IJCRR - 13(16), August, 2021
Pages: 10-16
Date of Publication: 30-Aug-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Bizygomatic Distance and Maxillary Sinus Dimensions as Predictors for Sex Determination: A Morphometric Analysis using Cone Beam Computed Tomography
Author: Aishwarya R, Patil K, Mahima VG, Jaishankar HP, CJ Sanjay, Nagabhushana D
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Many researchers have described the progression of genetically based differences in personality among sex groups and components of the genetics of individual differences in their masculinity and femininity within each sex group. This has made the basis, for both legal and humanitarian purposes. Aims and objectives: The study was aimed to measure, compare and distinguish the sexual dimorphism in the bizygomatic distance and dimensions of maxillary sinuses on Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) images and to evaluate their reliability in sex determination that might serve as evidence in forensics. Methodology: Bilateral maxillary sinus CBCT images were obtained for 30 patients, 15 males and 15 females. Bizygomatic distance and maxillary sinus dimensions such as length, height, width, area, perimeter and volume were measured and evaluated. The data obtained was then subjected to descriptive statistical analysis followed by an Independent t-test and One-way ANOVA test to arrive at the results. Results: Comparison between CBCT images of male and female groups showed statistically significant differences in bizygoMatic distance and means of both the right and left maxillary sinus length, height, area, volume and left perimeter with P0.05. Conclusion: Sex determination with few linear measurements of bizygomatic distance and maxillary sinus dimensions was possible among the study population. It was found that males had wider bizygomatic distance and larger sized maxillary sinus when compared to females. Hence this study positively recommends the use of bizygomatic distance and maxillary sinus dimensions for sex determination in the field of forensics.
Keywords: Bizygomatic distance, Cone Beam Computed Tomography, Maxillary sinus, Sex determination, Forensic Odontology, Zygomatic arch
Full Text:
Introduction:
Evolution of human life began millions of years ago, probably when some ape-like creatures began to walk habitually on two legs. Eventually, by the end most of the millennium, the perspective of minds as empty slate was rigorously disconfirmed by the temperament and behaviour genetics research.1 Many researchers have described the progression of genetically based differences in personality among sex groups and components of the genetics of individual differences in their masculinity and femininity within each sex group.2 This has made the basis, for both legal and humanitarian purposes. Establishment of one's individuality is important for unknown deceased person in homicide, accident, suicide, mass disasters and for culprits those who are hiding their identity. 3,4
As there are tremendous advancements in field of science, medicine and technology natural catastrophe, misdeed and unfortunate events persist till the date. At such instances, there is a need to collect all possible information to identify the victim. There are many features which differentiate the sex groups, among which the skeletal structures play a major role as they are strongest and are often the sole remnants of a fossil.5Presently identifying these executioners has become slightly trouble-free as a result of evolution in various fields of forensics.6
This ideology could be implicated in radiological identification as no two radiographs are alike. Many studies have shown that the skeletal remains especially the pelvis and skull bones show the greatest sexual dimorphism of around 98%. Skull consists of bones, teeth and air-filled spaces.
Air-filled spaces present within bones surrounding the nasal cavities are known as paranasal sinuses. Paranasal sinuses include frontal, ethmoidal, sphenoidal and maxillary sinus. All of these show minor changes among the sex groups radiographically. Among the paranasal sinuses, maxillary sinuses are first to undergo development and are the largest occupying the maxillary bone bilaterally.7 It is been reported in few studies that maxillary sinus and zygomatic bone will remain intact even though skull and other different bones are badly disfigured among victims.8 Both maxillary sinuses and bizygomatic arches show greatest sexual dimorphism. Maxillary sinus often tends to appear towards the end of second embryonic month and forms completely by 18 to 20 years of age.9
Earlier two-dimensional imaging modality was used for study purposes. Recently, Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT), is being used as the standard imaging modality for visualizing both soft tissues and skeletal structures in multiple views with thin sections and is widely accepted because of its accuracy in three-dimensional imaging, high-quality tissue contrast, better resolution by eliminating overlapping of adjacent structures and also because of its low cost. It can produce images with significantly less radiation exposure.10
Worldwide in few studies, it has been proven that the bizygomatic distance and maxillary sinus dimensions help in sex determination. The bizygomatic distance and all the dimensions of maxillary sinuses are well appreciated in the CBCT images, which varies from one individual to another. This study was undertaken to ascertain if any sexual dimorphism exists in the bizygomatic distance and maxillary sinus dimensions.11
Materials and Method:
Study was a prospective observational study conducted on 30 apparently healthy subjects of age group 20 - 60 years selected by simple purposive sampling for whom CBCT had been advised for assessment/treatment of any oro dentofacial conditions without any developmental defects or trauma to head and neck region with no evidence of midfacial fracture, for which ethical clearance was obtained from institutional ethical committee No- 27/2018.
