IJCRR - 13(15), August, 2021
Pages: 30-35
Date of Publication: 10-Aug-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Biosorption of Cadmium and Lead through Lactobacillus reuteri and Lactobacillus plantarum and its Exopolysaccharides: A Comparative Study
Author: Singh A, Saini P, Srivastava U, Kushwaha R
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Cadmium and lead are toxic elements among the heavy metals group. Through water, it enters into the food chain and became hazardous to all living bodies, so its removal is important. Biosorption through Lactic acid bacteria is the most effective technique for the removal of these hazardous metals from water even at very low concentrations. Aims: In the present study, using two strains of Lactic acid bacteria i.e. L. reuteri and L. Plantarum and its exopolysaccharides (EPS) biosorption of Cadmium and Lead were performed due to a well-known toxicant and hazardous to humans and other living bodies. Methodology: Firstly, EPS were isolated from both strains. Biosorption tests were performed using various condition like pH (pH2.0, 4.0, 6.0, 8.0), temperature (37\?C,42\?C and 50 \?C) and contact time (6, 24 and 48 hours). Cadmium and lead sorption were tested in both strains and their Exopolysaccharides through atomic absorption spectrophotometer (AAS). Results: Biosorption of cadmium through EPS was higher as compared to cells in both strains. Lactobacillus reuteri showed 89% biosorption of cadmium through EPS and EPS of Lactobacillus Plantarum showed 51% biosorption of lead. In the case of cells, biosorption of lead was more i.e. 57% through Lactobacillus reuteri and 43% through Lactobacillus Plantarum as compared to cadmium. Conclusion: Exopolysaccharides showed comparatively maximum biosorption as compared to cells. Both strains and their EPS biosorption may be applied in metal detoxification of the environment and different food and pharma industries.
Keywords: Atomic absorption spectrophotometer, Biosorption, Exopolysaccharides, Detoxification, Heavy metals, Lactic acid bacteria
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Water is essential for all types of living moieties. However, raised anthropogenic activities are causing high Cd and Pb exposure to the water bodies. These are the most toxic heavy metals, tending to accumulate in the environment occupationally and non-occupationally. These biodegradable hazards entered into the food chain through soil and water. 1, 2 Thus food and water are the primary sources of cadmium and lead exposure among the non-smoking population. However, excessive use of fertilizers in agriculture, dumping of sewage sludge, mining and smelters are anthropogenic sources that release cadmium and lead into the environment. Chronic exposure to these metals, even in very low quantities may lead to developing adverse health effects. 3,4,5 According to WHO and the Food safety standard act of India (FSSAI) the concentrations of cadmium and lead in water should not exceed the guideline values of 0.003and0.01mg/L, respectively. According to the Expert Committee FAO/WHO has set tolerable weekly intake of Cd at 7 mg/kg body weight through Food Additives.6 So the removal of these metals from the environment and even from the human body is essential.
Numerous conventional methods are being continuously used in the eradication of these heavy metals. But recently the biotechnological innovative technique biosorption is being explored as the most promising phenomenon. It is a physiochemical, economical and eco-friendly approach towards heavy metal removal. This process involves the removal of heavy metal through adsorption, surface precipitation complexation, and ion exchange mechanism.7 The biosorption process requires an aqueous solution of heavy metals and solid inactive biomass/ biosorbent materials for accumulating these metals.
