IJCRR - 13(4), February, 2021
Pages: 39-43
Date of Publication: 16-Feb-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Detection of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus using Chromogenic Agar and their Antimicrobial Susceptibility Pattern
Author: Priyadarshini Bhoi, Bichitrananda Swain, Sarita Otta
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), a major nosocomial pathogen is a challenge in treatment as it is ineffective to most antibiotics. So quick and accurate detection of MRSA is essential to avoid treatment failure and to contain the spread of this organism. Objective: This study aims to compare the conventional cefoxitin disc diffusion method with MRSA Chrom agar method for detection of MRSA and to note the resistance pattern of the organisms. Methods: In this prospective study S.aureus identified using conventional methods for the pus, nasal swabs and blood samples as a part of surveillance by hospital infection control unit. All S.aureus were screened for methicillin resistance by cefoxitin disk diffusion, MIC (by Vitek 2) and MRSA Chromagar.S.aureus ATCC strains were used for quality control. Antibiotic sensitivity was done by Kirby Bauer's disc diffusion method using CLSI guidelines. Data maintained in Microsoft office Excel was analyzed with statistical tools such as the Chi Square test for significance. Results: Out of 125 S. aureus isolated, 48 (38.4%) were MRSA. By cefoxitin disk diffusion method the sensitivity and specificity were 100% and 100% respectively when compared with Vitek2 MIC while, the sensitivity and specificity of Chromagar-MRSA were93.75% and 97.36%, respectively. The earliest turnaround time for MRSA identification with the conventional method was 48 hours (37.5%) only while by Chrom agar detection 91.11% were identified in the first 24 hours itself. All MRSA isolated were susceptible to Vancomycin, Linezolid and resistant to commonly used antibiotics. Conclusions: Cefoxitin disk diffusion method is having higher sensitivity and specificity for MRSA detection than the Chrom agar MRSA method. As the later is having good sensitivity, specificity and can detect the majority of MRSA with a significantly less TAT, it can be used for screening of MRSA.
Keywords: Cefoxitin resistant, S. aureus, MeReSachrom agar, MRSA, Vitek
Full Text:
Introduction
Staphylococcus aureus is a common human commensal well as a pathogen causing widespread infections.1 Infection caused by S. aureus specially Methicillin resistantS.aureus(MRSA) is associated with significant morbidity and mortality.2 The incidence of nosocomial as well as community-acquired infections caused by MRSA is increasing worldwide.3 This further promotes to the overuse of anti-MRSA drugs which has led to the emergence of vancomycin-resistant and intermediateS. aureus.4 Preventive strategies include hand hygiene practices properly with cleaning and disinfection and timely identification and isolation of MRSA from colonized or infected patients.5 So MRSA screening is important for epidemiologic and therapeutic reasons. To identify these strains in clinical samples, screening methods should have high sensitivity and specificity and early reporting is of paramount importance to reduce its further spread. A solution for this is by use of selective media and chromogenic agar media containing cefoxitin which can be useful for identification ofStaphyloccus aureus and MRSA in one step from clinical samples.6So this study was designed to know the best method for early MRSA detection and its prevalence by comparison of chromogenic agar (MeReSa chrome agar) with other conventional detection methods. One of the MRSA preventive strategies is also proper & effective treatment of MRSA infected patients. So to choose the appropriate antibiotic or for empiric therapy knowledge of the resistance, the pattern is of utmost importance.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sample collection
This prospective study was performed in the Microbiology Department of IMS and SUM hospital from January to June 2020. The samples included were the surveillance culture of the hospital infection team which consisted of blood, pus or wound swabs and nasal swabs of indoor patients with septicemic or pyogenic infection. In the study period, 414 total samples i.e. 299 pus samples, 45 blood culture and 70 nasal swabs were received by the hospital infection control unit.
