IJCRR - 13(7), April, 2021
Pages: 04-08
Date of Publication: 12-Apr-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Antiprostatic Activity of Ferulene in Male Rats
Author: Tukhtasheva Visola Farmonovna, Rejepov Jumadilla, Djakhangirov Farkhod Nabievich, Zakhidova Lola Tishaevna, Halilov Ravshanjon Muratjanovich, Saidkhodjayeva Dilfuza Mir-Taxirovna
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Studied the antiprostatic activity of the sum of esters of sequiterpine alcohols obtained by ferula thin-braided (ferule). Objective: The purpose of the study was to substantiate the feasibility of using the developed new drug ferulene as a means of antiprostatic action in the body. Methods: To assess the effect of ferulene on androgen-dependent organs, the drug was administered to male rats orally using a metal probe at doses of 1-5-10 mg/kg for 10 days. Each dose of the drug was tested on 10 rats. Results: It was found that ferule has a pronounced ant prostatic effect when administered orally, reduces the mass of adreno�genesis-dependent organs (ventral prostate, coagulating gland, seminal vesicles, and testes) and reduces the level of testoster�one in the blood. In terms of ant prostatic activity, ferule is not inferior to surgical castration. Conclusion: Long-term use of ferulene is well tolerated by experimental animals and does not have a toxic effect on the part of biochemical parameters, a decrease in the mass of androgen-dependent organs (ventral prostate, coagulating gland, seminal vesicles, testes) and a decrease in the content of testosterone in the blood associated with the specific activity of the drug about target organs.
Keywords: Ferula finely dissected, Ferula tenuisecta, Esters of sequiterpine alcohols, Ferulen, Prostate, Chronic toxicity
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Prostate cancer (PC) is currently one of the most pressing diseases in urology oncology. Survival outcomes for patients with hormonal treatment are different. PC is a fairly common disease. On average, 71 cases per 100 thousand men are registered per year. Moreover, in the last decade, there has been an increase in the incidence of 3% annually. This is an alarming signal that suggests an increase in the number of registered cases by almost 2 times already by 2030. Treatment of patients with prostate cancer is an important task of modern urology due to the prevalence of the disease and the unresolved issues of its therapy. Drug therapy occupies an important place in the treatment of patients with prostate cancer and is based on the results of the latest research on the pathogenesis of this disease. For the drug treatment of patients with prostate cancer, 5-α-reductase inhibitors, α1-adrenergic receptor blockers, polyene antibiotics, antiandrogens, estrogens, and preparations of plant and biological origin are used.1,2
Prostate cancer is one of the most common diseases of men of elderly and senile age, occupying the 2-3rd place in the structure of oncological diseases of the male population and showing a clear tendency to an increase in frequency.3,4
The main functions of the gland are the partial production of semen (about 30% of the total volume), as well as participation in the process of ejaculation. A man's ability to retain urine is also related to prostate function.5,6 Because of the above, the creation of a new agent for the treatment of adenoma and prostate cancer is a scientific novelty and an urgent task.
Based on the esters of ferutinin (C22H30O4), ferutin (C23H32O5), tenuferin (C23H32O6), tenuferidine (C22H30O5) and fertidine (C27H36O4) isolated from the roots of the finely dissected ferula (Ferula tenuisecta celery), a new family has been created. the drug "Ferulen" for the treatment of adenoma and prostate cancer.3
Technology has been developed for the preparation of ferulene, which consists in the extraction of plant materials with alcohol, thickening of the alcohol extract, dilution with water and extraction of esters with ethyl acetate, treatment with 5% potash solution, extraction of esters with 1% KOH solution, acidification with sulfuric acid, extraction with ethyl acetate, evaporation of ethyl acetate solution, chromatographic purification of esters on a column of silica gel (eluent - ethyl acetate-hexane 1: 3) and drying of the esters by adding microcrystalline cellulose. The yield of the ferulene substance is 18.6% by weight of the raw material, esters - 80% of the content in the raw material.4,7 The purpose of the study was to substantiate the feasibility of using the developed new drug ferulene as a means of antiprostatic action in the body.