Lactic acid bacteria are the most promising and efficient biosorbents used in different studies.8-12 LAB also has the potential of being probiotic. Due to probiotic characteristics, it has a great capacity of having antioxidant, antibacterial, antibiotic properties, tolerance against gastric juice and bile juice and heavy metals. Some species of lactobacillus mainly Lactobacillus Plantarum, Lactobacillus casei and others have characteristics of folic acid and B12 synthesis.13 LAB also has managing properties of lactose intolerance, cholesterol-lowering effect, improve cholesterol removal from the body through faeces, preventing cancers and improve immunity.14,15,16 It shows different health implications like probiotic effect, anti-gastric and antiulcer effect, cholesterol-lowering effect, anti-mutagenic property, Adhesion and Colonization and anti-tumour property.17,18,19 It has also a capacity of neutralizing the effect of heavy metal-induced free radical toxicity. Many of its species produce Exopolysaccharides (EPS), which has wide application in different industrial productions like cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, food production, biodegradable packaging etc.20,21 EPS synthesized by LAB play a major role in the manufacturing of fermented dairy products such as yoghurt, cheese, fermented cream, milk-based deserts etc. The major attributes for consumer preference of dairy products are firmness and creaminess. EPS can decrease syneresis and improve product stability. Therefore, it has been reported the EPS can positively affect gut health.22 EPS have potential in heavy metal binding and removal. Heavy metal binding by EPS is a metabolism-independent process; binding of metal is depending upon functional groups presents on EPS.23 In general the biosorption phenomenon is relatively economical and simple because of the low value associated with their commercial applications.24 To explore this applicability the study has focused on the biosorption of cadmium and lead through Lactobacillus reuteri and Lactobacillus Plantarum and their EPS.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains and culture
L.plantarum and L reuteri were used in the study, obtained from the National Collection of Dairy Culture (NCDC), ICAR- National Dairy Research Institute Karnal, India. The lyophilized cultures of L.plantarum and L reuteri were maintained in glycerol stock and from glycerol stocks transferred to de Man, Rogosa and Sharpe agar broth (MRS) plates and cultured anaerobically for 48h at 37°C. Bacterial strains were propagated twice at 37OC for 18 h in MRS broth with 2% (v/v) inoculum before the experiments Catalase test negative colony from the plate was transferred to MRS broth and incubated under anaerobic conditions for 48 h at 37°C. Both bacterial strains were subcultured twice before the experiment.
Extraction of bacterial culture
The bacterial strains of L.plantarum and L reuteri were cultured at 37°C for 18 h in MRS broth (Difco Laboratories, Detroit, MI) using a loopful inoculum in the Growth medium (De Man, Rogosa and Sharpe, specific media for LAB) containing glucose 10.0 g/L, peptone 5.0 g/L, yeast extract 3.0 g/L, malt extract 3.0 g/L, MgSO4 7H2O 1.0 g/L, KH2PO4 0.3 g/L, vitamin B1 0.001 g/L and pH was fixed at 6.5.25 The cells were separated by centrifugation at 5000 rpm for 15minutes. Bacterial cells after centrifugation were washed three times with sterile distilled water. Collected the cell palettes and freeze-dried.
Exopolysaccharide isolation and extraction
Both the strain were inoculated in the EPS production medium (MRS Broth) containing glucose 10.0 g/L, peptone 5.0 g/L, malt extract 3.0 g/L, yeast extract 3.0 g/L, MgSO4 7H2O 1.0 g/L, KH2PO4 0.3 g/L, vitamin B1 0.001 g/Land pH was adjusted to 7.0.25 and incubated in a rotatory shaking incubator at 120 rpm for 72 h at 40°C. After the completion of incubation time, the cultures were steamed at 10 psi for 20 min. This treatment will lose the attached polymer, and then it was centrifuged at 8000 rpm and the solution was collected. The collected supernatant solution was cooled and an equal amount of ethanol was added and agitation was done for proper mixing. This mixture was left overnight at 4°C to settle down and finally precipitated EPS were extracted after centrifugation at 10000 rpm for 20 min.26,27 The supernatant was removed and precipitates were collected and freeze-dried.
Cadmium and lead biosorption assay
Cadmium and Lead standards of 1000 ppm solution (Cd (NO3)2 and Pb (NO3)2 in 0.1 M HNO3) (HiMedia) was diluted with 10mM citrate phosphate buffer (pH 4.0) and used as a 1 ppm Cd and lead solution. 10mg of bacterial strains (Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus reuteri) as well as their EPS were suspended in 1ppm Cd and Pb solution and incubated it at 37° C, 42° C and 50° C for 6hours to 48 h using various pH conditions 2, 4, 6 and 8. After incubation the bacterial cells and EPS were removed/ separated by centrifugation at 9000 rpm, the Cd and Pb concentration of the filtrate was measured using an AAS, citrate phosphate buffer was used as the negative control. The metal biosorption potential is detected by calculating accordingly.28 Metal removal (q), from the solution, expressed as mg metal removed/g dry weight-1, which was calculated using the following formula
q (mg g-1) = V(C i - Cf )m-1
Where, V = sample volume (l), Ci and Cf = initial and final metal concentrations (mg/l), respectively; m = amount (g) of dry biomass.