Isolation of S. aureus
Nasal swab &pus samples were cultured on 5%sheep blood agar (BA), MacConkey’s agar(MCA). Blood sample collected in blood culture bottles was cultured by the automated blood culture system (BacT/Alert, Bio Merieux). The specimen signalling growth were subcultured on above media and incubated at 35°C in 5%CO2for 18-24 hours. Opaque, beta haemolytic colonies having positive for catalase, slide & tube coagulase test, growth on mannitol salt agar and Gram-positive cocci on microscopy, were identified as S.aureus.
Detection of MRSA by cefoxitin disc method
On Mueller–Hinton agar plates all strains of S. aureus with a suspension of 0.5 McFarland were tested with 30 µg cefoxitin discs (Hi-Media). After 16–18 h of incubation at 37ºC it was interpreted according to CLSI (2017) criteria as per the size of the zone of inhibition; susceptible if >22 mm and resistant if it is <21 mm.7Oxacillin sensitive S.aureus ATCC 29213 and resistant S.aureus ATCC 43300 were used as quality control for all procedure.
MRSA Chrom agar method
It was prepared by adding MeReSa selective supplement and cefoxitin supplement to chromagar base. All the samples on receipt were directly inoculated on MRSA ChromAgar(HiCromeTMMeReSa Agar)at parallel along with the conventional inoculation. For blood culture, the sample was inoculated on the chromogenic media after receipt of positive signal from the automated blood culture system.MRSA Chromagar was incubated at 37°C. The specimen showing bluish-green colour colonies in 18-24 hours of incubation were considered as the MRSA. The culture plates were incubated for another 24 hours if no colour change observed in 1st 24hours.
MRSA detection by Vitek 2
Methicillin resistance was cross-checked by automated method (Vitek2, Biomeriux) for all the MRSA strains detected by chromagar and the disc diffusion methods. Though the molecular method of detecting mecA gene by PCR is considered as the gold standard for MRSA detection; due to its limited availability, an alternative method Vitek 2 system was used for this purpose which uses both the cefoxitin and oxacillin to detect methicillin resistance by the MIC method, better than the single cefoxitin disc diffusion method.8 Antibiotic susceptibility testing was done for the isolated MRSA strains by modified Kirby Bauer’s disc diffusion method as per CLSI Guidelines.7
Ethical issues
As the samples were submitted for surveillance purpose by hospital infection control team with no direct involvement of the patient in our study ethical committee approval was not essential.
Statistical analysis
Data was entered in excel format and analysis was done using standard statistical methods.
Results
A total of 414 nasal swabs, pus and blood culture specimens were collected. (Table 1)Nasal swabs were collected from 70 patients among which Staphylococcus aureus was isolated in 31 samples out of which 12 (38.7%) were MRSA and rest 19 were MSSA. Of the 299 collected pus samples, S.aureus was isolated in 79 specimens, out of which 26(8.7%) were MRSA and 53 were MSSA. Other organisms isolated were CoNS 12, Gram-positive cocci in pairs 7, Gram-negative bacteria 108 and only one Candida. There was no growth in 97 samples. Similarly, from 45 blood cultures, 10 samples showed MRSA (22.22 %) and 5 samples showed MSSA (33.33%) (Table 1). So the MRSA collected from nasal swab was 12/70(17.14%), pus 26/299 (8.7%) and blood culture were 10/45(22.22%). Thus 38.4% of all S.aureus were MRSA.
