IJCRR - 13(17), September, 2021
Pages: 37-43
Date of Publication: 12-Sep-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Perceptions of University Students of the Challenges Faced by Children Whose Fathers are Unable to Participate in Their Early Education: A Quantitative Evaluation
Author: Okeke Charity, Ugwuanyi Christian, Okeke Chinedu
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Despite empirical evidence on the positive correlation of parents' involvement and early education of children, research shows that there is a lack of parental involvement in South Africa. Objective: This study sought the perceptions of university students on the challenges faced by children whose fathers are unable to participate in their early education. Method: A descriptive survey research design was adopted for the study with a sample of 300 university students in Eastern Cape-based University. A 16-item questionnaire titled \"Challenges Faced by Children Questionnaire\" was used for data collection. An internal consistency reliability index of the items of the instrument is 0.86. Data collected were analysed using mean and analysis of variance. Results: The findings of the study revealed that the challenges faced by children whose fathers are uninvolved in their early education include poor intellectual, behavioural and social development among others. Conclusion: South African children whose fathers do not participate in their early education face a lot of difficulties which hinder that their educational development.
Keywords: Children, Early childcare, Education, Participation, Perception, University students
Full Text:
Introduction
There have been problems surrounding the issue of parental involvement in school which is a very important factor on children’s academic development.1 In line with the above claim, previous research findings revealed that parental involvement in education correlates very positively with academic achievement 2, self-esteem of children 3 and school retention.4 Moreover, home learning environment that children experience early from their parents is highly predictive of their later academic competencies.5 Fathers’ parenting practices likely play an important role in promoting healthy behavior in children, but the evidence base is limited.6 One of the beneficial factors in young children’s learning is the active involvement of family in Early Childhood Special Education (ECSE).7 Despite the above empirical evidence on the positive correlation of parents’ involvement and early education of children, research shows that there is a lack of parental involvement in South Africa.
In South Africa, most children experience their early beginning without ever knowing who the father is.8-11 An abundance of evidence suggests a scenario where men who desire to be good fathers often find themselves not knowing how to be the fathers they want to be.12 Moreover, fathers, irrespective of their ages, are confronted with uncertainty about what it means to be an involved father, let alone how to participate in their children’s lives.13,14Makusha and Richter 15 as cited by Mathwasa and Maphosa 16 found that father-absence has caused many social ills and psychological damage due to situations such as divorce or death which are more permanent. Besides, another situation in this phenomenon is where the father is absent due to lackadaisical attitude of neglect, yet they may be physically present.17,16 Despite that parent involvement is fundamental for school functioning, the nature and extent of such involvement in South Africa are debatable and contested amongst stakeholders.18 Majority of the South African parents are not actively involved in the schoolwork of their children and that it adversely affects the functioning of the school, according to the teachers.19This situation in South Africa coupled with the fact that no research has been conducted to explore the perceptions of university students on the challenges faced by children of the uninvolved fathers necessitated this research.
Children in the United Kingdom who do not enjoy parents’ participation in their early education have a deficiency in attitudes, behaviour and mental health development.20 It is only when parents are involved in the early education of their children that the academic, social, and emotional needs of the latter are bound to happen naturally otherwise such development will be hampered.21 Parents’ failure to engage in educationally supportive activities is associated with children’s poorer academic and behavioral outcomes.22 Spanish children whose parents exhibited more family involvement tended to demonstrate better results than those from homes with non-participatory parents.23 Chinese parents who compete for high-quality educational opportunities for their children, enable the children to cultivate good learning habits and achieve better academic performance than the children whose parents are uninvolved in the early education.24 There are differences in Chile children’s academic achievement between the parental involvement profiles, indicating children whose parents have a low involvement have lower academic achievement.1 Children of parents that volunteer, attend meetings, help with homework, and set high expectations, tend to do better at school than those whose parents are uninvolved.25
Research has clearly shown that most South African fathers are not actively involved in the early education of their children. Lack of parental involvement especially fathers’ involvement has been an issue that has attracted the attention of several researchers in other countries as shown in the reviewed literature. Even though children whose parents do not actively participate in their early education encounter difficulties in their early education, no research has looked for the perceptions of university students on the challenges such children face. On this premise, this study sought the perceptions of university students on the challenges faced by children whose fathers are not involved in their early education at Eastern Cape-based University.
Research Questions
-
Whatare the challenges faced by children whose fathers are uninvolved in their early education as perceived by the University students?
