IJCRR - 13(5), March, 2021
Pages: 70-74
Date of Publication: 03-Mar-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Study to Evaluate the Adverse Drug Reactions in a Teritary Care Teaching Hospital in Tamilnadu - A Cross-Sectional Study
Author: Kumari PM, Jamuna Rani R, Shivani KP
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: The ADR monitoring centre is under the PvPI working for the safety and welfare of patients, in coordinating all the clinical and respective paramedical departments by prompt detection, monitoring and reporting of the ADR and providing proper management. This study aims to evaluate the ADRs from our hospital so that physicians will be cautious while prescribing these drugs with ADRs. Objective: To study the adverse drug reaction in various departments of a tertiary care teaching hospital. Methods: A cross-sectional study conducted on 50 patients of all age groups who developed adverse drug reactions. Causality assessment was done based on Naranjo's probability scale. Modified Hartwig's criteria were used to assess the severity of ADRs into seven levels. Results: A total of 50 ADRs were reported, 44% were males and 56% were females. The female adult population was 42%. The majority of ADRs were due to antimicrobial agents, especially beta-lactam antibiotics (32%) followed by quinolones (10%). A maximum number of patients (74%)were reported with dermatological manifestations. The department of medicine reported the highest number of ADRs (20%). As per Naranjo's scale,56% of reports were assessed as possible. 54% of reports were documented as moderate according to Modified Hartwig's criteria for severity assessment. Conclusion: Hospital admissions due to adverse drug reactions (ADRs) are a major concern in the health care system. Healthcare practitioners need to be more conscious not only of the potential for adverse drug reactions but also of the avoidance (or) minimization of the incidence of ADRs.
Keywords: Pharmacovigilance, Adverse drug reactions, Tertiary care teaching hospital, Antimicrobial agents
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
One of the main unavoidable risk factors in the use of drug therapy is the adverse reactions to the drugs. It is, therefore, one of the major concerns in medicine. Most of the drugs do not cause adverse drug effect; even those reactions which had occurred might be attributed to their Pharmacogenomics pattern. The World Health Organization has described ADR as a response to a drug that is noxious and unintended and that develops at doses commonly used in individuals for prophylaxis, diagnosis, or management, or alterations in physiological function.1 ADRs are common, at times can be life-threatening and in general leads to increased expenses.
This is the reason that the clinicians are requested to be aware of the reactions that can be caused by the drugs before prescribing them. ADRs are common in the hospital setup. They have been classified into two types, one that is the cause of hospitalization and the other which occurs after hospitalization. It is estimated that 5% of the hospitalizations and one in 10-20% of the hospitalized patients are due to drug reactions. In 1994, it was suggested by Lazarou J et al., that 10000 deaths in the USA had occurred due to ADRs, although this was considered to be biased and inflated data.2,3 Consequently, a few studies were conducted wherein the data accumulated was small, and thus the documentation of the ADRs was minimal. The study found that hospital admissions due to ADR accounted for 0.7% of total admissions and ADR deaths reported for 1.8% of total admissions to the Territorial Referral Center in South India.4
Pharmacovigilance Programme of India (PvPI) 2014 stated that 6.7% of patients had serious adverse events. Similar studies have documented those hospital admissions due to ADR were 3.4%, hospital readmissions 3.7%, and mortality 1.8%. Adverse reactions are recognized as the fourth-leading cause of death in the developed world.5 Currently, 179 teaching hospitals and multi-speciality hospitals approved by the Medical Council of India have been established across the country as ADR Monitoring Centers (AMCs). These centres are covered for administrative and organisational purposes by four zonal offices of the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO).6 These AMCs (reporting through VigiFlow; WHO-Uppsala Monitoring Centre [UMC] software) are associated with international networking. Via VigiFlow, the programme owned by WHO-UMC, (Sweden), these AMCs report ADRs to NCC. The reluctance to report is now evolving as the PvPI has released a detailed plan for a proactive pharmacovigilance framework that will raise understanding of the benefits of ADR reporting. The NCC has played a significant role in raising concern among healthcare professionals over five years of reporting ADRs with more than 1,49,000 registered ADRs until December 2015. India's contribution to the global Individual Case Safety Reports (ICSRs) database of the WHO is currently 3%. Our hospital is one of the centres for monitoring and reporting ADRs through this programme.7-9
