IJCRR - 13(8), April, 2021
Pages: 137-142
Date of Publication: 25-Apr-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A Study to Find Out the Correlation of Mobile Phone Addiction with Anxiety, Depression, Stress and Sleep Quality in the College Students of Surat City
Author: Sonali Tanmay Choksi, Nipa Patel
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Smartphones are an important part of adolescent's life. Smartphone addiction is a common worldwide problem among adults, which might negatively affect their mental and physical wellbeing. Objective: Examine the relationship between mobile phone use and mental health by measuring the levels of depression, anxiety, stress and sleep quality among college students of Surat city. Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted on a total of 100 numbers of college students. Data were collected by 3 Self-reported questionnaires including depression, Anxiety and Stress scale (DASS), Insomnia was assessed using Athens Insomnia Scales (AIS), and Smartphone addiction scale - Short version (SAS-SV). Results: Statistical analysis indicates that 27% of students were addicted to the smartphone. Stress, anxiety, depression and sleep quality have a positive significant correlation with smartphone addiction (p< 0.05). Anxiety (p=0.000) and stress (p=0.000) were highly correlated with smartphone addiction followed by depression(0.002) and sleep quality (0.004). The results revealed there were high chances of anxiety and stress for cell phone addicts. Conclusion: There was a highly significant positive correlation between smartphone addiction and stress as we as between smartphone addiction and anxiety. Apart from this, a moderate correlation was found between smartphone uses and seep quality as well as between smartphone use and depression. So the intensity of mobile phone use could be a factor that can influence causal pathways leading to mental health problems.
Keywords: Mobile phone addiction, Adolescents, Sleep quality, Depression, Anxiety, Stress
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Mobile phone use has become a necessity, due to widespread availability.1 Addiction to smartphone usage is a common problem among adults worldwide which is manifested as excessive usage of phones, while engaged in other activities such as studying, driving, social gatherings and even sleeping.2 However, many people don’t realize that addiction to the smartphone is a serious issue leading to a negative effect on the person’s thoughts, behaviour, tendencies, feelings, and sense of well-being.3 In particular, it can be a risk factor for depression, loneliness, anxiety and sleep disturbances.4 Recent types of research have shown that the use of the mobile phone is associated with headaches, neurovegetative dystonia, irritability, sleep disorders, fatigue, and dizziness.5-9
Even though there are numerous evidence that shows positive/useful examples of mobile phone use (mostly smartphones) in medicine, education, and other fields10-14, Due to high degree of Internet use leads to addiction and behavioural changes.15
Even though there are no discrete diagnostic criteria for smartphone addiction, it includes areas of behavioural addiction (i.e., gambling, internet gaming).16 This type of addiction is more common in adults who have more negative effects because it is a sensitive period with the occurrence of many physiological, psychological and social changes.17,18 Addiction is manifested in various forms such as tolerance, lack of control, withdrawal, mood modification, conflict, lies, excessive use and loss of interest.19 Most common issues which are proven include stress, anxiety, depression, attention deficit, insomnia or other sleep quality-related issues and effect on academic performance
“Depression” derives from the word “depressed” in Latin, means pressing down, suffering, exhausted, woeful, sorrowful, discouraged, and deaden.19 Depression is one of the most common mental disorders in young people and causing severe disruptions in psychosocial and academic functioning.19 Many studies have revealed a positive correlation between smartphone addiction and depression; however, all these studies were conducted in specific populations. Demirci K confirmed females were more prone to develop smartphone addiction compared to males20, while Augner C et al concluded an association between stress, low emotional stability, female gender, young age and depression with mobile addiction.21 Yen C, confirmed that adolescents with significant depression due to phone addiction are more likely to develop four or more behavioural symptoms.22 This positive correlation with depression is alarming. So, reasonable usage of smartphones is advised, especially among younger adults, as they have a higher risk of depression19 so in this study, we are going to focus on the effect of smartphone addiction in adults as they are more prone to get smartphone addiction.
