IJCRR - 8(4), February, 2016
Pages: 01-05
Date of Publication: 21-Feb-2016
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A STUDY OF THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN STRESS, ADAPTABILITY AND TEMPOROMANDIBULAR DISORDERSY
Author: Vidhya Kalanjiam, G.V. Murali Gopika Manoharan
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Aim: The aim of the study is to explore the influence of stress in patients with temporomandibular disorders
Objectives: Stress affects the physiological, cognitive, emotional, behavioural functioning of human being. Initially our body compensates for stress, but when we cannot cope up with it, disorder arises. One such manifestation of stress in human body is temporomandibular disorders. The objective of the study is to first establish the diagnosis of the patients' complaints pertaining to temporomandibular joint based on clinical and radiological examinations; then to assess the degree of stress using stress assessment questionnaire and finally to study the relationship between stress and adaptability in temporomandibular disorders. Materials and Methods: 60 patients who reported with pain, tenderness in the temporomandibular joint, clicking or crepitus, tenderness in muscles of mastication, restricted mouth opening, deviation of jaw, restricted jaw movements, and with altered condylar movements were selected for the study. Clinical examination of signs and symptoms were assessed along with a stress assessment questionnaire. Finally, statistical analysis was performed on the responses received from the patients. Results: Significant difference was found in the pain threshold i.e. pain perception between patients with stress and without stress. This leads to the conclusion that stress has a major role in affecting the adaptability of the body, and it is a front runner for various deleterious effects. Conclusion: Stress levels of patients with temporomandibular disorders should be always evaluated and in case the stress levels are high, it must be treated with appropriate stress management therapy.
Keywords: Stress, Pain threshold, Questionnaire, Temporomandibular disorder
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION American Association of Orofacial pain (AAOP) defines Temporomandibular Disorder as a collective term embracing a number of clinical problems that involve the masticatory musculature, the temporomandibular joint and the associated structures or both. [1] The etiology of temporomandibular disorder is complex and multifactorial. Some of the etiological factors which are commonly associated with temporomandibular disorder are occlusal condition, trauma, emotional stress, parafunctional activities and deep pain input. [2] Even though there are enough evidences to support the contribution to temporomandibular disorder symptoms by these etiological factors, few common questions that remain unanswered are - are there varying degrees to which each of these factors affect.
Temporomandibular joint function? Does the interplay between these factors cause different effects than the individual factors? In healthy condition, our masticatory system functions smoothly but at times, an event may interfere with the normal function of the masticatory system. When the effects of the influencing factor are lower than the patient’s adaptability, no clinical effects are noticed. However, if the factors become more significant, it may exceed the patient’s adaptability and symptoms arise. [2] We observed a pattern in the case histories of patients reporting in with temporomandibular disorder - a very large population reported their lives were very stressful.
This formed the motivation for this study In this modern age, with our ever increasingly complicated lives we continue to discover that our body and mind are interlinked in complex ways. Stress takes a toll on our bodies both physically and mentally. Hans Selye described stress as the nonspecific response of the body to any demand made upon it. [3] [4] When stress acts upon the human body, it is first alerted for the changes. This is followed by activation of the autonomic activity to prepare the body to deal with the stress (host resistance). Finally, if the stress continues beyond the capacity of the body to respond, the system is damaged and may collapse. [2] Numerous studies have been conducted through the years to explore the relation between stress and temporomandibular disorders.
Many studies have proven that patients with stressful jobs are more prone to temporomandibular disorders. For example, Uhac et al conducted a study with the war veterans diagnosed with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in Croatia that concluded that war stress was directly related with temporomandibular disorders.[5] We took this endeavour to try to further explore the relationship between temporomandibular disorder and stress, to learn more deeply about the various stresses present in patients’ lives and its relationship to age, sex, predominant side affected, measure the level of pain in the stressed patient and in non-stressed patients and the interplay between stress and other confounding factors for temporomandibular disorder.
