IJCRR - 13(10), May, 2021
Pages: 05-10
Date of Publication: 19-May-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Effect of Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy, Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy and Drug Therapy on Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome: A Prospective Randomized Study
Author: Mostafa Ahmed Abdelhameed, Adel Abdelhamid Nossier, Haidy Nady Ashm, Ahmed Mohamed Zaky Anwar
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: chronic pelvic pain syndrome is one of the most common diseases in urology, the disease involving discomfort in the perineal area, pelvis, pubic area with ejaculatory and voiding problems. Objective: The main objective of the current study to evaluate the therapeutic effect of Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT), Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy (PEMF) and Drug therapy in treating chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Methods: Seventy-five male patients with chronic prostatitis assigned into three main groups twenty-five for each Group A received Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) for one month, group B received pulsed electromagnetic therapy for one month and Group C received drug therapy for one month, the treatment plan was pretreatment evaluation by both measures NIH-Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH-CPSI) and ultrasonography which were used to evaluate the patients, all were assessed before and after treatment. Results: There was a significant decrease between pre and post values of (shockwave, Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy (PEMF) and Drug Therapy group on the NIH scale and in the US Examination. Conclusion: ESWT is effective in treating non-inflammatory chronic pelvic pain syndrome in men as manifested by a decrease in prostate volume and NIH-CPSI also PEMF and drug therapy are effective in the treatment of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPP) but the ESWT is more effective.
Keywords: Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome, Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy, Pulsed Electromagnetic Field therapy, NIH-Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Prostatitis is one of the most common urological problems and results in > 2 million doctor visits in the U.S. every year.1 Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS) is defined as the presence of chronic pelvic pain without documented infection or any other clear local pathology that explain pain for more than 3 months.2 The National Institutes of Health (NIH) defines CP/CPPS as type III prostatitis which is prevalent in men before the age of 50.3 The NIH-Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH-CPSI) is the standard used tool for assessment of symptoms severity in patients with CP/CPPS and includes, pain, urinary symptoms and quality of life QOL impact.4
Extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) was introduced in the past for kidney stones destruction and in the management of musculoskeletal disorders; nowadays, it has been vastly utilized in pain and wound management.5 ESWT must be considered as a promising new therapy for CPPS, in particular as it is easy to apply and causes no side effects.6
Magnetic stimulation provides a new treatment option for CP/CPPS patients who do not respond to pharmacotherapy.7 Drug therapy whether single or in combination is a commonly prescribed treatment for CP / CPPS 8. There is a lack of ideal treatment of CP/CPPS probably because of the uncertainty of aetiology and the best evidence-based management of CP/CPPS strongly suggests a multimodal therapeutic approach addressing the individual clinical phenotypic profile.9 So, the purpose of this study was to evaluate the therapeutic effect of ESWT, PEMF and Drug therapy in treating chronic pelvic pain syndrome.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Seventy-five patients with CP/CPPS according to NIH classification 3 were enrolled in this study from 20 of October 2017 to 15 June 2019 and were randomly distributed into three equal groups using the closed envelop method
Group A: Included 25 patients with CP/CPPS who received ESWT for one month.
Group B: Included 25 patients with CP/CPPS who received PEMF for one month.
Group C: included 25 patients with CP/CPPS who received drug therapy for one month.
Procedure
The technique of Extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT)
The patients in (Group A) treated by Shockwave device shock master 500 Gymna. Patients were reclined in an adjustable plinth, and their testicles were pushed forward gently during the procedure. Shock waves were applied directly to the perineal area over the maximum site of pain. Ultrasound gel was used as a coupling agent and the applicator of ESWT was held perpendicular to the treatment surface throughout the treatment. During the initial impulses, patients were instructed to adjust the applicator to feel the shock waves targeting the localized region of pain.
Patients were treated by ESWT once a week for 4 weeks. Energy density was adjusted to 3000 impulses each time, with 0.25 mJouls/mm2 and 3Hertz of frequency were delivered, although 0.05 mJouls/mm2 was added in each week (0.3 mJouls/mm2 in week two, 0.35 mJouls/mm2 in week three, and 0.4mJouls/mm2 in week four).10 The treatment impulses were 12000 extracorporeal shock wave impulses in 4 sessions over four weeks (3000 extracorporeal shock wave impulses every session) Frequency: 3 Hz was used for all the treatments. The position of the shock wave transducer was changed after every 500 pulses, to adjust the duration of the session to 5-15 minutes depending on patient tolerability.