RESULTS
The results showed that both the strains i.e. Lactobacillus Plantarum and Lactobacillus reuteri, and their isolated EPS were able to biosorbe heavy metals cadmium and lead. After analysing the treated samples by AAS, the cells and the EPS of isolates showed good biosorption ability of the tested metals. The biosorption ability of both strains and their EPS is species-specific but EPS showed better biosorption ability as compared to their cells. In the present study, emphasis has been laid on three major factors i.e. tempreture, pH and contact time.
Both the LAB strains and their EPS were tested for Cd (II) and Pb biosorption at different temperature ranges from 37°C, 42°C and 50°C. EPS and cells of Lactobacillus reuteri reduced 890ppm and 160ppm cadmium at 50°C and 37°C while lead was reduced to 570ppm and 360 ppm at 50°C and 37°C. EPS and cells of Lactobacillus Plantarum reduced 180ppm and 110ppm of cadmium at 50°C and 37°C were as lead reduced 630ppm and 181ppm at 50°C and 37°C (Fig. 1a-f).
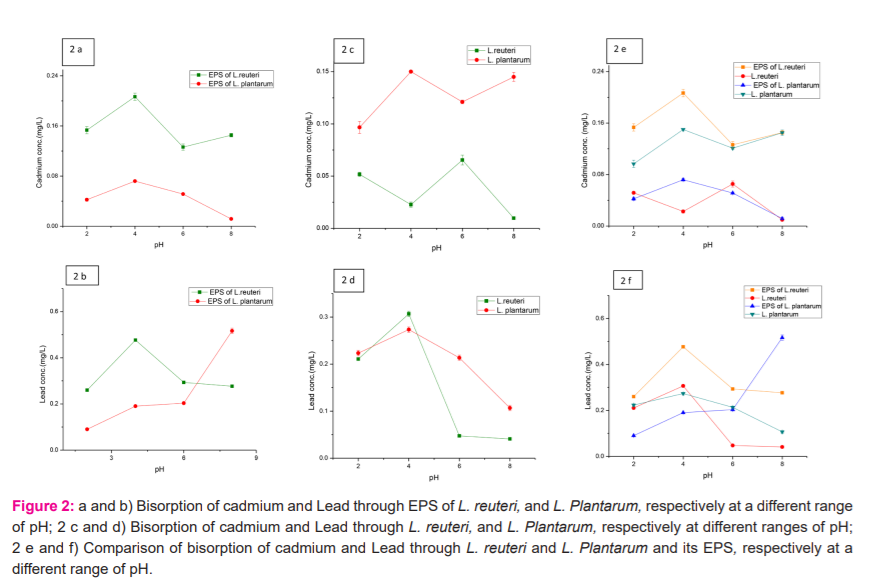
The LAB strains and their EPS were tested for Cd (II) and Pb biosorption at pH 2.0, 4.0, 6.0, and 8.0. EPS and cells of Lactobacillus reuteri reduced 210ppm and 65 ppm of cadmium at pH 4.0 and pH 6.0 while lead reduced more by 480 ppm to 310 ppm at pH 4. EPS and cells of Lactobacillus Plantarum reduced 72ppm and 150ppm of cadmium at pH 4 and 510ppm and 270ppm of lead at pH8.0 and pH 4.0 (Fig. 2a-f). The results showed that pH significantly affected the Cd biosorption and lead. Both strains showed Cd (II) and Pb(II) biosorption, although the biosorption ability of each was different.