The origin of the word “anxiety” is “anxiety” in Greek, meaning “worry, fear, curiosity”. In other words, anxiety is a mood, experienced in the face of danger resulting externally.26 According to Aydemir anxiety is a reaction that is unconscious and unknown by a person and that occurs against internal threats.23 Various epidemiological studies have revealed that its prevalence in adolescent psychiatry is the highest.24 Many kinds of research proved the correlation between “depression and anxiety”. According to classical theory, anxiety and depression do not differ from each other and may exist together.25 So in this study effect of smartphone addiction on depression and anxiety are studied together
The word “stress” is a Latin word, which refers to a warning sign on the health and peace of people,26 Stress is a result of external conditions; it can result from the perspective of events of individuals.26 various studies show the high, medium and low correlation between stress and excessive mobile phone use.26-28 so to strengthen the literature about stress and mobile phone use in adults we have added stress component in our study along with depression and anxiety.
Insomnia is diagnosed based on the patient's subjective perception of unsatisfactory sleep quantity and/or quality. So, for the diagnosis of insomnia impaired sleep quality is given equal importance as that of reduced sleep quantity. 29 It is proven that mobile phone use in bed at night negatively impacts sleep outcome,30-32 this is due to the disturbances in circadian rhythm and sleep quality due to the exposure to bright light from electronic devices.32-35 In the present study we have focused on the overall effect of mobile phone addiction with insomnia rather than the use of mobile phone only while sleeping.
Nowadays, adolescents are likely to use mobile phones for more hours per day, which can lead to different psychological and physiological problems. Even though the use of the mobile phone has been proven positive in many areas like medicine, e-learning, social media marketing, entertainment etc. but when the use of the mobile phone becomes addictive it leads to a negative effect on different components of health. So this study has been conducted to correlate mobile phone addiction with stress, anxiety, depression and insomnia in young adults.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
-
Study design: Co-relation study
-
Study population: 18 to 23 years old adult students of S.P.B physiotherapy college, Surat.
-
Sample size: 100
-
Sampling Technique: Convenient Sampling
-
Inclusion criteria: 1) Students who agreed to participate in the study.
-
Minimum use of mobile phone >1 hour/day.
-
Those who use the smartphone with an active internet connection.
2) Who didn't give their informed consent.
3) Known case of other psychological disorders.
-
Depression, Anxiety and Stress scale-21 [DASS] 36
-
Athens Insomnia scale [AIS] 37
-
Smartphone addiction scale - Short version [SAS - sv] 38
Procedure for data collection
One hundred college students (19 males and 81 Females) whose age ranged from 18 to 23 years participated in the study. Participation in the study was voluntary and informed consent was taken before participation. They were selected by convenient sampling. All the subjects were explained about this study and about the questionnaires that were to be filled before the participation. 3 Questionnaires i.e DASS-21 (depression anxiety stress scale), AIS (Athens insomnia scale) and SAS-SV (Smartphone addiction scale-short version) were then handed out amongst the students of SPB Physiotherapy college and collected after being filled.
