IJCRR - 13(13), July, 2021
Pages: 175-183
Date of Publication: 05-Jul-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Effect of Cartoon Animation Movie on Level of Pain During Intravenous Cannulation Among Children
Author: Thakur P, Deol R, Kaur N, Bains HS
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Pain is such an uncomfortable feeling that even a tiny amount of it is enough to ruin every enjoyment. Painful medical procedures such as immunizations and intravenous cannulation done in hospitals comprise a significant portion of the average child's experience with painful events. Inadequate relief from pain during childhood may have long term negative effects on future pain tolerance and pain response. Objective: To assess the effect of cartoon animation movie on the level of pain during intravenous cannulation among hospitalized children. Methodology: An experimental research design was used to assess the effect of cartoon animation movie on the level of pain during IV cannulation in 100 children of 2-7 years of age selected by convenience sampling. Results: The mean pain score during IV cannulation in the experimental group was lower (02.52 \? 03.37) than the control group (04.9 \?0 3.03) and this difference was statistically significant (p0.05). At three minutes after the IV cannulation procedure, the mean pain score in the experimental group was 0.00\?0.00 while in the control group was 02.43 \? 02.50 (p>0.05). Conclusion: Cartoon animation movie significantly reduces the level of intravenous cannulation procedural pain in children in the experimental group as compared to the control group.
Keywords: Cartoon animation movie, Level of pain, Intravenous cannulation, Hospitalized children, FLACC scale
Full Text:
Introduction
The word pain is derived from the Latin word “poena” which means punishment, which in turn is derived from the Sanskrit word “pu” meaning purification.1 The International Association for Study of Pain defines it as, “An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage”.3 Perception of pain among children is complex and entails physiological, psychological, behavioural and developmental factors. It has been seen that children, who experience pain in early life, show long term changes in terms of pain perception and related behaviour.4
It has been seen that children as compared to adults are more vulnerable to pain-related complications. They suffer more because of their lower pain threshold, sensitization from repeated pain and immature systems for maintaining homeostasis. Repeated painful procedures among them may affect the long term neurobehavioral outcome.5
Intravenous cannulation is one of the most common procedures among hospitalized children that always causes moderate and severe pain among them. It also creates lots of anxiety and fear. The anticipation of pain during intravenous cannulation is generally underestimated and unappreciated. So to reduce the level of pain during cannulation procedures, some institutions have procedures for minimizing it by using certain kind of interventions.6
Distraction (such as cartoon animation movie) is one of the most frequently used non-pharmacological intervention to guide children’s attention away from painful stimuli and reduce anxiety related to pain. It is most effective when adapted according to the developmental level of the child. Distraction techniques are often provided by nurses in hospitals. Current research has shown that distraction can lead to reducing in procedure times and the number of staff required for the procedure.
It had been observed that no intervention was being used in the study setting to alleviate the intravenous cannulation related pain in children. So children show temper tantrum, making excuses to get rid of this painful procedure and cry a lot to avoid or postpone the procedure. This resulted in an increased level of anxiety among both parents and children.
Hence, the researchers planned to assess the effect of a cartoon animation movie to alleviate the level of pain during intravenous cannulation. This in turn may provide benefits to the children, their parents and decrease the fear of pain during intravenous cannulation in children.
Material and Methods
An experimental research design was used to assess the effect of cartoon animation movie on the level of pain during intravenous cannulation among all children (2-7 years) admitted in paediatric wards of DMC & Hospital, Ludhiana Punjab.
The independent variable i.e. cartoon animation movie was shown to the experimental group before, during and after intravenous cannulation and withheld in the control group.