Eligibility criteria:
Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
Method
The clinical examination was carried out after obtaining the written consent from the selected cases and the clinical findings were recorded in individual proforma specially designed for the study. Individuals satisfying the eligibility criteria were subjected to CBCT examination at fixed operating parameters based on the built of the subject by adopting requisite radiation protection measures. Linear measurements were performed on axial and coronal sections for both right and left maxillary sinuses using Planmeca Romexis 5.3 (3D Software). (Figure 1) (Figure 2) (Figure 3) (Figure 4)
Each of these measurements was made twice by the same observer at 15 days interval and the average was considered to avoid intra examiner variability. With the help of these measurement’s other parameters like area, perimeter and volume were calculated using the following formulae.
“Area = Length x Width (cm2)
Perimeter = 2 x Length + 2 x Width (cm)
Volume = Length x Width x Height x ½ (cm3)”
-
Bizygomatic distance
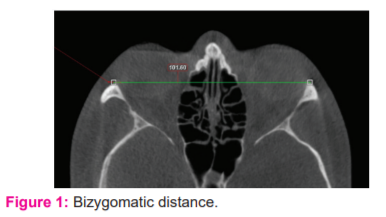
The bizygomatic width: Maximum distance between the most prominent points on both right side and left side zygomatic arches on axial sections.
-
Maxillary sinus dimensions
-
Length of the maxillary sinus

The length of the maxillary sinus: Longest anteroposterior distance from the point most anteriorly to the point most posteriorly on axial sections.
-
Height of the maxillary sinus
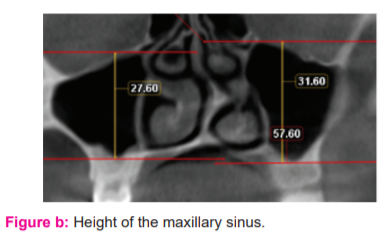
The height of the maxillary sinus: Longest distance from the point most inferiorly on the sinus floor to the point most superiorly on the sinus roof in the coronal sections.
(c) Width of the maxillary sinus
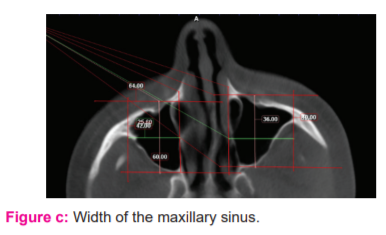
All the obtained data were tabulated and analysed statistically and compared between the right and the left maxillary sinuses of the same individual and between the sex groups respectively using SPSS software version 22.0. The data was then subjected to descriptive statistics, Independent t-test and One-way ANOVA test to arrive at the results.The width of the maxillary sinus: Longest distance perpendicularly from the medial wall of the maxillary sinus to the outermost point on the lateral wall of the lateral process on axial sections.
RESULTS
Of the 30 subjects, 15 (50%) were females and 15 (50%) were males. Each age group comprised of 05 (25%) males and 05 (25%) females with a mean age of 43.1333 for males and 41.8667 for females with a Std. Deviation 14.53993 for males and 13.64795 for females.