-
What is the influence of race on the university students’ perceptions of the challenges faced by children whose fathers are uninvolved in their early education?
-
What is the influence of age on the university students’ perceptions of the challenges faced by children whose fathers are uninvolved in their early education?
Methods
The design of the study was descriptive survey research. Survey design provides a quantitative description of attitudes or opinions of a population by studying a sample of that population.26This design has been adopted by 27-33 in similar studies.
The target population for this study was all the university students in the Faculty of Education of one Eastern Cape-based University. A sample size of 300 University students was selected for the study. Using a simple random sampling technique, a sample of 300 students from the Faculty of Education of the participating University was drawn across the different levels of study.
An instrument titled Challenges Faced by Children Questionnaire was used to obtain quantitative data from the 300 University students. The instrument is a 16-item questionnaire structured on a 5-point response option of strongly agree (SA), agree (A), undecided (U), disagree (D) and strongly disagree (SD). The minimum score on the questionnaire is 16 while the maximum score is 80.
To ensure the face validity of the instruments, copies of the instrument were given to experts for their constructive criticisms. The comments of the validators were used to arrive at the final version of the instrument which was later subjected to trial testing. To ensure the reliability of the instrument, the field test of the instrument was conducted. The internal consistency reliability index of the items of the instrument was obtained to be 0.86 using Cronbach’s alpha method.
Data were analyzed using mean and analysis of variance. Mean was used to answer the research questions while analysis of variance was used to test the null hypotheses at 0.05 level of significance.
Results
Research Question One: What are the challenges faced by children whose fathers are uninvolved in their early education as perceived by the University students?

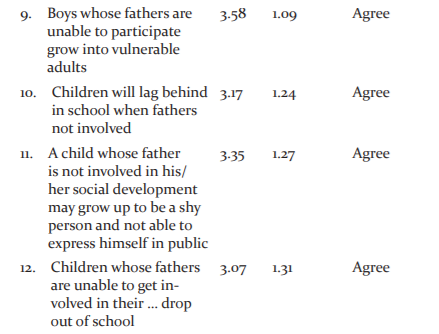
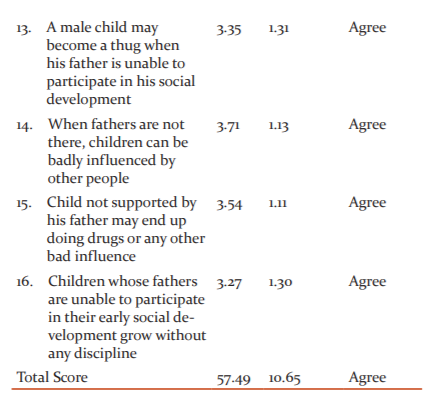
Table 1 shows the mean ratings of the university students on the challenges faced by children whose fathers are uninvolved in their early education. It shows that the mean ratings of the students on items 1 to 16 are more than the criterion mean of 3.00 for decision rule. This indicates that the university students agree to the statements of items 1 to 16 as the challenges faced by children whose fathers are uninvolved in their early education. Thus, the challenges faced by children whose fathers are uninvolved in their early education include seeking support elsewhere when fathers are unable to support them, exposure to serious dangers outside, suffering of child abuse when their fathers are unable to participate in their early development, missing the guidance they need from fathers among other.
Research Question Two: What is the influence of race on the university students’ perceptions of the challenges faced by children whose fathers are uninvolved in their early education?
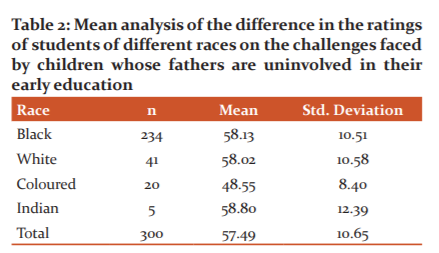
Table 2 shows that the Black university students had mean perception rating of 58.13 with a standard deviation of 10.51, White university students had mean perception rating of 58.02 with a standard deviation of 10.58, Coloured university students had mean perception rating of 48.55 with a standard deviation of 8.40 while the Indian university students had mean perception rating of 58.80 with a standard deviation of 12.39. This implies that there are variations in the mean perception rating of the university students of different races on the challenges faced by children whose fathers are uninvolved in their early education.
Ho1: Race has no significant influence on the university students’ perceptions of the challenges faced by children whose fathers are uninvolved in their early education.