?ATERIALS AND METHODS
Animals and habitat
All animals were kept in stationary vivarium conditions on a regular diet with free access to water. Experiments with them were carried out by the rules adopted by the International Convention for the Protection of Vertebrate Animals used for Experimental Purposes.6,8
Experimantal design
To assess the effect of ferulene on androgen-dependent organs, the drug was administered to male rats orally using a metal probe at doses of 1-5-10 mg/kg for 10 days. Each dose of the drug was tested on 10 rats. The control group of animals under similar experimental conditions was injected with a solvent (distilled water with the addition of apricot gum). After the end of the experiment, all experimental and control animals were decapitated, the weight of the ventral prostate, coagulating gland, seminal vesicles and testes was determined; the content of testosterone in the blood serum was determined by the radiomunal method on the counter "Gamma-12" with kits for the in vitro radioimmunoassay and the immunoenzyme (Human GmbH (Germany) kit "Diagnostiksistema", Russia) by the method for the determination of testosterone in the blood serum of the Czech company "JMMUNOTECH as" Content of bioactive luteinizing hormone in the blood plasma of male rats was determined using the enzyme immunoassay analyzer MINDRAY-MR-96A. (the work was carried out at the Research Institute of Endocrinology, Ministry of Health of the Republic of Uzbekistan), histological studies were also carried out.
The study of the effect of ferulene on androgen-dependent organs in comparison with surgical castration was carried out on white male rats weighing 300-320 g. the drug was administered orally using a metal probe at a dose of 10 mg/kg for 10 days. Surgical castration (orchiectomy) was performed with a longitudinal incision at the base of the scrotum, the skin and testicular membrane were dissected to the albuminous. The testicle with the epididymis and part of the spermatic cord was bluntly isolated. The rope was clamped in parts with a clamp and crossed. The proximal part of the transected cord was sutured with strong ligatures and the testicle and cord were removed. The control group of animals was injected with a solvent under similar experimental conditions. After the end of the experiment, all experimental and control animals were decapitated, the weight of the ventral prostate, coagulating gland, seminal vesicles and testes was determined; determined the content of luteinizing hormone and testosterone in the blood serum.3,4
The study of the chronic toxicity of the drug Ferulen was carried out in experiments on 40 white outbred rats - males. The drug was injected into the stomach daily at doses of 10-25-50 mg/kg for 2 months. Each dose was tested in 10 rats. The control group of animals was injected with the solvent under similar conditions. All experimental and control animals were kept in the same conditions and on the usual diet.
Statistical analysis
The digital material obtained during the experiments was statistically processed using the Student's t-test.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
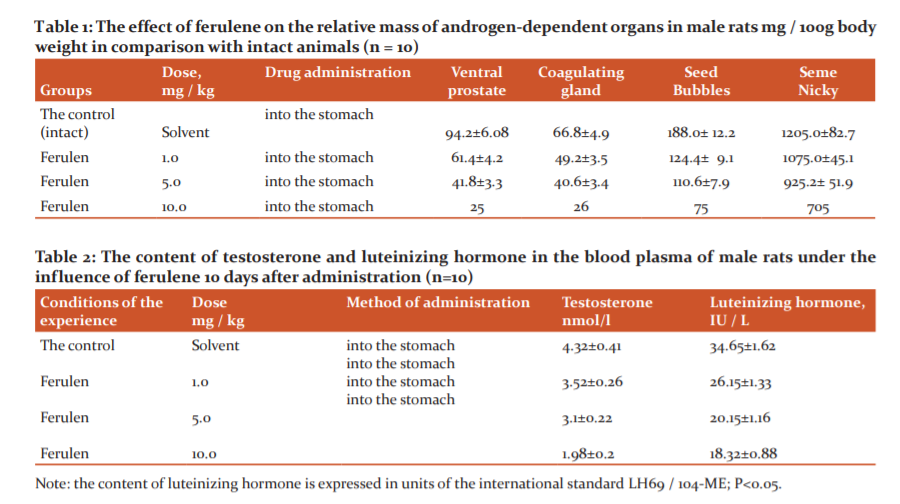
The results of the studies showed that oral administration of ferulene at a dose of 1 mg/kg reduced the weight of the ventral prostate, coagulating gland, seminal vesicles and testicles compared with the control group of rats by 35%, 26.2%, 34% and 11%, respectively. With an increase in the dose of the drug to 5 mg/kg, ferulene reduced the mass of these organs by 56%, 39%, 41% and 23%, respectively. A further increase in the dose of ferulene to 10 mg/kg reduced the mass of the ventral prostate and the coagulating gland to values close to post-castration and compared with the control group, the mass of the ventral prostate decreased by 73%, the coagulating gland by 61%, seminal vesicles by 60% and testes by 41% (Table 1).
The results of the studies carried out to assess the content of luteinizing hormone and testosterone in the blood serum showed that ferulene with 10 days of oral administration in doses of 1-5-10 mg/kg leads to a decrease in testosterone, compared with control animals by 19%, 28% and 54 % of a luteinizing hormone by 24.5%, 31% and 47.13%, respectively (Table 2).
