IJCRR - 13(17), September, 2021
Pages: 143-148
Date of Publication: 12-Sep-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Magnitude of Polytrauma Injury Due to Motorised Two-Wheeler Vehicles Road Traffic Accident in Tertiary Care Trauma Centre
Author: Shukla Arvind, Sheikh Zafar, Ahirwar Tanuj
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Poly-trauma injury due to Two Wheelers road traffic accidents is emerging as an epidemic worldwide. Aims: Study the magnitude of poly-trauma injury due to Two Wheelers driver's road traffic accident. Effect of use of the helmet in pattern and severity of injuries. Effects of alcohol intake on incidence and severity of injuries. Methodology: This was a prospective-epidemiological study. Study of 250 polytrauma patients (two-wheeler driver) admitted at the trauma centre, M.G.M. medical college and M.Y. Hospital Indore. All patients aged >18 years with a history of polytrauma injury due to road traffic accidents were included in the study. Results: GCS score was significantly higher in helmet users. Fewer helmet users had an AIS ≥3 over the head/neck, face, thorax, and extremities, compared with without helmet users. A lower Injury Severity Score was also observed in motorcyclists with helmet use. When analyzing four subgroups of trauma patients, the Patient wears a helmet and alcoholic (n=21) compare with the Patient not wear a helmet and alcoholic (n=97) Glasgow Coma Scale relationship (p-value < 0.0001) and ISS relationship (p-value 0.3199). Patient wear helmet and non-alcoholic (n=25) compare with Patient not wear helmet and non-alcoholic (n=107) GCS relationship (p-value = 0.0005) and ISS relationship (p-value = 0.5719). Conclusions: Motorcycle helmet users also had a better GCS score and a lower ISS score. A study found that alcohol intoxication did not impact injury severity or injury pattern.
Keywords: Injury Severity Score, Abbreviated injury scale, Polytrauma, Trauma, Road Traffic Accident, Two-wheeler accident
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Road traffic accident represents a leading cause of death and permanent disability.1 such severely injured patients are termed as ‘polytrauma patients’. ‘Polytrauma’ is defined as having at least two severe injuries in different body regions that are potentially life-threatening. The severity of trauma is typically indicated by the Injury Severity Scores (ISS). 2
India has experienced a very rapid population increase from 48 million to 1.2 billion over the last five decades.3 Road transport is vital for growth because it provides mobility for both people and goods. It also exposes people to the chance of road accidents, injuries, and fatalities.4 Exposure to an adverse traffic climate is high in India due to the unparalleled pace of motorization and increasing urbanization fuelled by high economic process rates.5
Motorcycle accidents are a major cause of head injury. Evidence exists to suggest that the use of helmets can reduce the risk and occurrence of both head injuries and death due to motorcycle accidents, and in turn reduce hospitalization and morbidity.6
An important means of increasing the wearing of helmets in low- and middle-income countries is legislation; where helmet-wearing rates are low and a large number of people use motorized two-wheelers. In most low- and middle-income countries, especially in Asia, a motorbike is the common vehicle for the family. Helmet use among motorcycle road users is low. Young motorcycle users, in particular, are generally less likely to wear a helmet than those who are older.7
Impairment by alcohol is a crucial factor influencing both the danger of a road crash also because of the severity of the injuries that result from crashes. The frequency of drinking and driving varies between countries but it's almost universally a significant risk factoring for a road traffic crash. In many high-income countries, about 20% of fatally injured drivers have excess alcohol in their blood (i.e., above the legal limit). Studies in low-income countries have shown alcohol to be presented in between 33% and 69% of fatally injured drivers.8
MATERIAL AND METHODS -
This was a prospective-epidemiological study of polytrauma patients admitted at Trauma centre, M.G.M. Medical College and M.Y. Hospital Indore, M.P.
Study period- November 2018 to July 2020.
Sample size- 250 patients of polytrauma admitted at the trauma centre, M.G.M. Medical College and M.Y. Hospital Indore.
Inclusion Criteria -
1. All patients (two-wheelers driver) with polytrauma injury due to road traffic accident.
2.Patients > 18 years.
3. Patients or attender’s who give written informed consent.
Exclusion Criteria -
1. All patients where the mode of road traffic accident was not due to Two wheelers or not known.
2. Patients under the age of 18 years were excluded from the study as Abbreviated Injury Scale (AIS) and Injury Severity Score (ISS) perform differently in paediatric trauma patients compared to adult patients.
