a quantifiable measurement and analysis of the outcomes to augment practices based on data and substantiation. The norm of calculating and assessing through disease severity scores came into existence 25 years back and was created to get an indication for risk stratification of critically ill patients. Subsequently, several disease severity scoring systems have been established considering the diverse conditions and the aetiology of the disease. Hence a vital part of the management of all critical cases is evaluating the prognosis of these patients.1The scoring systems are used for risk stratification, thereby segregating the critically ill patients and classifying them into a specific risk category based on clinical and laboratory parameters. For the improvement of treatment, standards of care and the outcome in patients, it is essential to use these scoring systems in the ICUs.3 Knaus et al in 1985 stemmed the APACHE II score which is a disease severity scoring system for the evaluation of morbidity and mortality in ICU patients.4 based on data collected on the day of admission in the ICU the scores are calculated e.g. SAPS (Simplified Acute Physiology Score), APACHE. All scoring systems usually comprise of two parts: an estimated probability of morbidity and mortality, and a severity score, which is a number (the severity of the condition rises with a higher score).5,6 The standard process of determining the severity of sepsis is by the calculation of Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II score ( APACHE II). Practicing physicians must comprehend the significance of disease severity scores and utilize these scoring systems in daily practice.7
OBJECTIVES
To study clinical and laboratory parameters of patients with severe sepsis and septic shock.
To calculate Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation-II score (APACHE-II).
Echocardiographic evaluation of cardiac functions (LV systolic function, diastolic function and resting Regional Wall Motion Abnormality).
To assess cardiac biomarkers like Troponin-T and creatine phosphokinase myocardial band (CPK-MB) at the time of admission and to find its relation with the outcome of sepsis with septic shock.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
This was a prospective, observational descriptive cohort study. The study was conducted in the Intensive care unit of the Krishna Institute and Medical Research Centre (KH&MRC), Karad, Maharashtra, India. The study duration was from October 2018 to March 2020. (18 months). The study was approved by Institutional Ethics and Protocol Committee (IEC) [Protocol No: 0248/2018-2019]. The Sample size was calculated based on the Prevalence of Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock.
Z = standard constant value at 95% CI= 1.96
P= proportional rate of sepsis in general population= 25%
Q = no proportion = 75%
L = allowable error = 10%
N = (1.96)2(25) (75)/ (10)2
= 3.84 x 1875/100
= 7200/ 100
= 72
All participants were included in this study after a written and informed consent was taken from them or their relatives.
Inclusion Criteria
-
Patients above18 years of age were admitted to the Medical intensive care unit with the diagnosis of sepsis and septic shock.
Exclusion Criteria
-
Patients with chronic renal disease.
-
Patients with systemic diseases- (Diabetes Mellitus, Hypertension, HIV disease, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, Collagen Vascular Disease etc)
-
Patients with severe anaemia. ( Haemoglobin <7 g/dl)
-
Patients with Cerebrovascular Accident.
Patients were diagnosed and classified into the following 2 groups using criteria for SIRS namely severe sepsis and septic shock based on the 1991 ACCP/SCCM Consensus Conference. All patients who met the inclusion criteria were enrolled in the current study. 7-10
Method:
Subjects aged 18 and older were included in this study after obtaining written and informed consent. A detailed history was obtained from these subjects, general examination and systemic examination of all patients were done.
INVESTIGATIONS:
All patients who signed up for the study undertook the following investigations:
Laboratory investigations:
Troponin-T
Roche cardiac Troponin-T sensitive test has been used in this study.
CPK-MB
A Red-top tube is used. The serum is analysed. Normal range 5-25 IU/L. Cut off value 5 IU/L.