Statistical analysis
Data analysis was done using SPSS 20 and frequency distribution. P-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
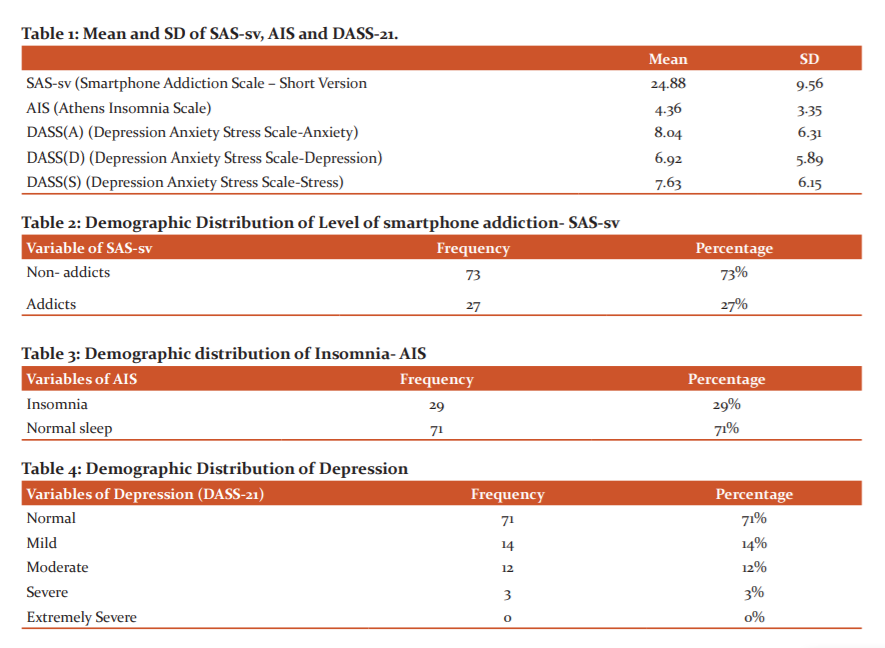
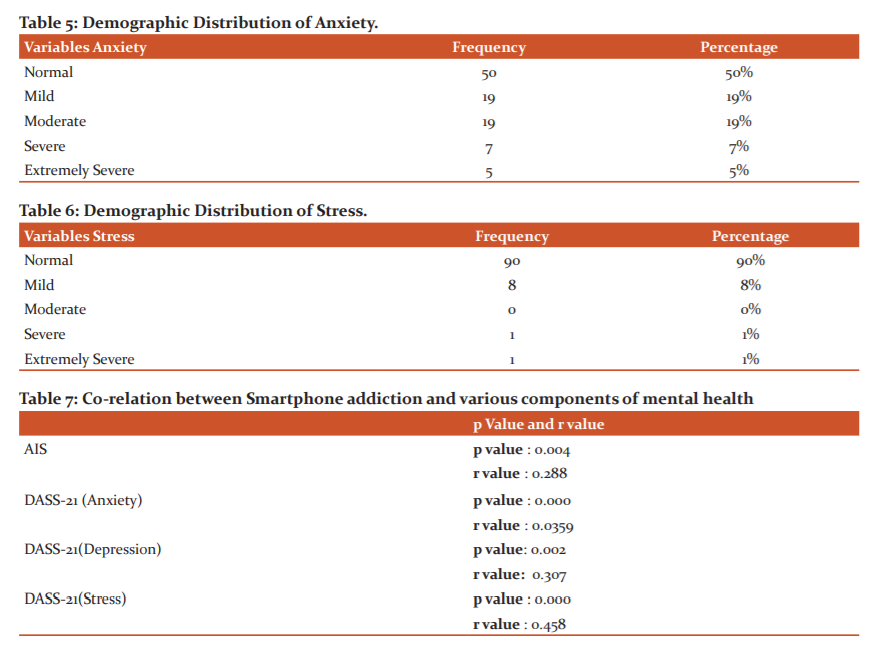
Table 1 shows the mean and standard deviation of SAS-SV is 24.88 and 9.56 respectively. The value of the mean and standard deviation of AIS is 4.36 and 3.35 respectively. The value of the mean and standard deviation of DASS(A) is 8.04 and 6.31 respectively. The value of the mean and standard deviation of DASS(D) is 6.92 and 5.89 respectively. The value of the mean and standard deviation of DASS(S) is 7.63 and 6.15 respectively. According to table 2; 73% of subjects are non-addicted and 27% of subjects are addicted to the smartphone. Table 3 shows 29% of subjects had Insomnia and 71% of subjects had normal sleep. Table 4 describes depression distribution; 71% were normal, 14% subjects had mild symptoms of depression, 12% subjects had moderate symptoms of depression, 3% subjects had severe symptoms of depression. According to table 5; 50% didn’t have anxiety, 19% had mild anxiety, 19% had moderate anxiety, 7% had severe anxiety and 5% had extremely severe anxiety. Table 6 shows 90% of subjects didn’t have stress, 8% had mild stress, 0% had moderate stress, 1% had severe stress and 1% had extremely severe stress.
