IJCRR - 13(15), August, 2021
Pages: 89-94
Date of Publication: 10-Aug-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Efficacy of Cervical Manipulation on Hand Grip Strength and Upper Limb Function: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Author: Anjali, Malik M, Gera C, Kaur J
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Non- specific neck pain is the most common health concern among the general population. It leads to functional disabilities of upper limb and pain. Assortment of approaches includes manual therapy has been used for the management of neck pain. Improving Grip strength, reducing functional disabilities of upper limb and reducing pain intensity are important objectives in the treatment of non-specific neck pain. Methods: A randomized, controlled trial with concealed allocation, intention-to-treat analysis and blinded assessors in which patients were randomly allocated into 2 groups; Experimental group (n=26) and Control group (n=26). Patients in experimental group were received the cervical manipulation session; hot pack and TENS for two weeks. Patients in control group were received the hot pack and TENS alone for two weeks Participants were recruited from different clinics and hospitals of Hisar. The outcomes were DASH Score and hand grip strength. All subjects were evaluated at the baseline and post session (after 2 weeks). Results: A total of 52 subjects were participated in the study, including 18 males and 33 females. The mean ages of the subjects were 33.05 years old. Data analysis was done by using paired t \?test. This study resulted that the grip strength and DASH Score after the intervention were significantly improved in experimental group as compared to control group. In addition, the performance of hand grip strength [left (p≤0.000) (95% CI= -13.11, -9.85) and right (p≤0.000) (95% CI= -12.57, -9.85] and upper limb functions [DASH Score (p≤0.000) (95% CI= -14.25, -19.46] was superior in experimental group as compared to that of the control group. Ethics and Dissemination: The proposed examination was done after moral endorsement from the Institutional Ethics Committee, Departmental Research Committee, and B.O.S. & R. of the Department of physiotherapy, G.J.U.S&T, Hisar in September 2019, Vide letter no. PTY/2019/1014, dated 11.09.19. Conclusion: Cervical manipulation can improve the Hand grip strength and upper limb functions in non-specific neck pain.
Keywords: Cervical manipulation, Manualtherapy, Gripstrength, Upper limb function, Non-specific neck pain and DASH score
Full Text:
Introduction
“Non-specific neck pain (NP) is characterized as pain in the back and parallel part of the neck between the superior nuchal line and the spinous process of the thoracic vertebra without any signs or indications of major basic pathology and no significant impedance with exercises of everyday life just as with the absence of neurological signs and explicit pathologies like fracture and tumor”.1
Non – explicit neck pain may radiate down to the shoulder, arm, and fingers giving "a tingling sensation", crunching sound when turning the neck, functional limitation, and pain while moving the neck.2 Upper appendage disability can be estimated utilizing the inability of the arm, shoulder, and hand (DASH) scale which is a reliable outcome measure in estimating upper appendage incapacity in vague neck pain. Handgrip strength can be evaluated by estimating the measure of static power that the hand can press around a dynamometer.3
The primary symptom of non-specific neck pain is the pain around the cervical area, occipital area, suboccipital muscles, shoulders, and upper appendages. Numbness, paresthesia, tingling, and weakness also occur in upper appendages. Tenderness is also present, mainly in the lower cervical areas (C5-C6), where disc degeneration is progressively obvious.4 The cause of neck pain can be disc herniation, extreme movement of the cervical spine, long term awkward posture and lifestyle choices, and tissue injury in the neck. Cervical stability continuously diminishes and can prompt the loss of cervical lordosis.5Assortment of approaches has been successful for the management of neck pain. These strategies of treatment include home exercise programs, manual therapy, endurance training, strength training, and electrotherapy modalities.6
Manual therapy such as cervical mobilization and cervical spinal manipulation (CSM) are used as an effective treatment of patients with neck pain and headache. CSM is defined as low amplitude and high velocity thrust that applied passively to articular surfaces of a joint within its anatomical limit to restore functionsand to reduce pain. 7 Manipulation of the spine involves a high –velocity thrust that is applied through either a long or short lever arm. The “long lever” method involves numerous vertebral articulations at the same time (e.g. rotatory manipulation of the thoracolumbar spine) while the “short –lever” method include a low amplitude thrust that is aimed at a particular degree of the vertebral segment. Manipulation has been utilized in the treatment of muscle tension-type headache, migraine, neck pain, and stiffness. Mobilization includes low -velocity passive movement which can be halted by patient. The speed of the technique (not really the measure of power), in this manner, separates manipulation from mobilization.8 Literature suggests that the use of manual therapy (manipulation & mobilization) can reduce pain and functional limitation in patients suffering from non-specific neck pain.