The results of a histological study showed that the introduction of ferulene at a dose of 1 mg/kg caused in some animals a slight decrease in the amount of secretion in the lumen of the prostate, a decrease in the height of epithelial cells and an increase in the connective tissue of the organ. In other animals, the reaction to the introduction of ferulene at a dose of 1 mg/kg was significantly stronger.
When the dose of ferulene was increased to 5 mg/kg, the histological changes became permanent and deeper. The size of the lumens of the end sections of the gland decreased, even more, the volume of the cytoplasm of epithelial cells, their shape changed, they became low-cylindrical or cubic. Desquamation of the epithelium from a large area of the alveoli was observed. The connective tissue grew, replacing the atrophied secretory parts of the gland. The cells of the basal layer of the glandular epithelium had a pycnotic nucleus and an optically transparent cytoplasm. Hypertrophy and hyperplasia of myocytes around the secretory glands were observed.4,7-9
With a further increase in the dose of ferulene to 10 mg/kg against the background of hyperplasia of connective tissue and muscle elements, pronounced dystrophic and destructive changes in the secretory epithelium were observed.
Thus, the results of the studies carried out have established that, depending on the administered dose, ferulene, to varying degrees, reduces the mass of androgen-dependent organs, causes dystrophic destructive changes in the prostate and reduces the content of luteinizing hormone and testosterone in the blood serum of male rats (Table 1 and 2).
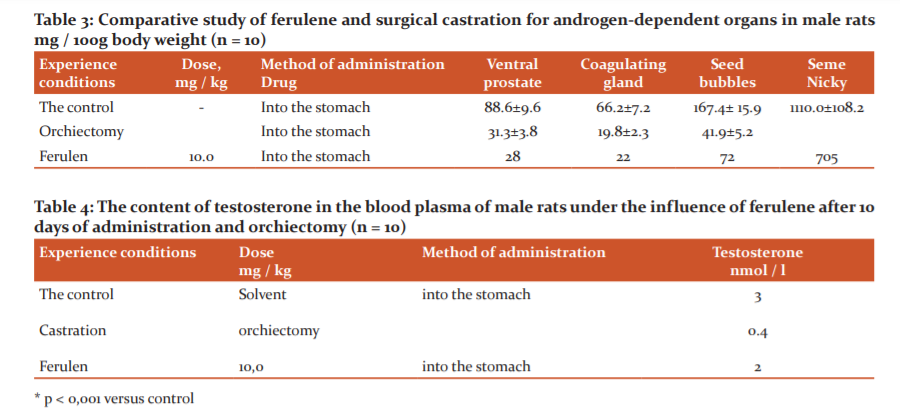
The results of the studies on the effect on the mass of androgen-dependent organs in comparison with orchiectomy are presented in Table 3. As can be seen from the table, ferulene at a dose of 10 mg/kg reduced the mass of the ventral prostate and coagulating gland at the level of surgical castration, and compared with the control animals, the mass of the ventral prostate decreased by 67%, the coagulating gland by 66%, seminal vesicles by 59%. and testicles by 35% (Tables 3, 4 and 5).
The results of the studies have shown that long-term oral administration of ferulene at doses of 10-25-50 mg/kg is well tolerated by experimental animals. All experimental animals did not differ from control rats in general condition, in haematological parameters (Tables 6 and 7).