Correlation of smartphone addiction with sleep quality, anxiety, depression and stress was done using Karlpearsons correlation coefficient which shows significant correlation i.e. p-value = 0.004, 0.000, 0.002 and 0.000 respectively. (Table 7)
DISCUSSION
The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship of smartphone use with anxiety, depression, stress and quality of sleep. With the growing popularity of smartphone technology among young adults, it is important to understand predictive factors of stress, depression, anxiety and quality of sleep to prevent negative outcomes.39
Cell phone use has dramatically increased in today's world. Since electromagnetic waves are used for data transmission by cell phones, some concerns have been raised about their negative impacts on public health. The effect of cell phone use on anxiety, depression, stress and sleep quality is among these concerns, which can be evaluated by laboratory methods, epidemiological surveys, and standard questionnaires.40
In this study, by using three standard questionnaires (AIS, DASS-21, SAS-sv), the relationship between cell phone overuse and anxiety, depression, stress and sleep quality was assessed among medical students. According to some previous studies, the increased incidence of insomnia is attributed to increased emotional reactivity. In previous studies, SMS users were more likely to be neurotic, depressed, or anxious, indicating the possibility of disturbance in sleep quality.40 The present study showed that excessively long hours of mobile phone use were associated with insomnia, which increases with an increased hour of mobile phone use. The result of this study favours the study on adolescents in Hong Kong, which concludes long hours of mobile phone use were correlated with short sleep duration, poor sleep quality, and excessive daytime sleepiness.41
In our study 71% were normal, 14% subjects having mild symptoms of depression, 12% subjects having moderate symptoms of depression, 3% subjects having severe symptoms of depression. Increased hour of mobile phone use was correlated with increased depression. However, the purpose of mobile phone use was not considered in this study. This study showed that long hours of mobile phone use were at more risk for insomnia. An association between smartphone addiction and altered lifestyle habits was found in various studies. Mobile phone addicts are at higher risk to skip meals, eating unhealthy diets, gaining weight, and experience sleep disorders compared to less addicted smartphone users. These can be accounted as predisposing factors to Depression.36
SMS (e.g., Facebook, Twitter or Instagram) and online chat (e.g., Line, Skype, Kakao Talk) are popular online communication tools among adolescents. Some earlier studies have indicated that their use is associated with mental health problems as their uses enable one to communicate and interact with a large number of people.41
In our study 90% are normal, 8% of subjects having mild symptoms of stress, 0% of subjects having moderate symptoms of stress, 1% subjects having severe symptoms of stress and 1% subjects having extremely severe symptoms of stress. Over usage of smartphones causes problems with attention and focusing that leads to the development of stress. Young adults with personality type A are more susceptible to develop smartphone addiction and high level of stress because of lacking positive stress coping mechanisms.36
Different kinds of stress are risk factors for developing an anxiety disorder, and these can, in turn, cause or worsen sleep disorders. Similarly, stress can trigger depression, which can then be complicated by anxiety. Several animals and human basic research studies indicate the effects of using mobile phones on cognition and brain functions. Our and similar research confirm the findings on the manifestation level of those complex conditions. Even if the exact underlying mechanisms are not clear because the conditions modified by mobile phones per se still do not have a fully explained etiopathogenesis, the quantity of new evidence indicates that mobile phone usage is part of multiple underlying causal links to those described conditions.19 The study is limited to Surat City only. The study is limited to the young adult population. The study is limited to 100 subjects for questionnaire-based variables.
