IJCRR - 13(9), May, 2021
Pages: 150-155
Date of Publication: 07-May-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Role of Perioperative Administration of 5% Dextrose in Reducing the Incidence of Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting in Laparoscopic Surgeries - A Randomized Control Trial
Author: Priya Ranjan, Sandip Roy Basunia, Suman Chattopadhyay
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) are one of the major concerns for patients undergoing laparoscopic surgeries. There is conflicting evidence that whether perioperative intravenous dextrose reduces PONV. Objective: To establish the role of dextrose in preventing PONV after laparoscopy. Methods: A prospective double-blind study was conducted with 60 non \? diabetic, non-smoker, ASA-I female patients, 18 \? 60 years of age posted for laparoscopic surgeries (LS) under general anaesthesia (GA). All patients were randomized into 2 groups: Group \? D received 5% Dextrose @ 125 ml/hour and Group \? N received 0.9% Normal Saline solution@ 125 ml/hour for 2 hours, beginning with the start of surgical closure. PONV scores, hemodynamic parameters, total rescue antiemetic and analgesic consumption were noted in the first 24 hours. Results: Out of 60 patients, Group D, 11(36.7%) patients and Group-N, 19(63.3%) patients need rescue antiemetic. The inci�dence of PONV was most significant on admission to PACU (p = 0.0388). The overall incidence of PONV was reduced by 26.9% in Group D which was significantly less compared to Group N (P= 0.0029). No statistically significant difference in terms of de�mographic characteristics, mean duration of surgery, difference of mean capillary blood glucose (CBG) level and requirement of rescue analgesia were noted among 2 groups. Conclusion: Perioperative administration of 5% dextrose reduces the incidence of PONV and consumption of antiemetics in patients undergoing LS under GA.
Keywords: Dextrose, Laparoscopic surgeries, Nausea, Postoperative, Vomiting
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) are one of the major concerns for patients undergoing laparoscopic surgeries.1 It may cause aspiration pneumonia, dehydration, prolonged stay in a post-anaesthesia care unit (PACU), increased hospital stay cost, wound dehiscence, water, electrolyte disturbances and acid-base imbalances.2,3 The risk of PONV is 30% in patients undergoing general surgery without prophylactic interventions, whereas the incidence rises to 80% in high-risk patients i.e. female gender, non-smoking, history of PONV, post-operative use of opioids4 and laparoscopic surgeries. The incidence of PONV dropped down to 30% with the implementation of advanced anaesthetic techniques and better anaesthetic drugs.5 Patients usually reported PONV to be more problematic than postoperative pain.6 Therefore PONV prevention is vital, economical, improving outcomes and patient satisfaction.
Both pharmacological and non-pharmacological approaches have been used for preventing PONV.7Antiemetic medications like serotonin 5 HT3 receptor antagonist, dexamethasone or droperidol are commonly used for prophylaxis of PONV. But these drugs are relatively expensive and associated with side effects such as hypotension, dry mouth, oversedation, dysphoria and arrhythmias.8
Preoperative fasting associated with hypovolemia causes gastric mucosal hypoperfusion that may be an important causative factor of PONV.9 Many studies in the past have proved that IV fluid or dextrose administration in the perioperative period is associated with decreased PONV frequency or severity probably by reducing hypovolemia9-13 and probably by reducing the postoperative catabolism and insulin resistance by preoperative administration of carbohydrate load.14-15 However, the data that indicates the use of IV dextrose solution following surgery to reduce nausea and vomiting are limited and show mixed results.16-19
Thus considering the importance of PONV prevention and conflicting and limited evidence that IV administration of 5% dextrose in the prevention of PONV, our study evaluated the role of perioperative dextrose in the prophylaxis of PONV in laparoscopic surgeries under general anaesthesia.
Material And Methods
This prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study was conducted in a tertiary care hospital in eastern India after getting approval from the institutional ethics committee (MMC/IEC-2-2017/2623 dt. 13/12/2017) and obtaining written informed consent from each of the patients over 18 months (February 2017 - July 2019). We enrolled a total of 60 non – diabetic, non-smoker, female patients between the age of 18- 60 years with ASA Grade-1 scheduled for elective laparoscopic surgery under general anaesthesia. We excluded patients with a history of PONV and motion sickness, any cardiac, renal or hepatic dysfunction, diabetes mellitus, pregnant patients, allergy to study fluid, operative time more than 2 hours, inability to insert venous cannulae into dorsum of both hands and sustained perioperative hypotension.