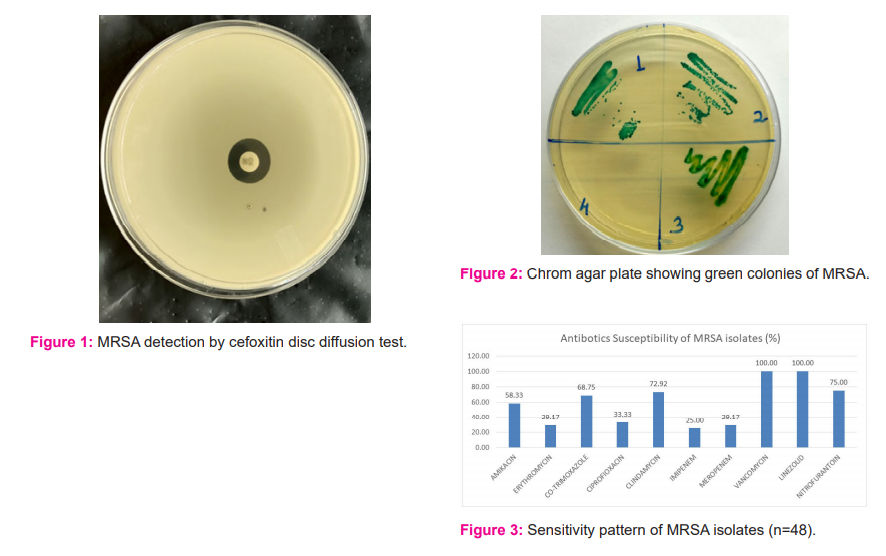
All the S. aureus isolated from different samples were differentiated to MSSA or MRSA by Cefoxitin Disc diffusion method (Figure 1). By chromagar method the bluish-green colour colonies were presumed as MRSA (Figure 2). Time taken for isolation and identification of MRSA by both methods was compared. By conventional culture techniques, in some pus samples and nasal swab specimen, S. aureus growth was interspersed with the normal flora, thus reporting was delayed for up to 72 hours or more. The earliest turnaround time for MRSA identification with the conventional method was 48 hours. 18 isolates (37.5%) were reported in 48 hours, 20 isolates (41.6%) in 72 hours, 8 isolates (16.6%) in 96 hours and 2 isolates (4.1%) even in 120 hours. On the other hand on using Hi-CromMeReSaTM Agar total of 47 MRSA detected by seeing green coloured colonies. 41 isolates (41/45,91.11%) of these were identified in 24 hours. The remaining 6 MRSA were identified at 48 hours (4/45, 8.89%)of which 2 isolates were excluded as MSSA after confirmation by Vitek 2 (Table 2).
The MRSA detected by both the methods were reconfirmed with the Vitek 2 system. By conventional method 48 isolates were read as MRSA and 77 as MSSA which was imperfect linearity as Vitek 2 results. But 3 isolates of MRSA, as noted by Vitek 2, were not detected by Chrom agar method. Similarly, out of 47 MRSA detected by Hi-CromMeReSaTM, 45 isolates were MRSA on confirmation and 2 were detected as MSSA (Table 3).
Sensitivity and specificity of different methods are illustrated in Table 4. The sensitivity of the chromogenic and the conventional method was 93.75% and 100% respectively, whereas the specificity by these two was 97.4% and100% respectively (Table 4). The two methods had almost perfect agreement(95% confidence interval is from 0.842 to 0.988) as calculated by the kappa value of 0.915. The Pearson Chi-square value for this is104.71. The two-tailed ‘P-value’ is less than 0.0001indicating that the difference between the two methods for MRSA detection to be statistically significant.
The result for all the 48 MRSA strains, susceptibility testing to different antibiotics is shown in Figure 3. All these MRSA were sensitive to vancomycin & linezolid. These are resistant to most of the antibiotics such as erythromycin, ciprofloxacin, imipenem and the meropenems. The MRSA isolated from nasal swab had similar resistance pattern as those isolated from clinical samples.
Discussion
The emergence of methicillin resistance in Staphylococci is a great challenge for the treatment of many communities and hospital-acquired infections caused by it. Rapid screening of MRSA in clinical specimens is therefore essential for time management with appropriate antibiotics and instituting isolation measures. So, it is necessary for evaluating an accurate, sensitive and simple cost-effective method to be used in Microbiology lab for early MRSA detection.