A total of 100 hospitalized children admitted in selected paediatric units were selected by convenience sampling technique as the study sample. Random assignment of subjects into experimental group and control group was done by lottery method. Out of 100 hospitalized children, 50 children were taken in the experimental group (shown cartoon animation movie 3 minutes before, during and till 3 minutes after intravenous cannulation procedure) and the remaining 50 were taken in the control group (routine intravenous cannulation procedure) as per the slips picked by children. The tool for data collection was divided into the following two parts:
Part A (I): Socio demographic profile of child
Part A (II): Clinical profile of the child
Part B: FLACC- Behavioral Pain Assessment scale (Terri Voepel Lewis)
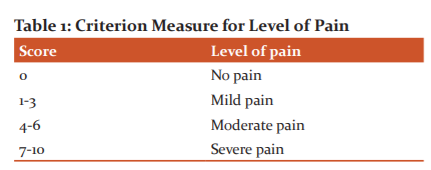
Table 1 shows the criterion measure for the assessment of pain. The reliability of the tool was found to be 0.87. The study was done after appraisal from the ethical committee of Dayanand Medical College & Hospital (DMCH), Ludhiana, Punjab. Written permission was taken from the Principal, College of Nursing and Head of Department of Paediatrics, DMC & Hospital, Ludhiana. Informed written consent was taken from parents of the hospitalized children for participation in a research study during the intravenous cannulation procedure.
Analysis of data was done following the objectives of the study. Both descriptive and inferential statistics were used for analysis. Calculations were carried out manually with the calculator and with the help of Microsoft Excel and SPSS (Statistical Package for Social Sciences) version 16 and Smith’s Statistical Package.
Results
Sample demographics
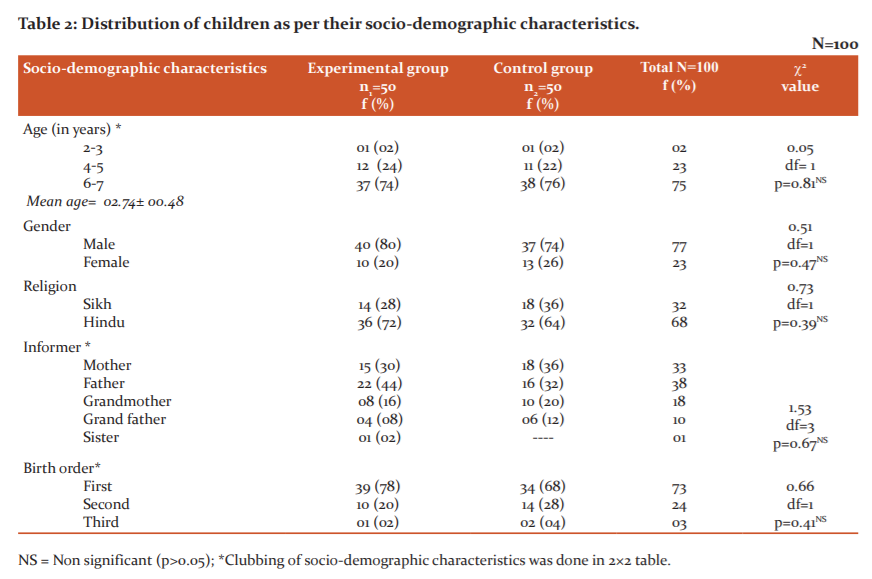
A total of 100 samples participated in the study as summarised in Table 2. It depicts that 74% of children from the experimental group and 76% from the control group belonged to 6-7 years of age, 80% from the experimental group and 74% from the control group were males, 72% from the experimental group and 64% from control group belonged to Hindu religion, 44% of informers from the experimental group were fathers and 32% from the control group were mothers and 78% from the experimental group and 68% from the control group were a firstborn child in the family.
Table 3 shows the distribution of children as per educational, occupational and socio-economic status of parents.50% of fathers from the experimental group and 56 % from the control group were graduate and above.52% of mothers from the experimental group and 50% from the control group had secondary level of education. The majority of fathers i.e. 98% from the experimental group and 96% from the control group were working,74% of mothers from the experimental group and 82 % from the control group were non-working, 56% of parents from the experimental group and 50% from control group belonged to the upper middle class (II).
Table 4 depicts the distribution of children as per their clinical profile. it depicts that majority of children 98% from the experimental group and 92% from the control group had thalassemia,94% from the experimental group and 90% from the control group were admitted to the thalassemia ward and 98% from the experimental group and 90% from the control group were admitted in the hospital for one day only.
