IJCRR - 13(16), August, 2021
Pages: 03-09
Date of Publication: 30-Aug-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Evaluation of Temporomandibular Joint Disorders Among Delta State University Students in Abraka, Nigeria
Author: Ese Anibor, Yvonne O. Mabiaku, John C. Oyem, Vivian I. Ugbechie
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background and Aim of the Work: Population studies on the prevalence of Temporomandibular Disorders (TMD) and its symptoms amongst Nigerians overlap. Hence, this cross-sectional survey study assessed TMD prevalence, its symptoms, and causes among students attending Delta State University in Abraka, Nigeria. Methods: Three hundred and eighty-four students from Delta State University Abraka, Nigeria, were enrolled in this study and completed a self-administered questionnaire consisting of students' socio-demographic data and TMD symptoms. Data obtained from the survey were subjected to SPSS. A Chi-square test was used to test sex differences and the relationship between socio-demographic variables and TMD symptoms. Data were presented using pie charts and tables. Results: We recorded a TMD prevalence of 44%. Male had a higher TMD prevalence of 52.4% than females, who had a prevalence of 47.6%. Our findings demonstrated no significant relationship between sex and TMD prevalence, with significant associations between age and TMD symptoms. Pain on chewing was most common and closely followed by limitations in opening the mouth in subjects between 21 and 26 years. Our study demonstrated that TMD is caused by injury to the head and neck and stressful conditions in both sexes. Conclusion: TMD is highly prevalent among students attending Delta State University in Nigeria; its prevalence is higher in males than females, and most subjects experienced pain on chewing. Considering the high prevalence value of TMD recorded in this study, screenings should be recommended for its diagnosis and management.
Keywords: Temporomandibular, Disorders, Prevalence, Pain, Chewing, Mandible
Full Text:
Introduction
Temporomandibular joint disorders (TMD) represent common health disorders that encompass dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) and mastication muscles. This health problem is characterized by severe pain, followed by limited mandibular movements, and TMJ noise during jaw movement, mandibular deviation, and chewing disability.1, 2 Although the symptom associated with TMJ disorders is not life-threatening, it has been confirmed to pose adverse effects on an individual's health.3
The pathophysiology of this disorder is described to be multifactorial, resulting from several dental dysfunctions, including parafunctional habits, trauma, restorative procedures or orthodontic treatment, occlusion, emotional stress, trauma, the anatomy of the disc, pathophysiology of the muscles, psychosocial factors, genetics, age and gender. 4
The most prominent TMD symptom reported by patients and clinicians is pain; it is often the main reason patients seek medical help. 5 TMD pains result from mandibular movement; these pains cause restrictions in mandible movement and thus protect it from further damages. 6 TMD may also result from the pain associated with non-dental origin in the orofacial musculature, including the head, face, and related structure. 6] Although restriction in mouth opening is linked to painful mandibular movement, it may or may not be accompanied by pain. 7
Other common TMD symptoms include joint sounds (clicking or noise) and headaches. 8 In TMJ disorders, the joint sound is not often seen as a challenge but more as a possible cause. 9 Displacement of TMJ disc, condyle abnormalities, and mechanical disc distortion may cause joint noise without malfunction or pain. 9 Magnusson et al. (2005) showed an increase in TMJ sound incidence among patients between 15 and 25 years of age. 10
Susanna and Anders in 2007 carried out a cross-sectional survey aimed at investigating TMD prevalence during a one-year period and to investigate confounders linked with TMD manifestations. 11 The clinical manifestations examined in their study-included mobility, pain and TMJ sounds, morphological and dental functional occlusion. Their findings revealed that the prevalence of TMJ manifestations was 12%, with no gender difference. Other findings, such as reported TMJ sounds, accounted for 10%, while clinically registered TMJ pain accounted for 8%. However, the 1-year prevalence of TMJ pain and dysfunction was highest among 1st-year university students.
Another cross-sectional survey study aimed at evaluating the relationship between nutritional and parafunctional habits and the TMD incidence in children with primary dentition demonstrated that atypical swallowing and feeding methods were not determinants for TMD occurrence in the studied population. 12
Soukaina and colleagues in 2009 carried out a study on the incidence of TMD amongst Jordan University students. 13 They reported earaches or pain around the cheek as the most frequent symptom faced by TMD patients, followed by joint clicking (sound). Bora et al. (2012) investigated TMD incidence and manifestations among patients referred to the Prosthodontics unit. 14 Temporal muscle pain was the most prominent, followed by pain during TMJ movement (89%) in males and females. TMJ and masseter muscle pains, grinding, clicking, and anti-depressant use was reported in females compared to males. Age had a significant association with the incidence of TMD. They concluded that girls had more TMD compared to boys in their study population. The most frequent classical sign reported in both genders was pain.