The causality algorithm of the Naranjo is commonly used to assess the probability that an ADR was related to the medication found by the clinical event monitor rather than the product of other variables. To determine a weighted score based on responses to a brief standardised questionnaire that correlates with the likelihood of causality, the Naranjo algorithm is used. Computer warning signals with a score of 1 on the Naranjo scale, suggesting a potential ADR, were rated as true positives, similar to other clinical event monitoring tests.10-12
The process by which the degree of the relationship between a drug and a suspected reaction is determined is causality evaluation. Actually, in individual patients or case studies, a wide range of causality assessment scales exist to assign clinical outcomes to medications, each with its advantages and disadvantages. These measures include the WHO probability scale, the scale of Naranjo, the scale of Karch & Lasagna, the quantitative imputation scale of Spanish, the scale of Kramer, the scale of Jones, the method of European ABO and the Bayesian system. The most widely used scales are the Naranjo scale and the WHO scale of evaluation.13-15
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A cross-sectional study was conducted for a duration of 16 months from June 2019 to September 2020 at SRM Medical College Hospital and Research Centre after obtaining the approval of the Institutional Ethics Committee. ADR details were collected from the patient after the written informed consent. 50 patients of all age groups who developed adverse drug reactions were included in the study. During this period, routine ward rounds were carried out and awareness was given to all healthcare professionals for the voluntary reporting system. The ADR information was documented based on the treating physician’s report. Patient information such as age, gender, IP number, weight, diagnosis, relevant investigations, and drug information such as the name of the drug, dose, route of administration, frequency of administration, duration of therapy, types of ADR, treatment and outcome of the reaction were collected and the data were documented in the study proforma; each reported patients were assessed individually. Causality assessment was done based on Naranjo’s probability scale. The total score was calculated based on the score and it was categorized as certain (score >9), probable (score 5-8), and possible (score1-4). Modified Hartwig’s criteria were used to assess the severity of ADRs into seven levels: Levels 1 and 2 was classified as a mild category; levels 3 and 4 as a moderate category; levels 5, 6, and 7 were grouped as the severe category.
RESULTS
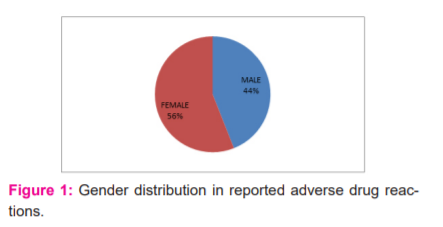
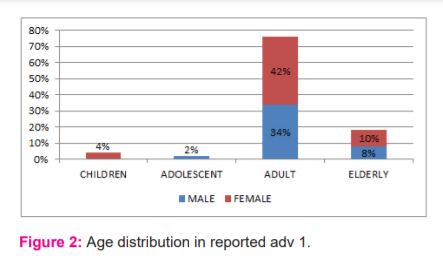
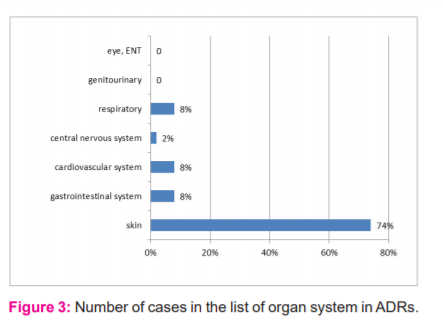
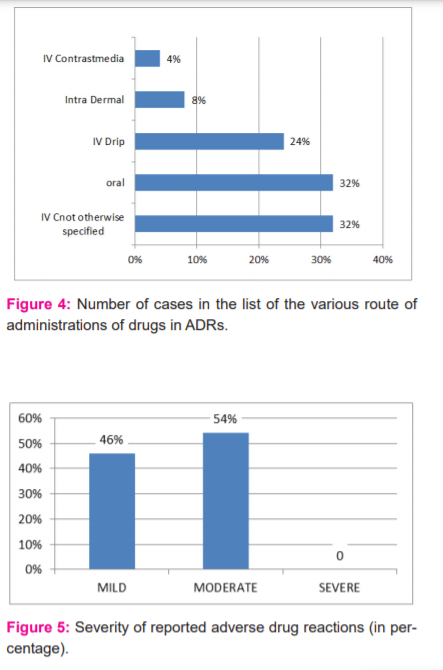
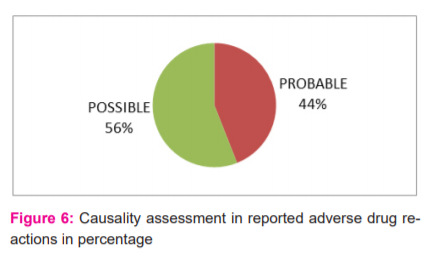
During the period of this study, 50 ADRs were reported. Of these 22 (44%) were males and 28(56%) were females (Figure 1). The maximum number of ADRs which were reported in this study was adult females (42%) of age group 18-60 years followed by adult males (34%) of the same age group adolescent age group (12-18yrs) is 2% only, children of age group <12 yrs was 4% (Figure 2). Maximum ADRs were reported from the Department of Medicine (20%) followed by general surgery (16%) dermatology (10%), O&G (8%) orthopedics (6%) pediatrics (4%) urology(4%) neurosurgery (4%), nephrology (4%) isolation ward (4%) (Figure 3). 32% ADRs were due to beta-lactam antibiotics followed by fluoroquinolone and NSAIDS (Figure 4). Itching and rashes are common sign of drug ADR. (Table 1) Based on the severity of the reaction, mild was 25 (50%) and moderate were 25 (50%) (Figure 5). Causality assessment was done by using both Naranjo’s and WHO scale. Causality assessment showed 56% of cases in the possible category, 44% of cases in the probable category (Figure 6).