-
Other Laboratory Investigations
-
Blood urea via the urease-GLDH process
-
Serum creatinine via Modified JAFFE’S process
-
Serum sodium via ion-selective electrode process
-
Serum potassium via ion-selective electrode process
-
Liver function tests by Calorimetry
-
The complete blood count was performed, in a 3 part mechanized analyser via Nihon Kohden. (MEK 6420P)
-
Blood Culture
Statistical Analysis
The data was recorded in a study proforma sheet and analysed by using Microsoft Excel. Variables like sex, age, groups of sepsis etc were analysed and represented in percentage form. Categorical variables were assessed by using the chi-squared test. Positive Troponin-T was analysed and presented in terms of Mean and standard deviation, median with interquartile range since data were not normally distributed. The association between Positive Troponin-T and various categorical variables such as outcome, culture growth and APACHE II score was evaluated by Chi-squared test. APACHE II score was represented as median with interquartile range and mean with standard deviation. Pearson’s correlation method was used to gauge the relationship between APACHE II and CPK-MB levels. The p-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
DIAGNOSIS
In the present study, we observed the various systems involved in the study subjects according to their diagnosis. We observed that Severe sepsis was the most common diagnosis (34.72%), followed by Septic shock among 29.16% of subjects, Urinary tract infection among 20.83% of study subjects, pneumonia among 13.89%, Acute respiratory distress syndrome was seen among 1.39% of the subjects. [Table 1]
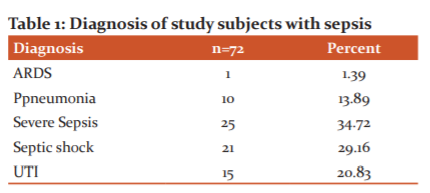
Association among creatine phosphokinase myocardial band (CPK-MB) levels and Culture
In the present study, we examined the association between the blood culture reports and CPK-MB levels amongst the study subjects using the Student’s t-test. We discerned a significant association between CPK-MB levels and culture-positive status. (The t-value is 3.18.) [Table 2]
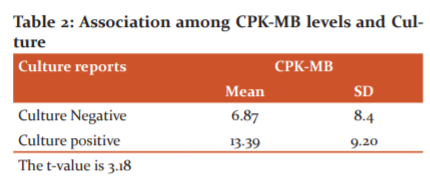
Association of Culture and Troponin-T
We evaluated the association between the culture reports and positive troponin-T among the study subjects using the Student’s t-test. A significant relationship between positive troponin-T and culture-positive status was noted. [Table 3]

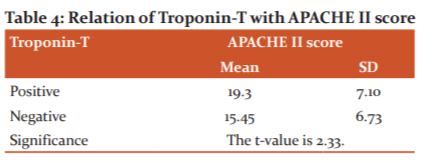
APACHE II and Troponin-T
In this study, we paralleled the APACHE II score with positive troponin-T using Student’s t-test. We discerned a significant association between positive troponin-T and APACHE II score. (The t-value is 2.33.) [Table 4]
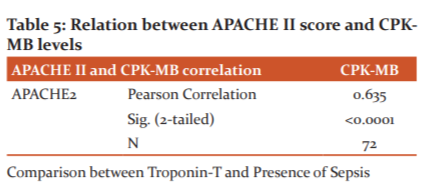
APACHE II and CPK-MB levels
In the current study, we gauged the relationship between APACHE II score and CPK-MB levels using Pearson’s Correlation Method. We have taken CPKMB levels on the x-axis, APACHE II score on the y-axis and measured the strength of association between the two variables. A positive correlation was observed between both the parameters. (r=0.635, p-value<0.0001) [Table 5]
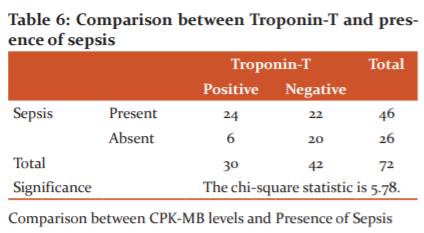
Comparison between Troponin-T and Presence of Sepsis
In this study, we discerned the association between positive troponin-T and the presence of sepsis. Troponin-T was positive among the subjects presenting with severe sepsis and septic shock. The result was found to be statistically significant. [Table 6]
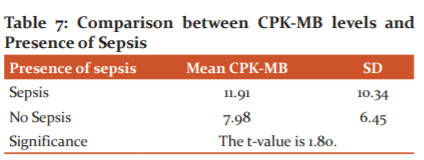
Comparison between CPK-MB levels and Presence of Sepsis
In the current study we compared the mean CPK-MB levels with the presence of sepsis, student’s t-test was used. The interpretations were found to be statistically significant. [Table 7]
OUTCOME of patients with sepsis in the study cohort