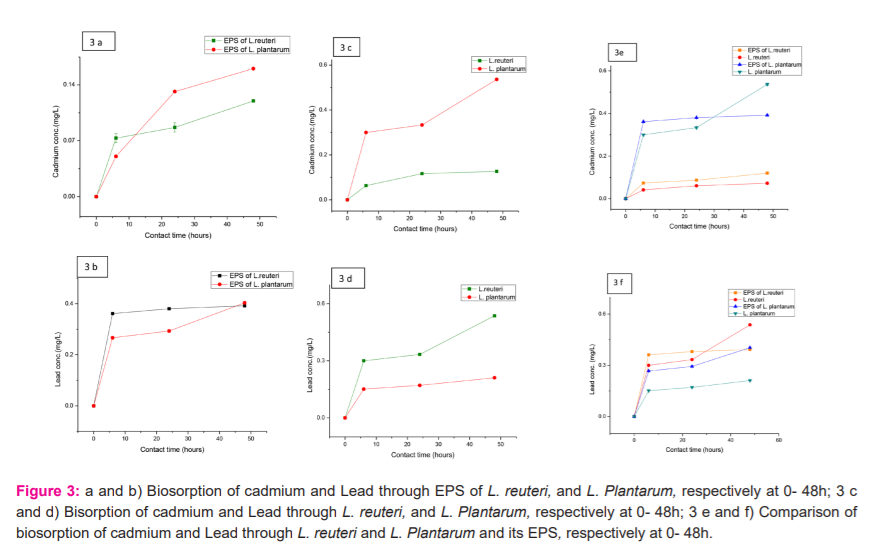
At different contact times of 6h, 24h, 48h both the LAB strains and their EPS showed Cd (II) and Pb biosorption. EPS and cells of Lactobacillus reuteri reduced 120ppm and 70 ppm cadmium at 48h while lead reduced 390ppm and 540ppm at 48h. EPS and cells of Lactobacillus Plantarum reduced 160 ppm and 130ppm cadmium at 48h while lead reduced 400ppm and 210ppm at 48h (Fig.3a-f).
DISCUSSION
Biosorption of cadmium through EPS was higher as compared to cells in both strains. Lactobacillus reuteri showed 89% biosorption of cadmium through EPS and EPS of Lactobacillus Plantarum showed 51% biosorption of lead. In the case of cells, biosorption of lead was more i.e. 57% through Lactobacillus reuteri and 43% through Lactobacillus Plantarum as compared to cadmium. It is accepted that bacterial EPSs can interact with toxic metals by various mechanisms including van der Waals’ forces, electrostatic attraction and surface complexation.29, 30 Bhakta et al.,9 reported seven and four LAB strains isolated from mud and sludge that displayed relatively elevated Cd (II) and Pb (II) removal efficiencies from water. Lactobacillus reuteri Cd70-13 and Pb71-1 showed the highest Cd (II) (25%) and Pb (II) (59%) removal capacity from MRS culture medium.8
Numbers of factors play important role in the biosorption process, which may enhance or diminish the process of biosorption of heavy metals. With heat treatment, the bacterial cells may be disrupted using heating so that intracellular proteins may bind the Cd and Pb. The study reported that exopolysaccharide of Lactobacillus Plantarum showed maximum adsorption of Pb at 50°C.31 This suggests that EPS is related to biosorption of Cd and Pb in strains, and it may be broken or modified by heat treatment. Schut et al.,12 reported that one of the lactobacillus strains on boiling at 1000C for 1 hr showed maximum biosorption of copper. The binding may be different for each strain and heavy metal.