DISCUSSION
India, with a population of 1.27 billion, is the fourth largest pharmaceutical producer globally with more than 6,000 licenced manufacturers and more than 60,000 branded products on the market.7 In our study, the number of women (56%) was slightly higher than that of the male population (44%). However, this number was not found to be significant. These results were similar to other studies by Saravanan et al., Jerin James et al., and Naranjo et al.8,9,17 In contrast, in a study by Palanisamy et al., Kumar et al, the number of males affected by ADRs was more than the females.11,12 Thus, the gender was not found to be a risk factor for the development of ADR. The age group to be more affected was the adult group i.e. between 19 to 60 years. Similar results were observed previously.11,12,16
The majority of ADRs (76%) were seen in younger adults in the age group of 18–39 years. This was comparable with the previous study by Kumar et al. in Himachal Pradesh, India.12 This could be due to a greater number of patients getting admitted for treatment in this age group.18 Department of general medicine in our study had more number of ADRs. This could be because there was more inflow of patients in that department. This was followed by a general surgery department and OBGY. ADR in medicine in larger numbers was also observed by Vora et al., in his study.13 Of the drugs, Beta-lactams were the most common cause of ADRs as they were the most common antibiotics prescribed. This was in concurrence with other similar studies by Rodriguez-Pena et al, and Raut et al.14,15 The number of ADRs were high in general medicine and general surgery departments due to the amplified usages of antibiotics in these departments for the treatment and prophylaxis of various diseases and also since the patients admitted were with multiple comorbidities requiring polypharmacy in concurrence with observation done by Vora et al.13
In our study, the skin was the most common organ to be affected (74%) with the predominant symptom being skin rashes seen in 44% of the patients, urticaria in 14%, and dermatitis in 16%. GIT was another prominent site of reactions, with 8% with vomiting. Headaches were observed in 6.4 of the patients and dizziness in 3.6%. In a study by Naranjo et al, 75% of the patients had cutaneous reactions.10 Similar results were reported by Chawla et al, and et al Martin et al.16,17 GIT was the most affected site in studies by Kumar et al.12 On analyzing the fate of the suspected drugs, it was found that the drug was withdrawn in most of the cases and the dose was reduced in some while no change was made in others considering the risk-benefit ratio in particular patients. It was also found that the most common route of administration for suspected drugs of ADRs was Intravenous (not otherwise specified) (32%), oral (32%), followed by intravenous drip (24%).17,18
Most of the ADRs in the study were moderate (54%), while 46% were mild. No severe cases found. This was by a study by Shamna et al and Naranjo et al, who also observed that most of them were moderate (63.26%) followed by mild and severe reactions.10,18 About 74.2% of the cases were moderate in a study by Kumar et al.12 The causality evaluation was carried out using both the Naranjo and WHO scales. The Naranjo scale evaluation has shown that out of 50 ADR’s 28 (56%) ADR’s were possible, 22 (44%) ADR’s were classified as probable and none of the ADR was related to the drug (certain).