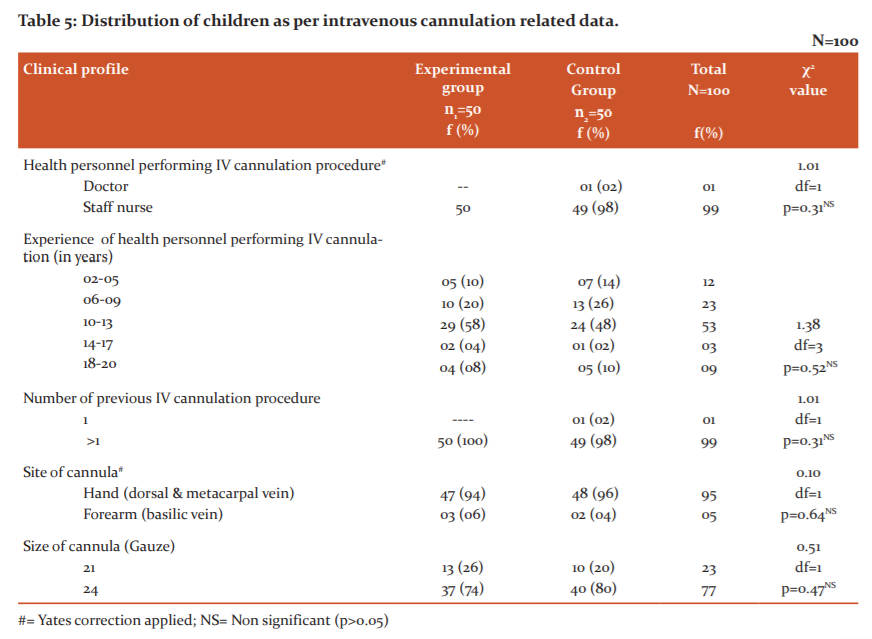
Table 5 depicts the distribution of children as per IV cannulation related data. It depicts that 100% cannulation in the experimental group and 98% from the control group was done by staff nurses, 58% of health personnel from the experimental group and 48% from the control group had 10-13 years of experience,100% of children from the experimental group and 98% from the control group had the previous history of IV cannulation procedure more than three times94% of children from the experimental group and 96% from the control group were cannulated on hand( dorsal and metacarpal vein), 74% children from the experimental group and 80% from control group received cannulation from 24 gauze needle.
Table 6 depicts the level of pain among children in the experimental group. It depicts that 100 % of children experienced no pain before IV cannulation procedure, during IV cannulation procedure, 44% experienced no pain, 28% mild pain, 12 % moderate pain and 16 % experienced severe pain, at one minute after IV cannulation procedure, 94% children experienced no pain and 6% experienced mild pain and at 3 minutes after IV cannulation procedure, all the children i.e. 100% experienced no pain.
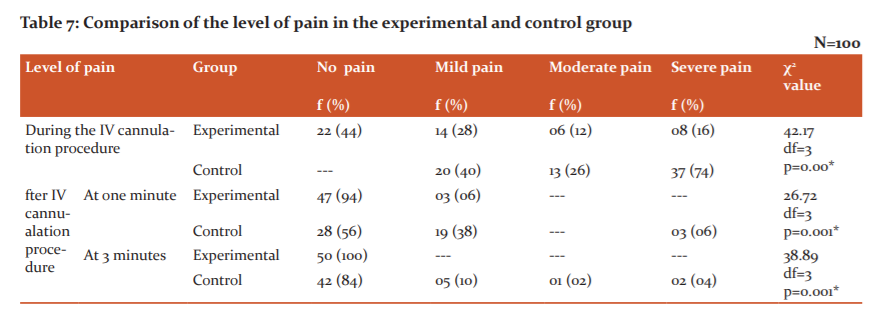
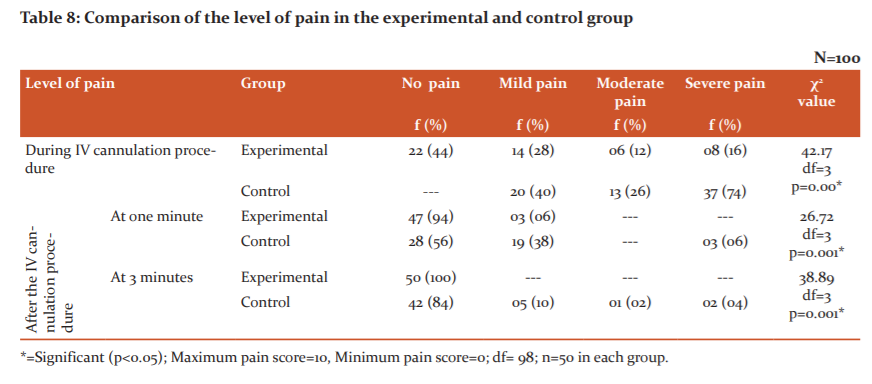
Table 7 depicts the level of pain among children in the control group. It depicts that all the children 100% had no pain before IV cannulation procedure, mild pain during IV cannulation were experienced by 40% of children, moderate pain was experienced by 26% and severe pain was experienced by 34% of children, at one minute after IV cannulation mild pain was experienced by 38% children, and severe pain was experienced by 6 % children, no pain was experienced by 56% children, at three minutes after IV cannulation procedure, 10% children experienced mild pain, 2% experienced moderate pain and 4% experienced severe pain, majority of children 84% experienced no pain at three minutes duration.