On the preceding day of operation a final pre-anaesthetic check-up was done and patients were instructed to rate the intensity of nausea and vomiting by verbal descriptive scale (VDS).20 All patients were advised to fast for at least 6 hours for solid food and 2 hours for clear liquid before surgery.
A total of 74 patients were assessed for eligibility. However, 8 patients were excluded and 6 patients declined to participate in the trial. The remaining 60 patients were randomized and allocated to two equal groups i.e. Group D and Group N respectively of 30 patients each. All the patients were followed up throughout the study period. There was no loss to follow-up or at the stage of analysis (Figure 1).
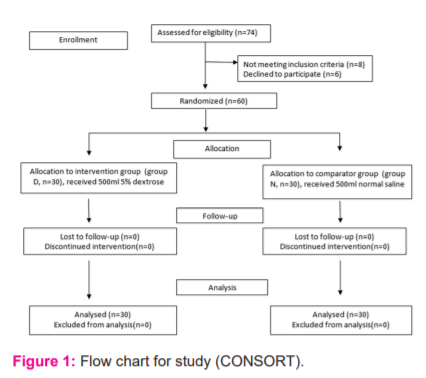
All 60 patients were randomized into 2 groups: the intervention group (Group – D) received 5% Dextrose and the control or comparator group (Group – N) received 0.9% Normal Saline solution. Randomization was performed by opening a closed envelope inside the preoperative holding area containing the computer-generated random assignment number ranging from 1 to 60. The anaesthesia providers, surgeons, perioperative nurses, PACU nurses and patients were blinded to group assignment throughout. One of the anaesthesia providers gave the study solution and another anaesthesia provider collected the data. Any anaesthesia personnel concerned with the study fluid preparation were not included in the data collection.
On arrival of the patient to the operating room, two 18 G IV cannula was inserted at the dorsum of each hand and 5 leads ECG, NIBP & pulse oximeter monitoring were attached and baseline hemodynamic parameters were recorded. Capillary blood glucose level (CBG) was recorded before induction, 15 mins after stopping of study fluid infusing and after 12 hours of induction by using Dr TrustTM USA Gold standard 9001 machines. No prophylactic anti-emetics were given as premedication, to decrease the possibility that treatment effects of study fluid administration could be masked.
All the patients were pre-oxygenated with face-mask @10 litres/min for 3 minutes, and pre-medicated with glycopyrrolate 10 mcg/kg, midazolam 30 mcg/kg. Ringer’s Lactate solution was started @ 3 ml/kg/hr in one hand and 100ml of paracetamol infusion on other hand was given at the beginning of surgery. Both the groups received Ringer Lactate intravenously as intraoperative maintenance fluids at 3 mL/Kg/hr in one dorsum. On the dorsum of the other hand, either the intervention drug (5% Dextrose) or comparator/control drug (0.9% Normal Saline) were infused by an infusion pump at a fixed rate such that Group N (30 patients) received 0.9% normal saline and the patients of group D (30 patients) received 5% dextrose @ 125 ml/hour for 2 hours (250 ml) beginning with the start of surgical closure. Both the study fluid (dextrose) and placebo fluid (normal saline) were delivered in opaque bags labelled with the randomization number of a particular patient with the help of an infusion pump (DP2070- Perfusor CompactTM), thus blinding them to patients and doctors alike inside OT.
All patients have followed a uniform standard technique for GA using IV thiopentone sodium 5 mg/kg for induction, IV fentanyl 2 mcg/kg to attenuate stress response and analgesia, IV atracurium 0.5 mg/kg to facilitate intubation and maintenance. Anaesthesia was maintained with isoflurane 0.5 to1.0 % in a mixture of oxygen and nitrous oxide (33%:66%). Neostigmine 50 mcg/kg and glycopyrrolate 10 mcg/kg IV were used to reverse residual muscle relaxation. No narcotic was given after surgery and in the post-anaesthesia care unit (PACU). However to maintain postoperative analgesia one dose of diclofenac 1.5 mg/kg IV and if still there was pain 2 doses of paracetamol 1% 100ml infusion (maximum 4 doses) was given. A decrease in mean arterial pressure (MAP) by more than 20% from baseline value or systolic blood (SBP) pressure less than 90 mm Hg were treated with 100 mcg phenylephrine IV bolus. Any patient receiving more than 3 doses of phenylephrine were excluded from the study.