In this study, different methods were used for the detection of MRSA. Total 125 number of S. aureus (MRSA & MSSA) was isolated from 414 different samples & MRSA was 48/125(38.4%). The finding was like the range of MRSA (38.23%, 32%, 41.6%) isolated by other workersrespectively.9,10,11
In the present study, for the detection of MRSA, we assessed two different phenotypic methods. A total of 125 S. aureus isolated from different clinical samples were processed for methicillin resistance detection. By the cefoxitin disc diffusion test, 48 (38.4%) of these were observed as Methicillin-Resistant S. aureus (MRSA). By chrom agar method 47 were detected as MRSA. The result of cefoxitin disc diffusion method &chrom agar was cross-checked byMIC determination by Vitek method and we observed the same 48 strains as MRSA as was by cefoxitin disc diffusion method. So, the cefoxitin disc test was having 100% sensitivity and 100% specificity with 100% positive and negative predictive value. With the cefoxitin disc diffusion, method other workers had also reported 100% sensitivity and 100% specificity.12,13 But in the present study, out of 47 MRSA strains detected by chrome agar method, 45 were the MRSA, 2 were MSSA with 93.75% sensitivity and 97.4% specificity, similar to a finding of 98.07% sensitivity and 97.80% specificity by an author.13 For detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus(MRSA), Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute has replaced oxacillin with cefoxitin as cefoxitin disk diffusion method is a better than the disk diffusion tests using oxacillin and the former is supported by a molecular study of MRSA detection by PCR for mecA gene.12
Time taken for isolation and identification of MRSA by both these methods was compared. The earliest turnaround time for MRSA identification with the conventional method was 48 hours. 18 isolates (37.5%) were reported in 48 hours, 20 (41.6%) in 72 hours, 8 (16.6%) in 96 hours and 2 4.1%) in 120 hours.
By chromagar method, 41 isolates (41/45, 91.11%) were identified in the first 24 hours. The remaining 6 MRSA of which 2 excluded as methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus MSSA after confirmation of all isolates by Vitek2 were identified at 48 hours (4/45, 8.89%). The finding is similar to the studies9,14 where90% &88.88% were detected in 24 hrs while 10% and 11.11% were detected in48 hrs respectively.
In this study, 91.11 % strains of MRSA were detected by Chromagar within 24 hrs directly. This was highly significant than the cefoxitin disc diffusion method for early detection with a P-value of <0.0001 and sensitivity, specificity, PPV and NPV of 93.75%, 97.36 %, 95.7& 96.1 % respectively. The early detection is a highly necessary step to spread transmission of the bug.
A nasal swab was used as a sample to evaluate the usefulness of Chrom agar method when the sample has a propensity to contain associated commensal flora which can influence isolation. But the Chrom agar method proved useful in early identification of MRSA even in large loads of contaminating bacteria.
In this study, the MRSA show a higher level of resistance to commonly used antibiotics. All of them were sensitive to vancomycin and linezolid. This result was comparable to the studies carried out by other workers.13-17 In the present study the MRSA isolated from nasal swab had a similar resistance pattern as those isolated from clinical samples. It strongly indicates the nasal carrier might be the source for nosocomial infection. So MRSA surveillance, proper health practice ®ular screening with local treatment of the nasal carriers is essential for preventing transmission of this dangerous infection especially in the high-risk zone in the hospital.
An early detection method by Chrom agar can be chosen replacing the time taking multistep conventional method which will benefit the patient by early treatment & further preventing transmission of MRSA strains.
Conclusion
In this study, cefoxitin disc diffusion is the most accurate method for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus detection. But the main demerit is that it is time-consuming. So a highly specific and sensitive single step Chrom agar method can be a better option for routine and timely identification & rapid screening of MRSA from the clinical samples particularly in high-risk wards and ICUs to aid in early diagnosis and further to prevent the transmission of MRSA strains.