Figure 1 reveals that during the IV cannulation procedure 44% of children in the experimental group experienced no pain as compared to 0% in the control group. A mild level of pain was experienced by 28% of children in the experimental group and 40% in the control group. Moderate level of pain was experienced by12% of children in the experimental group and 26% in the control group. Severe pain was experienced by only 16% of children in the experimental group as compared to 34% of children in the control group during the IV cannulation procedure.
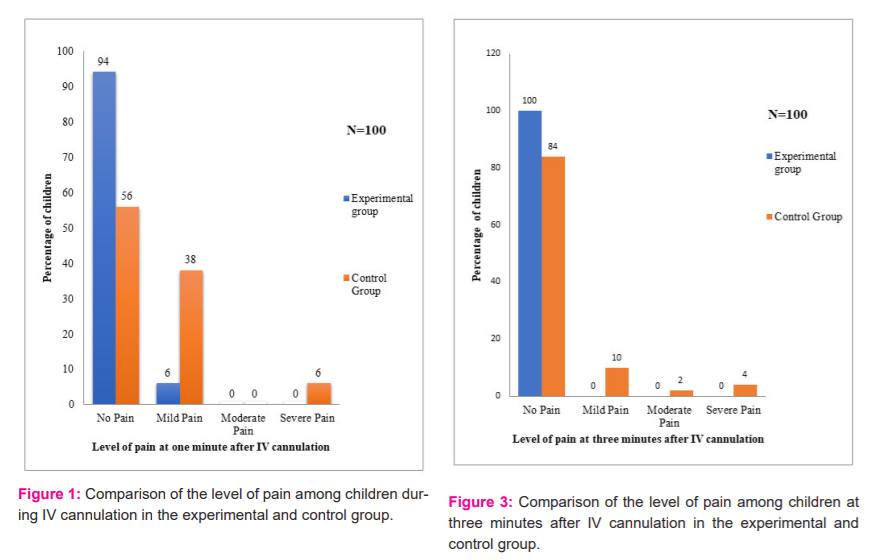
Figure 2 depicts the comparison of the level of pain among children in the experimental and control group at one minute after the IV cannulation procedure. At one minute after the IV cannulation procedure, no pain was experienced among 94% of children in the experimental and 56% of children in the control group. A mild level of pain was experienced by 38% of children in the control group as compared to only 06% in the experimental group. 06% of children in the control group and none of the children 0% in the experimental group experienced severe pain at one minute after the IV cannulation procedure.
Figure 3 illustrates the comparison of the level of pain among children at three minutes after the IV cannulation procedure in the experimental and control group. It shows that 100% of children in the experimental group and 84% in the control group experienced no pain. Only 10% of children experienced mild pain in the control group. 02% of children in the control group experienced moderate pain and 02% experienced severe pain at three minutes after the IV cannulation procedure. None of the children in the experimental group experienced mild, moderate and severe pain at 3 minutes after the IV cannulation procedure.
Table 8 shows the comparison of the level of pain among children in the experimental and control group. It shows that during the IV cannulation procedure 44% of children from the experimental group experienced no pain as compared to none of the children in the control group. A mild level of pain was experienced by 28% of children in the experimental group as compared to 40% in the control group. A moderate level of pain was experienced by 12% of children from the experimental group as compared to 26% from the control group. A severe level of pain was experienced by 16% of children from the experimental group as compared to 74% from the control group.