PONV scores were assessed at 0,30,60,120 min in the PACU and 6,12 and 24 hours postoperatively in the ward by verbal descriptive scale (VDS)20 which consist of score 0= no PONV: no complaint of nausea and vomiting, score 1 = mild PONV: complains of nausea but refuse antiemetic treatment, score 2 = moderate PONV: the patient has nausea and allow treatment with antiemetic and score 3 = severe PONV: the patient has nausea with episodes of emesis (retching or vomiting) requiring treatment. Rescue antiemetic treatment (Ondansetron 4mg IV) was given when VDS scores were 3 or more, only after excluding other cause of PONV such as hypotension, hypoxia (SpO2 ≤ 90%), etc. All patients received supplemental oxygen (5L/min) using a well fitted facemask for 4 hours and Ringer’s lactate (2ml/kg/hr) postoperatively for 24 hours. Study was completed after 24 hours of completion of surgery. Statistical analysis
The minimum study sample size was estimated at 42 based on a two-sample proportions test (Pearson's chi-squared test) based on data on proportions of patients having PONV in a relevant previous study1 and taking the alpha value of 0.05 and power of 0.2 as adequate for the current study. For enhancing the validity of the study and to compensate for any loss of patients during the study period the total sample size was enhanced to a total of 60 divided into two groups for purpose of the study. For statistical analysis including sample size calculation SPSS (version 24.0; SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) software was used. Data for a test statistic that either exactly follows or closely approximates a t-distribution under the null hypothesis is given. Unpaired proportions were compared by Chi-square test or Fischer’s exact test, as appropriate. If the calculated p-value is below the threshold chosen for statistical significance (≤ 0.05) then the initial null hypothesis is rejected in favour of the alternative hypothesis.
Results
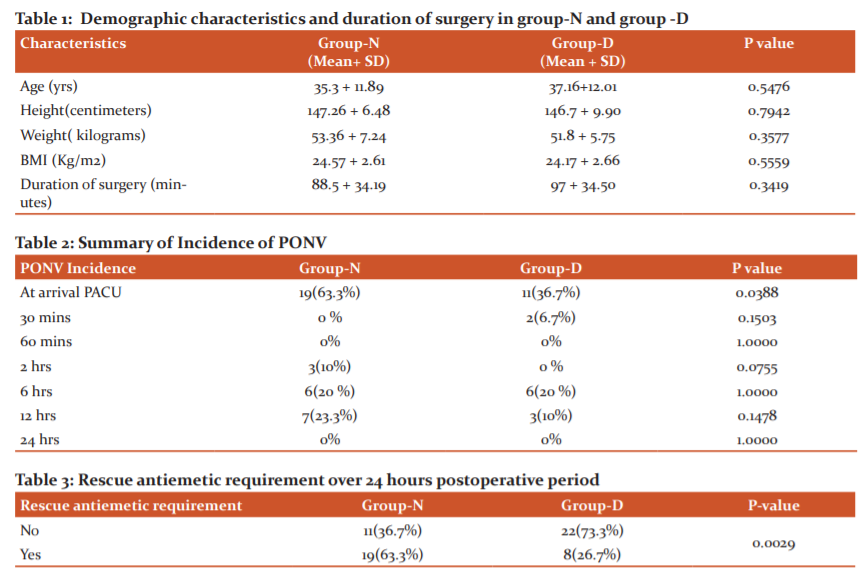
Overall 74 patients referred to our hospital during the study period. Out of which, 8 patients did not meet the inclusion criteria and 6 patients declined to participate in the study. So data were analysed with 60 patients who completed the study. Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients age, height, weight and BMI and duration of surgery are comparable in both groups (p>0.05) (Table 1). In terms of intra-operative haemodynamic characteristics of participants like HR, SBP, DBP, MAP were also comparable between two groups (p > 0.05).
Out of 60 patients, 19 (63.3%) patients in group-N and 11 (36.7%) patients in group-D had a VDS score ≥of 3 at arrival in PACU within 30 mins and rescue antiemetic was given. In this study we found, the incidence of PONV was significant only on admission to PACU (p = 0.0388) in Group N. At other times till 24 hours post-op. the incidences of PONV were comparable between the two groups (p>0.05) (Table 2 and Figure 1).