Written consent was obtained from the patient or attendant. A comprehensive history was taken from the Patient or the attendant and a questionnaire was filled for every patient. A set protocol was made for the management of polytrauma patients and the patient was evaluated according to it. ethical clearance number-EC/MGM/JUNE-19/07
Simple, rapidly manoeuvred’s, such as the administration of intravenous fluids, endotracheal intubation, and compressive dressings on sites of active emergency on the arrival of patients to trauma centre done.
Resuscitation primary priorities-
After resuscitation required investigations were performed:
Complete Blood Count, coagulation studies, blood type, and blood cross-match (if indicated). Urinalysis, urine toxicological screen, and Serum electrolyte values, creatinine level, and glucose values are often obtained for reference. Lipase or amylase level. Imaging studies (USG, X-RAY, CT Scan, MRI etc.)
Demographic data extracted included, gender, and age. Given the quantity and diversity of injuries, the motorcyclists presented with injuries were grouped into categories. Once categorized, the injuries were sorted into one among six body regions: head and neck, face, chest, abdomen, extremities (including pelvic girdle), and external body to align with regional AIS (anatomical score) scoring parameters and to permit comparison of regional injury frequency with severity. ISS (anatomical score) was categorized as mild (<9), moderate (9–15), serious (16–24), severe (25-49) and critical (50-74) and 75 maximums. To calculate an ISS, take the highest AIS severity code in each of the three most severely injured ISS body regions, square each AIS code and add the three squared numbers for an ISS (ISS = A2 + B2 + C2) where A, B, C are the AIS scores of the three most injured ISS body regions). The ISS scores range from 3 to 75 (i.e., AIS scores of 5 for every category). If any of the three scores could be a 6, the score is automatically set at 75. Since a score of 6 ("unsurvivable") indicates the futility of further medical aid in preserving life, this could mean a cessation of further care in triage for a patient with a score of 6 in any category.
The initial Glasgow Coma Scale score (physiological score) was used to evaluate the severity of injuries. Based on three aspects of behavioural response (eyes opening, verbal response, and motor response), the GCS ranges from 3 to 15, with three indicating the most severe injury. Consistent with the United States Centres for Disease Control and Prevention’s classifications, injuries were categorized as severe (score: 3–8), moderate (score: 9–12), and mild (score: 13–15). The GCS is a reliable measure of injury severity when used by trained evaluators and assessments of injury severity do not need to be modified for intoxicated patients.
Statistical Analysis Used- The study was conducted after ethical approval from the ethical committee This data was analysed using Univariate statistical analyses were conducted with the statistical software package SPSS version 22.0 (IBM, New York, USA), and based on this analysis, detailed results were prepared. Descriptive statistics were presented in the form of numbers and percentages. Comparison of means between two groups was done using unpaired T-test. Comparison of means of more than 2 groups was done using one-way ANOVA. a p value of less than 0.5 was taken as statistically significant.
Result
Out of the total of 250 patients with polytrauma, mean age 36.180 ± 13.106 years, range 18-70 years, Majority (n=146) of the patients were in the age group 21-40 years followed by 41-60 age group (n=68) and 18 -20 age group (n=27) and (n=9) in the age group 61-70 years. There were 11 (4.4%) females and 239 (95.6%) males.