The technique of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy (PEMF)
The patients in (group B) were treated by PEMF electromagnetic device; ASA, magneto therapy pmt qs Italy. The active treatment regime was empirical and consisted of 2 sessions weekly for 4 weeks (total 8 sessions). The frequency was set low at 10 Hz for the first 15-minute period and was increased to 50 Hz for the second 15-minute period.11 During the half-hour period of the session, the patient would keep the supine position.
Drug therapy
The patients in (group C) were treated with a combination of drug therapy in the form of (Tamsulosin 0.4 mg one capsule at bedtime for one month, diclofenac potassium 50 mg/ tablet twice daily after meals for one month and baclofen as a muscle relaxant 10mg twice daily for one month.12
Outcome measures
NIH-CPSI
Patients were monitored by NIH-CPSI before the start of therapy and one month after completion of the therapy, we used the Arabic version which previously republished by Elnashaar et al.13
Prostatic volume
Abdominal ultrasound was used in the current study to evaluate prostate volume before and after treatment and to assess if there is a relation between the volume of the prostate and treatment of CP/CPPS. Imaging of the prostate was performed in sagittal and axial views; volume should be measured with the machine settings using the length width and height. Abdominal ultrasound is an effective modality to evaluate prostatic enlargement 14. Ultrasound diagnostic system CMS180 CONEC with Sony video graphic printer up-895MD was used to determine prostatic volume in a cubic centimetre.
Statistical analysis
Descriptive statistics including the mean, standard deviation of post-treatment data (pain, Urinary symptom, quality of life, total score and Prostatic Volume) as compared to pre one. 3 x 2 mixed design Multivariate Analysis of Variance (MANOVA) was used to compare the therapeutic effect of ESWT, PEMF and Drug therapy on pain, Urinary symptom, quality of life, total score and Prostatic Volume in participants with chronic pelvic pain syndrome. The study included two independent variables. The first independent variable (between-subject factor) was the tested group with three levels: experimental group (A), experimental group (B), and control group (C). The second independent variable (within-subject factor) was the testing time with two levels: pre-testing and post-testing. The four dependent variables were pain, Urinary symptom, quality of life, total score and Prostatic Volume. All statistical measures were performed using SPSS version 23 for Windows. The level of significance for all statistical tests was set at p<0.0.5
RESULTS
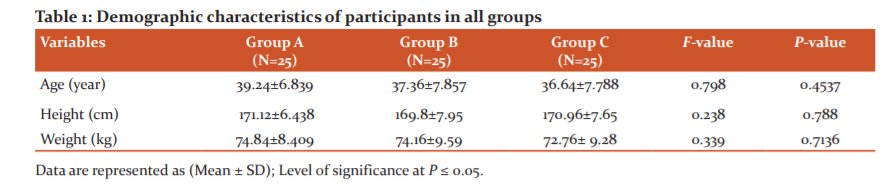
Results revealed non-significant differences (P>0.05) between the three groups regarding to demographic characteristics as shown in Table 1.
3× 2 mixed design MANOVA
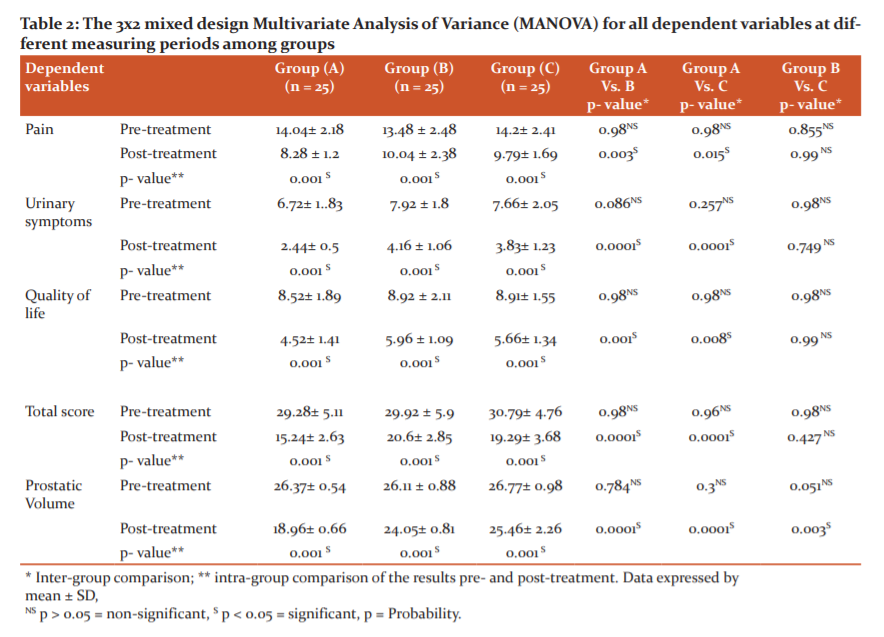
Multivariate tests for outcome measures indicate a statistically significant effects for group (F= 13.645, p= 0.001, Partial η2= 0.505), time (F= 262.81, p= 0.001, Partial η2= 0.951, and group-by-time interaction (F= 22.671, p= 0.001, Partial η2= 0.629). Within-group analysis revealed a statistically significant reduction (p < 0.05) for pain, Urinary symptom, quality of life, total score and Prostatic Volume) in the three studied groups. Comparing the results among the three tested groups, it was revealed that there was a significant improvement (p < 0.05) in the post-testing mean values of pain, Urinary symptom, quality of life, total score and Prostatic Volume in the experimental group (A) and group (C) compared with the group (B). There was no significant difference in the post-testing mean values of all measured variables except ultrasound between the two experimental groups (A) and (A) as shown in Table (2).