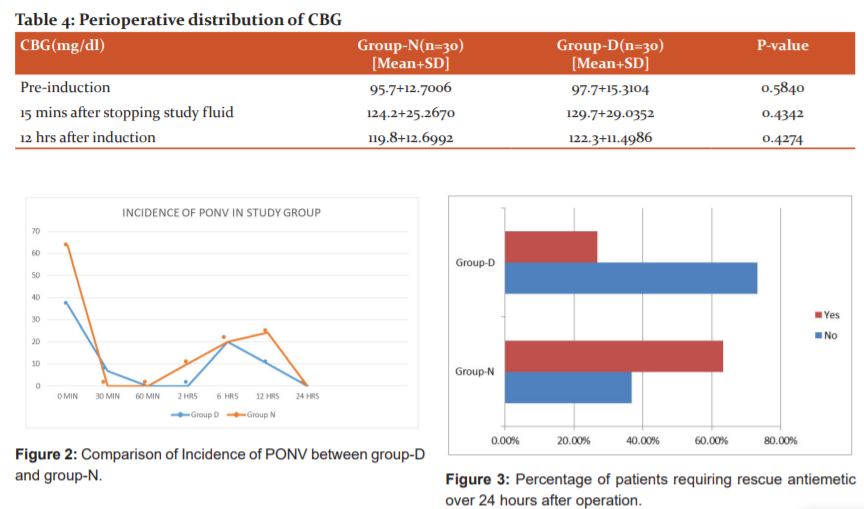
Overall 27(45%) patients had an incidence of PONV. In group-D 8 (36.4%) patients and group-N 19 (63.3%) patients needed rescue antiemetic 24 hrs after surgery. The incidence of PONV was reduced by 26.9 % in group D which is significantly less (p-value = 0.0029) (Table 3, Figure 2).
Perioperative difference of CBG before induction, 15 mins after stopping of study fluids and after 12 hrs of induction in group N and group D were comparable (p>0.05) and were within normal range throughout the perioperative period (Table 4). No adverse effects were observed in any patient during the study period.
Discussion
Laparoscopic surgeries are associated with a higher incidence of PONV.21 It may be due to stimulation of the mechanoreceptor of the gastrointestinal tract because of carbon dioxide pneumoperitoneum, which leads to the release of serotonin and other neurotransmitters.
Different antiemetic medications were tried in the past for preventing PONV with a variable success rate but with lots of side effects. The data regarding the effect of perioperative fluid therapy and glucose administration on PONV is also controversial and somewhat scarce.18-20 In the present study, we observed the effectiveness of perioperative IV dextrose administration for the prevention of PONV after laparoscopic surgeries. The principal findings of this study were that cumulative incidence of PONV and overall rescue antiemetic requirement was significantly less in patients of Group-D (P= 0.0029) with comparable perioperative blood glucose level with the control group.
Perioperative dextrose for prophylaxis of PONV because of its high osmotic pressure might reduce muscle contraction of the gastrointestinal tract,13,20 inhibition of vagal cholinergic pathways by the reduction in gastric acid secretion. Hyperglycemia also leads to an increase in plasma cholecystokinin level which decreases pain and anxiety by modulating brain function with a decrease in postoperative pain as well as nausea and vomiting.23-25 Another hypothesis of reduction of incidence of PONV in this study was caloric supplementation in the form of dextrose which leads to a reduction in postoperative catabolism and insulin resistence.22
Our study was similar to the study by Saleh et al. in which 10% dextrose was administered after laparoscopic surgery and found a lower incidence of nausea and rescue antiemetic consumption.21-23 Atashkhoei et al. in their study administered 5% dextrose intraoperatively in patients undergoing diagnostic gynecologic laparoscopy and found that there is the decrease in incidence and severity of PONV as well as frequency and reduced total dose of rescue antiemetic.24,27 In the study, Firouzian et al. concluded that administration of IV dextrose in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy, before induction of anaesthesia leads to significant decreased incidence and severity of PONV and antiemetic medication requirement in comparison to the control group.19,25 Consistent with our study Mishra et al. concluded that perioperative administration of 5% dextrose in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomies at 100ml/hr can reduce the incidence of PONV by 38% and decrease the consumption of rescue antiemetics.1,26 Our study is also supported by Dabu-Bondoc S et al. where postanaesthesia IV dextrose administration resulted in a reduction in rescue antiemetic medication requirements and PACU length of stay.13,27 In contrast to our data, Rao V et al. had found that the incidence of antiemetic requirements was similar.28 Patel P et al. had found that there were no significant intergroup differences in time of onset of PONV, duration of PONV, or the number of antiemetic doses or drug classes given to control PONV.29 McCaul et al. had found that administration of dextrose containing IV fluids was not effective in preventing PONV when compared to dextrose free IV fluid administered after gynaecological laparoscopy.30 Yokoyama et al. had found that compared to placebos, perioperative intravenous dextrose administration may decrease postoperative nausea but not vomiting. 31
