IJCRR - 13(4), February, 2021
Pages: 123-131
Date of Publication: 16-Feb-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Epileptic Seizure: Classification Using Autoregression Features
Author: Rajendran T, Sridhar K P, Vidhupriya P, Gayathri N, Anitha T
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: This research focuses on neural networks based biological signal processing to solve the complex classification problems. Many types of research of classification algorithms have been published, but none has effectively focused on implementing them in brain Epileptic Seizure Electroencephalography pattern analyses and lobe classification. Objective: To develop different autoregression feature extraction algorithms for identifying accurate features in the epileptic seizure EEG signals for the neural network-based classification. Methods: In this research, the Probabilistic Neural Network (PNN) is considered for classifying the brain tissue samples by mapping the input pattern to several classifications. The dataset is retrieved from the Karunya University Epileptic Seizure Database for verifying the experiment with 10-20 electrodes. Different mental tasks are considered here to verify the proposed Probabilistic Neural Network-based Epileptic Lobe Seizure classifier. Results: The experiments are carried out with several Auto Regression features. Further, the obtained result proves that the proposed PNN model has a maximum accuracy of 96.30%. Conclusion: This research work has aimed to design a PNN classifier for detecting Seizure by incorporating AR parametric features. The proposed system bears the potential of providing an exact identification of faults and noise with various age criteria. It will help process the data in a user-friendly manner.
Keywords: Classification, Discrete Wavelet Transform, Electroencephalography, Epileptic seizure, Probabilistic Neural Network, Feature extraction
Full Text:
Introduction
In the human body, the brain is the major source to manage all the organs, internal glands, body temperature, and breathing. The brain helps self-triggering based on the surroundings and makes a person active. It processes a constant stream of sensory data, which are the stored record of every moment of human activity. Many researchers state that brain waves are collected as electrical signals.1 It is believed that the electrical signals generated by the brain represent not only the brain function but also the status of the whole body throughout life. This assumption motivates to apply advanced digital signal processing methods to the electroencephalogram (EEG) signals measured from the brain of a human subject. As shown in figure 1, the frontal lobe is classified as superior, middle, inferior and medial frontal gyri. The parietal lobe is used for sense and navigation purpose. The occipital lobe is considered as a visual processing centre and temporal lobe is for auditory processing. The common problem identified in each lobe is complex seizure detection.2
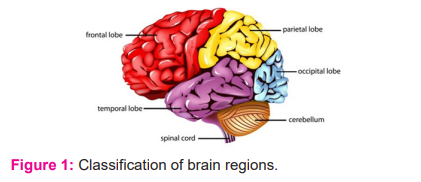
With recent advancement, diagnosing is an important factor that may decide the whole framework. In this research, classification is considered an important process that helps us to understand group seizures in various aspects. The major requirement of Epileptic Seizureclassification is to analyze patients by miscellaneous audiences (i.e., pharmacists, researchers, clinicians, etc.). The classification must be taken care of for long-term prognosis.
The classification helps us to characterize epilepsy disorders, anticipate seizures, and recognize potential seizure triggers. Figure 2 provides the initial stages of the classification process and its spectral analysis.
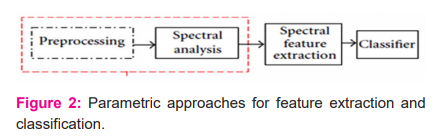
New classification strategy must have a deliberate and organized process to follow a patient’s data that determine epilepsy. An exact characterization of epilepsy may not only enhance the performance but also give a clear idea to improve collective research. The main objective of this research is to develop the optimum feature extraction algorithm to classify seizure disorder activities and develop optimum Probabilistic Neural Network based on Parametric Features and classify the seizure disorder activities in the brain. Finally, the results of developed classifiers are recognized with seizure disorder activities.3,4,5
This research concentrated on Parametric Features such as AR Burg (ARB), AR YuleWalker (ARYW), AR Covariance (ARC), AR Modified Covariance (ARMC), and Levinson Durbin Recursion (LDR), and Linear Prediction Coefficient (LPC) is analyzed with the EEG dataset considered from Karunya University and another open-access database. Further, this research is organized as follows: Section 2 provides a detailed review of the usefulness of EEG in assessing neurological disorders and analyzed different statistical techniques based on brain-maps and some ongoing research activities. Different causes of epilepsy and classification are analyzed. Section 3 discusses the outcome of the survey and mentioned some exact problems in classification. Then, the proposed detection module with a Probabilistic Neural Network (PNN) classifier is discussed in section 4. Section 5 provides test results and its validated discussion. Finally, the research is summarized in section 6.