In this study, we assessed the outcome among the study subjects. We observed that 59.72% of subjects survived, while mortality witnessed in the present study was 40.28%. [Table 8]

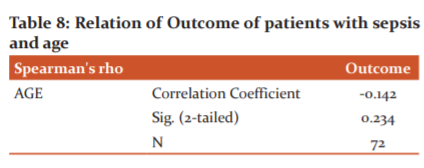
Comparison between Outcome of sepsis and age
In the present study, we gauged the association between the age of the subjects and the outcome. We observed that there is no significant correlation between the age of the subjects and their survival. (r=0.142) [Table 8]
COMPARISON BETWEEN OUTCOME AND GENDER
In the present study, we paralleled the association between gender of the subjects and outcome. We observed that there is no significant association between the gender of the subjects and their survival in the present study. (Chi-square value: 0.01)
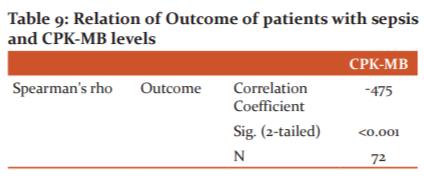
OUTCOME AND CPK-MB LEVELS
We observed a substantial association between the outcome of the study subjects and CPK-MB levels. As the levels increased, the chances of survival of the subject worsened. (r-value: -0.47) [Table 9]
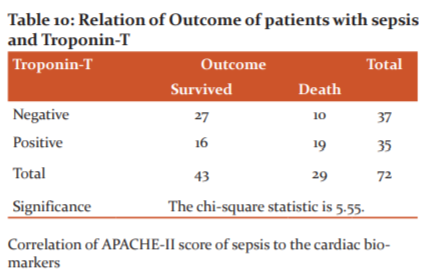
OUTCOME AND TROPONIN-T
We observed a significant relationship between Troponin-T and the outcome. It was noticed that with positive Troponin-T among the study subjects, their survival was poor. (The chi-square statistic is 5.55.) [Table 10]
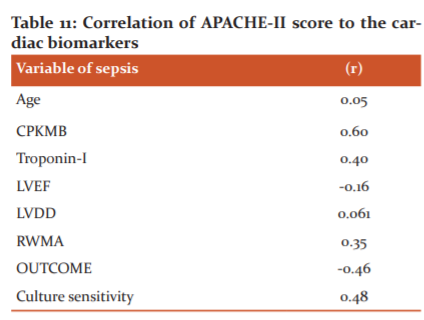
Correlation of APACHE-II score of sepsis to the cardiac biomarkers
APACHE II score has a weak positive correlation with age(r=0.05). CPK-MB has a strong positive correlation with the APACHE II score (r=0.60). Troponin-T has a moderate positive correlation with the APACHE II score. (r=0.40). APACHE II score has a weak negative correlation with left ventricular ejection fraction (r- 0.16). Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction has a weak positive correlation with the APACHE II score (r=0.06). APACHE II score has a moderate positive correlation with Regional wall motion abnormality. (r=0.35). APACHE II has a strong negative correlation with the survival of patients (r -0.46). APACHE II has a strong positive correlation with blood culture sensitivity reports. (r= 0.48). [Table 11]
DISCUSSION
APACHE II Score
In this study, we calculated the APACHE II score among the study subjects. A mean APACHE II score of 10.04 ± 9.21 was noted. The minimum score was 2.8, while the maximum score was 54 with the median being 6.65. Similarly, Raja et al. observed similar results. Correspondingly, Faochen et al, in their study observed that APACHE-II scores for patients with normal LVEF and patients with left ventricular dysfunction groups were 18.9±3.2 and 19.4±2.8 (p=0.193).12
LV Systolic Function
We assessed the LV systolic functions among the study subjects. It was noticed that the mean LV systolic function was 59.26 ± 6.64. With a minimum LV systolic function of 30 and a maximum of 67. The median LV systolic function was 60.50. Similarly, Raja et al. in their study observed that the mean LVEF was depressed in patients with sepsis, with a mean LVEF of 50.06±13.7% against 61±12% in controls. Myocardial dysfunction was observed in 50% of cases. Havaldar et al in their study of 58 subjects observed that APACHE II and LVEF were significant covariates in logistic regression with ROC (0.95). LVEF was assessed showing, severe LV dysfunction in (14.63%) patients. Severe LV systolic dysfunction was seen in non-survivors as compared to survivors with p<0.05.13
TROPONIN-T
