IJCRR - 13(4), February, 2021
Pages: 117-122
Date of Publication: 16-Feb-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Formulation and Evaluation of Polyherbal Gel for the Management of Acne
Author: Ajinkya Mate, Padmashri Ade, Ajay Pise, Sachin More, Shilpa Pise, Rohini Kharwade
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Acne vulgaris is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the skin which affects approximately 80% adolescent during puberty stage. The increasing frequency of intake of antibiotics to overcome this problem explores several side effects. Therefore it needs to focus on the herbal formulation as a topical first-line treatment. Objective: In the present study, three medicinal plants Citrus sinensis, Curcuma longa and Aloe barbadensis having significant antibacterial potential were selected to formulate a polyherbal gel for the management of acne vulgaris problem. Method: Extraction of Citrus sinensis, Curcuma longa and Aloe barbadensis was done and characterized. The topical gels were prepared which comprised extract of orange peel, aloevera, and turmeric with a different concentration. The prepared gel was kept at room temperature for 24 hours and evaluated. Result: Based on this study, polyherbal anti-acne gel showed significant antibacterial activity on Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermis with no irritation. The physicochemical evaluation of developed formulation showed clear, uniform and free from fibre and particle. It was also observed good spreadability and consistency with pH nearer to skin. Conclusion: Thus the study result concluded that the polyherbal gel with extract of Citrus sinensis, Aloe barbadensis and Curcuma longa with concentration 0.2%, 1% and 0.8% respectively was an appropriate formulation for the first-line topical treatment of acne vulgaris.
Keywords: Polyherbal Gel, Anti-acne formulation, Acne vulgaris, Citrus sinensis, Curcuma longa
Full Text:
Introduction
Skin disease normally arises due to accumulating toxins in blood due to impurities in blood, improper food habits and lifestyle. Acne vulgaris is a disorder of the skin which affects most of the adolescents during puberty stage due to hormonal changes which changes path-physiologic factors.1 This condition is related to obstruction in follicular distention with activation of inflammatory response with open or close comedones, inflammatory papules and nodules. Gram-positive bacterium such as Staphylococcus, Propionibacterium and Escherichia species are linked to the skin condition of acne. Acne vulgaris normally affects the skin areas with dens sebaceous follicles such as the face, upper chest, back. Symptoms of acne vulgaris include pain, tenderness, or erythema.2
Various synthetic antibiotic drugs such as clindamycin, doxycycline, minocycline are used to overcome this problem. Most of the time topical therapy is the first-line treatment with benzyl peroxide and retinoids. However, increasing frequency of antibiotics and its side effects there should be necessary to focus on the exploration of herbal drugs. Its reported safety with minimal adverse effect, in recent years there is a gradual development of interest in the use of the medicinal plant. Several Indian medicinal plants certified with various pharmacological activities due to diversified classes of phytoconstituents. Literature also proved that medicinal plant with varying potency when combined, it produces the synergistic therapeutic effect with improving patient’s compliance.3
Plant such as Citrus sinensis, Curcuma longa and Aloe barbadensis possess many potential therapeutic activities due to individually presence of rich phytoconstituents. The ripen pericarp of Citrus sinensis (Rutaceae) is reported to have several bioactive compounds including geranial, Beta linalool, D – limonene, Beta myrcene, Diethyl phthalate which are mostly used in brighten the skin, removing tan layer and provide fairness. This essential oil also used to treat erythema, papules, and vesicles upon the skin. Rhizomes of Curcuma longa (Zingiberaceae) have more potent superoxide anion, hydroxyl radical, singlet oxygen, peroxynitrite and nitric oxide which shows anti-inflammatory, antioxidant property and therefore used in various skin infection. Leaves of Aloe barbadensis (Liliaceae) is reported to have Bradykinase helps to reduce excessive inflammation when applied to the skin topically and Aloin and emodin act as analgesics, antibacterials.4,5
Moreover, these medicinal plants are easily available, cost-effective and commonly used by human beings. Taking these facts into considerations, the present study was designed to systematically explore and analyse the phytoconstituents of these plant extracts and formulate a new polyherbal gel formulation under their antiacne potential effects.
Material and Methods
Materials
Collection of the specimen such as Ripen pericarp of fruits Citrus sinensis (Rutaceae), leaves of Aloe barbadensis (Liliaceae) and Rhizomes of Curcuma longa (Zingiberaceae). The specimens for the proposed study were collected and authenticated. Other chemicals were obtained from Himedia Laboratories Pvt. Ltd, and Loba Chemie, Mumbai.