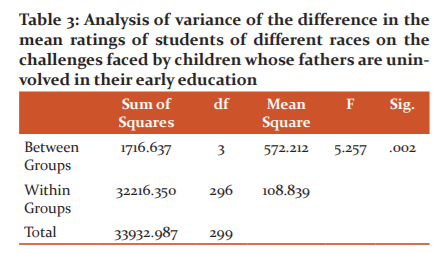
Table 3 shows that there is a significant difference in the mean ratings of students of different races on the challenges faced by children whose fathers are uninvolved in their early education, F (3, 296) = 5.257, p = .002. Thus, the null hypothesis was rejected since the probability value of 0.002 is less than the 0.05 level of significance.
Table 4 shows the pair-wise comparison test for the significant difference in mean ratings of students of different races on the challenges faced by children whose fathers are uninvolved in their early education. It shows that the mean difference between Black and Coloured university students had a significant positive mean difference (MB-C = 9.58) at p = .002 and thus contributed most to the significant influence of race on the university students’ perceptions on the challenges faced by children whose fathers are uninvolved in their early education followed by the mean difference of White and Coloured university students (MW-C = 9.47, p = .012).
Research Question Three: What is the influence of age on the university students’ perceptions of the challenges faced by children whose fathers are uninvolved in their early education?
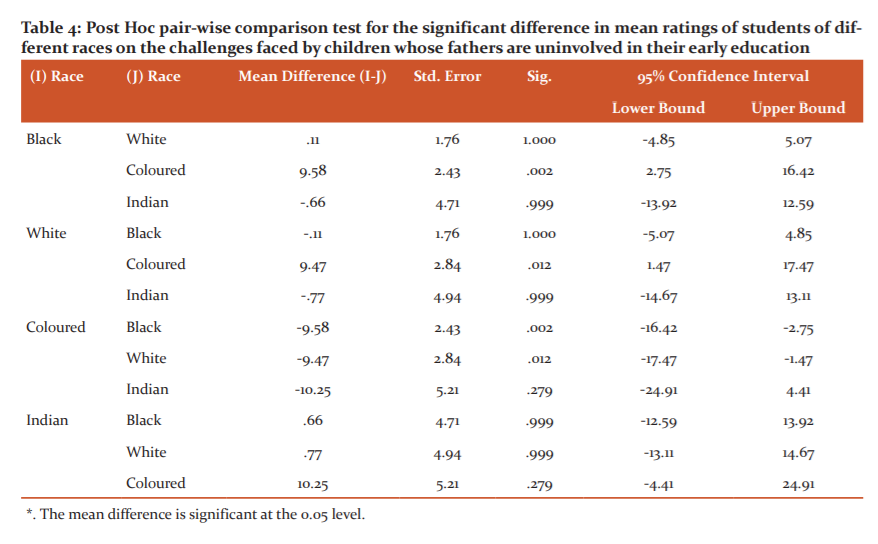
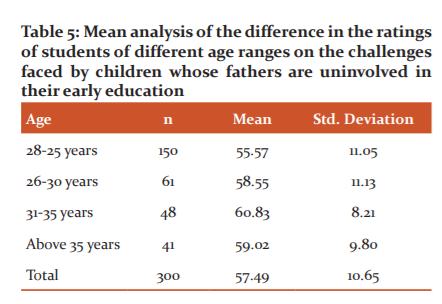
Table 5 shows that the university students within the age range of 28-25 years had mean perception rating of 55.57 with a standard deviation of 11.05, university students within the age range of 26-30 years had mean perception rating of 58.55 with a standard deviation of 11.13, university students within the age range of 31-35 years had mean perception rating of 60.83 with a standard deviation of 8.21 while the university students who are above 35 years of age had mean perception rating of 59.49 with a standard deviation of 10.65. This implies that there are variations in the mean perception rating of the university students of different age ranges on the challenges faced by children whose fathers are uninvolved in their early education.
Ho2: Age has no significant influence on the university students’ perceptions of the challenges faced by children whose fathers are uninvolved in their early education.
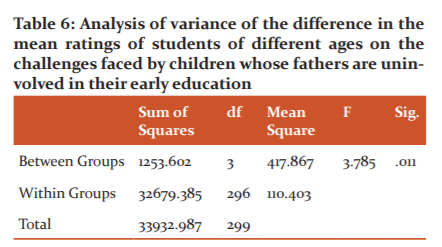
Table 6 shows that there is a significant difference in the mean ratings of students of different age ranges on the challenges faced by children whose fathers are uninvolved in their early education, F (3, 296) = 3.785, p = .011. Thus, the null hypothesis was rejected since the probability value of 0.002 is less than the 0.05 level of significance.
