IJCRR - 8(4), February, 2016
Pages: 54-60
Date of Publication: 21-Feb-2016
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
TISSUE DISTRIBUTION AND PHARMACOKINETICS OF BROMOXYNIL IN RAT
Author: Ahmed K. Salama, Khaled A. Osman, Ahmed S. El-Bakary, Maher S. Salama
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:The tissue distribution and excretion of bromoxynil were studied in male rat. A single oral dose of 12.9 mg bromoxynil /kg body weight was administered to rat. Rats were killed after 0.5, 1, 3, 6, 12, 24, 48, 72, 120, and 168 h. At termination of 24 h, 2.80 and 0.01 % of the compound were excreted in the urine and feces, respectively. By 168 h the urinary and fecal cumulative excretion rose to 21.90 and 14.11%, respectively. Bromoxynil was readily absorbed and subsequently distributed throughout the body. Bromoxynil concentrations increased in serum as the time passed reaching a peak concentration of 256.09ng/ml at 48 h following administration. Peak concentrations of bromoxynil were also reached at 48 h in liver (345.15ng/g) and brain (67.85ng/g). However, bromoxynil level in kidneys reached peak concentration (647.19ng/g) at 24 h after dosing. Bromoxynil begin to decline in the tissues as time passed to reach 10.67, 27.86 and 22.31ng/g(ml) in serum, liver and kidneys, respectively. In case of brain, the lowest amount of bromoxynil (23.01ng/g) reached at 120 h and disappeared after 168 h following administration. Bromoxynilwas disappeared biexponentially from serum, liver, kidneys and brain. The terminal half-life t½ of bromoxynil was 48.0, 62.0, 60.0, and 34.8 h for the serum, liver, brain and kidneys, respectively. This indicates that there was no tendency for bromoxynil to retain in rat tissue.
Keywords: Bromoxynil, Pharmacokinetics, Distribution, Excretion, Rat
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
The benzonitrile herbicides including bromoxynil have been widely used in agriculture and households to control growth of weeds (Agriculture Canada, 1989, U.S. EPA, 1997, 1998 and Tomlin, 1997) and their residues persist in the environment. The studies addressing the fate of benzonitrile herbicides in the environment show that some metabolites of these herbicides are very persistent. The toxicity studies of these pesticides in many prokaryotic and eukaryotic systems provided detailed information on acute and chronic toxicity, carcinogenicity, and mutagenicity ( USEPA, 1998). The chronic exposure to bromoxynil is of public health interest. It is classified as moderately hazardous (Class II) by the World Health Organization (IOMC, 2004). In this concern, the cytotoxic effects of benzonitrile herbicides including bromoxynil and their microbial metabolites using two human cell lines, Hep G2 and HEK293T were carried out by Lovecka et al (2015). They indicated that bromoxynil has moderate cytotoxic effect at concentration several times higher than its limit allowed in the drinking water. However, this does not exclude its potential risk connected with chronic exposure to such compounds.
A review carried out by Deziel et al (2015) summarizes the evidence for the contribution of non occupational pathways to pesticide exposures in women living in North American agricultural areas, who may be exposed to a greater number of pesticides and at higher concentrations than women in the general population. Pharmacokinetics is a comprehensive study with concurrent absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination of the compound by determining the target organ dose of toxic moiety over time, and in turn the magnitude and duration of toxicity (Caldwell et al, 1995 and Xie et al, 2011). Pharmacokinetics was studied in male and female Sprague Dawley rats given single oral doses of 14C-bromoxynil octanoate. Radioactivity was distributed in most tissues where the highest concentrations were observed in blood, plasma, liver, kidneys and thyroid (especially in females). Levels of radioactivity in tissues were generally higher in females than in males. Seven days following oral administration, 84 -89% of the radioactivity were excreted in male urine and 76-80% were found in female urine. However, lesser amounts (6- 10%) were detected in the feces of both males and females (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, 2005). In another study by Stahler et al (1991), the bromoxynil concentrations measured in serum proceed with a terminal half-life of 20 h. However, kidneys showed saturation kinetics after oral administration of a high dose (100 mg/kg) in case female rats. Cessna and Grover (2002) reported that the exposure to bromoxynil in agricultural regions may be via inhalation of ambient air and/or dermal contact with surface water where the pesticide is actively being used. They found that the median value of bromoxynil inhaled by farmers during applying the pesticide was 0.018 μg/ kg body weight. They also found that the amounts of bromoxynil excreted via urine were increased over the first few days after application and then remained relatively constant during the study period of 10 days. Series of our studies were conducted to examine the pharmacokinetic profile of pesticides in rat (Salama et al, 1992a, 1992b, 1992c and 1993) and mouse (Salama, 1992 and Bakry et al, 1999). Therefore, the present study aimed to investigate the pharmacokinetic pattern and tissue distribution of the phenolic herbicide,bromoxynil in male rat following oral administration of 12.9 mg/kg body weight.