Literature Survey
In some cases, the Second-Order Difference Plot (SODP) is the model used for detecting the congestive heart failure employing classification. Similarly, Pachori and Patidar1,6 focussed on seizure-free classification technique applied to the EEG signals by combining the SODP and Intrinsic Mode Functions (IMFs) as a hybrid model for achieving the decomposition module. Initially, it acquires dataset from the Andrzejak.7,8 The analysis is completely carried out by MATLAB based on varying different ellipse area and its structure to find the exact classification.
Joshi3 utilized the sample values for training the EEG signal with a Support Vector Machine (SVM). The process is completely admitted with two types of samples named as A and B. Finally, the SVM is considered for maximizing the boundary for those two samples to classify the ictal and seizure-free structure. The normal EEG signal contains spikes and some sharp waves. To identify such exact patterns and avoid the unwanted patterns, Srinivasan4 presented a concept with the ANN. Subasi5 presented a dynamic wavelet network for detecting the non-stationary signals in EEG recorded wave. Here, feed-forward error-back propagation artificial neural network detection module is outperformed by the proposed wavelet detection module. Tzallas6 concentrated on time-frequency (t-f) analysis to achieve good localization effect in EEG classification. Some extension of the Fourier transform was carried out to measure the Power Spectrum Density (PSD). Mormann2,7 critically discussed seizure prediction and suggested related concepts to utilize the overall technology. Ponten8 presented an intracerebrally recorded mesial temporal lobe seizure to characterize synchronization patterns in intracerebral EEG recordings.9
In recent days, the detection of Epileptic diseases has been automated. For example, an automated detection module framed by Dogali and Bozkurt10 detected the normal and epileptic structures by analyzing the two datasets from the University of Bonn, Germany. Then the data reduction process applied by non-parametric features is handled by interfacing the graphical user interface module in MATLAB and tested with various samples. The process is completely trained and classified by ANN. Patnaik and Manyam11 analyzed the ANN and genetic algorithm (GA) for classifying the EEG signal obtained from Albert-Ludwigs-University, Germany. They selected level 5 wavelet decomposition for initiating individual coefficient and windowing technique for decomposition. The process was completely trained and tested by the neural network and further, it proceeded to post-classification. If the samples were valid then the process terminated, else it further moved to genetic algorithm stage for computation to maximize the sensitivity.
To identify the spectral differences in EEG signals, Sakkalis12 have examined mild epilepsy in children.12 It helps to test controlled epileptic conditions in both cases (i.e., nonparametric and parametric analysis). It is designed for maintaining the reliability in classification. Similar to this concept, Raja and Priya13,14 presented recent research in the diagnosis of the autism spectrum disorder with 92.69 % classification accuracy as maximum with the utilization of FFNN. Later, they extended the same research with Elman neural network and traditional Cascade forward back propagation neural network to improve the classification accuracy of the detection.15,16 Finally, they pointed out the best combination as ENN with AR Burg extraction with the maximum accuracy rate of 95.63%. Some recent researchers have focused on error-free EEG signal empirical mode decomposition and approximate entropy (ApEn) is proposed by Ramakrishnan and Kanagaraj17, Novel Signal Modeling Approach by Gupta18 and a Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm by Narang for epileptic seizures.19,20
Problem Statement