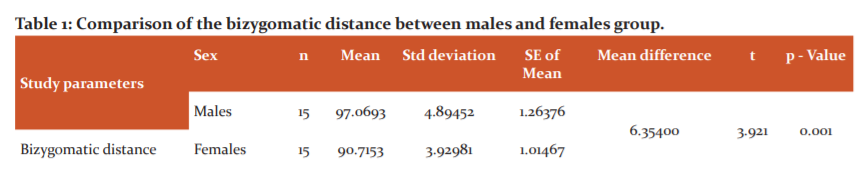
On comparing the mean value of BIZYGOMATIC DISTANCE among 15 males and 15 females, a significant difference was noted with males depicting comparatively higher values than females, which was statistically significant. This was further confirmed by independent sample t-test. (Table 1)
The right and left maxillary sinus parameters were measured and compared between males and females. (Table 2)

The difference in the mean value obtained for length, height, area, volume between males and females was statistically significant and was non-significant for width and perimeter. (Table 3)
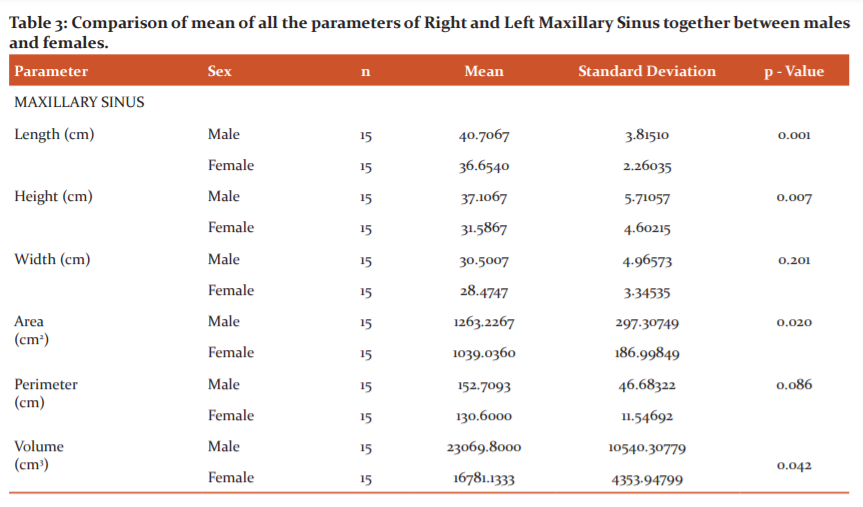
To summarize the male group revealed statistically significant higher values than the female group for the following dimensions.
Length – Right side and Left side & Mean length,
Height – Right side and Left side & Mean height,
Area - Right side and Left side & Mean area,
Volume – Right side and Left side & Mean volume,
Perimeter – Left side"
Following parameters revealed no significant difference statistically between both the sex groups.
Width – Right and left side & Mean width,
Perimeter – Right side & Mean perimeter”
DISCUSSION
From ancient times it is believed that "everybody is unique" in their own way. This uniqueness helps in individual’s identity where identification of an individual becomes difficult. During the due course, forensic science has progressed enormously. In the field of forensic sciences, identity is defined as the recognition of the individuality of a person, alive or dead. An individual can be identified based on age, sex, ethnicity, and appearance which includes weight, height, skin, cornea, hair colour, face contour etc.6
Sex determination is considered to be the classic procedure in the field of forensics as they form a major inceptive step in pragmatic identification of the dead person and building a post-mortem profile which aids in narrowing down the prediction of an unknown cadaver towards a correct probability.12,13
According to many works of literature, it has been stated that the precision rate of sex determination from the skeleton is 100%12,13 because it anatomically withstands heavy injuries. All the structures of the craniofacial region have their own advantages of being composed greatly of the hard tissues, that are comparatively non-breakable, due to which the probability of getting intact maxillary sinus and zygomatic complex without deformity is high. This can be worth using for the purpose of sex determination.
Hence the present study was framed based on the above background to determine the reliability of the bizygomatic distance and maxillary sinus dimensions as a method for sex determination using Cone Beam Computed Tomographic (CBCT) images of 30 subjects, comprised of 15 males and 15 females.
A study by Akhiland Chaurasia14 evaluated sexual dimorphism in the bizygomatic distance and paranasal sinus of 202 subjects using CBCT images. No significant difference was obtained between both the males and females for paranasal sinuses parameters. It was found that the bizygomatic distance was significantly higher in males than in females with a statistical significance of 0.01.
A study conducted by Jehan M et. al.,15 in 2014 on the Sexual Dimorphism of Bizygomatic distance and the Maxillary sinus using CT images and a study by Vidya C.S et.al.,16 on the anthropometric predictors for the sexual dimorphism of skulls of the South Indian population, has been proved that sexual dimorphism exists in the bizygomatic distance. In our study, measurements were made on CBCT images for its advantages over other imaging techniques. Results obtained are in consistent with these studies and showed significant sexual dimorphism in the bizygomatic distance with statistical significancep<0.05.
A study conducted by Uthman et. al.,8 found that males had the maximum values for the length of the right side and the left side maxillary sinus which was of statistically significant greater value than that of the females with p<0.005. In our study, we found similar results for males, where the length of the right maxillary sinus was 40.5733mm and in females was 36.9613mm, length of the left maxillary sinus in males was 40.8433mm and in females was 36.2400mm, mean of right and left side length in males was 40.7067mm and females was 36.6540mm which proved to be significant statistically p< 0.05.
Amin MF and Hassan EI17 concluded from their study that the height of maxillary sinus was one of the most reliable predictors for sex with predictive accuracy rate being 70.8% among males and 62.5% among females accordingly. In our study too, the right height left height and mean of both right and left height showed significant differences statistically among males and females with p<0.05. The males had higher measurements for maxillary sinus height compared to females.