MATERIALS AND METHODS Chemical Bromoxynil (3,5-dibromo-4-hydroxybenzonitrile) was supplied by Chem Service, West Chester (98.9% purity). All other chemicals used in this study were obtained either from Sigma or BDH Companies and they were of the highest grade available. Animals Adult male Ratusnorvegicus rats weighing an average of 75g ± 5 were obtained from the High Institute of Public Health, Alexandria University. Animals were randomly separated and housed in stainless steel cages (four per cage) and left two weeks under the laboratory conditions. Rats were kept under 12 h light/dark cycle and about 23° C. They provided feed and water ad libitum.
Pellet feed containing 23% crude protein and 7% crude cellulose. The use of animals for this study was approved by the Ethics Committees of the High Institute for Experimental Animals, Alexandria University. Treatment of animals Thirty male rats were used for the study. Animals were received a single oral dose of 12.9 mg bromoxynil/kg body weight in corn oil (4ml corn oil/kg) using a glass syringe at tached with a curved stainless steel animal intubation needle with a spherical ball tip.
Three animals were orally received corn oil as the same manner of pesticide treated animals and served as vehicle control. The condition of the animals was monitored after bromoxynil treatment and there is no any adverse effect on the overall health of the animals was noticed. There is no animal died without euthanasia during the work study. Also, there is no any unintended death of animals during the study.
Tissue samples Blood samples were withdrawn from eyes without anesthesia following the time intervals of 0.5, 1, 3, 6, 12, 24, 48, 72, 120 and 168 h. Blood collected in non-heparinized glass vials and then centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 5 min at room temperature to separate the red blood cells from serum. At each time interval, three animals were killed by decapitation. To minimize suffering of the animals, they anaesthetized with diethyl ether just before decapitation. Brain, liver, and kidneys were removed rapidly, weighed, placed in glass vials and stored at -18 °C until analysis.
Collection of excreta Animals were individually placed in glass metabolism cages at least 24 h prior to dosing for acclimatization and the collection of control samples. Immediately after oral administrant, the animals were replaced in their metabolism cages which were designed for the studyto separate urine and feces. Excreta were collected at the end of each time intervals of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7 days.
Extraction of bromoxynil from tissues and excreta Extraction of bromoxynil from serum, liver, kidneys or brain tissue was carried out according to the method described by EPA (1974) with major modifications. Tissue sample was placed into flask and then 2.5 ml of 5% methanolic potassium hydroxide per g (ml) tissue was added. Samples were refluxed for one hour on a hot plate in the presence of porcelain chips and then left to cool at room temperature. Samples were filtered and then 0.75 ml of concentrated sulfuric acid per g (ml) tissue was added.10 ml of saturated sodium chloride solution and 30 ml of distilled water per g (ml) tissue were added.
Samples were filtered through a bed of florisil (5g) and then extracted three times with methylene chloride (10 ml per g or ml tissue). The organic layers were taken, combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and rotary evaporated at 40 °C to 5 ml. Extraction of bromoxynil from feces and urine was carried out according to the method of EPA (1979) with slight modifications. Urine samples were taken in a conical flask and then 2ml of 2% acetic acid and 3 ml of hexane were added.