All bacteria have the potential for biosorption of heavy metals though there is a difference in their abilities. Biosorption of both metals Cd (II) and Pb (II) tended to be high at mild acidic to slight alkali pH. This focused that the vital activity of LAB becomes weak in very low pH and Cd (II) and Pb(II) absorption are decreased and the protein that is present on the cell surface is positively charged below the isoelectric point and have difficulty adsorbing Cd (II) and Pb (II)at very low pH. Cadmium and lead removal by LAB was enhanced at higher pH.8,32 The anion of the salt that used to prepare the metallic solutions, the EPS confining system or the pH can significantly affect the biosorption.22,33
Ibrahim et al.,10 reported binding isotherms for Cd (II) and Pb (II) were characterized for Lactobacillus rhamnosus LC-705, Propionibacterium freudenreichii subsp. shermanii JS and a mix showed Cd (II) and Pb (II) sorption. This suggests LAB is potential biosorbents of heavy metals and have metal-binding proteins or EPS on the cell surface. The EPS extracted from B. licheniformis NSPA5, B. cereus NSPA8 and B. subtilis NSPA13 showed very distinct abilities as compared with lead and cadmium.34
CONCLUSION
The biosorption process is the most effective strategy for the removal of heavy metals and it can become more effective by using different strains of LAB. These probiotic bacteria have the potential to produce EPS and both bacteria as well as extracted EPS can detoxify the adverse effect of heavy metals. In this study, the comparison between the biosorption ability of cells and exopolysaccharides of the same strains are discussed. Both the strains Lactobacillus Plantarum and Lactobacillus reuteri and their EPS can bind cadmium and lead efficiently. Although both the strains have the potential to remove heavy metals the produced EPS from both the strains are more efficient to remove heavy metal 89% through L.reuteri and 63%by L.plantarum as compare to cells 54% through L.reuteri and 27% by L.plantarum. Extensive use of LAB and its EPS are seen in different food sectors and pharmaceutical industries so both the strains may be recommended as an inexpensive tool to detoxify heavy metal contamination from the environments and food products for industrial-scale applications.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors would like to express their sincere gratitude to the Centre of Food Technology, University of Allahabad, Prayagraj and Prof. Neelam Yadav for providing all the essential help and support.
Conflict of Interest:
Authors have no conflict of Interest.
Funding:
The authors received no financial support for the research and publication of this article.
Author Contribution:
Anchal Singh: Study conception and design, writing, validation
Pinki Saini: Supervision, reviewed the results
Urvashi Srivastava: Editing
Radha Kushwaha: Statistical analysis

References:
-
Järup L, Åkesson A. Current status of cadmium as an environmental health problem. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2009 Aug 1;238(3):201-8.
-
Satarug S, Garrett SH, Sens MA, Sens DA. Cadmium, environmental exposure, and health outcomes. Environ Health Perspect. 2010 Feb;118(2):182-90.
-
International Agency for Research on Cancer. Beryllium, cadmium, mercury, and exposures in the glass. Apresentado em: IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans: Beryllium, Lyon 1993.
-
Satarug S, Moore MR. Adverse health effects of chronic exposure to low-level cadmium in foodstuffs and cigarette smoke. Environ Health Perspect. 2004 Jul;112(10):1099-103.
-
IWG on the Evaluation IW. Inorganic and Organic Lead Compounds. Inorganic and Organic Lead Compounds. International Agency for Research on Cancer.2006.
-
Evaluation of certain food contaminants: 64th report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. Geneva. FAO/WHO 2006; Retrieved from http:// whqlibdoc.who.int/trs/WHO_TRS_930_eng.pdf Accessed 21.01.15.
-
Volesky B. Detoxification of metal-bearing effluents: biosorption for the next century. Hydromet. 2001 Feb 1;59(2-3):203-16.
-
Kinoshita H, Sohma Y, Ohtake F, Ishida M, Kawai Y, Kitazawa H, et al. Biosorption of heavy metals by lactic acid bacteria and identification of mercury binding protein. Res Microbiol. 2013 Sep 1;164(7):701-9.
-
Bhakta JN, Ohnishi K, Munekage Y, Iwasaki K, Wei MQ. Characterization of lactic acid bacteria?based probiotics as potential heavy metal sorbents. J Appl Microbiol. 2012 Jun;112(6):1193-206.
-
Ibrahim F, Halttunen T, Tahvonen R, Salminen S. Probiotic bacteria as potential detoxification tools: assessing their heavy metal binding isotherms. Can J Microbiol. 2006 Sep 1;52(9):877-85.
-
Lin Z, Zhou C, Wu J, Zhou J, Wang L. A further insight into the mechanism of Ag+ biosorption by Lactobacillus sp. strain A09. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2005 Apr 1;61(6):1195-200.
-
Schut S, Zauner S, Hampel G, König H, Claus H. Biosorption of copper by wine-relevant lactobacilli. Int J Food Microbiol. 2011 Jan 31;145(1):126-31.
-
Srivastava U, Saini P, Singh A. Effect of Natural Fermentation on Antioxidant Activity of Pearl Millet (Pennisetum glaucum). Curr Nutr Food Sci. 2020 Apr 1;16(3):306-13.