The present study was done to evaluate the efficacy of cervical manipulation on handgrip strength and upper limb functions in patients of non-specific neck pain.The study includes Grip strength as an outcome measure because in this study we want to show the impact of neck pain on hand grip strength and if the neck disability index was considered as an outcome measure than the focus of the study would be neck disability instead of hand grip strength.As the title of the study was "Efficacy of Cervical Manipulation on Hand Grip Strength and Upper Limb Function" so in this study grip strength took as primary outcome measure.
Methodology:
A randomized controlled preliminary was conducted after approval from the Institutional Ethics Committee of the Department of Physiotherapy, G.J.U.S&T, Hisar. The RCT was registered with the Clinical trial registry of India (Registration no. CTRI/2020/01/022638.
Consent was taken from each participant. Following study enrollment and completion of baseline evaluation, members were arbitrarily designated into the experimental or control group using computer generated random number tables and delineated by gender.
Sample size calculation
The sample size was calculated using (Minimally Clinical Important Difference) MCID of DASH score=13.0 along with standard deviation of DASH score=17.6 from previous studies considering a dropout rate of 5%. 9 Using the following formula.10
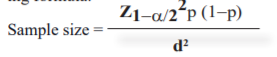

Here, Z1-α/2 = is standard normal variate as in most of the studies P esteems are viewed as huge underneath 0.05, thus 1.96 is utilized in equation
p = Expected extent in population dependent on past investigations or pilot considers
d = Standard deviation.
Selection criteria
Patients suffering from non -specific neck pain were included in this study. In the study patients with radicular and withoutradicular pain both were included. Patients having a complaint of neck pain with age group between 18-65 years who did not receive any concomitant intervention for neck pain were included in this study. Patients having a past history of stroke or transient ischemic attack, severe neck pain due to infection, fracture, progressive neurological deficiency, herniated nucleus pulposus, and myelopathy were excluded from selection criteria.
Procedure:
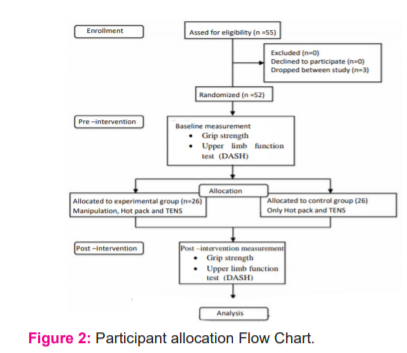
52 subjects took part in the examination, including 19 guys and 33 females. The participants were randomly allocated into 2 groups i.e. Experimental group (n=26) and the Control group (n=26) respectively as explained in the flowchart of Figure -2. Grip strength was evaluated by using a handheld dynamometer and upper limb functions were assessed by the DASH (disabilities of the arm, shoulder, and hand) scale. To measure grip strength we used a Jamar hydraulic dynamometer that is an easy, fast, and reliable method. The Jamar hydraulic dynamometer was seen as exceptionally dependable (ICC= 0.98) i.e. 98% and substantial (ICC =0.99) i.e. 99% for estimating handgrip strength. 11 The dynamometer was lightly held around the readout dial by the examiner to prevent inadvertent dropping. As shown in Figure-1 the subjects were in sitting situation with their shoulder adducted, impartially pivoted elbow flexed at 90° lower arm in nonpartisan position, wrist between 0-30° dorsiflexion and 0-15° ulnar deviation for each strength test scores were recorded for each treatment. The therapist was standing in front of the subject.
Assessment and examination: Patients were thoroughly assessed and examined by using palpation and prone leg length test to evaluate cervical malalignment. Functional movements were examined for any limitation and dysfunction. Special tests like the Spurling test and slump test were used to exclude specific pathologies.

Intervention: Before giving any intervention, the pre-intervention data was collected in which the handgrip was measured Experimental group received sessions of cervical manipulation, hot pack, and TENS for two weeks, thrice weekly. Cervical manipulations include: Axis lateral correction technique, Atlas correction, and Diagonal correction atlantoid arch, “The Pistol”- Ventral malaligned vertebrae, Rotational adjustment of the axis, Rotational correction of C3-C6 and C7 rotation correction.