Ahmed and Abuaffan (2016), in their special issue on TMD prevalence among University of Sudan students, showed 77.8% of the participants experienced TMD symptoms while 22.8% of the participants were negative. 15 They recorded a very high prevalence (77.8%), with 43.5% clicking (highest recorded symptom), which was followed by joint tenderness 123 (31.6%).
The incidence of TMD in different study populations reported in different cross-sectional studies varies widely across different populations because of variations of examining practitioners and racial differences, different criteria for diagnosis, and different examination methods. 16
A large body of work had successfully investigated the prevalence of the temporomandibular joint disorder in different populations globally. 10 - 16 Nevertheless, there is an overlap in TMD prevalence in some study populations in Nigeria; therefore the current study investigated the incidence of TMD and its manifestations among Delta State University Students in Abraka, Nigeria.
Materials and Methods
Study Design and Area: This study adopted a descriptive cross-sectional survey and was carried out among Delta State University (DELSU) students, in Abraka. Initially, the institution was a Government Teachers Training College. From 1971 – to 1985, It became a College of Education that issued the Nigerian Certificate of Education (NCE). In 1981 – 1985, the Faculty of Education of the former Bendel State University was affiliated to the University of Benin, Benin City. The establishment of the Edo and Delta States in August 1991 and the conversion of the then Bendel State University's main campus, Ekpoma, to Edo State University in December 1991, mandated the establishment of an autonomous Delta State University, Abraka, on 30th April 1992. Its main campus is in Abraka, Delta State, and other campuses are situated in Anwai and Oleh. Delta State University, Abraka comprises ten faculties, including the Faculty of Basic Medical Sciences.
Sample and Sampling Techniques and Sample size: Authors adopted the multistage/cluster sampling technique for this research work, while the sample size constituted 384 participants, made up of 196 males and 188 females.
Subject Selection Criteria: Students of DELSU, Nigeria, who gave their consent to participate and were between the age range of 15 – 32 years were included in this study. Incomplete questionnaires were excluded. Also, participants with occlusal splints, dental prosthesis, facial and dental anomalies, and extensive dental destruction were excluded from the present study.
Ethical consideration: Approval for this study was obtained from the Research and Ethics Committee of the Department of Human Anatomy and Cell Biology, Faculty of Basic Medical Sciences, DELSU, with IEC number DELSU/CHS/ANA/2017/118. Informed consent was also obtained from all participants. The study adopted the ethical guidelines of Helsinki's Declaration.
Procedure and Protocol for Data Collection
A well-structured self-administered questionnaire was used for data collection. The survey questions contained the following details; age, sex, marital status, joint sound, limitations in opening the mouth, earache, joint locking, pains associated with chewing, head and neck injury, and stressful conditions . Each participant was examined based on the features listed above.
Data Analysis: Data obtained was subjected to Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS version 22). Results were presented in frequency distribution, pie charts, and cross-tabulation. Chi-square test was used to test for significant gender differences at a confidence level of 95%, while P ≤ .05 was considered as statistically significant.
RESULTS
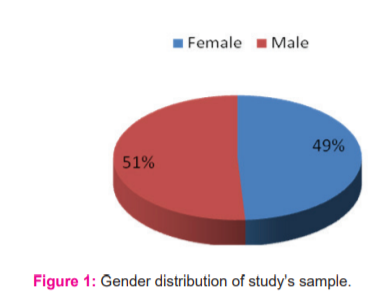
The pie chart above (figure 1) shows that out of the 384 subjects who responded to the questionnaire and were considered fit for this study, 49.0% were female while 51.0% were male participants.
TMD prevalence was found in 44% of the studied population. Asymptomatic subjects or subjects who had no form of TMD accounted for 56%.