Procedures
Extraction of the pericarp of fruits Citrus sinensis (Orange peel)
Citrus sinensis peels were collected from an orange juice manufacturer. The peels were then washed and fully dried in an oven at 60oC for 72 hrs. Using Mortar and pestle the dried peels were powdered with particle size ranging of 0.5 mm to 0.1 mm and socked in methanol with mass to volume ratio 1:25(g/mL) for 72 hrs. It was then filtered through Whatman No. 1 filter paper and collected into glass Petri plates (Figure 1). This complete process of extraction and purification was repeated two-three times followed by evaporation of the collected extracts and dry at 37? . 6, 7
. 6, 7

Extraction of leaves of Aloe barbadensis (aloe vera)
Aloe Vera leaves collected from the local nursery. The leaves washed with water and rinds were removed (Figure 2). The inner gel scrapped and cut into pieces, solar-dried at 30-45oC for 3 weeks and dry gel particles were collected.8

Extraction of Curcuma longa (Turmeric extract)
Take 20gm of Curcuma longa powder was mixed with a sufficient amount of n-Hexane and kept aside for 2 hrs. Then the solution was filtered and then precipitated powder was mixed within acetone for 10-15 minutes. The solution was filtered again and the filtrate was dried in air (Figure 3), the extracted curcumin was isolated by scrapping using a spatula.9,10

Evaluation and Phytochemical screening of extract
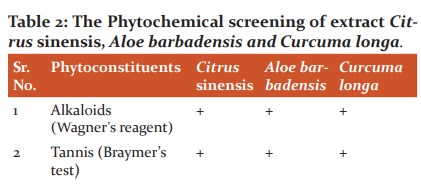
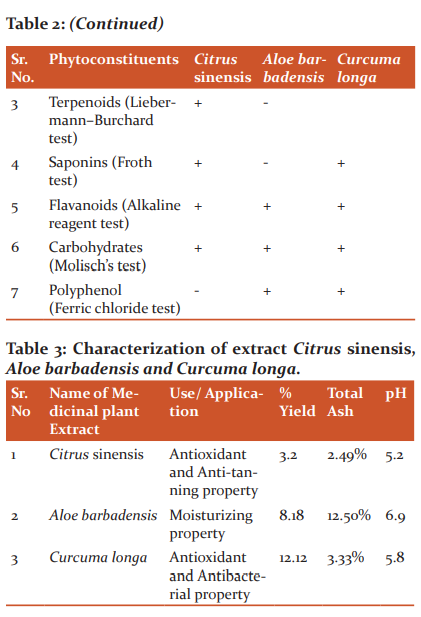
All extract was analyzed by FTIR and for its phytoconstituents such as saponins, anthraquinone glycosides, phytosterols, tannins, flavonoids, carbohydrates, triterpenoids, polyphenol and alkaloids. 11,12
Antibacterial Activity
Preparation of inoculum
Uniform suspension of microorganism is obtained by suspending 24 h fresh culture of bacteria (S. aureus and S. epidermis) in several 15mL of the sterile water.13
Determination of the zone of inhibition
Agar well diffusion method was used to determine the antibacterial activity of the prepared extract. Transferred 20 mL of liquefied agar medium previously inoculated with 0.1 mL bacteria into the sterile petri dish having an internal diameter of 8.5 cm and allowed to form the uniform thickness of the medium in the petri dish. After complete solidification of the liquefied inoculated medium, the wells were made aseptically with cork borer having 6 mm diameter. 100mg/mL of each extract was carefully added into the well and the plates were kept for 30 min for pre-diffusion of the extracts. After pre-diffusion, the Petri plates were incubated at 37ºC for 24 hrs in the incubator and measured the zone of inhibition for its antibacterial activity.13, 14
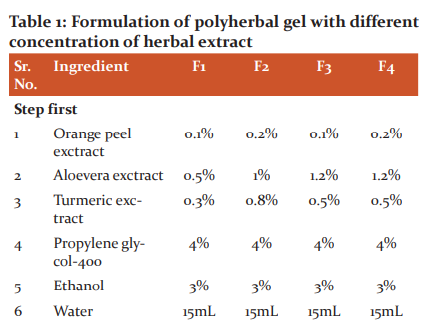
Method of Preparation of Gel Containing Extract
The topical gels were prepared which comprised extract of orange peel, aloe vera, and turmeric with a different concentration (Table 1). The gels were prepared by using Carbapol 940, propylene glycol-400, ethanol, methylparaben, propylparaben, EDTA, triethanolamine and required amount of water in a sufficient quantity to prepare 50 g of gel. Water required for these formulations was divided into two parts. In one part, an accurate amount of extracts were separately dissolved in 15 mL of water and to this calculated quantity of propylene glycol-400 and ethanol were added.8 In another part, Carbapol-940 was dissolved in 35 mL and to this solution methylparaben, propylparaben and EDTA(Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) were added.15 Both of these solutions were mixed in a beaker and triethanolamine was added dropwise to the formulation for adjustment of required skin pH (6.8—7) and to obtain the gel with required consistency. It was then stirred by using propeller for 2 hours at 500 rpm. After stirring, the prepared gel appeared to be homogeneous and devoid of any bubbles. The prepared gel was kept at room temperature for 24 hours. 16

Physicochemical evaluation of formulations
Physical evaluation
Physical parameters such as colour, homogeneity, phase separation and consistency were checked visually.