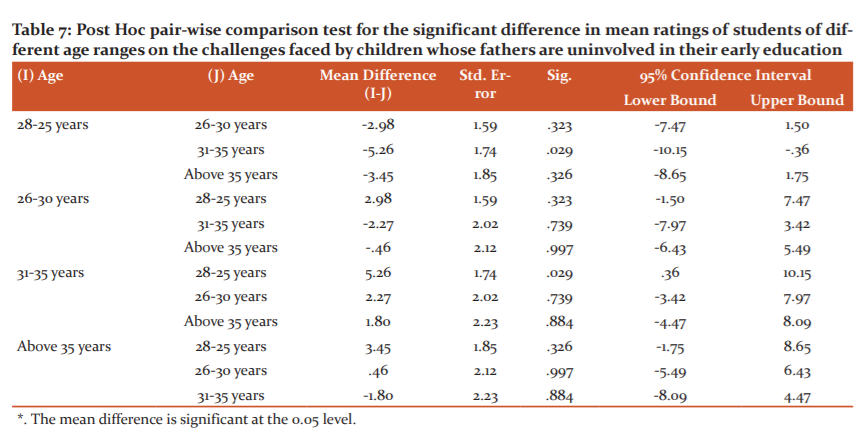
Table 7 shows the pair-wise comparison test for the significant difference in mean ratings of students of different age ranges on the challenges faced by children whose fathers are uninvolved in their early education. It shows that the mean difference between university students within the age range of 31-35 years and those within the age range of 28-25 years had a significant positive mean difference (M = 5.26) at p = .002 and thus contributed most to the significant influence of age on the university students’ perceptions on the challenges faced by children whose fathers are uninvolved in their early education.
Discussion of the Findings
The findings of the study revealed that the challenges faced by children whose fathers are uninvolved in their early education include seeking support elsewhere when fathers are unable to support them, exposure to serious dangers outside, suffering of child abuse when their fathers are unable to participate in their early development, missing the guidance they need from fathers, poor academic achievement, poor social skills and behavioural development among other. Further analysis showed that race and age of the students had a significant influence on their perceptions of the challenges faced by children of uninvolved fathers. These findings are in tandem with the findings of. 22,34,35,23,20,21,25,26
Fathers’ failure to engage in educationally supportive activities is associated with children’s poorer academic and behavioral outcomes.22 Leidy, Schofield and Parke34, as cited in McMunnet al.35 found that decreased interaction with fathers deprives children of the opportunity to learn social skills and enjoy emotional as well as instrumental support from their fathers. According to Lang et al.36 as cited in McMunnet al.35, fathers’ lack of participation in child-related activities leads to poor children’s cognitive, linguistic, and socioemotional development across early childhood independent of mothers’ involvement.
Spanish children whose fathers exhibited more family involvement tended to demonstrate better results than those from homes with non-participatory fathers.23Children in the United Kingdom who do not enjoy fathers’ participation in their early education have a deficiency in attitudes, behaviour, and mental health development.20 It is only when fathers are involved in the early education of their children that the academic, social, and emotional needs of the latter are bound to happen naturally otherwise such development will be hampered.21 There are differences in Chile children’s academic achievement between the parental involvement profiles, indicating children whose fathers have a low involvement have lower academic achievement.25 Children of fathers who volunteer, attend meetings, help with homework, and set high expectations, tend to do better at school than those whose fathers are uninvolved.26 From the discussions above, the findings of the study have validated the findings of the previous studies in other countries other than South Africa on the challenges faced by children of uninvolved fathers in their early education. These findings have contributed to the body of knowledge in the area of early childhood care and education in South Africa particularly since no such study has been conducted in the past. This finding implicates children’s physics education career choice in that their career choices in physics education will be marred at the face of the numerous challenges they encounter at early education.
Conclusion and recommendations
The researchers concluded based on the findings of the study that South African children whose fathers do not participate in their early education face a lot of difficulties paramount among others are poor intellectual, behavioural and social development which will culminate in their poor early childhood education. However, there exist variations in the perceptions of the university students of different races and age ranges on the challenges faced by children of uninvolved fathers with the black and coloured students affirming strongly those challenges the children face. This is a serious situation because South African studies have shown that the majority of the fathers do not participate in the education provisioning of their children.
Based on this, the researchers recommend that:
-
Adequate strategies should be put in place by the education ministry and other relevant bodies to sensitize fathers on the need for adequate participation in the early education of their children.