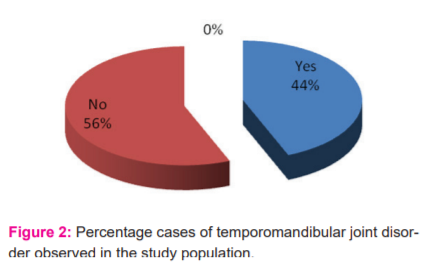
Table 1 shows that out of the 168 subjects who had TMD, 55 and 54 participants respectively who were aged between 21 – 26 years who experiences pain on chewing and limitation of mouth opening have the highest frequency of occurrence. Symptoms like presence of joint sound seen in 31 participants and limitations of mouth openings also seen in 31participants recorded the highest frequency in females aged between 21 – 26 years while pain on chewing seen in 29 participants recorded the highest frequency in males of the same age group.
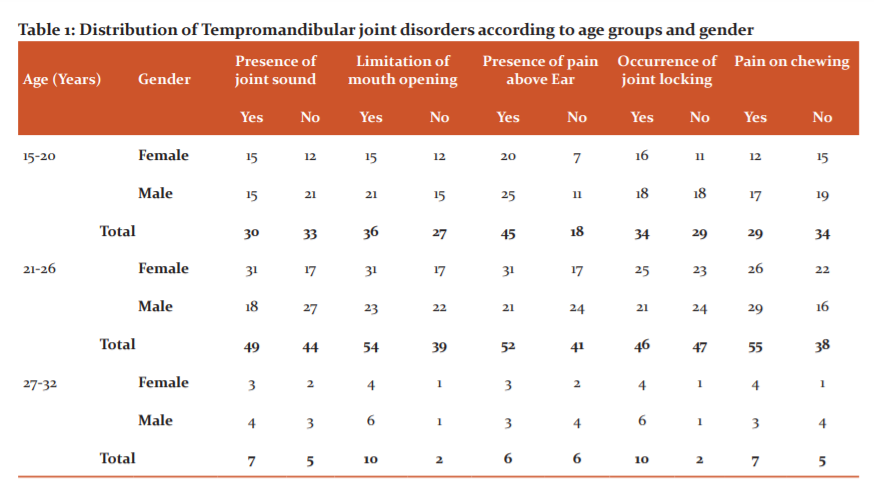
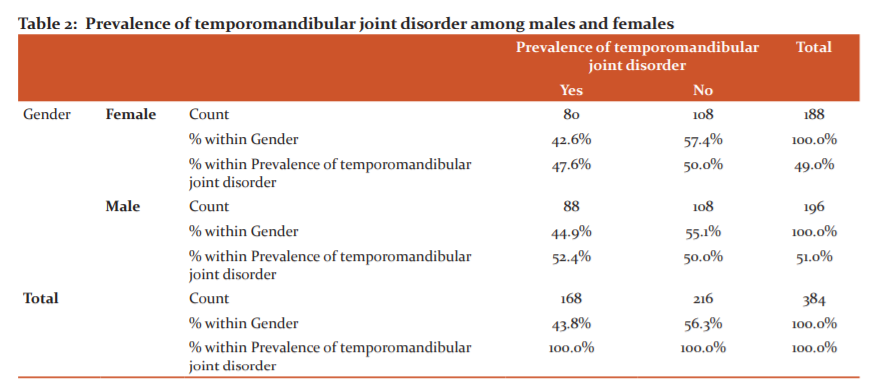
Table 2 showed the comparison between the prevalence of TMD and gender. Males were reported to have a higher percentage of TMD (52.4%) compared to females who had a lower percentage of TMD prevalence ( 47.6%).
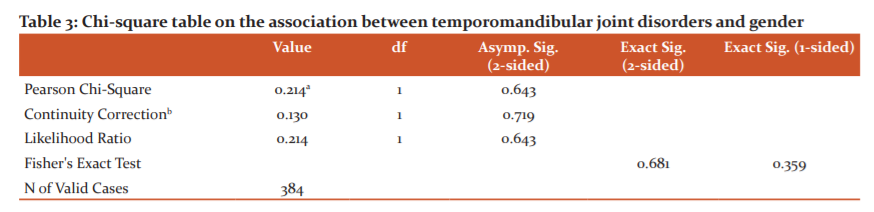 From the Chi square table (table 3) above the P value is eequals 0.643. This implies a no significant association between TMD occurrence and gender (P=0.643).
From the Chi square table (table 3) above the P value is eequals 0.643. This implies a no significant association between TMD occurrence and gender (P=0.643).