The existence of EEG signal processing, normalizing, classifying and detection process provides the motivation to apply more recent concepts to provide excellent EEG signal processing. Most of the brain signals are represented in electrical characteristics. Hence, to find the exact variation in EEG signal a representative must understand every activity, but it results in some wrong interpretations. Another major limitation is a misunderstanding of brain data and it may result in serious errors.18,19,20 The EEG signal is captured and recorded with the help of the electrode, but the electrode captures all the brain activities and its surrounding active electrical units. Hence, there is a need for a filtering process before the extraction process. In this research, an EEG analysis is carried out with the potential field on the scalp to classify the exact Epileptic seizure. From the previous research, the classification accuracy is reviewed and some improvement is suggested in the classifier stage. Hence, Probabilistic Neural Network-based classifier model is assumed here for training and classifying the EEG data.21-24
The Proposed detection module with a Probabilistic Neural Network (PNN) classifier
As shown in figure 3, the data acquisition process is carried out initially. The Karunya University data set is carried out throughout the research. It is donated with 175 epilepsy disorder patients’ record from the following link: (http://www.karunya.edu/research/EEGdatabase/public/view_all.php)21 and 71 non-epileptic seizure signal from Louis33 is used. The EEG data used in this work are acquired using 10-20 electrodes, stipulated by the standard international system. These data have been recorded from 18 channels (16 scalp electrodes and 2 periocular electrodes, concerning right and left mastoid) at a sampling rate of 256 Hz with an analogue passband of 0.01 to 100 Hz. The below figure 3 shows the flow chart for classifying the epileptic seizure signals using a probabilistic neural network. 25,26
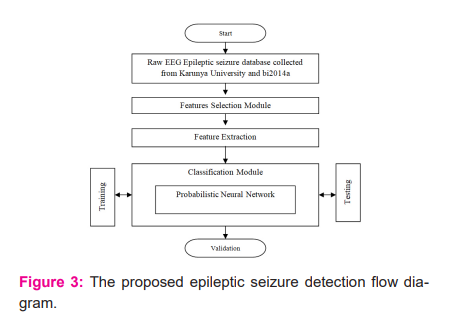
Next process followed by data acquisition is data reduction. The EEG signal is processed with the help of the Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) to reduce the noise present in the EEG recorded signal. It is selected because it can separate the EEG samples into wavelets with different series and it can localize frequency and time. Hence, for biomedical applications and real-time applications, DWT is preferred because of its detection speed of operation and Multi-Resolution Analysis (MRA).27,28
The feature extraction process helps to find the average accuracy of the system. The following coefficients such as Autoregressive (AR) Burg, AR Yule-Walker method, AR Covariance, AR Modified Covariance, Levinson Durbin Recursion, and Linear Prediction Coefficient are selected for verification of the extraction process. It helps to minimize the EEG structures and modules based on the training process.29-32
-
AR (Autoregression)
The autoregression model is used to reduce the least square model and prediction errors. The main advantage of selecting this module is that it remains stable while processing the signal. The input to this module is in the form of a column vector. Its parameters may be in terms of both several co-efficient and reflection coefficients. Wright15have reviewed some parameter estimate error and multiple regression analyses for EEG signal analysis. The AR module provides an alternative way of analyzing the EEG spectral properties estimation.33-36
Based on the discrete linear stochastic process, it is expressed as, yt = µ + et + y1 et-1 + y2 et-2 + ···
The errors are expressed as, et = yt - µ - y1 et-1 - y2 et-2 - ··· .
Assume the stationarity model that holds for et must hold true for et-1 , then et-1 = yt-1 - µ - y1 et-2 - y2 et-3 - ··· .
Finally, substitute the model for et-1 into the model for yt
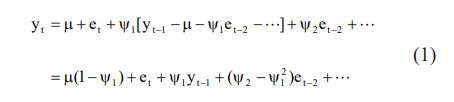
Where, y1, y2, ···, yn are the observations with a joint density Pr(y1, y2, ···, yn). et are the error concerning time.
-
AR Covariance
The parameter gj is known as theauto covariance XE "autocovariance” at lag j. Adding all results together, then it will be
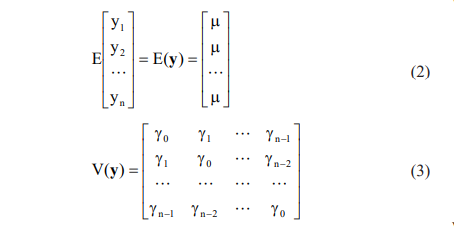
Like all covariance matrices, V(y) is symmetric. If E(yt) does not depend on t, which it should not with a stationary series, then we would ordinarily expect to find the series in the neighbourhood of µ. History tends to repeat itself, probabilistically.37,38
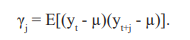
If gj > 0 we would expect that a higher than usual observation would be followed by another higher than usual observation. We can standardize the covariance by defining the autocorrelation,
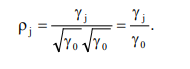
As usual, r0 = 1. The structure of the autocorrelations will greatly help us in understating the behaviour of the series, y.