-
Seminar in form of enlightenment programs should be organised at university levels to enable the male university students who are fathers already or fathers to be to understand the educational implications of fathers’ active participation in the early education of their children.
Acknowledgement
The researchers appreciate all the parents who participated in this study for their active and honest participation.
Authors’ contribution
This research was initiated by Prof Chinedu Okeke while Dr Christian Ugwuanyi and Mrs. Charity Okeke joined him to actualize the aims of the research. All the authors contributed substantively towards the success of the research.
Conflict of interest
NIL
Source of funding
NIL
References:
-
-
-
-
Lara L, Saracostti M. Effect of Parental Involvement on Children’s Academic Achievement in Chile. Front Psychol. 2019; 10:1464. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01464
-
Tárraga V, García B, Reyes J. Home-based family involvement and academic achievement: a case study in primary education. Educ. Stud. 2017; 44: 361–375. https://doi.org/10.1080/03055698.2017.1373636
-
Garbacz SA, Herman KC, Thompson AM, Reinke WM. Family engagement in education and intervention: implementation and evaluation to maximize family, school, and student outcomes. J Sch Psychol. 2017; 62:1–10
-
Ross T. The differential effects of parental involvement on high school completion and postsecondary attendance. Educ. Policy Anal Arch. 2016; 24: 1–38. doi: 10.14507/epaa.v24.2030
-
Foster TD, Froyen LC, Skibbe LE, Bowles RP, Decker KB. Fathers’ and mothers’ home learning environments and children’s early academic outcomes. Read Writ, 2016; 29:1845–1863, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-016-9655-7
-
Morgan PJ, Young MD. The Influence of Fathers on Children’s Physical Activity and Dietary Behaviors: Insights, Recommendations and Future Directions. Curr Obes Rep. 2017; 6:324–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13679-017-0275-6
-
Ancell KS, Bruns DA, Chitiyo J. The Importance of Father Involvement in Early Childhood Programs. Young Exceptional Children. 2018; 21(1). https://doi.org/10.1177/1096250615621355 http://yec.sagepub.com
-
Adams CGG. Fathers’ involvement in the social development of children under six years: A social capital perspective and implications for early childhood development in the East London Education District. (Unpublished doctoral thesis). University of Fort Hare, East London, South Africa. 2016.
-
Makusha T, Richter L. Non-resident Black fathers in South Africa. In Roopnarine, J. L. (Ed.), Father – paternity (pp. 30–33). 2016. Syracuse, NY: UNICEF.
-
Mathwasa J, Okeke CIO. Barriers educators face in involving fathers in the education of their children in the foundation phase. J Soc Sci. 2016; 46:229–240.
-
Mncanca M, Okeke CIO. Positive fatherhood: A key synergy for functional early. Childhood education in South Africa. J Soc Social Anthrop. 2016; 7:221–232.
-
Okeke CIO. Crises impacting South African men’s participation in early socio-education development of children and possible useful interventions. South African Journal of Psychology. 2017; 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1177/0081246317729572 journals.sagepub.com/home/sap.
-
Mncanca M, Okeke CIO, Fletcher R. Black fathers’ participation in early childhood development in South Africa: What do we know? J Soc Sci. 2016; 46:202–213.
-
Mercer GD. Do fathers care? Measuring mothers’ and fathers’ perceptions of fathers’ involvement in caring for young children in South Africa. (Unpublished doctoral thesis). The University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada. 2015.
-
Nduna M. Growing up without a father and a pursuit for the right surname. The Open Fam Stud J. 2014; 6:31–38.
-
Makusha T, Richter L. Gatekeeping and its impact on father involvement among Black South Africans in rural KwaZulu-Natal. Culture, Health & Sexuality. 2015; 18(3):308-320.
-
Mathwasa J, Maphosa C. Factors Hindering Men’s Capabilities to Actively Participate in the Early Social Development of Children: A Qualitative Approach. Anthropologist. 2018; 32(1-3):58-69. https://doi.org/10.31901/24566802.2018/32.1-3.2000
-
Spruijt E, Degoede M, Vandervalk I. The wellbeing of youngsters coming from six different family types. Patient Educ Couns. 2001; 45(4):285-294.