pH
The aqueous solution (1%) of the formulation was measured by using a calibrated digital pH meter at a constant temperature.
Rheological study
By using Cone and Plate viscometer, the viscosity of the formulated batches was determined. In a procedure, a definite quantity of gel was added to a beaker covered with a thermostatic jacket. The gel was rotated at 100 rotations per minute with spindle 7. 17
Spreadability
Two sets of a glass slide with standard dimension were taken. Polyherbal formulation gel was placed in between the two slides and sandwiched about the length of 60mm. Removed the adhered excess gel on the surface of the glass slides and fixed to a stand without any disturbance. In the upper slide, 20 g weight was tied and noted the time taken for movement of the upper slide to the distance of 60mm under the influence of weight.18 Meantime was calculated by repeating the experiment three times and the spreadability was calculated using the following equation 1.
Spreadability = (Weight × Length) / Time (Equation 1)
Antibacterial activity studies
Transferred 20 mL of liquefied agar medium previously inoculated with 0.1 mL bacteria into the sterile petri dish having an internal diameter of 8.5 cm and allowed to form the uniform thickness of the medium in the petri dish. After complete solidification of the liquefied inoculated medium, the wells were made aseptically with cork borer having 6 mm diameter. 500mg concentrations of polyherbal gel were weighed and diluted with 2 mL of sterile water in sterile test tubes. The drug solution was carefully transferred into the cup and incubated at 37 °C for 24 h and the zones of inhibition were measured. 13
Ex- vivo skin irritation studies
The albino Wistar rats were divided into two groups with 3 rats in each group. On the previous day of the experiment, the hairs on the backside area of rats were removed. The animals of group I was served as the control, without any treatment. Another group of animals (Group II) was applied with prepared polyherbal gel. The gel was applied once a day for 7days and the site was covered with a cotton bandage and observed for any sensitivity. The score of erythema is read and recorded as Score 0 for no erythema; Score 1 for Mild erythema (barely perceptible- light pink); Score 2 for Moderate erythema (dark pink); Score 3 for Severe erythema (Extreme redness). 19, 20
Accelerated Stability Studies
Stability testing of the formulation is a part of drug discovery and ends with the commercial product, to assess the drug and formulation stability, stability studies were done. The stability study was carried out for the most satisfactory formulation. The optimized gel formulation was sealed in a glass vial and kept at 40 ±2°C at 75 ± 5 % RH for 1months and analyzed. At the one month ending the samples were analyzed for the physicochemical analysis, pH, viscosity, phytochemical constituents. 19
Result
Pre-formulation study
The colour of Citrus sinensis, Aloe barbadensis and Curcuma longa were observed dark orange, white and brown powder respectively (Figure 1, 2, 3). The extracts are tested for its phytochemical analysis like saponins, anthraquinone glycosides, Phyto steroids, tannins, flavonoids, carbohydrates, triterpenoids, polyphenol and alkaloids. The phytochemical analysis and pH of the various extracts results are shown in Table 2 and 3.
Antibacterial Activity
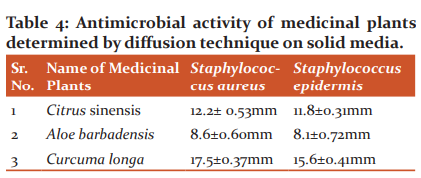
From the antibacterial activity study, it confirmed that all the selected herbal plants showed antibacterial activity against acne-causing bacteria staphylococcus aureus and staphylococcus epidermis. The antibacterial activity study results are shown in Table 4.