The samples were mixed very well with the presence of few drops of acetonitrile and then partitioned three times. The organic layers were separated and dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. Samples were rotary evaporated to dryness and then dissolved in 5 ml acetonitrile. Feces samples were homogenized with acetone (5ml/g sample). The homogenates were filtered and partitioned three times with hexane (3x5ml). Hexane layers were collected and concentrated to 2 ml using rotary evaporator.
Clean up procedure Tissue samples were cleaned up according to the method of Bogus et al (1990) with a slight modification. The sample (5 ml) was transferred to a column packed with 2g florisil (60-80 mesh) and 2 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate per gram tissue. The column was rinsed with 60 ml of petroleum ether. Samples were loaded onto the column and eluted with 100 ml of 5% ethyl ether: petroleum ether (40-60°C). The eluate was evaporated to dryness under nitrogen and the residue was dissolved in 2ml acetonitrile to be ready for high pressure liquid chromatographic determination. Urine and feces sample extracts were cleaned up onto a column packed with 2 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate and 2g activated florisil per g (ml) sample. Samples were eluted using 10 ml hexane. The eluates were evaporated to dryness and then dissolved in 2 ml acetonitrile to be ready for high pressure liquid chromatographic analysis.
Fortification Recovery percentages of bromoxynil from serum, brain, liver and kidneys were carried out by the addition of bromoxynil at two levels of 5 and 10 µg. Urine and feces were only fortified with one level of 10 µg of bromoxynil. The fortified samples were extracted and cleaned up as described before.
Chromatographic analysis Analysis was performed on Perkin-Elmer 200High pressure liquid chromatograph, equipped with UV/VIS detector set at 254 nm. The separation was performed with an inertsil ph-3 C18 stainless steel column (150 x 4.6 mm I.D.), using a mobile phase of acetonitrile: water (1:1) at a flow rate of 1 ml/min. Identification of bromoxynilin serum, liver, kidneys, brain, urine and feces was accomplished by retention times and compared with standards of bromoxynil at the same conditions. The quantities were calculated on peak height basis, except for broad peaks which were calculated from area under the peak.
Kinetic analysis Kinetic analysis of bromoxynil concentrations in serum, liver, brain and kidneys was performed. The terminal half-life of the compound in tissues was calculated from the elimina tion rate constant, β which was obtained by linear regression of terminal linear exponential decline in bromoxynil concentration using the formula: t ½ = 0.693 / β The total area under the bromoxynil concentration versus time curves for serum AUCserum, and the various tissues, AUCorgan, was counted by the numerical integration method and extrapolated to infinity by using the last data point and the respective terminal linear exponential decline.
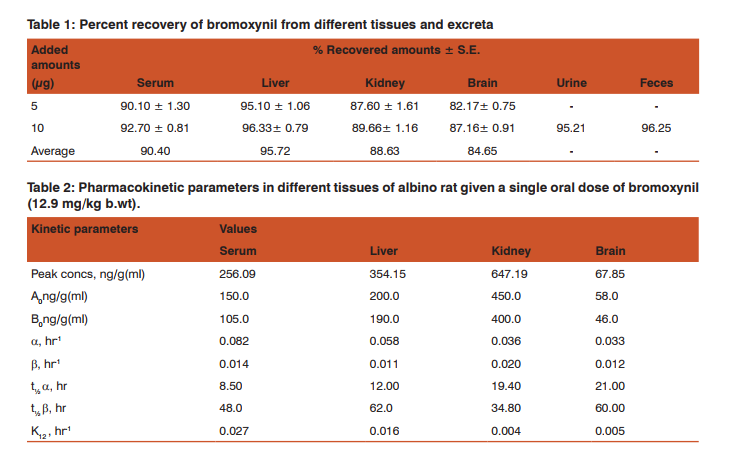
RESULTS Bromoxynil was extracted from serum, liver, kidney, brain, urine and feces as described before. Recoveries of bromoxynil from tissues and excreta at two different levels of fortification are presented in Table (1). The average recovery percentages were 90.40, 95.72, 88.63, 84.65, 95.21 and 96.25% for serum, liver, kidneys, brain, urine and feces, respectively.