-
AR Yule-Walker
Alkan and Yilmaz16 estimated the AR Yule walker function. It computes the AR parameters by forming a biased estimate of the signal’s autocorrelation function and solving the least square minimization of the forward prediction error. Here, the process directly depends upon the amplitude of a signal at a given period. The amplitude is obtained by summing different amplitudes of the previous samples and estimation error. The order of the filter directly depends on the number of AR coefficients. The modelling degree (p) always uses the Akaike Information Criteria (AIC).39,40,41
In general, an AR model of order p can be expressed as

The autocorrelations and the fi are related to each other via what are known as the Yule-Walker Equations XE "Yule-Walker equations”:
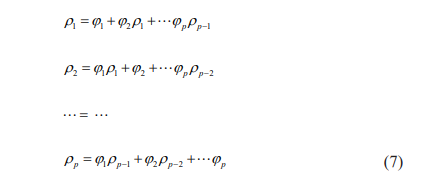
which can be used to estimate values.
The Yule-Walker AR methods are estimated by minimizing an estimate of the prediction error power.
d) AR Modified Covariance
The autoregressive modified covariance is used to estimates the power spectral density (PSD) of an EEG input signal. The main motive of this research is to minimize the forward and backward prediction errors in the least-squares sense. Finally, the estimation order parameter must be less than, or equal to, two-thirds of the input vector length to finalize the result. This process is entirely described by a linear combination of previous outputs and driving noise. It estimates the P coefficients, where P is the model order, by minimizing the forward and backward prediction errors in the least-squares sense.42,43
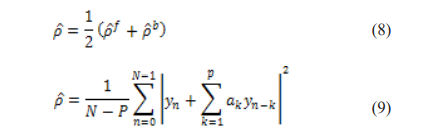
Where for the data length is N and is the AR coefficient of the term?
e) Levinson Durbin Recursion
It is a simple algorithm that is easy to solve; here, the system fork =1 and k +1 coefficients sized problems. The first step carried out in Levinson Durbin Recursion is to minimize the error. Then the input vector and error vector are computed. Compute the k values from o to m.
f) Linear Prediction Coefficient
In the autocorrelation method of linear prediction, the linear prediction coefficients are computed from the Bartlett-window-biased autocorrelation function.
g) Probabilistic Neural Network algorithmic steps
Step 1: Select the input layer and represent the training samples in the vector format.
Step 2: Initially, the training sample vector is transferred to neurons of the input layers.
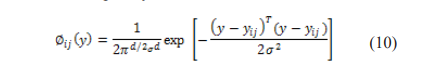
Where d is the pattern vector of y and its neuron vector is .
Step 3: Frame the connection weights between the input and pattern layers.
Step 4: Establish the relationship between the initial cell concerning the corresponding accumulate layer.
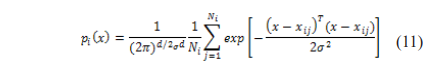
Where Ni denotes the total subcells in the EEG samples.
Step 5: Repeat all the steps until the remaining EEG vector samples.
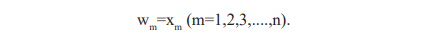
Step 6: Compute the distances from the input vector samples to train the EEG input samples.
Step 7: Process the training input with the first layer and contribute the class of inputs based on the input probabilities.
Step 8: Finally, an output transfer function is framed by second layer output with the maximum probabilities and make the process as 1 and 0 to state the difference.