Baweja et. al.,18 estimated the average width of maxillary sinus for males as 21.8±3.4 mm and for females as 21.6±3.7 mm. Similarly, another study by Teke HY et. al.,13 determined the approximate sinus width in males as 27.04±5.49 mm and in females as 24.36±3.795 mm. Indistinguishable results were obtained in our study with mean width of the sinus in males was 30.5007 mm and in females, it was 28.4747 mm which was statistically nonsignificant with p > 0.05.
Azhar A et. al.,11 carried out a discriminating analysis on the measurements of the maxillary sinus which showed that the maxillary sinus width of left side had an accuracy of 61.3% and was considered to be the best discriminating parameter. A study by Ayushee et.al.,10 also showed similar results where the left maxillary sinus width was the best parameter to determine sex with an accuracy rate of 60%. Comparable results were obtained in our study with the mean width of the sinus in males as 30.5007 mm and in females as 28.4747 mm, however which was statistically nonsignificant with p> 0.05.
Our study was aimed to determine whether the bizygomatic distance and both right and left maxillary sinuses together of an individual serve as sex predictor as a whole. The measurements of the right and left side along with their mean values were considered for determination of sex in this study statistically.
The study by SaccucciM et. al.,12 for determination of sex using maxillary sinus volume on CBCT images did not show any statistical difference between males and females. Hence, they stated that the maxillary sinus volume could not be utilized to perceive the sexual difference in an individual's identification.
In contrast, our study results showed a statistically significant difference in the sinus volume. The volume of the right side in males was 24121.466cm3 and females was 17019.8667 cm3, sinus volume of the left side in males was 24754.20 cm3, and in females was 16542.86 cm3 and mean volume of both right and left sinus among males was 23069.80 cm3 and females was 16781.13 cm3 which was significant with p< 0.05. Further studies are recommended with a bigger sample size that may throw better light on this parameter. This can be attributed to socio-economic, ethnic and racial differences.
Another study by Jehan et. al.,19 proved that altogether average dimensions of each individual variable were statistically greater among males 9.55±0.41cm when compared with females 9.26±0.52cm which was statistically significant. Similarly, we found that parameters of maxillary sinus such as right length, left length, mean of right and left length, right height, left height, mean of right and left height, right area, left the area and mean of right and left the area, right volume, left volume, mean of right and left volume and left perimeter were higher in males compared to females and were statistically significant with p-value < 0.05.
In the current study, we primarily aimed to determine if maxillary sinus dimensions were a good predictor of sex. Once this was substantiated, further studies could be undertaken for the sides which would be more accurate. This study suggests that in males the overall maxillary sinus measurements are larger to females.
Hence, the differences in few of the study results obtained for sex determination with bizygomatic distance including dimensions of the maxillary sinus may be attributed to the combination of various factors like sample size, the difference in ethnic groups and racial groups, variations in stature of body, size of skeletal components, their height and physique, environmental and genetic factors, anatomical differences of the sinus and zygomatic complex, variations in both the osteoclastic and osteoblastic activity and the pneumatization process of the sinus.7,14
CONCLUSION
Research in the field of forensics is being carried out since many ages on the living population to find out values and measurements that can be applied on to the skeletal remains for various purposes. Imaging forms the indispensable key tool for sex determination in the field of forensics. Out of many, the measurements of the bizygomatic distance and the maxillary sinus are of at most important as these can be considered as stable markers and strong parts which is found intact even when the skull is badly destructed.
The results obtained in the present study revealed that the bizygomatic distance and maxillary sinus dimensions show anatomic variations between both the sex groups. Therefore, it is concluded that the linear measurements on CBCT images with significant differences among males and females can be used in forensic anthropology as an aid for the determination of the sex. Hence these measurements are advocated for providing evidence in forensics, to augment the accuracy of estimation made by other means also especially when other bones of the skeleton are unavailable. Further, these can fortify the claim made regarding sex determination based on other methods.
LIMITATION
As this was a time-bound study best possible sample size was considered. Larger sample size needs to be considered to substantiate our findings. Further studies are recommended with the larger sample size including various ethnic and racial groups and for the generation of sex determination equation to the particular population.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors acknowledge the contributions of the authors, journal editors and publishers of the journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Conflict of interest: NIL
Source of funding: NIL
Individual Authors Contribution
Dr R Aishwarya – Carrying out the research
Dr Patil Karthikeya – Concept and Study design
Dr VG Mahima – Concept and Study design
Dr HP Jaishankar – Measurements and Interpretation
Dr CJ Sanjay – Measurements and Interpretation
Dr D Nagabhushana – Data analysis and Manuscript editing
References:
-
Dr Rick Potts. Introduction to Human Evolution, National Museum of National History. Jan.16, 2019. Page no. 1.