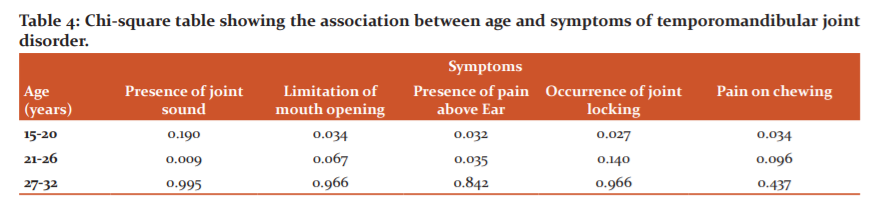
In examining the association of these symptoms with age using chi-square test, there was a significant association (P<0.05) between age group 15-20 years and limitations of mouth opening (p= 0.034), presence of pain above the ear (p=0.032), the occurrence of joint locking (p=0.027) and pain on chewing (p=0.034). A significant association was also observed between participants who are 21 – 26 years and symptoms like the presence of joint sound (p=0.009) and pain above the ear (ear ache (p= 0.035) (table 4). Table 4 also showed no significant relationships between subjects aged 27 – 32 years and TMD symptoms.

Table 5 shows that the most common cause of temporomandibular joint disorder in females is stress, which accounts for 85.6% while in males 77.6% reported that TMD results from head and neck injury while 77.0% reported that TMD results from stress.
Discussion
Temporomandibular joint disorder (TMD) is described as a universal set, which encompasses pain and dysfunctions in mastication muscles. 2 This multifactorial disorder is characterized by medical, mental, and dental dysfunction, including posture, parafunctional habits, orthodontic treatment, emotional stress and depression, trauma, disc displacement, age and gender, genetics, and muscle pathophysiology. 1 Understanding the early symptoms of the disease in younger generations is a key to its management and minimizing its impacts on individuals. 17 Thus, we evaluated TMD prevalence and symptoms among students aged 15 – 32 years attending Delta State University in Abraka, Nigeria.
We recorded a TMD prevalence of 44%. The prevalence rate in the current study was lower than that recorded by Alzarea (2017), 18 who reported a prevalence of 60.5% in Saudi Arabia, and that of Ahmed et al. (2018), 19 who recorded a prevalence of 77.2% among the University of Sudan students, but more significant than the prevalence rate (2.5%) recorded by Deepak et al. (2013), [20] in Himachal Pradesh, an Indian population. The prevalence value obtained in the current study may be attributed to the variation of age, criteria for diagnosis, and different examination methods. 16
Our study recorded a higher percentage of TMD prevalence in males compared to females. However, this association was not significant. This implied that TMDs are not gender-specific but higher in males than females in the studied population. This finding corroborated with that reported by several authors who stated no gender specificity in their studied population. 17, 21, 22 However, the prevalence value recorded in males from our study was higher than that observed by Nazih et al. (2015) in a Lattakia, Syria population, which recorded a prevalence of 34.92% in males. 23 These differences in findings could be linked to the awareness program implemented in the 21st century in Syria, which has exposed individuals to better and safety acts. 23
In this current study, we hypothesized significant associations between age and TMD symptoms across genders. We showed that TMD's signs and symptoms increase as age increases, and it affected mostly individuals that are 15 to 26 years, and as such, it becomes imperative for the early diagnoses and management of TMD. Interestingly, we observed a significant relationship between participants' age and TMD symptoms. Females between the ages of 21 and 26 who experienced joint pain had higher significant values than males in the same group. A similar observation was noted in a study by Bora et al. (2012), who noted significant gender differences regarding TMJ sounds (P<0.05) among patients referred to the Department of Prosthodontics, Trabzon in Northeastern Turkey. 14 Some studies reported that TMJ disc displacement, condyle morphology alterations, and mechanical disc distortion might cause joint noise without pain or joint dysfunction.9, 22 Consequently, clicking sounds was demonstrated to increase with age. Joint sounds may be caused by an incompatibility of the fossa and condyle contour due to calcification or modifications in its growth rate. 24
A slight sex difference was demonstrated in subjects that experienced pains on chewing across the age groups, with males having higher frequencies than females. Pains on chewing were the most prominent classical sign experienced by subjects, followed by limitations while opening the mouth. This finding is synchrony with the survey conducted by Soukaina et al. in 2009, who reported pain above the ear as the most experienced TMD symptom amongst Jordan University students. 13 Bora et al. reported a similar observation that the most common signs were pain in the temporal muscle, accompanied by pain during the mouth's opening in both sexes. This result pattern might be due to stress, head, and neck injury, as demonstrated by the current study. These two factors may result from wearing and tearing the chewing muscles, leading to difficulty opening the mouth and pains while chewing. Moreover, according to Farsi et al. (2003), TMD pains result from mandibular movements at rest or on palpation of the muscle and muscular activity modifications. 6