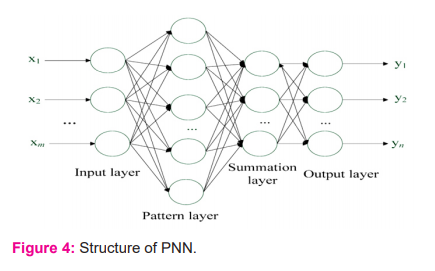
As shown in figure 4. It also stated that PNN was two lakh times faster than the back-propagation process. The important aspects of selecting this PNN were its simple training strategy and the ability to provide instantaneous results. 44,45
Figure 4: Structure of PNN
After completing feature selection and extraction, the PPN was utilized for both training and classification. Specht9 presented the PNN by replacing the sigmoid functions. It helped to the analysis of nonlinear boundaries and elucidates some complex optimization process. The term neuron helped to map several classifications. Most of the real-time applications and modules preferred this algorithm to represent individual subcategories. Hence, it would be helpful to solve more complex optimization problems. Traditionally, many applications and researches proved that PNN is active and more accurate than the multilayer perceptron networks. PNN is relatively insensitive to outliers and results on the predicted target.32,33
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
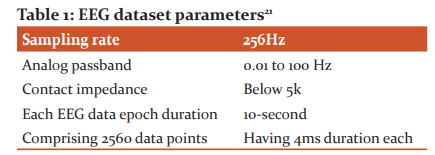
As shown in figure 5, the individual patient data are stored in the Karunya University website with a unique ID. Based on the tests, we have to select the region/lobe of focus in the brain. The corresponding data are collected and fed into the proposed algorithm to verify them. The detail of the dataset is considered here to display the exactness of research. It is acquired with 10-20 electrodes, as determined by the international standard system. The metrics are collected from the 16 scalp channels and two periocular electrodes. Some important metrics of the EEG dataset are shown in Table 1.21
Table 1: EEG dataset parameters21
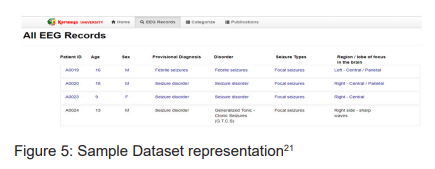
The patient information is mentioned in different definitions like a patient ID in 5 digit character alphanumeric term, age is mentioned in text integer, Sex is indicated through (M/F) and disorder/Seizure types are mentioned in the text format as shown in figure 5.
As shown in figure 6, the waves are stored with each seizure. For evaluation, the right region with sharp waves is considered. This research focused, particularly on Epileptic Seizure Classification.
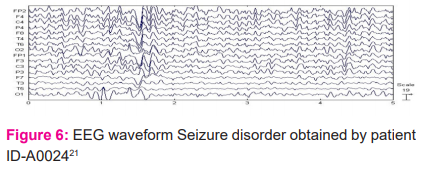
Table 2 shows the dataset representation of 11 patients which includes patient ID, age, sex, condition on the provisional diagnosis, disorder type, seizure types, and the region or lobe region of the brain
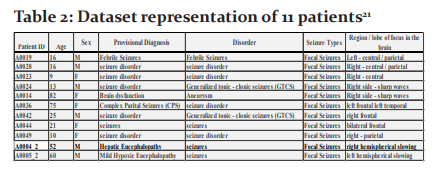
Figure 7 shows the Comparative analysis of two patient’s (A0019 and A0049) data classification using Probabilistic Neural Network for six different Autoregression features.
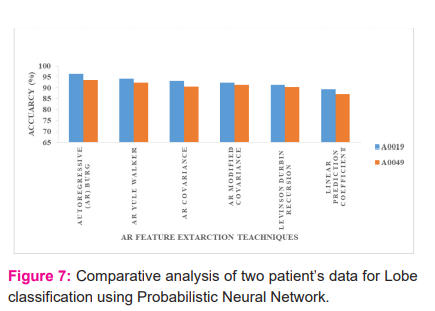
The performance of the PNN is shown in Figure 8, for the six parametric feature sets. It is observed that AR Burg outdid the other feature sets with the highest mean accuracy of 96.3% for the patient (IDA0023) aged 9. It has the lowest mean accuracy of 93.74% for subject 20.
The next best performance is observed for the AR Yule feature sets at 94.21% and the lowest mean accuracy for the same feature sets is 94.1% for the same patient. The Probabilistic Neural Network provides simple implementation and easy design with maximum classification accuracy.41-44
Another process is to analyze the classification based on the separation of age. It is attempted to check overall variations in the PNN algorithms with respect to the subjects. Here, the samples are collected from different age groups represented by their patient's ID. The age group is selected from the database: (Patients ID) 9 (A0023), 16 (A0019), 13 (A0023) and 82 (A0014).
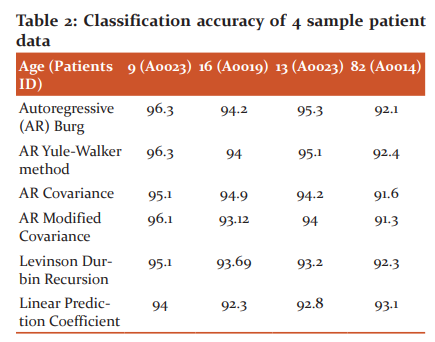
It is observed from the results that the younger age classification prediction is improved when compared with the other age groups. The parametric analysis of each sample is shown in figure 8. Its experimental outcome is listed in table 2.