Physicochemical Evaluation of Gel Formulation
The formulated gel formulations were evaluated visually for colour, homogeneity, consistency and phase separation (Table 5). The visual inspection of the prepared formulation indicated no lumps and to have uniform colour dispersion, free from any fibre and particle, easily washable. The pH of all formulation is nearer to the skin pH with better spreadability and viscosity (Table 6). From the physicochemical evaluation, F2 shows more compatible to skin with pH 6.9, Viscosity 6505 cps at room temperature and 11.87 g cm/ sec spreading coefficient.
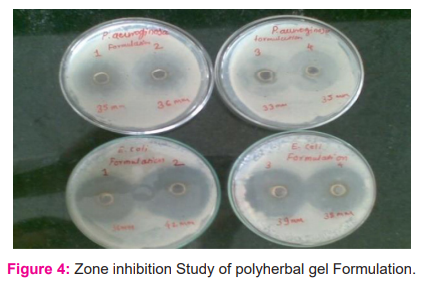
Antibacterial activity of the formulation
The antibacterial activity studies were performed by well diffusion method by measuring the zone of inhibition (in mm). The study results of the polyherbal gel showed antibacterial activity in a dose-dependent manner against the bacteria causing acne. The antibacterial activity study of the formulation is shown in Figure 4. From the antibacterial activity of all formulation, the formulated polyherbal gel F2 shows better antibacterial activity with the zone of inhibition 36 mm for Staphylococcus aureus and 44 mm for Staphylococcus epidermis. In addition to this, The polyherbal gels showed a synergistic effect as compared to individual extract which can be useful for the treatment of local inflammation. Thus this topical formulation was suitable for the treatment of local anti-acne application and selecting for further tests.
Ex- vivo skin irritation studies
From Antibacterial Skin Irritation studies were carried out on albino Wistar rats revealed that the gel formulation shows no erythema, oedema or ulceration. It shows to be non-irritant.
Accelerated Stability study
On storage of anti-acne polyherbal gel sample at 40 ±2°C at 75 ± 5 % RH, the appearance of the formulation was found to be clear with no significant variation in pH, spreading coefficient and viscosity. The results of accelerated stability studies are present in table 7.
 .
.
Discussion
Acne vulgaris is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the skin which affects approximately 80% adolescent during puberty stage. Gram-positive bacterium such as Staphylococcus, Propionibacterium and Escherichia species are linked to this skin condition. The increasing frequency of intake of antibiotics to overcome this problem explores several side effects. Therefore it needs to focus on the herbal formulation as a topical first-line treatment.1-4
Plant such as Citrus sinensis, Curcuma longa and Aloe barbadensis possess many potential therapeutic phytoconstituents which helps to reduce skin inflammation, prevent the skin from oily and dry with potential antibacterial activity. Taking these facts into considerations, the present study was designed to systematically explore and analyse the phytoconstituents of these plant extracts and formulate a new polyherbal gel formulation under their antiacne potential effects.
The extracts were tested for its phytochemical analysis, the reports showing that alkaloids and flavonoids were present in the extracts, which are responsible for antibacterial activity. 19,20 From the antibacterial activity study results, the inhibition zone for the acetone extract of Curcuma longa exerted an exclusive antibacterial effect against gram-positive staphylococcus aureus and staphylococcus epidermis bacteria with a zone of diameter 17.5±0.37mm and 15.6±0.41mm. This value showed a bactericidal effect.13-16 However, the zone inhibition study of extracts Aloe barbadensis and Curcuma longa exrted bacteriostatic effect. From the physicochemical evaluation, F2 shows more compatible to skin with pH 6.9, Viscosity 6505 cps at room temperature and 11.87 g cm/ sec spreading coefficient. Entrapment of water molecules and the presence of hyaluronic acid (extract of Aloe vera) in gel allow hydration without leaving a greasy residue on the surface of the skin. This is the reason that gel moisturizers go best with acne-prone, oily skin. 6,7 The abundant antioxidants in orange peel extract prevent the skin from oily and dry. It also works as a toner, removing dead cells and tightening pore.13,14 From the antibacterial activity of all formulation, the formulated polyherbal gel F2 shows better antibacterial activity with the zone of inhibition 36 mm for Staphylococcus aureus and 44 mm for Staphylococcus epidermis. In addition to this, The polyherbal gels showed a synergistic effect as compared to individual extract which can be useful for the treatment of local inflammation.18,19 Thus this topical formulation was suitable for the treatment of local anti-acne application with no irritation and selecting for further tests.