-
Ngun TC, Ghahramani N, Sánchez FJ, Bocklandt S, Vilain E. The genetics of sex differences in brain and behavior. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2011;32(2):227-246. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2010.10.001.Page no. 227-246.
-
Weisberg YJ, Deyoung CG, Hirsh JB. Gender Differences in Personality across the Ten Aspects of the Big Five. Front Psychol. 2011; 2:178. Published 2011 Aug 1. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2011.00178. Article 178. Page no. 1-11.
-
Maloth AK, Dorankula SP, Pasupula AP. Lip outline: A new paradigm in forensic sciences. J Forensic Dent Sci. 2016;8(3). doi:10.4103/0975-1475.195109. Page no. 178-9.
-
Sidhu R, Chandra S, Devi P, Taneja N, Sah K, Kaur N. Forensic importance of maxillary sinus in gender determination: A morphometric analysis from Western Uttar Pradesh, India. Eur J Gen Dent. 2014; 3 Page no. 53-56.
-
Rao NG. Text book of Forensic Medicine and Toxicology. 2nd ed. New Delhi: Jaypee Brothers; 2010. Page no. 1-6.
-
UroogeAyeesha, Patil B.A. Sexual Dimorphism of Maxillary Sinus: A Morphometric Analysis using Cone Beam Computed Tomography, Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research. 2017 Mar, Vol-11(3).Page no. ZC67-ZC70.
-
Uthman AT, Al-Rawi NH, Al-Timimi JF. Evaluation of foramen magnum in gender determination using helical CT scanning. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 2012;41(3). Page no. 197–202.
-
Masri AA, Yusof A, Hassan R. A Three-dimensional computed tomography (3DCT): A study of maxillary sinus in Malays. CJBAS. 2013;01(02). Page no. 125-34.
-
Tambawala S.S, Karjodkar F.R, Sansare Kanstubh, Prakash Nimish. Sexual dimorphism of maxillary sinus using Cone Beam Computed Tomography, Egyptian Journal of Forensic Sciences (2016)6. Page no. 120-125.
-
Azhar A, Ibrahim G, Salah F. Ct scan images analysis of maxillary sinus dimensions as a forensic tool for sexual and racial detection in a sample of kurdish population. ESJ. 2015;11(18). Page no.271-81.
-
M. SACCUCCI et.al., Gender assessment through three-dimensional analysis of maxillary sinuses by means of Cone Beam Computed Tomography. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences. 2015; 19. Page no. 185-193.
-
Teke HY, Duran S, Canturk N, Canturk G. Determination of gender by measuring the size of the maxillary sinuses in computerized tomography scans. SurgRadiolAnat 2007;29(1). Page no. 9–13.
-
ChaurasiaAkhilanand, Katheriya Gaurav. Morphometric evaluation of Bizygomatic distance and maxillary sinus width as dimorphic tool- A CBCT study. International Journal of Maxillofacial Imaging, October-December, 2016;2(4). Page no. 123-128.
-
Jehan M, Bhadkaria V, Trivedi A, Sharma SK. sexual dimorphism of bizygomatic distance & maxillary sinus using CT Scan. IOSR-J Dent Med Sci 2014;13(3). Page no. 91–5.
-
Vidya CS, Shamasundar N, Manjunatha B, Raichurkar K. Evaluation of size and volume of maxillary sinus to determine gender by 3D computerized tomography scan method using dry skulls of south Indian origin. Int J Cur. 2013;05(03). Page no. 97- 100.
-
Amin MF, Hassan EI. Sex identification in Egyptian population using multidetector computed tomography of the maxillary sinus. J Forensic Leg Med. 2012;19(2). Page no. 65– 69.
-
Baweja S, Dixit A, Baweja S. Study of age related changes of maxillary air sinus from its anteroposterior, transverse and vertical dimensions using Computerized Tomographic (CT) scan. IJBR 2013;04 (01). Page no. 22-25.
-
Jehan M, Bhadkaria V, Trivedi A, Sharma SK. sexual dimorphism of bizygomatic distance & maxillary sinus using CT Scan. IOSR-J Dent Med Sci 2014;13(3). Page no. 91–5.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License