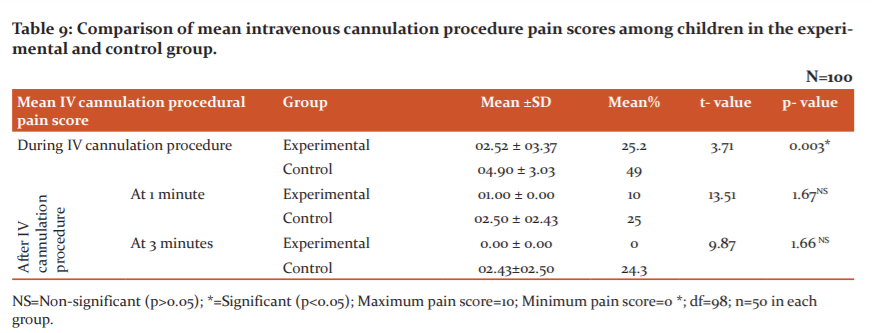
Table 9 shows the comparison of mean intravenous cannulation procedure scores among children in the experimental and control group. The mean pain score & mean % during IV cannulation in the experimental group was lower (02.52±3.37, 25.2%) than the control group (04.9±3.03, 49%) and this difference was statistically significant (p=0.0003). At one minute after the IV cannulation procedure, the mean pain score & mean % in the experimental group was lower (01±0.00, 10%) than the control group (02.5±2.43, 25%) (p>0.05). At three minutes after IV cannulation procedure, the mean pain score & mean % in experimental group was lower (0±0.00, 0%) than control group (02.43±2.50, 24.3%) (p>0.05).
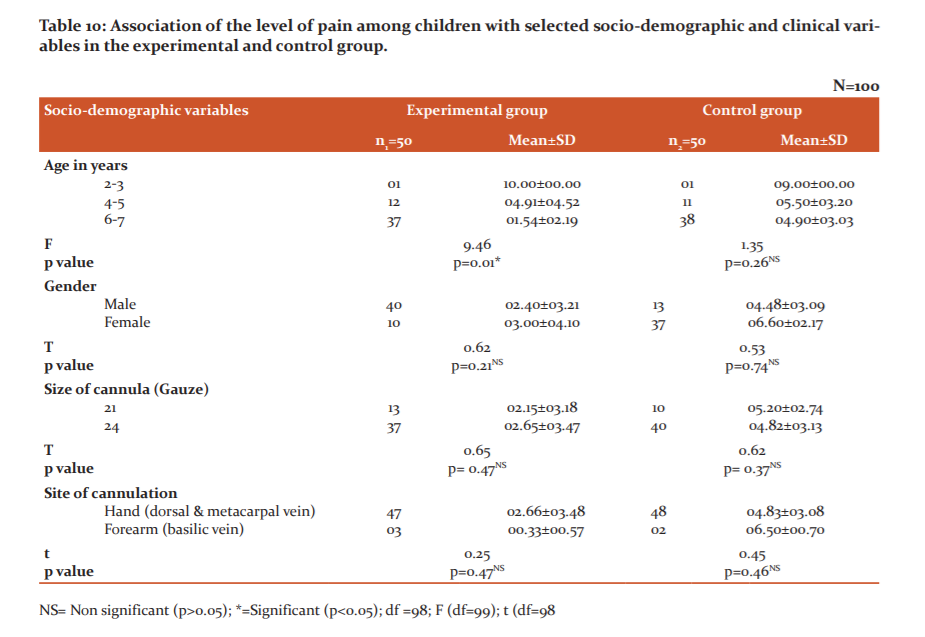
Table 10 depicts the association of level of pain among children with selected socio-demographic and clinical variables in the experimental and control group. A statistically significant association was found between age and pain scores (p=0.01) in the experimental group. Children in the younger age group like 2-3 years had higher mean pain scores (10±0.00) as compared to older children. (6-7 years had a mean score of 01.54±02.19).