CONCLUSION
The main purpose of this study was to find out the relation between smartphone addiction and various components like stress, anxiety, depression and sleep quality. There was a highly significant positive correlation between smartphone addiction and stress as we as between smartphone addiction and anxiety. Apart from this, a moderate correlation was found between smartphone uses and seep quality as well as between smartphone use and depression. So, smartphone addiction should be prevented in young adults to save them from getting behavioural problems such as stress, anxiety, depression and insomnia. Future studies can be done using larger sample size and on the different age group of people. Physical variables a=can be considered instead of behavioural variables.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS: The authors also wish to express gratitude to the students of spb physiotherapy college for their support during data collection
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: Nil
SOURCE OF FUNDING: Nil
References:
-
Aleksandar VC, Vladica VC, Dušan SC, Miodrag SC, Kristijan MC, Miodrag SC, et al. Relationship between the Manner of Mobile Phone Use and Depression, Anxiety, and Stress in University Students. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2018;15(4):697.
-
Harwood J, Dooley J, Scott A, Joiner R. Constantly connected – the effects of smart devices on mental health. Comput Hum Behav 2014;34:267–72.
-
Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. Arlington: American Psychiatric Publishing; 2013.
-
Gao Y, Li A, Zhu T, Liu X, Liu X. How smartphone usage correlates with social anxiety and loneliness. Peer J 2016;4:e2197.
-
Al-Khlaiwi T, Meo SA. Association of mobile phone radiation with fatigue, headache, dizziness, tension and sleep disturbance in Saudi population. Saudi Med J 2004;25:732–736.
-
Chiu CT, Chang YH, Chen CC, Ko MC, Li CY. Mobile phone use and health symptoms in children. J Formos Med Assoc 2015;114:598–604.
-
Melton BF, Bigham LE, Bland HW, Bird M, Fairman C. Health-related behaviors and technology usage among college students. Am J Health Behav 2014;38:510–518.
-
Roosli M, Moser M, Baldinini Y, Meier M, Braun-Fahrlander C. Symptoms of ill health ascribed to electromagnetic field exposure—A questionnaire survey. Int J Hyg Environ Health 2004;207:141–150.
-
Višnjic A, Velickovic V, Stojanovic M, Miloševic Z, Rangelov T, Bulatovic K, et al. The frequency of using screen-based media among children and adolescents and its impact on health-related behaviours. Acta Med. Med 2015;54:64–73.
-
Payne KB, Wharrad H, Watts K. Smartphone and medical related App use among medical students and junior doctors in the United Kingdom (UK): A regional survey. BMC Med Inform Decis Making 2012;12:121.
-
Roggeveen S, van Os J, Viechtbauer W, Lousberg R. EEG Changes Due to Experimentally Induced 3G Mobile Phone Radiation. PLoS One 2015;10:e0129496.
-
Zivin K, Eisenberg D, Gollust SE, Golberstein E. Persistence of mental health problems and needs in a college student population. J Affect Disord 2009;117:180–185.
-
Bayram N, Bilgel N. The prevalence and socio-demographic correlations of depression, anxiety and stress among a group of university students. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 2008;43:667–672.
-
Wittmann-Price RA, Kennedy LD, Godwin C. Use of personal phones by senior nursing students to access health care information during clinical education: Staff nurses’ and students’ perceptions. J Nurs Educ 2012;51:642–666.
-
Kawabe K, Horiuchi F, Ochi M, Oka Y, Uenno S. Internet addiction: prevalence and relation with mental states in adolescents. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2016;70(9):405–12.
-
Holden C. Behavioral addictions: do they exist? Science 2011;294(5544):980–2.
-
Beranuy M, Oberst U, Carbonell X, Chamarro A. Problematic Internet and mobile phone use and clinical symptoms in college students: the role of emotional intelligence. Comput Human behav 2009;25(5):1182–7.
-
Chóliz MM, Villanueva SV. Evaluación de la adicción al móvil en la adolescencia. Revista Española de Drogodependencias 2011;36:165–84.
-
Aljohara A. Alhassan1, Ethar M. Alqadhib1, Nada W. Taha1, Raneem A. Alahmari2, Mahmoud Salam3* and Adel F. Almutairi3. The relationship between addiction to smartphone usage and depression among adults: a cross sectional study. BMC Psychiatry 2018;18(1):148.