Our study showed significant sex differences in participants who reported limitations while opening the mouth as one of the classical signs of TMD. Male participants aged between 21 and 26 had higher frequencies than females, while females aged between 15 and 20 years have higher frequencies than males. We also recorded no significant gender difference and lesser frequencies among participants aged between 27 – 32 years who complained of limitations while opening the mouth. This was not in tandem with the survey carried out by Nazih et al. (2015), who observed a higher frequency in older populations. 23 Reasons for this dissimilarity may be due to the relatively large sample size employed in Nazih's study. Limitations when opening the mouth were the second prominent symptom of TMJ disorders reported among DELSU students. This contrasts with the findings reported by Ahmed and Abuaffan (2016), which identified limitation in mouth opening as the least symptoms faced by TMD patients in their survey in Sudan students. 15 The present study also showed that girls aged between 15 – 20 years have an excellent joint locking experience than boys among subjects who experienced joint locking. This observation agrees with the survey carried out by Soukaina and colleagues in 2009, who reported age group 20 -21 having the highest frequency (15.5%) of joint locking. 13
Another notable observation in our study is that males have the highest head and neck injury frequency than females. This agrees with Ahmed and Abuaffan's (2016) findings, who noted a similar result pattern. [15] Such observations can be credited to higher head trauma cases in males than females; males are actively involved in sports, reckless driving, and violent plays. Surprisingly, we also discovered that TMD caused by stress was higher in females compared to males. Ahmed and Abuaffan (2016) reported that TMD is more related to stress in males than in females in their studied population. 15 Bora et al. (2012) also reported that anti-depressant use was substantially more common in females than in males. 14 Although males are affected by stressful conditions, females have experienced higher levels of anxiety and stress—a study conducted in the past linked the influence of emotional stress on mastication muscles. Emotional stress leads to teeth clenching that produces blood circulation changes to the masticators, compression of pain receptors leading to edema in the muscle. 25
Reasons for this finding may be linked to Neurocognitive conditions that affect an individuals' mental health and are closely linked to TMD; heightened levels of stigmatization, depression or anxiety have been reported to affect TMD patients negatively compared to people without it. 26
Conclusion
The prevalence of TMD in this studied population was 44%, with males having a higher, TMD prevalence than females. Participants' age varied significantly with TMD manifestations, and almost all participants experienced pains and limitations while opening their mouths. The main causes of TMD, as demonstrated in the current study were head and neck injury and stress factors in both sexes. The authors recommend early screenings of TMD at health facilities because understanding the early symptoms of the disease in younger generations is a key to its management and minimizing its impacts on individuals as well as reducing its prevalence. Our study was conducted on a smaller sample size in Nigeria- therefore, a nationwide study should be conducted in larger sample sizes or other regions in Nigeria on the prevalence of TMD and its manifestations to create baseline data for its detection and diagnosis. In addition, findings from this study should be presented at hospitals and primary health care facilities to educate the masses as well as develop preventive strategies for the management of TMD. Furthermore, a similar study on TMD should employ the use of imaging modalities in the diagnosis in TMD because physical screening may present misleading results while imaging modalities provide additional information on suspected TMD manifestations.
Acknowledgment: Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Sources of funding: Nil
Author’s contribution: Ese Anibor: acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data for the research work; revising the article critically for important intellectual content. John C. Oyem
Drafting the manuscript, revising the article critically for important intellectual content. Yvonne O. Mabiaku: revising the article critically for important intellectual content. Vivian I. Ugbechie: substantial contributions to the conception or design of the research work.
References:
-
Cooper BC, Kleinberg I. Examination of a Large Patient Population for the Presence of Symptoms &Signs of Temporomandibular Disorders. J Craniomand Sleep Prac. 2007; 25(2): 114-126
-
Mujakperuo HR, Watson M, Morrison R, Macfarlane. "Pharmacological interventions for pain in patients with temporomandibular disorders". The Cochrane Database of Sys Rev. 2010;(10): CD004715.
-
Shi Z, Guo C, Awad M. "Hyaluronate for temporomandibular joint disorders". Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2003(1): CD002970.
-
Jensen R. Pathophysiological mechanisms of tension-type headache: a review of epidemiological and experimental studies. Cephalalgia. 1999;(19):602-621.