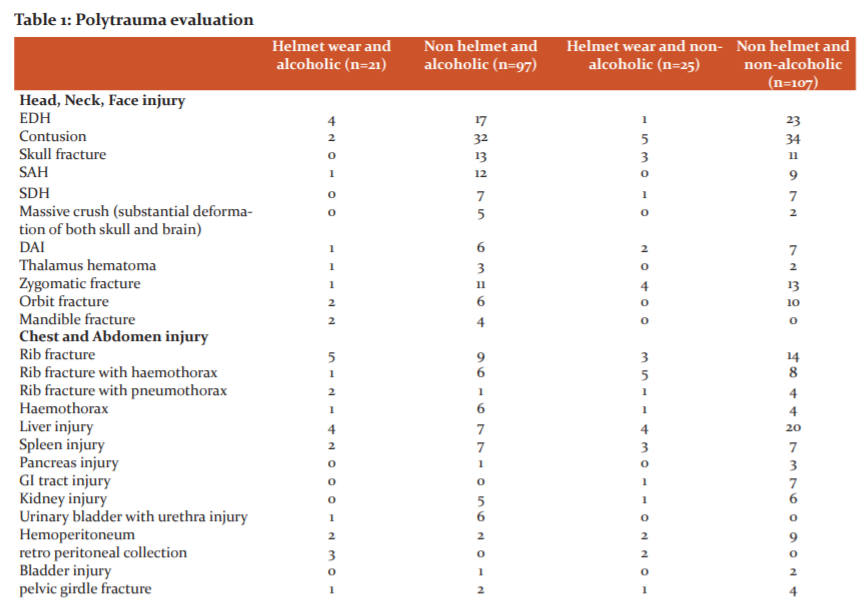
Subcategorized polytrauma patients into four groups (Table no.1)
-
Patient wearing helmet and under influence of alcohol (n=21)
-
Patient not wearing a helmet and under influence of alcohol (n=97)
-
The patient wears a helmet and is non-alcoholic (n=25)
-
The patient does not wear a helmet and is non-alcoholic (n=107)
Of the 250 patients included in the study, 46 (18.4%) patients wore a helmet, while the rest 204 (81.6%) patients were not wearing a helmet. 132 (52.8%) patients were not under the influence of alcohol intoxication and 118 (47.2%) patients were under the influence of alcohol intoxication, while they sustained injury. Glasgow coma scale score and injury severity score were comparable with these variables. (Table No.2)
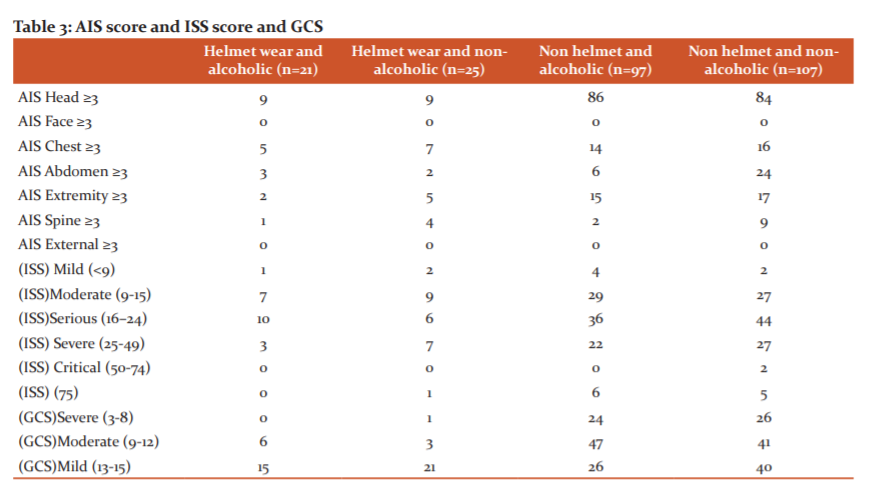
GCS evaluation of patient at the time of admission, 52 (20.8%) patients had a severe head injury, 95 (38.0%) patients had a moderate head injury and 103 (41.2%) patients had a mild head injury. the GCS score was significantly better for patients wearing helmet use. Significantly fewer helmet users had a GCS score ≤ of 12 upon arrival to the ED and a significantly greater number had a GCS score ≥ of 13 compared with without helmet users. (Table No.3)
On the evaluation of ISS score, in our study, 9 (3.6%) patients had mild ISS score, 72 (28.8%) patients had moderate ISS score, 96 (38.4%) patients had serious ISS score, 59 (23.6%) patients had severe ISS score,2 (0.8%) patients had critical ISS score and 12(4.8 %) patients had maximum ISS score. Less number of helmet users had an AIS ≥3 over the head/neck, face, thorax, and extremities, compared with without helmet users. A lower ISS was also observed in motorcyclists with helmet use and significantly fewer patients were severely injured compared with patients without helmet use. (Table No.3)
Discussion
This was a study of 250 cases of poly-trauma due to motorized two-wheeler road traffic accident, admitted in the trauma centre of MY Hospital MGM medical college Indore (M.P.) from November 2018 to July 2019.
In our study, the greatest number of patients sustaining poly-trauma belongs to the productive age group, i.e., 21-40 yrs. The experience of other workers within the field of poly-trauma is nearly the same. The mean age of patients was 40 years in study101 conducted by Jat A. A. et al.9
In our study, there were 11 (4.4%) females and 239 (95.6%) males, showing a male preponderance in the study. Menon et al.10 showed marked male preponderance in road accidents victims.