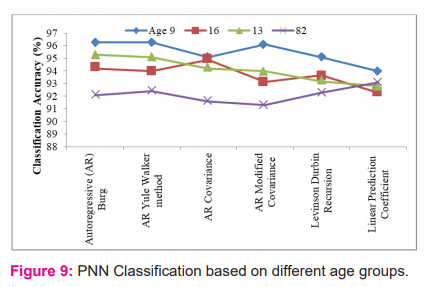
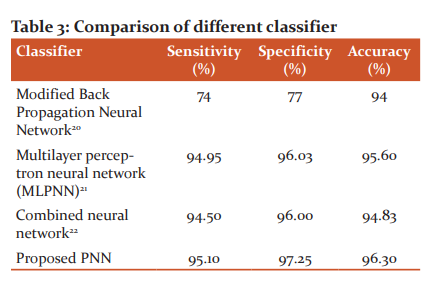
From the above results, the maximum performance will be achieved throughout in all types of age group, which is observed for the AR Burg feature sets for PNN classification. Further, the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy are calculated and compared with the traditional methodologies that are listed in table 3.
For two different training samples, the Back Propagation Neural Network has the same sensitivity as 74% and specificity as 60% for a constant threshold value. Its graphical representation is shown in figure 10.
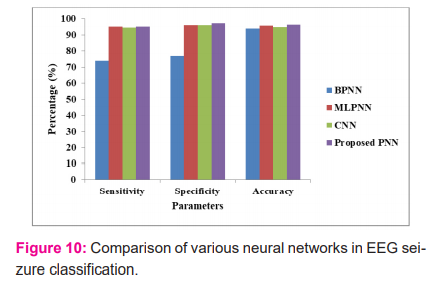
From the results, it is concluded that the proposed methodology named as PNN has the maximum accuracy of 96.30% when compared with the traditional methodologies.41-45
CONCLUSION
This research work has aimed to design a PNN classifier for detecting Seizure by incorporating AR parametric features. The proposed system bears the potential of providing an exact identification of faults and noise with various age criteria. It will help process the data in a user-friendly manner. One of the benefits is high accuracy when comparing it with a complex data set. Here, various complex datasets are collected from Karunya University. Based on the age group, the evaluation has been made, which is proved in the experimental section. For an exact verification, different parametric features are considered such as Autoregressive (AR) Burg, AR Yule-Walker method, AR Covariance, AR Modified Covariance, Levinson Durbin Recursion, and Linear Prediction Coefficient. It is observed that AR Burg outdid the other feature sets with the highest mean accuracy of 96.30% for the patient (IDA0023) aged 9. It has the lowest mean accuracy of 93.74% for subject 20. The proposed classification performs well when compared with the backpropagation, Multilayer perceptron neural network, and combined neural network concepts. In future, the classification accuracy is to be estimated with a huge difference among these comparisons and it must help to improve the diagnosis.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate: Not applicable.
Human and Animal Rights: No animals/humans were used for studies that are the basis of this research.
Consent for Publication: Not applicable.
Availability of Data and Materials: Available data and materials have been included in the article contents.
Funding: None.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise. Still, the authors would like to mention the earlier version of the article titled “Epileptic Seizure-Classification Using Autoregression Features”, which is communicated to the International Journal of Current Research and Review (Radiance Research Academy Publisher) is published under the title “Epileptic Seizure-Classification Using Probabilistic Neural Network Based on Parametric Features” (older version) in a predatory journal site (https://ijprjournals.com), which has been withdrawn to prove the authors' academic credibility. After the publication of this article titled “Epileptic Seizure-Classification Using Autoregression Features” (Present Version), and the same becomes the sole property of the concerned authors and the Radiance Research Academy Publisher and the “Epileptic Seizure-Classification Using Probabilistic Neural Network Based on Parametric Features” (older version) published in the https://ijprjournals.com becomes invalid.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Prof. Thomas George, Ph.D, and his team, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Karunya Institute of Technology & Sciences (Deemed to be University), Coimbatore, for their efforts in creating an open-access Epileptic Seizure database for the global research community and also Authors would like to thanks Dr. Louis Korczowski, Ph.D., and his team, GIPSA-lab, University of Grenoble-Alpes, France, for their P300 BCI (bi2014a) EEG open-access dataset which is used for normal brain activity classification in this research, without these two open-access databases my research work would not be possible.
References:
1. Pachori RB, Patidar S. Epileptic seizure classification in EEG signals using a second-order difference plot of intrinsic mode functions. Comp Meth Progr Biomed 2014;113(2):494-502.