-
Perdigon G, Galdeano CM, Valdez JC, Medici M. Interaction of lactic acid bacteria with the gut immune system. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2002 Dec;56(4):S21-6.
-
Lim BK, Mahendran R, Lee YK, Bay BH. Chemopreventive effect of lactobacttlus rhamnosus on the growth of a subcutaneously implanted bladder cancer cell line in the mouse. Jap J Cancer Res. 2002 Jan;93(1):36-41.
-
Hosono A. Bile tolerance, taurocholate deconjugation, and binding of cholesterol by Lactobacillus gasseri strains. J Dairy Sci. 1999 Feb 1;82(2):243-8.
-
Lam EK, Yu L, Wong HP, Wu WK, Shin VY, Tai EK, et al. Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG enhances gastric ulcer healing in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007 Jun 22;565(1-3):171-9.
-
Tok E, Aslim B. Cholesterol removal by some lactic acid bacteria that can be used as probiotic. Microbiol Immunol. 2010 May;54(5):257-64.
-
Suresh Kumar A, Mody K, Jha B. Bacterial exopolysaccharides–a perception. J Basic Microbiol. 2007 Apr;47(2):103-17.
-
Singha TK. Microbial extracellular polymeric substances: production, isolation and applications. IOSR J Pharm. 2012;2(2):271-81.
-
Singh P, Saini P, Srivastava U, Singh A. Microbial Polysaccharides as an Alternative Biodegradable Packaging Material. In Food Technology and Nutrition; 91:37.
-
Paperi R, Micheletti E, De Philippis R. Optimization of copper sorbing–desorbing cycles with confined cultures of the exopolysaccharide?producing cyanobacterium Cyanospira capsulata. J Appl Microbial. 2006 Dec;101(6):1351-6.
-
Kim SY, Kim JH, Kim CJ, Oh DK. Metal adsorption of the polysaccharide produced from Methylobacterium organophilum. Biotechnol Lett. 1996 Oct;18(10):1161-4.
-
Nies DH. Microbial heavy-metal resistance. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 1999 Jun;51(6):730-50.
-
Banerjee D, Jana M, Mahapatra S. Production of exopolysaccharide by endophytic Stemphylium sp. Micol Aplicada Int. 2009;21(2):57-62.
-
Brown MJ, Lester JN. Comparison of bacterial extracellular polymer extraction methods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Aug 1;40(2):179-85.
-
Donot F, Fontana A, Baccou JC, Schorr-Galindo S. Microbial exopolysaccharides: main examples of synthesis, excretion, genetics and extraction. Carbohydr Polym 2012 Jan 15;87(2):951-62.
-
Volesky B, Holan ZR. Biosorption of heavy metals. Biotechnol Prog. 1995 May 1;11(3):235-50.
-
Gutnick DL, Bach H. Engineering bacterial biopolymers for the biosorption of heavy metals; new products and novel formulations. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2000 Oct;54(4):451-60.
-
Guibaud G, van Hullebusch E, Bordas F. Lead and cadmium biosorption by extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) extracted from activated sludges: pH-sorption edge tests and mathematical equilibrium modelling. Chemosphere. 2006 Sep 1;64(11):1955-62.
-
Feng M, Chen X, Li C, Nurgul R, Dong M. Isolation and identification of an exopolysaccharide?producing lactic acid bacterium strain from Chinese Paocai and biosorption of Pb (II) by its exopolysaccharide. J Food Sci. 2012 Jun;77(6): T111-7.
-
Halttunen T, Salminen S, Tahvonen R. Rapid removal of lead and cadmium from water by specific lactic acid bacteria. Int J Food Microbiol 2007 Feb 28;114(1):30-5.
-
Pulsawat W, Leksawasdi N, Rogers PL, Foster LJ. Anions effects on biosorption of Mn (II) by extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) from Rhizobium etli. Biotechnol Lett. 2003 Aug;25(15):1267-70.
-
Shameer S. Biosorption of lead, copper and cadmium using the extracellular polysaccharides (EPS) of Bacillus sp., from solar salterns. Biotech. 2016 Dec;6(2):1-0.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License