Conclusion
Recently herbal medicines are more considered as safe with fewer side effects than synthetic drug for the treatment of acne vulgaris. Therefore In the global market. Natural remedies including herbal formulation are in great demand. It is a very good attempt to formulate and evaluate the polyherbal anti-acne gel along with the stability studies. Based on this studies, polyherbal anti-acne gel prepared from the extract of Citrus sinensis (0.2%), Aloe barbadensis (1%) and Curcuma longa (0.8%) showed significant antibacterial activity on Staphylococcus aureus and staphylococcus epidermis with no irritation. The polyherbal gel showed a synergistic effect as compared to individual extract with good stability. Thus the study result concludes that the formulated polyherbal gel with extract of Citrus sinensis, Aloe barbadensis and Curcuma longa with concentration 0.2%,1% and 0.8% respectively can be used for the treatment of acne vulgaris.
Conflict of Interest: None
Source of Funding: None
References:
References
1. Suva MA, Patel AM, Sharma N. A Brief Review on Acne Vulgaris?: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Treatment. Res Rev J Pharmacol 2016;4(1):1–12.
2. Prabu SL, Umamaheswari A, Kumar CA, Banumuthupriya M, Dhanasekaran D. Formulation and Evaluation of Polyherbal Gel Containing Natural Antimicrobials for the Management of Acne Vulgaris. Int Res J Pharm 2017;8(5):65–69.
3. Prasad SB. Acne vulgaris: A review on pathophysiology and treatment. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 2016;9(4):54–59.
4. Sinha P, Srivastava S, Mishra N, Yadav NP. New Perspectives on Antiacne Plant Drugs: Contribution to Modern Therapeutics. Biomed Res Int 2014;2014: 301304.
5. Mishra BP. A quest of Anti-acne Potential of Herbal Medicines for extermination of MDR Staphylococcus aureus. Int J Pharm Sci Invent 2014;3(6):12–17.
6. El-Ishaq A. Extraction of limonene from orange peel. Nutr Heavy Met 2015;1–15.
7. Gotmare S. Orange Peel: A Potential Source of Phytochemical Compounds. Int J ChemTech Res 2018;7(3): 231.
8. Arunkumar S, Muthuselvam M. Analysis of phytochemical constituents and antimicrobial activities of Aloe vera L. against clinical pathogens. World J Agric Sci 2009;5(5):572–576.
9. Rani. RHP shetty; M. Phytchemical analysis of methanolic exctract of Curcuma longa Linn Rhizome. Int J Univers Pharm bio Sci 2013;2(2):285–297.
10. Gangane PS, Ghughuskar SH, Mahapatra DK, Mahajan NM. Evaluating the role of Celosia argentea powder and fenugreek seed mucilage as natural super-disintegrating agents in gliclazide fast disintegrating tablets. Int J Curr Res Rev 2020;12(17):101–108.
11. Dhandapani R, Sabna B. Phytochemical constituents of some Indian medicinal plants. Anc Sci Life 2008;27(4):1–8.
12. Kharwade RS, More SM, Mahajan UN. Formulation and evaluation of gastroretentive floating tablet using Hibiscus rosa-Sinensis mucilage. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 2017;10(3):444–448.
13. Bhinge SD, Bhutkar MA, Randive DS, Wadkar GH, Kamble SY, Kalel PD, et al. Formulation and evaluation of polyherbal gel containing extracts of Azadirachta indica, adhatoda vasica, piper betle, Ocimum tenuiflorum and Pongamia pinnata. Marmara Pharm J 2019;23(1):44–54.
14. Singh S. Extraction and characterization of Orange peel. World J Pharm Res 2015;20.
15. Latha Samala M, Sridevi G. Role of Polymers as Gelling Agents in the Formulation of Emulgels. Polym Sci 2016;2(1):1–8.
16. Bhutkar K. Formulation and evolution of herbal. 2019;11: 291-295.
17. Misal G, Dixit G, Gulkari V. Formulation and evaluation of herbal gel. Indian J Nat Prod Resour 2012;3(4):501–505.
18. Rahman A, Hussain A, Hussain S, Singh LR. Lecithin-microemulsion based organogels as topical drug delivery system (tdds). 2011;03(03):22–33.
19. Kharwade RS, Mahajan NM. Formulation and Evaluation of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Based Anti-Inflammatory Gel for Topical Drug Delivery System. Asian J Pharm Clin Res. 2019;12(4):286–291.
20. Gatne MM, Tambe K, Adarsh, Ravikanth K. Acute Dermal Irritation study of polyherbal gel Mastilep in rabbits. Int J Pharm Sci Res 2015;6(8):3473–3476.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License