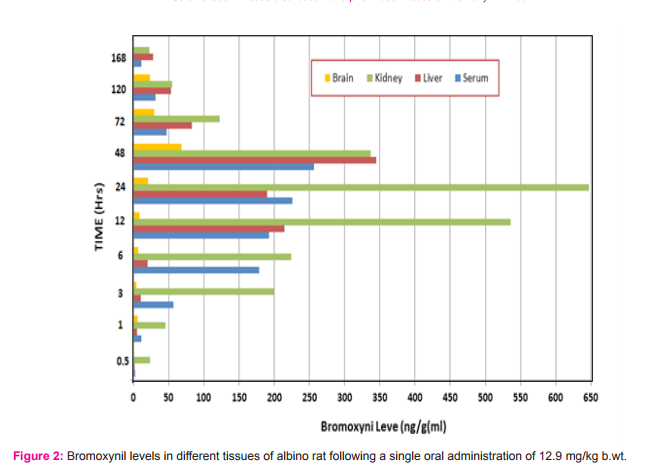
Tissue distribution of bromoxynil: Bromoxynil was readily absorbed and subsequently distributed throughout the body. Within 0.5 h. following administration, the compound was observed in all tissues analyzed. At this early time interval, the highest amount was observed in the kidneys (23.31ng/g tissue), while the lowest amount was associated with liver (0.33ng/g tissue). At this time point, brain does not show any appreciable amounts of bromoxynil. Bromoxynil concentrations increased in serum as the time passed reaching a peak concentration of 256.09ng/ ml at 48 h following administration.
Peak concentrations of bromoxynil were also reached at 48 h in liver (345.15ng/g) and brain (67.85ng/g). However, bromoxynil level in kidneys reached peak concentration (647.19ng/g) at 24 h after dosing. Bromoxynil begin to decline in all tissues as time passed to reach 10.67, 27.86 and 22.31ng/g(ml) in serum, liver and kidneys, respectively. In case of brain, the lowest amount of bromoxynil (23.01ng/g) reached at 120 h and disappeared after 168 h following administration (Figure 1).
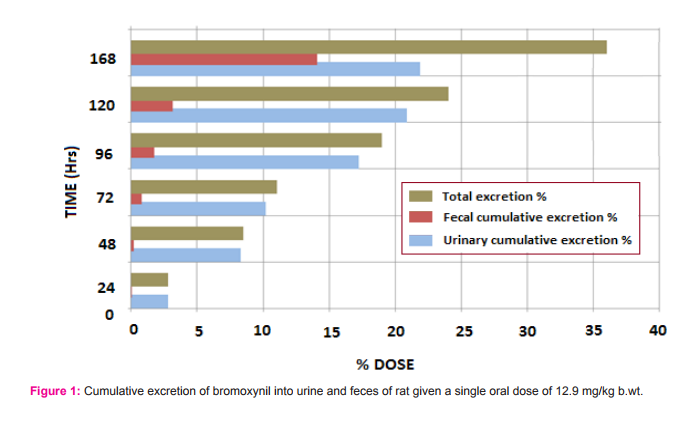
Excretion of bromoxynil: Bromoxynil was rapidly excreted via urine and feces soon after the oral administration. Thus, within 24 h of dosing, 2.80 and 0,01 % were eliminated in urine and feces, respectively. By 168 h the urinary and fecal cumulative excretion rose to 21.90 and 14.11%, respectively (Figure 2 ).