Conflict of interest- None
Funding- None
Name of the authors and their contribution
1. Dr. Priyadarshini Bhoi - design, the definition of intellectual content, literature search, data acquisition, manuscript preparation, manuscript editing, and manuscript review
2. Dr. Bichitrananda Swain- concepts, design, literature search, manuscript preparation, manuscript editing
3. Dr. Otta Sarita-literature search, manuscript preparation, manuscript editing, and manuscript review
Acknowledgement- We acknowledge SOA University, Bhubaneswar, Odisha for their help in doing this work
References:
-
Wertheim HF, MelleDC, Vos MC, van Leeuwen W, van Belkum, Verbrugh HA, et al. The role of nasal carriage in Staphylococcus aureus infection. Lancet Infect Dis 2005; 5:751-762.
-
Diekema DJ, Climo M. Preventing MRSA infections: finding it is not enough. J Am Med Assoc 2008; 299:1190-1192.
-
Muto CA, Jernigan JA, Ostrowsky BE, Richet HM, Jarvis WR, Boyce JM, et al. SHEA guideline for preventing nosocomial transmission of multidrug-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2003;24:362-386.
-
Mimica MJ, Berezin EN, Carvalho RL, Mimica IM, Mimica LMJ, Sáfadi MAPet al. Detection of methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus isolated from pediatric patients: is the cefoxitin disk diffusion test accurate enough? Braz J Infect Dis. 2007;11(4):415-417.
-
Solberg CO. A study of carriers of Staphylococcus aureus with special regard to quantitative bacterial estimations. Acta Med Scand Suppl 1965;436:1–96.
-
Lark RL, Saint S, Chenoweth C, Zemencuk JK, Lipsky BA, Plourde JJ. Four-year prospective evaluation of community-acquired bacteremia: epidemiology, microbiology, and patient outcome. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2001; 41(1-2):15–22.
-
Clinical and Laboratory standards institute (CLSI). The performance standard for antimicrobial susceptibility testing, 27th ed. Wayne, USA: CLSI; 2017.
-
Edward JPC, Paterson GK, Raven KE, Harrison EM, Gouliouris T, Kearns A et al.Use of Vitek 2 Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profile To Identify mec C in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol 2013; 51(8): 2732–2734.
-
Verma S, LaghaweA, Kaore NM, Jain A, Prabhu KT. The utility of Chromogenic Medium for Early Detection of Nasal Carriage of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) in Healthcare Professionals. JMSCR 2017;05(03):19647-19654.
-
Panda RK, Mahapatra A, Mallick B, Chayanne N. Detection of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus. J Clin Diagn Res 2016; 10(2): 19-21.
-
Singh AH, Aruna S. A study on the prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a South Indian tertiary care hospital. Int J Curr Res Rev 2014;23(6):19-22.
-
Anand KB, Agrawal P, Kumar S, Kapila K. Comparison of cefoxitin disc diffusion test, oxacillin screen agar, and PCR for mecA gene for detection of MRSA. Indian J Med Microbiol 2009;27(1):27-29.
-
Sharma S, Srivastava P, Kulshrestha A, Abbas A.Evaluation of different phenotypic methods for the detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of MRSA. Int J Community Med Public Health 2017;4(9):3297-3301.
-
Poojary AA, Bhandarkar LD. Rapid identification of Meticillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) using chromogenic media (BBL CHROM agar MRSA) compared with conventional methods. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci 2015;4(4):939-947.
-
Anupurba S, Sen MR, Nath G, Sharma BM, Gulati AK, Mohapatra TM. Prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a tertiary referral hospital in eastern Uttar Pradesh. Indian J Med Microbiol 2003;21:49–51.
-
Datta P, Gulati N, Singla N, Butta H. Evaluation of various methods for the detection of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains and susceptibility patterns. Department of Microbiology, Government Medical College Hospital, Chandigarh, India. J Med Microbiol 2011;60:1613–16
Kalayadav ML, Panicker GJ. Prevalence and antibiogram of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated in a tertiary care hospital in Bangalore, South India. Int J Curr Res Rev 2014; 17(6) :37-40.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License