Undesirable side effects
There were no side effects for the ESWT, PEMF groups but there were some side effects related to drug therapy in the form of dizziness, headache, postural hypotension and anejaculation.
DISCUSSION
Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS) is a common yet poorly understood condition, with severe impact on QOL of diagnosed patients, especially on sexual function. 15 Various lines of treatments for CP/CPPS are available including ESWT,16 PEMF 17 and drug therapy 18 whether in single or multimodal therapy. The current study is the first study to compare the efficacy of ESWT, PEMF and drug therapy on CP/CPPS in a prospective method.
The use of ESWT to treat CP/CPPS has been reported previously.10,16 There are different mechanisms through which ESWT reduces pain. Mechanical effects include; stimulation, promotion of revascularization and enhancement of the healing process.19,20 Another chemical effect is explained by the release of endorphins locally and it's probable that "gate control phenomena" enter into the explanation for healing.19,20
Zimmermann et al. reported a significant statistical improvement in pain and QOL in the ESWT group. Urinary symptoms improved, but voiding symptoms were temporarily improved with no statistical significance.16 Similar results were obtained by Zeng et al.21 after a 12-week follow-up. Moayednia et al. reported that after a short-term follow-up, they found that ESWT was a safe and effective therapy for CPPS.22 Vahdatpur et al. showed an improvement in NIH-CPSI score including; pain, QOL, urinary score, but a slight deterioration of all variables occurred during the 12 weeks follow-up.22 On the contrary, Al Edwan et al.23 reported the long-term efficacy and safety of ESWT on CPP/CP, They showed significant statistical improvement in pain level, CPPS-related complaints, micturition and QOL with the maintenance of the effect without any significant side effects over the 12 months follow up with ESWT. In our study there was a highly significant decrease between pre and post values of shockwave group in NIH scale with a percentage of improvement for a total score of NIH-CPSI was 47.95%, this compares favourably with previous studies.
Yang et al. reported that Both electromagnetic stimulation and biofeedback applied to the pelvic floor muscle are effective for pain reduction, increased QoL, and improvement of lower urinary tract symptoms in male. Electromagnetic stimulation showed significant improvement in all items of the NIH-CPSI score except in urinary and quality of life score was a slight improvement after the treatment.24 Kim et al. conceded that extracorporeal Magnetic Stimulation offers a new treatment option for patients with CP/CPPS who do not respond to pharmacotherapy. Patients who received electromagnetic stimulation showed significant improvement in all items of the NIH-CPSI score except in urinary symptoms and QoL score.25 There was a signi?cantly improved pain and lower urinary tract symptoms in CP/CPPS patients who did not respond to medical treatments and more than 70% of patients were satis?ed with electromagnetic stimulation. These data suggest that electromagnetic stimulation could be considered as a safe and effective treatment option for CP/CPPS patients who do not respond to pharmacotherapy. Paick et al. concluded that magnetic therapy offers a new approach for pelvic floor stimulation that improves CP/CPPS.26 A longer follow-up is required to determine how long the benefits of treatment will last and whether retreatment will be necessary. In addition, the next step in future research will be to determine possible mechanisms of action of magnetic therapy and to identify factors influencing the outcomes.26
In our study there was a significant decrease between pre and post values of the PEMF group in the NIH scale (pain, urinary symptoms and improve quality of life) with a percentage of improvement for a total score of NIH-CPSI was 30.22%. Drug therapy for CP/CPPS is variable and includes, α-blocker, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and muscle relaxants. These could be used in single or multimodal therapy.27 In a double-blind study by nickel et al .including 272 patients with CP/CPPS. Alfuzosin 10mg/d and placebo showed a significant decrease in the NIH score in both groups.28 Tu?cu stated that Doxazosin 4mg/d has a significant effect in the treatment of chronic prostatitis, with a significant decrease in the NIH score in the Doxazosin group over placebo.29 Kim et al. concluded that based on most studies to date, although the mechanisms of improvement conferred by alpha-blockers have not been verified, both alpha-blocker monotherapy and antibiotic combination therapy showed considerable improvement in CP/CPPS patients (by NIH-CPSI scores).29 However, the current treatment strategies, including antibiotics, alpha-blockers, anti-inflammatory agents, and other medical agents, are not effective for all patients with CPPS.30 In our study there was a significant decrease between pre and post values of the Drug Therapy group in NIH-CPSI scale (pain, urinary symptoms and improve quality of life) with a percentage of improvement for a total score of NIH-CPSI was 36.93%. In the current study, we used unpaired tests to compare different groups including ESWT, PEMF and drug therapy. ESWT Showed the most significant effect between the other groups in the NIH-CPSI score.