Study Design: 60 patients who reported to the Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology with symptoms of temporomandibular disorders like pain, tenderness in the temporomandibular joint, clicking or crepitus, tenderness in muscles of mastication, restricted mouth opening, deviation of jaw, restricted jaw movements were selected for the study. To remove any gender bias from the results of the study, the group was composed of 30 males and 30 female patients. The diagnosis of temporomandibular disorder was confirmed radiographically.
MATERIALS AND METHOD Detailed information about the age, sex, occupation, affected sides, family and social history, history of stress, sleep troubles, history of trauma and parafunctional habits were collected in case history document. Malocclusion, buccoverted, impacted, supraerupted teeth and missing teeth in the patients were also recorded. The clinical parameter the pain score was evaluated using Visual Analog Scale (0 to 10) given by Martin and Greenberg in 2003. To measure and compare the stress level in this group of patients we used a self-administrated questionnaire created by the Ministry of Social Security, National Solidarity and Reform Institu tions, Government of Mauritius. Questionnaires developed by this institution were used for their effective but simplistic approach of categorizing the overall stress level in patients into 4 categories and measurement of each individual question into simple 3 categories - low, medium and high.
These questionnaires have been used in many studies on stress previously.[6] [7] After giving the patients assurance of confidentiality, they were asked to complete the series of 20 question in the questionnaire. Each question is rated with a score between 0 and 3 with 0 meaning ‘no symptoms’, 1 meaning ‘rarely’, 2 meaning ‘sometimes’ and 3 being equal to ‘quite often’. Higher score indicates worse condition. Total score was calculated by adding the individual scores. The questions themselves are designed in such a way that scores of 0-20 are categorized as no stress, score values from 21-40 are good management of stress and score of 41-50 are patients in the danger zone of stress management and patients with score 51-60 points are the ones with unmanaged stress. For the patients whose stress scores were in high categories, additional data about the type of stress they were experiencing was recorded in their case histories. The questions in the questionnaire were as follows.
Questions
1. Do you neglect your diet? 2. Do you try to do everything yourself? 3. Do you seek help while doing your work? 4. Do you blow up easily? 5. Do you seek unrealistic goals? 6. Do you fail to see the humour in situations others find funny? 7. Do you get easily irritated? 8. Do you make a ‘big deal’ of everything? 9. Do you complain that you are disorganized? 10. Do you keep everything inside? 11. Do you neglect doing physical exercise? 12. Do you feel the absence of supportive relationships in difficult moments? 13. Do you feel you get too little rest? 14. Do you get angry when you are kept waiting? 15. Are you aware of your being under stress? 16. Do you put off things until later? 17. Do you feel that there is only one right way to do something? 18. Do you complain and dwell in the past? 19. Do you race through the day? 20. Do you feel that you have got too much to do at the same time?
Statistical Analysis: The patient group was originally divided into two groups – patients who had a stress score higher than good management of stress (group A) and patients who had scores lower than or equal to good management (group B). However, on analysing the data with patients who scored high, it was observed that some patients did not have any other etiological factors and displayed stress as the only factor for their disorder. This group was taken as a subset within group A thus giving rise to three groups – group A1 consisting of patients who had stress as the sole cause of temporomandibular disorder, group A2 consisting of patients who had stress along with at least one other factor for temporomandibular disorder and group B which had patients whose temporomandibular disorder was caused by any factor(s) other than stress.
Statistical analysis of the data was performed using SPSS for Windows version 17 software. The values were represented and mean ± standard deviation was calculated. For analysing the relation between multiple sets, ANOVA (analysis of variance) test was used. Statistical significance was considered to be 5% or p < 0.05 level. Since the group A was further split into subsets A1 and A2 resulting in uneven samples, we also tested using Kruskal-Wallis Test – a non-parametric method.