2. Andrzejak RG, Lehnertz K, Mormann F, Rieke C, David P, Elger CE. Indications of nonlinear deterministic and finite-dimensional structures in time series of brain electrical activity: Dependence on recording region and brain state. Phys Rev E 2001;64(6):061907.
3. Joshi V, Pachori RB, Vijesh A. Classification of ictal and seizure-free EEG signals using fractional linear prediction. Biomed Sign Proc Contr 2014;9(1):1-5.
4. Srinivasan V, Eswaran C, Sriraam AN. Artificial neural network-based epileptic detection using time-domain and frequency-domain features. J Med Syst 2005;29(6):647-660.
5. Subasi A. Epileptic seizure detection using dynamic wavelet network. Expert Syst Appl 2005;29(2):343-355.
6. Tzallas AT, Tsipouras MG, Fotiadis DI. Epileptic seizure detection in EEGs using time–frequency analysis. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed 2009;13(5):703-710.
7. Mormann F, Andrzejak RG, Elger CE, Lehnertz K. Seizure prediction: the long and winding road. Brain 2006;130(2):314-333.
8. Ponten SC, Bartolomei F, Stam CJ. Small-world networks and epilepsy: graph theoretical analysis of intracerebrally recorded mesial temporal lobe seizures. Clin Neurophysiol 2007;118(4):918-927.
9. Specht DF. Probabilistic neural networks. Neural Networks. 1990;3(1):109-118.
10. Dogali G, Bozkurt MR. The detection of normal and epileptic EEG signals using ANN methods with Matlab-based GUI. Int J Comput Appl 2015;114(12):45-50.
11. Patnaik LM, Manyam OK. Epileptic EEG detection using neural networks and post-classification. Comput Meth Progr Biomed 2008;91(2):100-109.
12. Sakkalis V, Cassar T, Zervakis M, Camilleri KP, Fabri SG, Bigan C, Micheloyannis S. Parametric and nonparametric EEG analysis for the evaluation of EEG activity in young children with controlled epilepsy. Comput Intell Neurosci 2008;2008:462593.
13. Raja L, Priya MM. EEG Based ASD Diagnosis for Children Using Auto-Regressive Features and FFNN. Int J Contr Theory Appl 2017;10(32):27-31.
14. Raja L, Priya MM. Neural Network Based Classification of EEG signals for diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder. Int J Pharma Bio Sci 2017;8(2):1020-1026.
15. Wright JJ, Kydd RR, Sergejew AA. Autoregression models of EEG. Biol Cybern. 1990;62(3):201-210.
16. Alkan A, Yilmaz AS. Frequency domain analysis of power system transients using Welch and Yule–Walker AR methods. Energy Convers. Manage. 2007;48(7):2129-2135.
17. Ramakrishnan J, Kanagaraj BR. Analysis of non-seizure and seizure activity using intracranial EEG signals and empirical mode decomposition based approximate entropy. Biomed Res 2018;S47-S51.
18. Gupta A, Singh P, Karlekar MA. Novel Signal Modeling Approach for Classification of Seizure and Seizure-free EEG Signals. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 2018;26(5):925-935.
19. Narang A, Batra B, Ahuja A, Yadav J, Pachauri N. Classification of EEG signals for epileptic seizures using Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm based Multilayer Perceptron Neural Network. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 2018;34(3):1669-1677.
20. Hemanth DJ, Anitha J. Brain signal based human emotion analysis by circular back propagation and Deep Kohonen Neural Networks. Comput Electr Eng 2018;68:170-180.
21. Thomas GS, Balakrishnan R, Stanly JJ, Easter SS. EEG database of seizure disorders for experts and application developers. Clin EEG Neurosci 2014;45(4):304-309.
22. Rajendran T, Sridhar KP. Epileptic seizure classification using feed forward neural network based on parametric features. Int J Pharm Res 2018;10(4):189-196.
23. Vuckovic A, Radivojevic V, Chen AC, Popovic D. Automatic recognition of alertness and drowsiness from EEG by an artificial neural network. Med Eng Phys 2002;24(5):349-360.
24. Übeyli ED. Combined neural network model employing wavelet coefficients for EEG signals classification. Dig Sign Proc 2009;19(2):297-308.
25. Valsalan P, Jisha P. Cryptography of medical images using hybrid advanced encryption system and cat map algorithm. Int J Adv Sci Technol 2020;29(5):4530-4542.