Our study did not include critically injured patients who died at the scene of an accident; The results of this study suggest no significant differences in injury severity between intoxicated and non-intoxicated trauma patients as measured by Injury Severity Score and GCS (Table No. 4). However, the intoxicated victims also had lower ISS which might lead one to predict a lower mortality rate during this study. But this doesn't answer the question on why intoxicated patients would have a lower ISS. Ward reported similar findings during a 1982 study which showed that intoxicated patients had no significant differences in ISS compared to non-intoxicated patients.11The findings reported during this paper support the results of an outsized prospective study published in 1993 by Jurkovich et al. which evaluated 3564 trauma admissions and found no significant differences in mortality rate or ISS based on acute intoxication .12
The results of this study highlight the protective effect of the helmet, with a significantly lower mortality rate among helmet users than without helmet users. helmet users also had higher GCS scores and lower ISS scores on presentation.
In our study, most of the victims are non-helmet users 204 (81.6%). When compared to them, those who had worn helmets are protected from head injuries (Table No. 4). The protective effect of motorcycle helmets is well established in the literature.6,13–20 Helmet use was found to benefit both riders and society, with improved discharge outcomes, as well as a decreased mortality rates, head injuries, and costs of hospitalization.6,13–20 Moreover, Hotz et al. report a marked increased number and severity of brain injuries following the repeal of a motorcycle helmet law.16
Out of total 250 patients of polytrauma (table.32), head injury present in 83.6%(n=209) patient, face & neck injury present in 21.2%(n=53) patient, thorax injury present in 28.4%(n=71) patient, abdomen injury present in 43.2%(n=108) patient, spine injury present in6.4%(n=16) patient, upper extremity injury present in 71.2% (n=178) patient, lower extremity injury present in 27.6%(n=69) patient and pelvis fracture present in 3.2%(n=8) patient.Reg G et al .21studied a total of 3406 patients with multiple trauma the majority of patients were males (73. 1%). Most of their patients (83%-89%) were injured in motor vehicle crashes (MVCs), fractures of the extremities 86%, head injuries 69%, thoracic trauma 62%, Intra-abdominal lesions 36%, pelvic injuries 28%, and spine injuries 14% were less frequent.
In our study Contusion 52(21.2), followed by extradural hemorrhage38(15.2 %) and subarachnoid haemorrhage 17 (6.8%) were commonly seen. Arvind Kumar et al. noted that from his study Subdural haemorrhage 89%, followed by subarachnoid haemorrhage 72% extradural 20.25%.22
In our study 14(5.6%) patients hemothorax was seen, in 9 (3.6%) patients single rib fracture was seen, in 31 (12.4%) patients multiple rib fracture was seen, Mohan Atri et al. also observed that rib fracture was the commonest injury (60%) followed by hemopneumothorax (51.7%), surgical emphysema (37.9), lung contusion (10.4%), flail chest (6.2%) etc.23
In our study, 3 (1.2%) patients bladder injury was seen, in 29(11.6%) patients liver contusion was seen and in 15 (2.0%) patients spleen contusion was seen and GI Tract injury 9(3.6) Anarase S, Anarase found that spleen and liver were the most commonly injured organs, 37.69% and 25% respectively. The hollow organ injury was less than solid organ injury.24
In the present study, on upper limb evaluation, 10 (4.0%) patients had radius fracture, 2 (0.8%) patients had ulna fracture, 19 (7.6%) patients had humerus fracture and 3 (1.2%) patients had shoulder dislocation and 60 (24 %) clavicle fracture. lower limb fractures were seen in 47 victims, out of which femur fracture is 36 cases (14.4 %), tibia in 15 cases (6%). But according to most other studies, the commonest fracture in the lower limb occurs in the tibia. Aslam M et al. said that the patients presenting with tibial injury were significantly higher than the bone injuries of other body parts. In 26% of patients, the fibula was also involved along with tibial fracture. Others were Femur 16%, Radius 9.2%, Humerus 8.3% .25
Conclusion
This study, conducted at M.Y. hospital trauma centre, revealed that motorcycle helmets provide protection to motorcyclists involved in traffic accidents and therefore their use is related to a decrease in mortality rates and the risk of various head injuries. Motorcycle helmet users also had a better GCS score and a lower ISS score. The study found that alcohol intoxication was not associated with increased severe injury, in this study alcohol use seems to be quite common roughly half of the trauma patients were under the influence of alcohol at the time of the injury, However, injury patterns between patients with alcohol intoxication and non-intoxicated were similar.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors acknowledge the enormous help received from the authors whose articles are cited and included in references to this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Conflict of Interest: Nil
Source of Funding: Nil
Authors’ contributions
Ahirwar Tanuj was involved in the data collection, statistical analysis and interpretation, and writing of the manuscript. Sheikh Zafar was involved in the study design, data collection, data analysis and interpretation, and drafting of the manuscript. Shukla Arvind conceived the study and was responsible for data collection, data analysis, and interpretation. All authors read and approved the final manuscript



References:
1. Ringburg, AN. Prevalence and prognostic factors of disability after major trauma. J. Trauma - Inj. Infect. Crit. Care.2011;70: 916–922.