The subjects in the Control group received only a hot pack and TENS for two weeks, thrice weekly. After 2 weeks post-intervention of handgrip strength and upper limb functions were re-evaluated. Data so obtained was analyzed for any statistical significance ( Figure 2).
Data analysis:
Outcome measures were analyzed for any statistical significance. SPSS latest version 26 programming was utilized to break down the information. Assessment for the differences between pre- and post- grip strength and DASH score of experiment and control group was done by Paired t-tests. The mean change in grip strength and DASH score between groups was compared to the independent t-test. P esteem was set at ≤ 0.05 level. 95% certainty 95% confidence interval was also Calculating
RESULTS:
A total number of 52 patients with non-specific neck pain were randomized into experimental (n=26) or control group (n=26). Intention to treat analysis was done. The mean age of patients in the experimental group was 31.15 and in the control group was 35.12. Three patients dropped out of the study. The post-intervention data were collected for ‘Intention to treat analysis’.Baseline characteristics were similar between the two groups
Baseline Comparisons-
As shown in Table 1 the baseline comparisons of outcome measure between the Experimental and Control Group. Baseline data was analyzed for any statistically significant difference. The Analysis shows that the baseline data was similar (p-value= 0.113, 0.130 and 0.04 respectively)
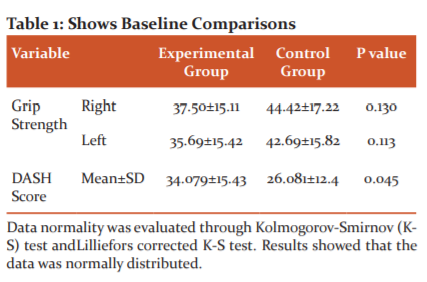
Data normality was evaluated through Kolmogorov-Smirnov (K-S) test andLilliefors corrected K-S test. Results showed that the data was normally distributed.
-
Pre-Post comparison-
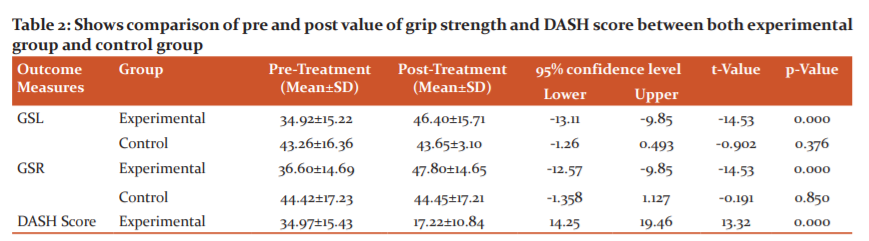
Results show a statistically significant improvement in Experimental group as compared to control group. As shown in Table-2 the grip Strength left (p≤0.000) (95% CI= -13.11, -9.85) and right (p≤0.000) (95% CI= -12.57, -9.85) as well as DASH Score (p≤0.000) (95% CI= -14.25, -19.46) were improved significantly in experimental Group. However, there was no significant improvement in control group.
-
Comparison between Groups:
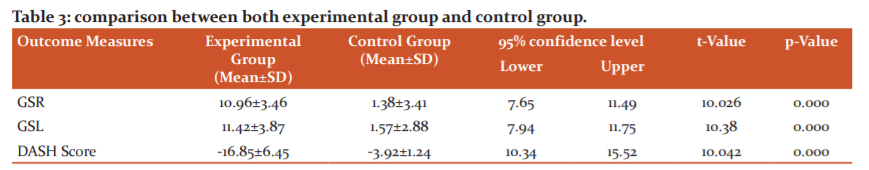
The examination between the experimental and control groups as shown in Table 3. Results show a statistically significant improvement of Experimental group (p≤0.00)in terms of grip strength right (MD=10.96; 95% CI= 7.65, 11.49), left (MD=11.42; 95% CI= 7.94, 11.75) and DASH score (MD=-16.85; 95% CI= 10.34, 15.52) as compared to control groupin grip strength right (MD=1.38), left (MD=1.57) and DASH score(MD=-3.92).