26. Venketkumar H, et al. Fuzzy multi-layer SVM classification of breast cancer mammogram images. Int J Mech Eng Technol 2018;9(8):1281-1299.
27. Eltigani AMY, Hassan IB. Classification of Diabetic Retinopathy using Stacked Autoencoder-Based Deep Neural Network. J Comp Sci Intell Technol 2020;1(1):09-14.
28. Afag SEB. Classification of Lung Nodules using Improved Residual Convolutional Neural Network. J Comput Sci Intell Technol 2020;1(1):15–25.
29. Valsalan P, Sriramakrishnan P, Sridhar S, Latha GCP, Priya A, Ramkumar S, Robert SA, Rajendran T. Knowledge based fuzzy c-means method for rapid brain tissues segmentation of magnetic resonance imaging scans with CUDA enabled GPU machine. J Ambient Intell Hum Comput 2020 (Article in Press).
30. Valsalan P, Baomar, T. A. B., Baabood, A. H. O. IoT based health monitoring system. J Crit Rev 2020;7(4):739-743.
31. Praveen KS. Developing a Model to Enhance the Quality of Health Informatics using Big Data. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on I-SMAC (IoT in Social, Mobile, Analytics and Cloud); 2020 Oct 7-9:pp. 1267-1272.
32. Praveen KS. Comparative Study on Skyline Query Processing Techniques on Big Data. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on I-SMAC (IoT in Social, Mobile, Analytics and Cloud) (I-SMAC); 2020 Oct 7-9:pp. 1045-1050).
33. Louis K, Ekaterina O, Anton A, Grégoire C, Pedro LCR, Violette G, et al. Brain Invaders Solo versus Collaboration: Multi-User P300-based Brain-Computer Interface Dataset (bi2014b). 2019. (Available from: https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-02173958).
34. Rajendran T, Sridhar KP. An overview of EEG seizure detection units and identifying their complexity- A Review. Curr Sign Transd Ther 2020;15(3):234-242.
35. Rajendran T, Sridhar KP, Deepa S. Performance Analysis of Fuzzy Multilayer Support Vector Machine for Epileptic Seizure Disorder Classification using Auto Regression Features. Open Biomed J 2019;13(Suppl-1, M2):103-113.
36. Rajendran T, Sridhar KP, Manimurugan S, Deepa S. Recent Advancements in Soft Computing Applications. Curr Sign Transd Ther 2019;14(2):129-130.
37. Anitha T, Santhi N, Sathiyasheelan R, Emayavaramban G, Rajendran T. Brain-Computer Interface for Persons with Motor Disabilities - A Review. Open Biomed. J. 2019;13(Suppl-1, M5):127-133.
38. Manigandan G, Sunny DAN, Aashish A. Chronic Hemifacial Spasm - A Masquerader of Epilepsia Partialis Continua. Int J Curr Res Rev 2014;6(8):14-17.
39. Praveen KS. Detection of Fraudulent Transactions in Credit Card using Machine Learning Algorithms. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on I-SMAC (IoT in Social, Mobile, Analytics and Cloud) (I-SMAC); 2020 Oct 7-9:pp. 659-663.
40. Praveen KS. Sampling Based Join-Aggregate Query Processing Technique for Big Data. Indian J Comp Sci Eng 2020;11(5):532-546.
41. Sasirekha SP, Priya A, Anitha T, P Sherubha P. Data Processing and Management in IoT and Wireless Sensor Network. J Phys Conf Ser 2020;1712(1):012002.
42. Anitha T, Latha GCP, Surendra PM. A Proficient Adaptive K-means based Brain Tumor Segmentation and Detection Using Deep Learning Scheme with PSO. J Comp Sci Intell Technol 2020;1(3):09–14.
43. Latha GCP. Sridhar S. Prithi S. Anitha T. Cardio-Vascular Disease Classification Using Stacked Segmentation Model and Convolutional Neural Networks. J Cardiovasc Dis Res 2020;11(4):26-31.
44. Narmatha C, Surendra PM. A Review on Prostate Cancer Detection using Deep Learning Techniques. J Comput Sci Intell Technol 2020;1(2):26–33.
45. Manimurugan S. Classification of Alzheimer's disease from MRI Images using CNN based Pre-trained VGG-19 Model. J Comput Sci Intell Technol 2020;1(2):34–41.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License