Discussion
The present study depicts that the baseline level of pain among all children in the experimental and control group was zero and was assessed three minutes before the IV cannulation procedure by using FLACC behavioural pain assessment scale by Terri Voepel-Lewis in 2010. The study findings are also supported by Downey AVL, Zun SL who conducted a randomized control trial among 82 children in the department of Roosevelt hospital, Chicago. The baseline level of pain among all children was zero and assessed five minutes before the procedure using Poker Chip Tool and Faces Scale in 2009.8
The present study depicts that the mean pain score during IV cannulation in the experimental group was lower (02.52±03.37) than the control group (04.09±03.03) and this difference was statistically significant (p<0.005). The study findings are supported by an observational study on 203 children of age group 2-15 years in the Health & Sciences Department, Italy. Results revealed that the mean scores of pain in children undergoing IV cannulation with cartoon animation movie was lower (02.53±01.76) than in those undergoing IV cannulation without it (05.22±02.53) (p<0.005). 9
During the IV cannulation procedure slightly less than half, 22 (44%) children from the experimental group experienced no pain as compared to none of the children in the control group. A mild level of pain was experienced by 14 (28%) children in the experimental group as compared to 20 (40%) in the control group. Moderate level of pain was experienced by only 06 (12%) children from the experimental group as compared to 13 (26%) from the control group. A severe level of pain was experienced by 08 (16%) children from the experimental group as compared to 37 (74%) from the control group. The study findings are supported by a quasi-experimental study on 50 children of age group 3-6 years undergoing IV cannulation procedure to assess the effect of the animated cartoon as a distraction strategy on the behavioural response to pain perception in Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh. During IV cannulation, none of the children experienced pain in both the experimental and control group. Only 04 (08%) children from the experimental group experienced mild pain as compared to 01 (02%) children from the control group. Moderate level of pain was experienced by 25 (50%) children from the experimental group as compared to 07 (14%) from the control group. A severe level of pain was experienced by 21 (42%) children from the experimental group as compared to 42 (84%) from the control group. 10,11,12
Conclusion
The study concluded that cartoon animation movie is effective in reducing the level of pain among children during IV cannulation procedure.
Source of funding: None
Conflict of Interest: None
Author Contribution: All authors contributed equally in all steps of the study.
References:
-
Smeltzer. C. Smeltzer, Brunner’s and Suddarth’s. Textbook of Medical-Surgical Nursing: definition of pain.10th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins. 2004; 789-92.
-
Henson John. Pain terms with definitions and notes on usage– Recommended by the ISAP Sub-committee on Taxonomy. Pain 1989; 17(9):239.
-
Hockenberry JM & Wilson D. Wong’s Essentials of Pediatric Nursing. 9th ed. Mosby Elsevier; 2009; 159-171.
-
Linhares MBM, Doca FNP, Martinez FE, Carlotti APP, Cassiano RGM et al. Pediatric pain: prevalence, assessment and management in a teaching hospital. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2012; 45(12):1287-129
-
Potter AP, Perry GA. Fundamental of nursing. 6th ed. Elseiver. 2007; 28-37.
-
Sparks L. Taking the "ouch" out of injections for children. Using distraction to decrease pain. Am J Matern Child Nurs. 2001; 26(2):72-78.
-
Cerne D, Sannino L, Peter M. A randomized controlled trial examining the effectiveness of cartoons as a distraction technique. Nurs Child Young Peo. 2015; 27(3):28-33.
-
Downey AVL, Zun SL. The impact of watching cartoons for distraction during painful procedures in the emergency department. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2012; 28(10):1033-1035.
-
Bagnasco A, Pezzi E, Rosa F, Fornoni I & Sasso I. Distraction techniques in children during IV cannulation: an Italian experience The nurses’ point of view. J Prev Med Hyg. 2012: 3(3):44-53.
-
James J, Ghai S, Rao KL, Sharma N. Effectiveness of animated cartoons as a distraction strategy on the behavioral response to pain perception among children undergoing IV cannulation, Chandigarh. Nsg and Mid Res J. 2013; 23(7):198-209.
-
Bagnasco A, Pezzi E, Rosa F, Fornoni I & Sasso I. Distraction techniques in children during IV cannulation: an Italian experience The nurses’ point of view. J Prev Med Hyg. 2012; 3(3):44-53 .
-
Talwar R, Yadav A, Deol R, Kaur J. Efficacy of distraction technique in reducing pain among children receiving the vaccination. Int J Cur Res Rev. 2014; 6(19): 42-46.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License