DISCUSSION:
The essential goal of this examination was to explore the impact of cervical manipulation on handgrip strength and upper limb functions. Effect of grip strength was evaluated using a hand-held dynamometer and upper limb function was evaluated using DASH questionnaires. DASH is a valid and reliable tool for testing upper limb disability.3
Data was analyzed by using a t-test and significant positive improvements in handgrip strength and upper limb functions were observed. Results of the present study suggest that cervical manipulation is effective in the improvement of grip strength and upper limb function in patients with non-specific neck pain. The Experimental group had a statistically significant increase in grip strength and decreases in hand and shoulder disability. The grip strength is a decline in subjects suffering from severe neck pain. 12 Reduction of hold quality and continuance is because of the impedance with the capacity of the nervous system to start hand muscle through motor units. Besides, fear-avoidance reaction was found in patients with incessant neck torment inspired by a paranoid fear of injury prompts disuse atrophy and decreases the inability to produce and retain force.2
Cervical manipulation can be beneficial in non-specific neck pain patients. Spinal manipulation works via neurophysiological and biomechanical mechanisms. During manipulation, the application of mechanical force may start many neurophysiological reactions that cause an increase in range of motion and decrease in pain.13 The experimental group end up being more helpful in all terms in treating mechanical Neck Pain and pain referred to the upper limb. Firstly, this can be since grip strength had straightforwardly identified with neck pain as grip strength was diminished in neck pain with serious neck disability. Hence, neck pain, grip strength, and neck inability are negatively correlated. 14 Grip strength was influenced by motor control. The neck muscles in the presence of neck pain and isometric muscle fatigue affect the handgrip. 15
Results showed a significant decrease in the DASH Score of experimental group i.e. improvement in useful exercises as per DASH with (p<0.001), therefore demonstrating the efficacy of cervical manipulation in improving functional abilities of patients with non-specific neck pain. The current examination had both abstract and target result measures and their outcomes are statistically significant. All the manipulative therapies not to have a similar impact and the differentiation may be mediated by neurological or biomechanical factors inalienable to each technique. Furthermore, the present study included TENS and Hot pack along with the manipulation.2Heat is mediated by calcium channels by increasing intracellular calcium. This influences the pain by generating action potentials and stimulation of sensory nerves. As heat relaxes the muscles and increase the circulation of the surface so the manual treatment can be done effectively. Apart from this, TENS activates the descending pain suppression system by stimulating large diameter afferent fibres that leads to reduction in pain. 16In this present study, the subjects of the experimental group were treated with cervical spine manipulation showed more improvement in handgrip strength and reduced disability of the upper appendage in subjects with vague neck torment when contrasted with Control Group.17
Future studies can be done to optimize the doses of cervical manipulations. Future examinations should likewise be possible to research the biomechanical instruments of manipulation. More ever, study the impacts of power application (sum and rate) and manipulation technique on spine kinematics during manipulation and to explore the relationship between these variables just as clinical and useful results after high – speed low amplitude manipulation. This was a solitary driven examination and extend or long term follow-up impacts were not checked. Besides, the impacts of just six sessions were evaluated. On the off chance that more number of meetings was incorporated, the patients would get totally recuperated. Intense and ceaseless cases dependent on the span of indications were not independently arranged.
CONCLUSION:
This study concluded that the experimental group showed significant improvementinincreasing Grip strength and reduced upper arm disability in patients with non-specific neck pain as compared to control group. Hence, cervical manipulation can be effective treatment in patients with non-specific neck painThis study is clinically significant as manual therapy can be used as an adjuvant therapy in the management of non-specific neck pain all over the world. Also this study is cost- effective and reduces the dependency on drug-dosages.
Declaration of Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Funding: This trial did not receive any grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sector.
Acknowledgement:
Authors acknowledge the support from the staff and O.P.D. of Department of Physiotherapy, GJUS&T, Hisar and its supporting staff.
Authors Contribution:
Authors Anjali and Malik M contributed with patients’ recruitment, datacollection. Gera C and Kaur J participated in thedesign of the study; Malik M carried out clinicaltests; Gera C and Kaur J draftedthe manuscript and Anjali and Malik Mperformed the statistical analysis.
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
References:
1. Hidalgo B, Hall T, Bossert J, Dugeny A, Cagnie B, Pitance L. The efficacy of manual therapy and exercise for treating non-specific neck pain: A systematic review. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2017;30(6):1149–69.