In our study, data suggested that during perioperative blood glucose levels was slightly higher in group-D as compared to group-N, though blood glucose levels are within the normal range (Table 4). Similar findings are shown in the previous studies.19,26 This is also supported by a study done by Patel et al in which, the patients who received the intravenous glucose during the emergence of anaesthesia had greater blood sugar level than the placebo group after study but within normal range.29
The present study showed that ondansetron requirement as ‘rescue antiemetic’ was significantly higher in Group N compared to Group D. 5% dextrose is considered cost-effective in terms of single preoperative administration versus multiple post-operative administration of antiemetics. We used. thiopentone sodium as an induction agent instead of propofol which has an additional antiemetic effect, confounding actual results.32 Our study has several limitations. As our study group was limited to ASA I, non-smokers, undergoing laparoscopic surgeries. The effect of our study may not be the same in patients undergoing surgeries of different duration and type. We have not included diabetic patients in our study, which demands further research. We did not evaluate postoperative pain as a risk factor for PONV. The sample size could have been larger. Lastly, total IV fluid received were calculated in fixed volume rather than dosages per Kg body weight for study purpose.30,31
CONCLUSION
Perioperative administration of 5% dextrose is a safe and effective method of reducing the incidence of PONV and consumption of antiemetics in adult non-smoking female patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery under general anaesthesia.
Acknowledgements: The authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed
No financial support
No conflict of interest
References:
-
Mishra A, Pandey RK, Sharma A, Darlong V, Punj J, Goswami D, et al. Is perioperative administration of 5% dextrose effective in reducing the incidence of PONV in laparoscopic cholecystectomy? A randomized control trial. J Clin Anesth 2017;40:7–10.
-
Le TP, Gan TJ. Update on the management of postoperative nausea and vomiting and postdischarge nausea and vomiting in ambulatory surgery. Anesthesiol Clin 2010;28(2):225–49.
-
Watcha MF, White PF. Postoperative nausea and vomiting. Its aetiology, treatment, and prevention. Anaesthesia 1992;77(1): 162–84.
-
Apfel CC, Korttila K, Abdalla M, Kerger H, Turan A, Vedder I, et al. A factorial trial of six interventions for the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting. N Engl J Med 2004;350(24):2441–51.
-
Cohen MM, Duncan PG, DeBoer DP, Tweed WA. The postoperative interview: assessing risk factors for nausea and vomiting. Anaesth Analg 1994;78(1):7-16.
-
Macario A, Weinger M, Carney S, Kim A. Which clinical anaesthesia outcomes are important to avoid? The perspective of patients. Anesth Analg 1999;89(3):652–8.
-
Apfel CC, Kranke P, Eberhart LH, Roos A, Roewer N, comparison of predictive models of postoperative nausea and vomiting. Br J Anaesth 2002;88(2):234-40.
-
Kranke P, Eberhart LH. Possibilities and limitations in the pharmacological management of postoperative nausea and vomiting. Eur J Anaesthesiol 2011;28(11):758–65.
-
Magner JJ, McCaul C, Carton E, Gardiner J, Buggy D. Effect of intraoperative intravenous crystalloid infusion on postoperative nausea and vomiting after gynaecological laparoscopy: comparison of 30 and 10 mL kg (-1). Br J Anaesth 2004;93(3):381–5.
-
Maharaj CH, Kallam SR, Malik A, Hassett P, Grady D, Laffey JG. Preoperative intravenous fluid therapy decreases postoperative nausea and pain in high-risk patients. Anesth Analg 2005;100(3):675–82.
-
Ali SZ, Taguchi A, Holtmann B, Kurz A. Effect of supplemental pre-operative fluid on postoperative nausea and vomiting. Anaesthesia 2003;58(8):780–4.
-
Moretti EW, Robertson KM, El-Moalem H, Gan TJ. Intraoperative colloid administration reduces postoperative nausea and vomiting and improves postoperative outcomes compared with crystalloid administration. Anesth Analg 2003;96(2):611–7.
-
Dabu-Bondoc S, Vadivelu N, Shimono C, English A, Kosarussavadi B, Dai F, Shelley K, Feinleib J. Intravenous dextrose administration reduces postoperative antiemetic rescue treatment requirements and postanesthesia care unit length of stay. Anesth Analg 2013: 117(3) :591-6.