In this study, we assessed positive Troponin-T among the study subjects. We observed that in patients with a positive Troponin-T, mortality was high in sepsis patients. Similarly Claudia Spies et al. of 26 patients, 69.23% had high troponin-T values with p=0.02.14 Similarly, Frenken et al in their study of 1124 patients found a similar result.15 Rosjo, H et al. in their study, noted that hs-cTnT levels on inclusion correlated with risk of sepsis, by (SAPS) II and (SOFA) scores.16 Choon-longarm T et al, in their study, The troponin T positive patients had a significantly higher mortality rate p<0.001).17 Landesberg G et al. in their study observed that High-sensitivity troponin-T predicted mortality in univariate analysis (Wald = 8.4; p = 0.004).18 Burton et al.19 reported higher specificity of troponin-T test of 91.9%. The sensitivity of the troponin-T test was found to be 100% in the studies done by Francois AM and Katus AM While the specificities in these studies were 86% and 78% respectively.20 Vallabhajosyula et al. Serial troponin testing at 3 hours and 6 hours was performed. An elevated delta troponin-T was present in 196 patients (26.8%) 185 (27.4%) with an elevated admission troponin-T and 11 (19.6%) without an elevated admission Troponin-T (p=0.27). 21, 22
Creatine-phosphokinase myocardial band (CK-MB)
In the present study, we assessed the CPK-MB level among the study subjects. It was noted that the mean CPK-MB levels were 10.04 ± 9.21. With minimum CPK-MB levels of 2.8 and a maximum of 54 with the median CPK-MB levels being 6.65. Sharma et al. in their study compared the positivity of troponin-T with CPK-MB, it was seen that CPK-MB was levels were higher only in the initial 2 hours of myocardial injury. Troponin-T was inferior in diagnosing myocardial injury in the first two hours. In this study specificity (73.8%) and sensitivity (67.3%) of troponin-T was higher in comparison with sensitivity (56.2%) and specificity (45.7%) CPK-MB. 23
Electrocardiogram
In the current study, we assessed the ECG findings among the study subjects. We observed abnormal ECG findings among 70.83% of study subjects, while the ECG reports were normal among 29.17% of them. As per Collinson, The amalgamation of, admission ECG, stress ECG and Troponin-T can be used for an all-inclusive risk stratification which can be completed within 24 hours of admission. Measurement of Troponin-T levels on admission allows division into high and low-risk groups in patients presenting with ECG changes. 23
Chest radiogram
In this study, we examined the chest radiogram among the study subjects. We observed abnormal chest radiogram findings (lobar pneumonia, aspiration pneumonia CAP, NCP, VAP etc) among 88.89% of study subjects, while the reports were normal among 11.11%.
Regional Wall Motion Abnormality (RWMA)
The study subjects were gauged according to the presence of Regional Wall Motion Abnormality. It was seen that RWMA was present among 37.50% of subjects and absent among 62.50% of them.
Diagnosis of patients with sepsis
In this study, we weighed the study subjects as per their diagnosis. We observed severe sepsis as the commonest diagnosis (34.72%), followed by septic shock among (26.39%) subjects, Urinary tract infection among (20.83%) of them, Pneumonia among (13.89%) of them, Septic shock among (2.78%) of them and Acute respiratory distress syndrome was noted among 1.39% study subjects and Raja et al discerned the same in their study.
Association of Creatine phosphokinase myocardial band with Culture reports
In the current st
References:
-
Iwashyna TJ, Ely EW, Smith DM, Langa KM. Long-term cognitive impairment and functional disability among survivors of severe sepsis. J Ame Med Ass. 2010;304(16):1787–1794.
-
Fleischmann C, Scherag A, Adhikari NK, Hartog CS, Tsaganos T, Schlattmann P et al. International Forum of Acute Care Trialists. Assessment of Global Incidence and Mortality of Hospital-treated Sepsis. Current Estimates and Limitations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016;1(2);193(3):259-72.