2. Gauns S V, Gurudut P V. A randomized controlled trial to study the effect of gross myofascial release on mechanical neck pain referred to upper limb. Int J Heal Sci (Qassim). 2018; 12(5): 51–59.
3. Roh YH. Clinical evaluation of upper limb function?: Patient’s impairment, disability and health-related quality of life. J Exercise Rehabil. 2013;9(4):400-405.
4. López-de-Uralde-Villanueva I, Sollano-Vallez E, Del Corral T. Reduction of cervical and respiratory muscle strength in patients with chronic nonspecific neck pain and having moderate to severe disability. Disab Rehabil. 2018;40(21):2495–504. https://doi.org/10.1080/09638288.2017.1337239
5. Mahmoud NF, Hassan KA, Abdelmajeed SF, Moustafa IM, Silva AG. The Relationship Between Forward Head Posture and Neck Pain?: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Curr Rev Musculosk Med. 2019;12:562–577. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12178-019-09594-y.
6. Hurwitz EL, Morgenstern H, Harber P, Kominski GF, Yu F, Adams AH. A Randomized Trial of Chiropractic Manipulation and Mobilization for Patients With Neck Pain?: Clinical Outcomes From the UCLA Neck-Pain Study. Am J Public Health. | 2002;92(10):1634–41.
7. Kranenburg HA, Schmitt MA, Puentedura EJ, Luijckx GJ, Schans CP Van Der. Adverse events associated with the use of cervical spine manipulation or mobilization and patient characteristics: A systematic review. Musculosk Sci Pract . 2017; 28:32-38.http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.msksp.2017.01.008
8. Griswold DW, Learman K, Kolber MJ, Relief P, Cleland JA. Pragmatically Applied Cervical and Thoracic Non-thrust versus Thrust Manipulation for Patients with Mechanical Neck Pain?: A Multicenter Randomized Clinical Trial. J Orthop Sports Physical Ther.2018;48(3):137-145.
9. Koorevaar RCT, Kleinlugtenbelt Y V., Landman EBM, van’t Riet E, Bulstra SK. Psychological symptoms and the MCID of the DASH score in shoulder surgery. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):1-7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-0949-0.
10. Charan J, Biswas T. How to calculate sample size for different study designs in medical research? Ind J Psych Med. 2013;35(2):121–6.
11. Bellace J V., Healy D, Besser MP, Byron T, Hohman L. Validity of the Dexter Evaluation System’s Jamar dynamometer attachment for assessment of hand grip strength in a normal population. J Hand Ther. 2000;13(1):46–51.
12. Kalra S, Pal S. Correlational study of chronic neck pain and hand grip strength in physiotherapy practitioners.Int J Yoga, Physioth Phys Edu. 2017;2(4):30–2.
13. Anderst WJ, Ms TG, Ms CL, Bs SR, Dc KG, Dc MS. Intervertebral Kinematics of the Cervical Spine Before, During and After High Velocity Low Amplitude Manipulation.The Spine J.2018 Dec;18(12):2333-2342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spinee.2018.07.026
14. Ramdati V, Soni N. The correlation between chronic neck pain and hand grip strength indentists of gujaraT.Int J Curr Adv Res.2019;8(09):8–10.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.24327/ijcar.2019.3899.20029
15. Egwu MO, Ajao BA, Mbada CE, Adeoshun IO. Isometric Grip Strength and Endurance of Patients With Cervical Spondylosis and Healthy Controls: A Comparative Study. Hong Kong Physiother J. 2009;27(1):2–6. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1013-7025(10)70002-6
16. Vance CGT, Dailey DL, Rakel BA, Sluka KA. Using TENS for pain control: the state of the evidence. Pain Manag. 2014;4(3):197–209.
17. Bautista-aguirre F, Oliva-pascual-vaca Á, Heredia-rizo AM, Boscá-gandía JJ, Ricard F, Rodriguez-blanco C. Effect of cervical vs. thoracic spinal manipulation on peripheral neural features and grip strength in subjects with chronic mechanical neck pain: a randomized controlled trial.Eur J Physic Rehab Med. 2017 June;53(3):333-41 doi: 10.23736/s1973-9087.17.04431-8.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License