-
Hausel J, Nygren J, Thorell A, Lagerkranser M, Ljungqvist O. Randomised clinical trial of effects of oral preoperative carbohydrates on postoperative nausea and vomiting after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Br J Surg 2005;92(4):415-21.
-
Griffenhagen GB, Hawkins LL. Facts and comparisons: handbook of non-prescription drugs.6th ed. Washington DC: Ame Pharm Assoc 1989:107.
-
Dagher CF, Abboud B, Richa F, Abouzeid H, El-Khoury C, Doumit C, et al. Effect of intravenous crystalloid infusion on postoperative nausea and vomiting after thyroidectomy: A prospective, randomized, controlled study. Eur J Anaesthesiol 2009 Mar;26(3):188-91.
-
Haentjens LL, Ghoundiwal D, Touhiri K, Renard M, Engelman E, Anaf V, et al. Does infusion of colloid influence the occurrence of postoperative nausea and vomiting after elective surgery in women? Anesth Analg 2009 Jun;108(6):1788-93.
-
Lauwick SM, Kaba A, Maweja S, Hamoir EE, Joris JL. Effects of oral preoperative carbohydrate on early postoperative outcome after thyroidectomy. Acta Anaes Belg 2009;60(2):67-73.
-
Firouzian A, Kiasari AZ, Godazandeh G, Baradari AG, Alipour A, Taheri A, et al. The effect of intravenous dextrose administration for prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting after laparoscopic cholecystectomy: A double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Indian J Anaesth 2017; 61(10): 803-10.
-
Boogaerts JG, Vanacker E, Seidel L, Albert A, Bardiau FM. Assessment of postoperative nausea using a visual analogue scale. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 2000 Apr;44(4):470–4.
-
Gan TJ, Diemunsch P, Habib AS, Kovac A, Kranke P, Meyer TA, et al. Consensus guidelines for the management of postoperative nausea and vomiting. Anesth Analg 2014 Jan;118(1):85-113.
-
Ljungqvist O, Nygren J, Thorell A. Insulin resistance and elective surgery. Surgery 2000 Nov;128(5):757–60.
-
Hasegawa H, Shirohara H, Okabayashi Y, Nakamura T, Fujii M, Koide M, et al. Oral glucose ingestion stimulates cholecystokinin release in normal subjects and patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 1996;91:196-202.
-
Kissin I, Bright CA, Bradly EL Jr. Acute tolerance to continuously infused alfentanil: The role of cholecystokinin and N-methyl-D-aspartate-nitric oxide systems. Anesth Analg 2000 Jul;91(1):110-6.
-
Mitchell VA, Jeong HJ, Drew GM, Vaughan CW. Cholecystokinin exerts an effect via the endocannabinoid system to inhibit GABAergic transmission in midbrain periaqueductal gray. Neur Pharmac 2011;36:1801-10.
-
Saleh AN, Emam DF, Kamal MM. Evaluating the Effect of Intraoperative Dextrose 10% Administration on Reducing Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting after Laparoscopic Surgery. Anesthesia J 2019;13:78-85.
-
Atashkhoei S, Naghipour B, Marandi PH, Dehghani A, Pourfathi H. Effect of intraoperative dextrose infusion for prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting in diagnostic gynecologic laparoscopy. Crescent J Med Biol Sci 2018;5:45-9.
-
Rao V, Bala I, Jain D, Bharti N. Effect of intravenous dextrose administration on postoperative nausea and vomiting in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a randomised controlled trial. Eur J Anaesthesiol 2017;34(10):705–7.
-
Patel P, Meineke MN, Rasmussen T, Anderson DL, Brown J, Siddighi S, et al. The relationship of intravenous dextrose administration during emergence from anesthesia to postoperative nausea and vomiting: a randomized controlled trial. Anesth Analg 2013;117(1):34–42.
-
McCaul C, Moran C, O’Cronin D, Naughton F, Geary M, Carton E, et al. Intravenous fluid loading with or without supplementary dextrose does not prevent nausea, vomiting and pain after laparoscopy. Can J Anaesth 2003;50(5):440–4.
-
Yokoyama C, T Mihara, Kashiwagi S, Goto T. Effects of intravenous dextrose on preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting: A systematic review and meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis. PloS One 2020;15(4): 2-17.
-
Pareek A, Mantan K, Vigneswaran P, Sharma A. Pre-Operative Administration of 5% Dextrose for Prevention of Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting after Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy. J Med Sci Res 2020;08(07):92-8.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License