2. Lefering R. Trauma score systems for quality assessment. Eur. J. Trauma. 2002;28:52–63.
3. Gupta, A, Gupta, E. Challenges in organizing trauma care systems in India. Indian J. Community Med.2009;34: 75–76.
4. Https://www.who.int/violence_injury_prevention/publications/road_traffic/helmet_manual.pdf. Helmets?: a road safety manual for decision-makers and practitioners.2006.
5. Https://nimhans.ac.in/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/UL_BR_b007_Summery-rprt.pdf. Advancing road Implementation is the key.
6. Liu, B. C. Helmets for preventing injury in motorcycle riders. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev.2008. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004333.pub3.
7. Peden TT. Road safety. Youth road safety. 1. Accidents, Traffic – Prev. Control. 2. Wounds Inj. – Prev. Control. 3. Safety. 4. Adolescent. 5. Child. I.World Heal. Organ. ISBN 92 4 159511 6 (NLM Classif. WA 275) ISBN 978 92 4 159511 7 123–166 (2013) doi:10.1201/b16346.
8. Krug EG. Risk factors for road traffic injuries. Am J Public Heal. 2000; 9(23): 523–526 .
9. Jat AA. Peer Review Audit of Trauma Deaths in a Developing Country. Asian J Surg. 27, 58–64 (2004).
10. Menon A. Pattern of fatal head injuries due to vehicular accidents in Mangalore. J. Forensic Leg. Med.2008;15, 75–77.
11. Ward, R. E. Effects of ethanol ingestion on the severity and outcome of trauma. Am. J. Surg. 1992;144, 153–157.
12. Jurkovich GJ. The Effect of Acute Alcohol Intoxication and Chronic Alcohol Abuse on Outcome From Trauma. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc.1993;270: 51–56.
13. Hooten KG. Helmeted vs nonhelmeted: A retrospective review of outcomes from 2-wheeled vehicle accidents at a level 1 trauma center. Clin. Neurosurg. 2012;59: 126–130.
14. Sosin DM. Head Injury—Associated Deaths From Motorcycle Crashes: Relationship to Helmet-Use Laws. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1990;264: 2395–2399.
15. Kraus JF. The Effect of the 1992 California Motorcycle Helmet Use Law on Motorcycle Crash Fatalities and Injuries. Am. Med. Assoc. 1994;272: 1506–1511.
16. Hotz GA. The impact of a repealed motorcycle helmet law in Miami-dade county. J. Trauma. 2002;52, 469–474.
17. Muller A. Florida’s Motorcycle Helmet Law Repeal and Fatality Rates. Am J Public Health. 2004;94: 556–558.
18. Notes N. Commentary: Motorcycle helmet law repeal: When will we learn ? or truly care to learn? Ann. Emerg. Med. 2006;47: 204–206.
19. Vaca F. Evaluation of the repeal of motorcycle helmet laws. Ann. Emerg. Med.2001;37, 229–230.
20. Vaca F. Motorcycle helmet law repeal - A tax assessment for the rest of the United States? Ann. Emerg. Med. 2001;37: 230–232.
21. Regel, G. MD. Treatment Results of Patients with Multiple Trauma: An Analysis of 3406 Cases Treated between 1972 and 1991 at a German Level I Trauma Center. 1995;38(1):70–78. doi:PMID 7745664.
22. Kumar Arvind MD. An epidemiological survey of fatal road traffic accidents and their relationship with head injuries. Indian J. Neurotrauma (IJNT).2005;5(2): 63–67 (2008).
23. Atri M. Chest trauma in Jammu region an institutional study. Indian J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 200622, 219–222.
24. Anarase S. Clinical Profile of traumatic abdominal injuries?: Cross-sectional study at the tertiary care centre. 2019;11: 35–37.
25. Mubashir A. Non-Fatal Limb Injuries in Motorbike Accidents. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pakistan 2008,18: 635–638.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License