-
Linde-Zwirble, WT, Angus, DC. Severe sepsis epidemiology: sampling, selection, and society. Crit Care. 2004; 8: 222–226.
-
Knaus WA, Draper EA, Wagner DP, Zimmerman JE. APACHE II: a severity of disease classification system. Crit Care Med. 1985;13(10):818-29.
-
Vincent J-L, Moreno R: Scoring systems in the critically ill. Critical Care. 2010, 14:207.
-
Rapsang AG and Shyam DC. Scoring systems in intensive care unit A compendium. Ind J Critic Care Med. 2014;18(4):220-8.
-
Lakhani J D. SOFA vs APACHE II as ICU scoring system for sepsis: A dilemma. J Integr Health Sci. 2015;3:3-7
-
Cerra FB. The systemic septic response: multiple systems organ failure. Crit Care Clin. 1985;1:591-607.
-
Bone RC, Sibbald WJ, Sprung CL. The ACCP-SCCM Consensus Conference on sepsis and organ failure. Chest. 1992;101: 1481-3.
-
Levy MM, Fink MP, Marshall JC, et al. 2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International Sepsis Definitions Conference. Crit Care Med. 2003;31:1250-6.
-
Soong J, Soni N. Sepsis: recognition and treatment. Clin Med. 2012;12(3):276-80.
-
Fa-Chao Chen, Yinchuan Xu, Zhao-cai Zhang. Multi-biomarker strategy for prediction of myocardial dysfunction and mortality in sepsis. J Zhejiang University Sci B. 2020. 21(3): 537-548.
-
Havaldar AA. Evaluation of sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction as a predictor of mortality. Cardiovasc Ultras. 2018.30;16(1):31
-
Claudia Spies, Volker Haude,Fitzne R. Serum Cardiac Troponin-T as a prognostic marker in early sepsis. Crit Care Med. 1998; 4:1055-1063.
-
Jos FF, Dirk W, Donker D, Cristian S, Marlies E. Koster-Brouwer, Ivo W. Soliman, et al. Myocardial Injury and Long-Term Outcome in Sepsis. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outc. 2018;11:e004040.
-
Røsjø H., Varpula M., Hagve TA. et al. Circulating high sensitivity troponin T in severe sepsis and septic shock: distribution, associated factors, and relation to outcome. Intensive Care Med. 2011;37:77–85.
-
Choon-Ngarm T, Partpisanu P. Serum cardiac troponin-T as a prognostic marker in septic shock. J Med Assoc Thai. 2008;91(12):1818-21.
-
Landesberg G, Jaffe AS, Gilon D, Levin PD, Goodman S, Abu-Baih A, Beeri R, Weissman C, Sprung CL, Landesberg A. Troponin elevation in severe sepsis and septic shock: the role of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction and right ventricular dilatation. Crit Care Med. 2014 Apr;42(4):790-800.
-
Burton E, Sobel MD, William SE. Serum enzyme determination in diagnosis and assessment of MI. Circul. 1972;2:1-28.
-
Katz AM. Physiology of the heart. New York Raven Press; 1977:99-10.
-
Vallabhajosyula S, Sakhuja A, Geske JB, Kumar M, Poterucha JT, Kashyap R, et al. Role of Admission Troponin-T and Serial Troponin-T Testing in Predicting Outcomes in Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017 Sep 9;6(9):e005930.
-
Frencken JF, van Baal L, Kappen TH, Donker DW, Horn J, van der Poll T et al. Members of the MARS Consortium. Myocardial Injury in Critically Ill Patients with Community-acquired Pneumonia. A Cohort Study. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2019;16(5):606-612.
-
Deep Chand Raja, Sanjay Mehrotra, Avinash Agrawal, Abhishek Singh, Kamlesh Kumar Sawlani, Cardiac Biomarkers and Myocardial Dysfunction in Septicaemia. J App Phy. 2017;65:14-19.
-
Sharma D, Gupta P, Srivastava S, Jain H. Sensitivity and specificity of cardiac troponin-T in the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction. Int J Adv Med. 2017;4:244-246.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License