CONCLUSION
Drug safety is a major health concern, especially nowadays with the vast number of new drugs coming into the market. No drug is perfectly safe. Aim of adverse drug monitoring is “No adverse drug effect should go un-noticed whether it is minor or serious”. ADR monitoring is a part of pharmacovigilance. Our study although a hospital-based observational study gives an idea about the pattern, frequency and severity of ADR in the wards of Tertiary care teaching centre which contributes to the assessment of benefit, harm & effectiveness, of medicines leading to maximisation of benefits and emphasise rational and cost-effective use of medicines.
Conflict of interest - No
Financial support - No
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
I am grateful to our respectable Medical Director, Dean(medical), Medical superintendent for their support and permission to carry out this study.
I also thank my HOD and Co-Author Dr. Jamuna Rani. R MD., for her valuable guidance, Dr.Kshirsagar Shivani, My teachers and my Colleges for helping me during this study.
References:
-
World Health Organisation: International drug monitoring: the role of the hospital. In Technical report series no. 425. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 1966: 1-24.
-
Lazarou J, Pomeranz BH, Corey PN. Incidence of adverse drug reactions in hospitalized patients: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. JAMA 1998;279(15):1200-1205.
-
Juntti-Patinen L, Neuvonen P. Drug-related deaths in a university central hospital. Eur J Clin Pharmac 2002;58(7):479-482.
-
Ramesh M, Pandit J, Parthasarathi G. Adverse drug reactions in a south Indian hospital—their severity and cost involved. Pharmac Drug Safety 2003;12(8):687-692.
-
Lihite RJ, Lahkar M. An update on the pharmacovigilance programme of India. Front Pharmacol 2015;6:194.
-
Kalaiselvan V, Thota P, Singh GN. Pharmacovigilance Programme of India: Recent developments and future perspectives. Ind J Pharmacol 2016;48(6):624.
-
Biswas P, Biswas AK. Setting standards for proactive pharmacovigilance in India: The way forward. Ind J Pharmacol 2007;39(3):124.
-
Saravanan SS, Kavitha P, Ponnuswamy TK. Patterns of adverse drug reactions in the medical intensive care unit of an Indian tertiary care hospital. Int J Pharm Biol Arch 2014;5(3):64-68.
-
James J, Rani J. A prospective study of adverse drug reactions in a tertiary care hospital in south india. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 2019;13(1):89-92.
-
Naranjo CA, Busto U, Sellers EM, Sandor P, Ruiz I, Roberts EA, Janecek E, Domecq C, Greenblatt DJ. A method for estimating the probability of adverse drug reactions. Clin Pharmac Therap 1981;30(2):239-245.
-
Palanisamy S, Arul Kumaran KSG, Rajasekaran A. A study on assessment, monitoring, documentation and reporting of adverse drug reactions at a multi-specialty tertiary Care teaching hospital in south India. Int J Phar Rev 2009;1:1519-1522.
-
Kumar A, Kansal D, Sharma PK, Bhardwaj A, Sawaraj S. To study the pattern of adverse drug reactions among patients hospitalized in the medical wards of a tertiary care hospital. Int J Bas Clin Pharmac 2016;5(5):1972.
-
Vora MB, Trivedi HR, Shah BK, Tripathi CB. Adverse drug reactions in inpatients of internal medicine wards at a tertiary care hospital: A prospective cohort study. J Pharmac Pharmacother 2011;2(1):21.
-
Rodriguez-Pena R, Antunez C, Martin E, Blanca-Lopez N, Mayorga C, Torres MJ. Allergic reactions to β-lactams. Exp Opin Drug Safety 2006;5(1):31-48.
-
Raut A, Pawar A, Pankaj M, Srivastava P, Mishra A. Clinical pattern and severity of cutaneous adverse drug reactions. Int J Pharm Sci 2013;5(2):612-616.
-
Chawla S, Kalra BS, Dharmshaktu P, Sahni P. Adverse drug reaction monitoring in a tertiary care teaching hospital. J Pharmacol Pharmac 2011;2(3):196-198.
-
Martin T, Li Severe cutaneous adverse drug reactions: a review on epidemiology, etiology, clinical manifestation and pathogenesis. Chin Med J (Engl) 2008;121(8):756-761.
-
Shamna M, Dilip C, Ajmal M, Linu Mohan P, Shinu C, Jafer CP, et al. A prospective study on Adverse Drug Reactions of antibiotics in a tertiary care hospital. Saudi Pharm J 2014;22(4):303-308.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License