-
Segoe BA, Bisschoff T. Parental Involvement as Part of curriculum Reform in South African Schools: Does It contribute to Quality Education? Africa Education Review. 2019; 16(6): 165-182, https://doi.org/10.1080/18146627.2018.1464692
-
Munje PN, Mncube V. The lack of parent involvement as hindrance in selected public primary schools in South Africa: The voices of educators.Perspect Educ. 2018;36(1):80-93. http://dx.doi.org/10.18820/2519593X/pie.v36i1.6
-
Garry H, Ian B. Barriers to parental involvement in education: an update. Educ Rev. 2018; 70(1):109-119. https://doi.org/10.1080/00131911.2018.1388612
-
Epstein JL. School, family, and community partnerships: Preparing educators and improving schools, 2nd ed. New York: Routledge. 2018. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780429494673
-
Morsy L, Rothstein R. Five social disadvantages that depress student performance: Why schools alone can’t close achievement gaps. Report. 2015.
-
Fernández-Alonso R, Álvarez-Díaz M, Woitschach P, Suárez-Álvarez J, Cuesta M. Parental involvement and academic performance: Less control and more communication.Psicothema. 2017; 29(4):453-461. https://doi.org/10.7334/psicothema2017.181
-
Li Z, Qiu Z. How does family background affect children’s educational achievement? Evidence from Contemporary China. J Chin Soci. 2018; 5(13). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40711-018-0083-8
-
Mbusi S.Opinion: We need to step up parental involvement in schools. 2020.
-
Creswell JW. Qualitative Inquiry & Research Design: Choosing among Five Approaches (4 ed.). Thousand Oaks CA: Sage. 2014
-
Eze KO, Ugwuanyi CS, Okeke CIO. Extent of the Upper Basic Education French Language Curriculum Content-Delivery with Technologies in Nigerian Secondary Schools. Int J Mech Prod Engg Res Devp (IJMPERD). 2020; 10(4): 311-318. https://doi.org/10.24247/ijmperdaug202027
-
Okeke CIO, Ugwuanyi CS, Mufutau MA. Stakeholders’ Views on Engaging Fathers in Early Childhood Care and Education. J Human Eco. 2020; 71(1-3): 177-186.https://doi.org/10.31901/24566608.2020/71.1-3.3233
-
Okeke CIO, Okeke CC, Ugwuanyi CS. Intervention strategies that can support young adults’ transition into positive fatherhood: implications for Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics Education. Int J Mech Prod Engg Res Development (IJMPERD). 2020; 10(3): 8585–8596. https://doi.org/10.24247/ijmperdjun2020816
-
Okenyi EC, Ngwoke AN, Ezema VS, Aneke AO, Asogwa HE, Ugwuanyi CS. Assessment of the perceived impact of home information and communication technology on pupils’ social skills development. International Journal of Mechanical and Production Engineering Research and Development. 2021; 10 (1):67-78. URL:http://www.tjprc.org/publishpapers/2-67-1611120431-6IJMPERDFEB20216.pdf
-
-
-
-
Ugwuanyi CC, Nwachukwu WC, Ugwuanyi CS, Okeke CIO, Nworgu BG, Nwoye MN, et al. Perceived Impact of the Use of Internet Resources on Undergraduate Students’ Academic Achievement in Mathematics: Implication for Physics and Engineering Teaching. Int J Mech Production Engg Res Devp (IJMPERD). 2020; 10(4):359-368. http://dx.doi.org/10.24247/ijmperdaug202031
-
Ezema VS, Okenyi EC, Ugwuanyi CS. Assessment of the extent of community involvement in the funding of primary schools in Enugu state, Nigeria: Implications for further research. Int J Mech Production Engg Res Devp. 2021; 10 (1):91-98. http://www.tjprc.org/publishpapers/2-67-1611554947-8IJMPERDFEB20218.pdf
-
Leidy MS, Schofield TJ, Parke RD. Fathers’ contribution to children’s social development. In Canbrera NJ, Tamis-LeMonda CS (Eds.). Handbook of father involvement: Multidisciplinary perspectives (pp. 151-167). New York, NY: Routledge. 2013
-
McMunn A, Martin P, Kelly Y, Sacker A. Fathers’ Involvement: Correlates and Consequences for Child Socioemotional Behavior in the United Kingdom. J Fam Issues. 2017; 38(8): 1109–1131. https://doi.org/10.1177/0192513X15622415
-
Lang SN, Schoppe-Sullivan SJ, Kotila LE, Feng X, Kamp Dush CM, Johnson SC. Relations between fathers’ and mothers’ infant engagement patterns in dual-earner families and toddler competence. J Fam Issues. 2014; 35:1107-1127.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License