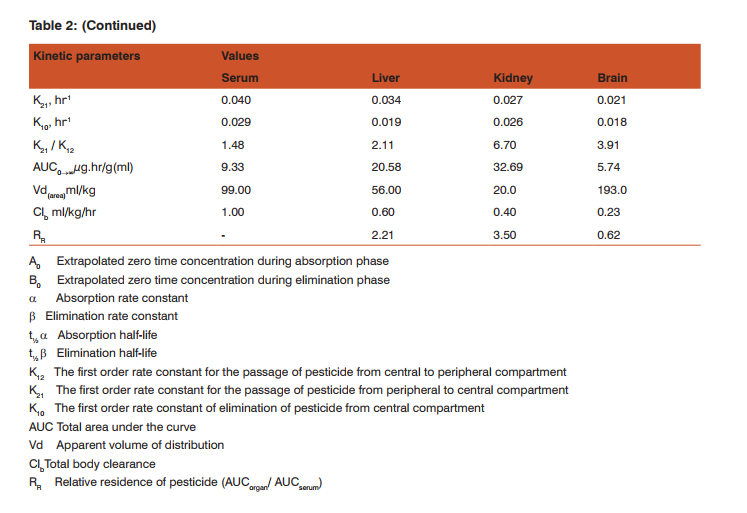
Pharmacokinetics of bromoxynil: The mean concentration of bromoxynil in serum, liver, kidneys and brain as a function of time were determined, and the pharmacokinetic profiles were fitted to a bi-exponential curve according to a two-compartment open model system (Gillette, 1974). The pharmacokinetic parameters were described by the exponential equation: Ct = A0 exp-αt + B0 exp-βt Where: Ct is bromoxynil concentration in the tissue at time t (h), α and β are the rate constants for the first and second phase of the biphasic model, respectively. The pharmacokinetic parameters for bromoxynil in different tissues are listed in Table (2).
DISCUSSION This investigation was carried out to study the pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution and excretion of a single oral dose of bromoxynil in male rats. The present data suggest that the compound was rapidly distributed and then eliminated from the animal. The longest elimination t½was associated with the liver (62.0 h) followed by the brain (60.0 h), while the shortest elimination was associated with the kidneys (34.8 h). Stahler et al (1991) found that the concentrations of bromoxynil measured in serum proceed with a terminal half-life of 20 h after oral administration of two dosages in male and female rats. However, kidneys showed saturation kinetics after oral administration of a high dose (100 mg/kg) in case female rats. AUC values were 9.30, 20.58, 32.69, and 5.74 for serum, liver, kidneys and brain, respectively.
This finding indicates that there was no tendency for the compound to retain in animal tissue. Most of bromoxynil was recovered in the urine (21.90% of the dose) 7 days following administration. The amount of bromoxynil excreted in the feces was 14.11% of the dose. The large amounts excreted in the urine may be due to the high aqueous solubility of the compound. Excretion study of 14C-bromoxynil octanoate in male and female Sprague Dawley rats following different single oral doses showed that Most radioactivity was excreted in the urine (about 84-89% in males and 76-80% in females at 7 days) and considerably lesser amounts in the feces (about 6-10% in both males and females at 7 days)(U.S. Environmental Protection Agency ,2005).The rapid distribution of bromoxynil after oral administration may be indicated by its high aqueous solubility. Therefore, bromoxynil is distributed primarily in body water.
The bromoxynil amount was reached the peak value in the kidneys following 24 h (647.19ng/g), however, it was reached the peak concentrations in the liver (345.15 ng/g), serum(256.09 ng/ml) and brain (67.85 ng/g) after 48 h. Large amounts of bromoxynil that observed in the kidneys during 24 h, indicating that the compound and/or its metabolites may be rapidly excreted in the urine. The absorption and distribution of 14C-bromoxynil octanoate in male and female Sprague Dawley rats given single oral doses indicated that the highest concentrations were observed in blood, plasma, liver and kidneys (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency,2005). They also found that levels of radioactivity in tissues were generally higher in females than in males.
CONCLUSION The study suggested that the herbicide bromoxynil was rapidly distributed in the body and there was no tendency for the compound to retain in animal tissue.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT The author extends his appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at Majmaah University for funding the work study. Authors also acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars.
References:
1. Agriculture Canada (1989): CAPCO (Canadian Association of Pesticide Control Officials) note on bromoxynil.Ottawa, Ontario: Pesticides Directorate, Agriculture Canada.
2. Bakry, N.M., Abdel-Halim, K.Y. and Salama, A.K. Placental and milk transfer of chlorpyrifos and profenofos in mice. Alex. J. Pharm. Sci. 1999; (13): 29 – 33
3. Bogus, E.R., Watschke, T.L. and Mumma, R.O. Utilization of solid-phase extraction and reversed-phase and ion-pair chromatography in the analysis of seven agrochemicals in water. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1990; 38: 142-144
4. Caldwell, J., Gardner, I., and Swales, N.An introduction to drug disposition: the basic principles of absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. ToxicolPathol. 1995; 23, 102-14.