-
Dao TT, LeResche L. Gender differences in pain. J Orofac Pain. 2000;(14): 169-84.
-
Farsi NM. Symptoms and signs of temporomandibular disorders and oral para functions among Saudi children. J Oral Rehabil. 2003;(30): 1200-1208.
-
Cairns BE. Pathophysiology of TMD pain – basic mechanisms and their implications for pharmacotherapy. J Oral Rehabil. 2010;(37):391 - 410.
-
Schmitter M, Rammelsberg P, Hassel A. The prevalence of signs and symptoms of temporomandibular disorders in very old subjects. J Oral Rehabil. 2005;(32):467-473.
-
Tanaka E, Detamore MS, Mercuri LG. (2008). Degenerative disorders of the temporomandibular joint: etiology, diagnosis, and treatment. J Dent Res. 2008;(87):296-307.
-
Magnusson T, Egermarki I, Carlsson GE. A prospective investigation over two decades on signs and symptoms of temporomandibular dis-orders and associated variables. A final summary. Acta Odontol Scand. 2005;(63):99-109.
-
Sussana M. Anders W. Incidence and prevalence of temporomandibular joint pain and dysfunction. A one-year prospective study of university students. Acta Odontol. Scand 2007;65(2):119-27.
-
Castelo PM, Gavião MBD, Pereira LJ, Bonjardim LR. Relationship between oral parafunctional/nutritive sucking habits and temporomandibular joint dysfunction in primary dentition. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2005;15(1):29-36.
-
Soukaina R, Zaid HB, Wala MA, Faleh S, Osama S, Darwish HB. Prevalence of Temporomandibular Joint Disorders Among Students of the University of Jordan. J Clin Med. 2009;1(3): 158-164.
-
Bora B, Elif AA, Sedanur T, Rukiye D, Mutlu O. Gender difference in Prevalence of Signs and Symptoms of Temporomandibular Joint Disorders. a Retrospective Study on 243 Consecutive Patients. Int J Med Sci. 2012; 9(7): 539-544.
-
Ahmed LI, Abuaffan AH. Prevalence of Temporomandibular Joint Disorders Among Sudanese University Students. J Oral Hygiene Health. 2016; (4): 200.
-
Sena MF, Mesquita KS, Santos FR, Silva FW, Serrano KV. Prevalence of temporomandibular dysfunction in children and adolescents. Rev Paul Pediatr. 2013; 31(4):538-45.
-
Fernandes G, van Selms MK, Goncalves DA, Lobbezoo F, Camparis CM. Factors associated with temporomandibular disorders pain in adolescents. J Oral Rehabil. 2015; (42): 113 -119.
-
Al Zarea BK. Prevalence of temporomandibular dysfunction in edentulous patients of Saudi Arabia. J Int Oral Health. 2017;(9):1-5.
-
Ahmed MR, Khalid B, Orakzai GS, Khan RS, Mahmood A, Hassan R.: DentistryIncidence of Temporomandibular Disorders Among Dental Students. Int J Contemp Med Res. 2018;5(4): 23.
-
Deepak G, Amar SR, Varun KV. Treatment of recurrent TMJ dislocation in geriatric patient by autologous blood – A technique revisited. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2013;(1):39–41.
-
Al-Khotani A, Naimi-Akbar A, Albadawi E, Ernberg M, Hedenberg-Magnusson B, Christidis N. Prevalence of diagnosed temporomandibular disorders among Saudi Arabian children and adolescents. J Headache Pain. 2016;(17): 41.
-
Franco AL, Fernandes G, Goncalves DA, Bonafe FS, Camparis CM. Headache associated with temporomandibular disorders among young Brazilian adolescents. Clin J Pain. 2014;(30): 340-345.
-
Nazih I, Naser B, Maria M. Prevalence of Symptoms of Temporomandibular Joint Disorder in Lattakida, Syria. Int J Biomed Eng Clin Sci. 2015;1(2): 23-28
-
Torii K. Longitudinal course of temporomandibular joint sounds in Japanese children and adolescents. Head Face Med. 2011;(7): 17.
-
Christensen LV. Facial pain and internal pressure of masseter muscle in experimental bruxism in man. Arch Oral Biol. 1975;(16):1021-31.
-
Ferrando M, Andreu Y, Galdón MJ, Durá E, Poveda R, Bagán JV. Psychological variables and temporomandibular disorders: distress, coping, and personality. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2004;98(2):153-60.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License