They noted the feasibility of the prostate transabdominal dynamic contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging, taking advantage of the lower ultrasound frequencies suitable for contrast-specific imaging. Time-intensity curves in 10 patients were successfully extracted and analyzed. Given the high incidence of prostate pathology, especially prostate cancer, and the evolving role of dynamic contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging in its localization, the use of a transabdominal prostate approach may be a clinically useful option for patients to be selected for biopsy, active monitoring and treatment monitoring and follow-upm.31 Our current study is the first one at which we used abdominal ultrasonography to evaluate CP/CPPS and its symptoms through the prostate volume, we suggest that the tool of evaluation needs more research and studies to prove its quality to evaluate CP/CPPS. The current study has some limitations, including small number of cases, short follow-up time, use of abdominal us instead of transrectal us. In addition, many points supporting the study including prospective nature, it was a single centre study and it was the first study to compare ESWT, PEMF and Drug therapy.
CONCLUSION
ESWT is effective in treating non-inflammatory chronic pelvic pain syndrome in men as manifested by a decrease in prostate volume and NIH-CPSI. This study demonstrated that using the ESWT is beneficial in decreasing prostate volume, decreasing the NIH-CPSI and improving quality of life in patients with non-inflammatory chronic pelvic pain syndrome also PEMF and Drug therapy each of them has the efficacy to improve CPP/CP but lesser than the efficacy of ESWT.
Conflict of Interest: None
Source of Funding: None
Authors Contribution
Adel Abdelhamid Nossier (preparation of the research project, interpretation of data, preparation of the manuscript and development literature)
Mostafa Ahmed Abdelhameed (preparation of the research project, data collection, statistical analysis, interpretation of data, preparation of the manuscript, development literature and obtaining funds).
Ahmed Mohamed Zaky Anwar (preparation of the research project, preparation of the manuscript and development literature)
Haidy Nady Ashm (preparation of the research project, data collection, statistical analysis, interpretation of data and preparation of the manuscript)
References:
1. Zimmermann R, Cumpanas A, Hoeltl L, Janetschek G, Stenzl A, et al. Extracorporeal shock-wave therapy for treating chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Br J Urol Int 2008;102(8):976–980.
2. Fall M, Baranowski AP, Elneil S, Engeler D. EAU guidelines on chronic pelvic pain. Europ Urol 2010;57(1):35-48.
3. Schaeffer AJ, Datta NS, Fowler JE. Overview summary statement. Diagnosis and management of chronic prostatitis/ chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS). Urology 2002;60(6):1-4.
4. Wagenlehner FM, Van Till JO, Magri V, Perletti G. National Institutes of Health Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH-CPSI) symptom evaluation in multinational cohorts of patients with chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Eur Urol 2013;63(5):953-9.
5. Aboelnour NH, Ewais NF and Hamada HA. Focused versus radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy in post burn hypertrophic scar: A single blinded randomized controlled trial. Fizjoterapia Polska 2019;19(4): 150-155.
6. Kim YW, Shin JC, Yoon JG, Kim YK, et al. Usefulness of radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the spasticity of the subscapularis in patients with stroke: a pilot study. Chinese Med J 2013;126(24):4638-43.
7. Kim TH, Han DH, Cho WJ, Lee HS, et al. The efficacy of extracorporeal magnetic stimulation for treatment of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome patients who do not respond to pharmacotherapy. Urology 2013;82(4):894-8.
8. Khan A, Murphy AB. Updates on therapies for chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. World J Pharmacol 2015;4(1):1-6.
9. Magistro G, Wagenlehner FM, Grabe M, Weidner W, et al. Contemporary management of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Eur Urol 2016;69(2):286-97.