-
Demirci K, Akgönül M, Akpinar A. Relationship of smartphone use severity with sleep quality, depression, and anxiety in university students. J Behav Addict 2015;4(2):85–92. 12.
-
Augner C, Hacker G. Associations between problematic mobile phone use and psychological parameters in young adults. Int J Public Health 2011; 57(2):437–41.
-
Yen C, Tang T, Yen J, Lin H, Huang C, Liu S, et al. Symptoms of problematic cellular phone use, functional impairment and its association with depression among adolescents in southern Taiwan. J Adolesc 2009;32 (4):863–73.
-
Ömer A, ?smet K , Tülay S , Burak U Reliability and Validity of the Turkish Version of the Health Anxiety Inventory Noro Psikiyatr Ars 2013; 50(4):325-331
-
Aydemir Ö, ve Bayraktar E. Genel T?pta Anksiyete (II). Psycho Med 1996;2(4):134-140
-
Kashani JH, Orvaschel H. A Community Study of Anxiety in Children and Adolescents. Am J Psychiatry 1990;147: 313-318
-
Ertan B, Mehmet K Depression, Anxiety and Stress Scale (DASS): The Study of Validity and Reliability. Uni J Edu Res 2016;4(12):2701-2705.
-
Zahra V, Alyssa S The association between smartphone use, stress, and anxiety: A meta?analytic review. Stress Health 2018;34(3):347-358.
-
Gligor ?, Mozo? Indicators of smartphone addiction and stress score in university students. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2019;131(5-6):120-125.
-
Maya S, Nazi Relationships among smartphone addiction, stress, academic performance, and satisfaction with life. Comp Human Behav 2016;75:321–325.
-
Constantin R. Soldatos, Dimitris G. Dikeos, Thomas J. Paparrigopoulos. Athens Insomnia Scale: validation of an instrument based on ICD-10 criteria.
J Psychosom Res 2000;48(6):555-60
-
Munezawa T, Kaneita Y, Osaki Y, Kanda H, Minowa M, Suzuki K, et al. The association between use of mobile phones after lights out and sleep disturbances among Japanese adolescents: A nationwide cross-sectional survey. Sleep 2011;34:1013–1020.
-
Exelmans L, van Den BJ. Bedtime mobile phone use and sleep in adults. Soc Sci Med 2016;148:93–101.
-
Fossum IN, Nordnes LT, Storemark SS, Bjorvatn B, Pallesen S. The association between use of electronic media in bed before going to sleep and insomnia symptoms, daytime sleepiness, morningness, and chronotype. Behav Sleep Med 2014;12:343–357.
-
Cho CH. Moon JH, Yoon HK, Kang SG, Geum D, Son GH, et al. Molecular circadian rhythm shift due to bright light exposure before bedtime is related to subthreshold bipolarity. Sci Rep 2016;6:31846.
-
Cain N, Gradisar M. Electronic media use and sleep in school-aged children and adolescents: A review. Sleep Med 2010;11:735–742.
-
Haruka T, Tomoko N, Akiyo T and Hisataka S Association between Excessive Use of Mobile Phone and Insomnia and Depression among Japanese Adolescents. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2017;14(7):701.
-
Lovibond SH, Lovibond PF. Manual for the Depression Anxiety & Stress Scales. (2nd Ed.) Sydney: Psychology Foundation. 1995.
-
Soldatos CR, Dikeos DG, Paparrigopoulos TJ. Athens insomnia scale: validation of an instrument based on ICD-10 criteria. J Psychosom Res 2000;48(6):555–560.
-
Kwon M, Kim DJ, Cho H, Yang S. The smartphone addiction scale: development and validation of a short version for adolescents. PLoS One 2013;8(12):e83558
-
Elizabeth ML. The relationship between smartphone use, symptoms of depression, symptoms of anxiety, and academic performance in college students, 2017. Iowa State University, 1-64
-
Mohamad R, Bayatiani, Fatemeh S, Akram B The Correlation between Cell Phone Use and Sleep Quality in Medical Students. Iranian J Med Phy 2016;12:8-16.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License