5. Cessna, A.J. and Grover, R. Exposure of Ground-Rig Applicators to the Herbicide Bromoxynil Applied as a 1:1 Mixture of Butyrate and Octanoate. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology. 2002; 42(3): 369-382.
6. Deziel, N., Friesen, M., Hoppin, J. Hines, C. Thomas, K. and Freeman, L. (2015). A Review of Nonoccupational Pathways for Pesticide Exposure in Women Living in Agricultural Areas. Environ Health Perspect. 123(6): 515–524.
7. EPA (1974): Manual of analytical quality control for pesticides in human and environmental media. Research Triangle Park, N.C. 27711, USA
8. EPA (1979): Manual of analytical quality control for pesticides in human and environmental media. Research Triangle Park, N.C. 27711, USA
9. Gillette, J.R. The importance of tissue distribution in pharmacokinetics. In: Pharmacology and pharmacokinetics, ed. Toerell, T; Dedrick, R.L.; Canliffe, P.G. 1974;(pp. 209-231) Plenum Press, New York.
10. Inter-Organization Programme for the Sound Management of Chemicals (IOMC) (2004): International Programme on Chemical Safety: The WHO recommended classification of pesticides by hazard and guidelines to classification 2000–2002.
11. Lovecka, P., Thimova, M. Grznarova, P., Lipov, J., Knejzlik, Z., Stiborova, H., Nindhia, T., Demnerova, K., Ruml, T. (2015). Study of Cytotoxic Effects of Benzonitrile Pesticides. Biomed Res Int. 2015: 381264.
12. Salama, A.K. Pharmacokinetic and metabolism of methamidophos in female mice following a single oral administration. Alex. J. Agric. Res. 1992; 37(1): 431-445.
13. Salama, A.K., Bakry, N.M., Aly, H.A. and Abou-Donia, M.B.Placental and milk transfer, disposition, and elimination of a single oral dose of [14C-acetyl] acephate in Sprague-Dawley rats. J. Occupational Medicine and Toxicology. 1992a; 1(3): 265- 274.
14. Salama, A.K., Bakry, N.M., Aly, H.A. and Abou-Donia, M.B. (1992b).Placental and milk transfer, disposition, and metabolism of a single oral dose of [14CH3 S] methamidophos in SpragueDawley rats. J. Occupational Medicine and Toxicology. 1992c; 1(3): 275-291.
15. Salama, A.K., Radwan, M.A. and Bakry, N.M.Pharmacokinetics and excretion of ametryn in rat following a single oral administration. J. Pest Cont. Environ. Sci. 1993; 5(1): 61-76
16. Salama, A.K., Radwan, M.A. and El-Shahawi, F. Pharmacokinetic profile and anticholinesterase properties of phenamiphos in male rats. J. Environ. Sci. and Health B. 1992; 27(3): 307-323
17. Stahler, M., Gericke, S. and Beitz, H. Results of the toxicokinetics of bromoxynil in rats. Zeitschriftfur die Gesamte Hygiene und Ihre Grenzgebiete. 1991;37(2): 56-58.
18. Tomlin, C. D. S., ed. (1997): The pesticide manual: A world compendium, 11th ed. Farnham, Surrey, United Kingdom: British Crop Protection Council.
19. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (1997): Bromoxynil; Pesticide tolerances. Fed. Reg. 62(85):24065–24073. Available from http://www.epa.gov/fedrgstr/EPA-PEST/1997/May/Day02/p11504.htm.
20. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (1998). Registration Eligibility Decision (RED) Bromoxynil. Washington, DC, USA: United States Environmental Protection Agency.
21. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (2005): Bromoxynil. EPA738-R-98-013 December 1998. Available from, as of Feb. 1, 2005:http://www.epa.gov/pesticides/reregistration/status.htm
22. Xie, Y., Zhong, G., He, H., Fan, G. and Wu, Y. Pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution and excretion of porcine fibrinogen after intraperitoneal injection of a porcine-derived fibrin glue to rats. J Pharm Biomed Anal.2011; 54: 148-53.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License