10- Zhang ZX, Zhang D, Yu XT, Ma YW. Efficacy of radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy for chronic pelvic pain syndrome: A nonrandomized controlled trial. Am J Men's Health 2019;13(1):1557988318814663.
11. Rowe E, Smith C, Laverick L, Elkabir J. A prospective, randomized, placebo controlled, double-blind study of pelvic electromagnetic therapy for the treatment of chronic pelvic pain syndrome with 1 year of followup. J Urol 2005;173(6):2044-7.
12. Rayegani SM, Raeissadat SA, Taheri MS, Babaee M, et al. Does intra articular platelet rich plasma injection improve function, pain and quality of life in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee? A randomized clinical trial. Orthop Rev 2014;6(3).
13. El-Nashaar A, Fathy A, Zeedan A, Al-Ahwany A, et al. Validity and reliability of the arabic version of the National Institutes of Health Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index. Urol Int 2006;77(3):227-31.
14. Manzoor T, Shahid K, Ibrahim M, Waris N. Role of abdominal ultrasound in evaluating patients with urinary retention due to benign prostatic hyperplasia. Biomedica 2016;32(2):101.
15. Zhao Z, Xuan X, Zhang J, He J. A prospective study on association of prostatic calcifications with sexual dysfunction in men with chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS). J Sexual Med 2014;11(10):2528-36.
16. Zimmermann R, Cumpanas A, Miclea F, Janetschek G. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the treatment of chronic pelvic pain syndrome in males: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Eur Urol 2009;56(3):418-24.
17. Kessler TM, Z'Brun S, Haeni K, Burkhard FC. Combined sono-electromagnetic therapy for treatment of refractory chronic pelvic pain syndrome: A new therapeutic possibility? Eur Urol Suppl 2008;7(3):159.
18. Nickel JC, Touma N. α-Blockers for the treatment of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: an update on current clinical evidence. Rev Urol 2012;14(3-4):56.
19. Yan X, Yang G, Cheng L, Chen M, et al. Effect of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on diabetic chronic wound healing and its histological features. Chinese J Rep. Reconstr surgery. 2012;26(8):961.
20. Tassery F, Allaire T. Radial shock wave therapy for the treatment of lower limbs. FIBA Assist Mag 2003;3:57-8.
21. Zeng XY, Liang C, Ye ZQ. Extracorporeal shock wave treatment for non-inflammatory chronic pelvic pain syndrome: a prospective, randomized and sham-controlled study. Chinese Med J 2012;125(1):114-8.
22. Moayednia A, Haghdani S, Khosrawi S, Yousefi E, et al. Long-term effect of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on the treatment of chronic pelvic pain syndrome due to non bacterial prostatitis. J Res Med Sci 2014;19(4):293.
23. Al Edwan GM, Muheilan MM, Atta ON. Long term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy [ESWT] for treatment of refractory chronic abacterial prostatitis. Ann Med Sur 2017;14:12-7.
24. Yang MH, Huang YH, Lai YF, Zeng SW, et al. Comparing electromagnetic stimulation with electrostimulation plus biofeedback in treating male refractory chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Urol Sci 2017;28(3):156-61.
25. Kim W, Lee JS, Lee G, Cho W, et al. The efficacy of electromagnetic stimulation for treatment of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome patients who do not respond to pharmacotherapy. J Urol 2011;185(4S):e572-3.
26. Paick JS, Lee SC, Ku JH. More effects of extracorporeal magnetic innervation and terazosin therapy than terazosin therapy alone for non-inflammatory chronic pelvic pain syndrome: a pilot study. Prostate Can Prost Dis 2006;9(3):261-5.
27. Khan A, Murphy AB. Updates on therapies for chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. World J Pharmacol 2015;4(1):1-6.
28. Nickel JC, Downey JA, Nickel KR, Clark JM. Prostatitis?like symptoms: one year later. BJU Int 2002;90(7):678-81.
29. Tu?cu V, Ta?ç? A?, Fazl?o?lu A, Gürbüz G. A placebo-controlled comparison of the efficiency of triple-and monotherapy in category III B chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS). Eur Urol 2007;51(4):1113-8.
30. Thakkinstian A, Attia J, Anothaisintawee T, Nickel JC. α?blockers, antibiotics and anti?inflammatories have a role in the management of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. BJU Int 2012;110(7):1014-22.
31. Mischi M, Demi L, Smeenge M, Kuenen MP. Transabdominal contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging of the prostate. Ultrason Med Bio 2015;41(4):1112-8.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License