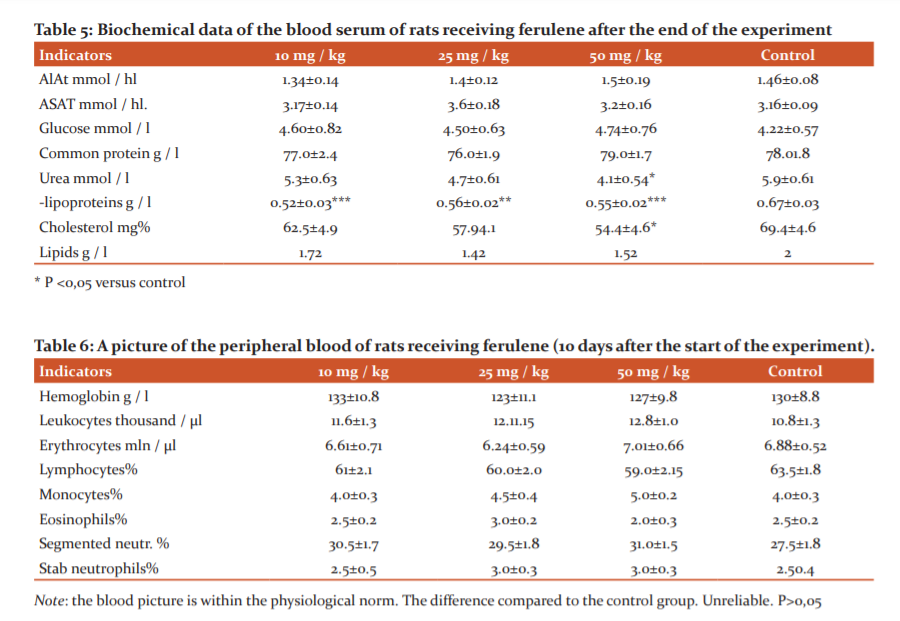
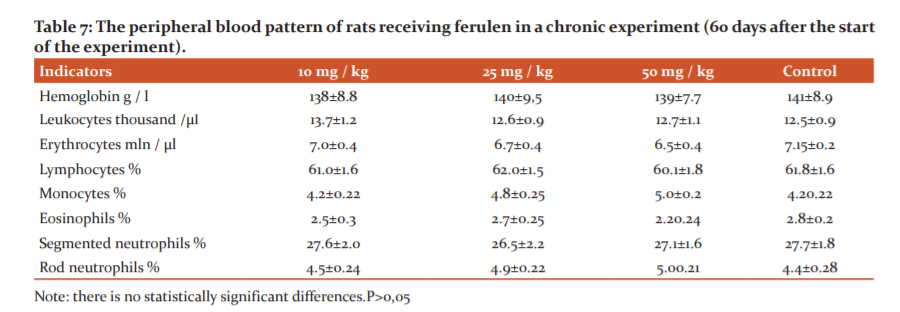
The results of the studies have shown that long-term oral administration of ferulene at doses of 10-25-50 mg/kg is well tolerated by experimental animals. All experimental animals did not differ from the control rats in general condition, behaviour, and haematological parameters (Table 6 and7). On the part of biochemical parameters, a decrease in urea was noted, b- lipoproteins, cholesterol and lipids (Table 5)
CONCLUSION
The studies carried out in this work showed that ferulene has a pronounced antiprostatic effect when administered orally, reduces the mass of adrenogenesis-dependent organs (ventral prostate, coagulating gland, seminal vesicles, testes) and reduces the level of testosterone in the blood. In terms of antiprostatic activity, ferulene is not inferior to surgical castration. When applied again, it does not accumulate. Long-term use of ferulene is well tolerated by experimental animals and does not have a toxic effect on the part of biochemical parameters, a decrease in the mass of androgen-dependent organs (ventral prostate, coagulating gland, seminal vesicles, testes) and a decrease in the content of testosterone in the blood associated with the specific activity of the drug concerning target organs.
Conflict of Interest: None
Source of Funding: None
References:
-
Huggins C, Hodges CV. Studies on prostatic cancer: I. The effect of castration, estrogen and of androgen injection on serum phosphatases in metastatic carcinoma of the prostate. Cancer Res 2019;1(19):293-297.
-
Tukhtasheva VF, Rejepov J, Djakhangirov FN, Azamatov AA, Zakhidova LT. Preclinical study of safeness of the drug ferulen. Am J Med Sci Pharm Res 2020;2(6):134-143.
-
Guryeva MV, Yu. B, Kotov VA. Daily monitoring of blood pressure and heart rate in the diagnosis. Russ Bull Obstet Gynecol 2013;3:4-9.
-
Wu YW, Colford Jr JM. Chorioamnionitis as a risk factor for cerebral palsy: a meta-analysis. JAMA 2000;284(11):1417-142
-
Fox R, Kitt J, Leeson P, Aye C, Lewandowski AJ. Preeclampsia: Risk Factors, Diagnosis, Management, and the Cardiovascular Impact on the Offspring. J Clin Med 2019;8(10):162
-
Vasiliev V, Tyagunova AV, Drozheva VV. Renal function and indicators of endogenous intoxication with gestosis. Obstet Gynaecol 2013; 4:16-20.
-
Mallick S. Study on the clinical profile of patients with cerebral palsy (Doctoral dissertation) 2011; 52(172):127-4
-
Tukhtasheva VF, Rejepov J, Djakhangirov FN, Azamatov AA, Amonov MA. Study on the antiandrogen activity of ferulen in the experiment. Eur Appl Sci 2018;1:30-32.
-
Garg, SA, Chakravarti R, Singh NR, Masthi RC, Goyal GR. Jammy E. Dengue serotype-specific Seroprevalence among 5- to 10-Year-Old Children in India: A Community-Based Cross-Sectional Study. Int J Infer Dis 2017;54:25–30.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License