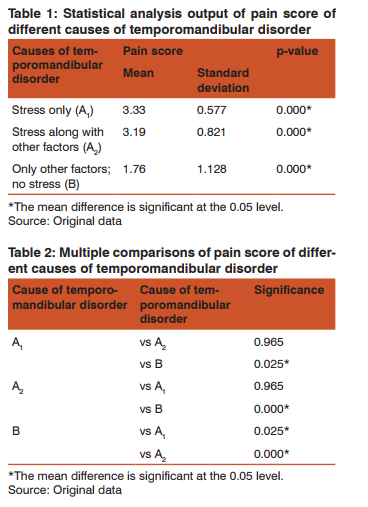
RESULTS The composition of the study population was that age group 20-30 years composed 38.3% of the total, patients among 31-40 years composed 25%, 41-50 years 25% and the remaining 11.7% were either older than 50 or younger than 20. Case history shows that 46.7% of the patients complained of pain on the left side of the temporomandibular joint, 43.3% complained of pain on both the sides and 10% of the patients complained of pain in the right side. From the radiographs of the patients, we observed 85 % had bony changes (flattening of anterior slope of the condylar head) and the rest 15% did not have any change in the condylar morphology. Study of the stress levels recorded using the questionnaire reveals that out of 60 patients, 11.7% had no stress, 31.7% experienced stress but it was under control (good management), 50% of the patients were in danger zone and 6.7% of them had a stress score in excess of 50 which is so high that immediate counselling is recommended. Of the 60 patients, it was observed that 5% had temporomandibular disorder caused due to stress alone, 2% due to parafunctional habits, and 17% due to partially edentulous conditions while trauma accounted for the disorder in 2%, malocclusion in 11% and buccoverted, impacted and supra erupted teeth in 10% of the patients.
All the other 53% percent had more than one factors causing the disorder one of which was stress. (Figure 1) Of the total population, 35 patients had a stress score indicating stress was a factor contributing to their temporomandibular disorder. As stated above, this group was further split into group A1 (stress as the sole cause) which accounts for 5% of the total and group A2 (stress along with at least one other cause) accounting for 53.3% of the total patients. Group B consisting of patients that had low stress scores consisted of 25 patients which amounts to 41.7% of the total.
Cross tabulating the pain score with the causes of temporomandibular disorders, shows that for Group A1 and Group A2 , the mean pain score were 3.33 (standard deviation 0.577) and 3.19 (standard deviation 0.821) respectively, which are significantly higher when compared with Group B, mean pain score of 1.79 (standard deviation 1.128) (Table 1 and 2). There was significant difference (p value less than .05) between A1 and B, A2 and B. This shows that the pain threshold significantly decreased in stressed patient but not in patients without stress.
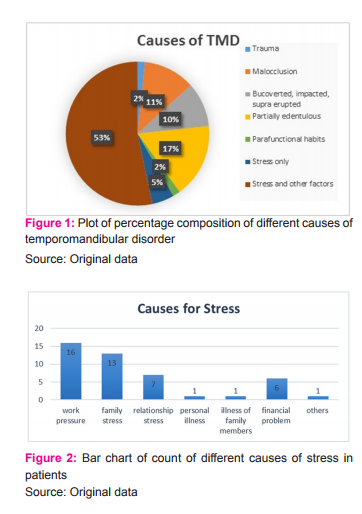
In other words, this means that for a patient who has malocclusion with stress, the pain tolerance will be significantly lower compared to a patient who has malocclusion alone as the etiology for temporomandibular disorder. Study of the patient data showed that most of the patients who had high stress scores were software engineers and house wives and the type of stress that seemed to be affecting them most were work pressure and family problems followed by stressors like relationship problems, financial problems and stress due to personal illness or the illness of a family member. Few of them even had more than one cause of stress in their lives. (Figure 2)
DISCUSSION Stress is not always bad. Sometimes, stress can be a motivational force to complete a task when it is within the limits. However, when it exceeds the tolerance level of the patient, it has an adverse impact on the physiological (non-functional parafunctional habits), cognitive (decreased attention span, increased distractibility and deterioration in both short-term and long-term memory, unpredictable response speed, increased error rate, and reduced powers of planning and organization), emotional (panic, hopelessness or even suicidal thoughts) and behavioural (risk health behaviours like smoking, alcoholism, altered diet) functions.[3] When an individual is experiencing high levels of emotional states, such as fear, anxiety, frustration or anger, it excites the hypothalamic-pituitary adrenal (HPA) axis. On upregulation it activates the gamma efferent system.
Increased gamma efferent activity causes contraction of the intrafusal fibers, resulting in partial stretching of the sensory regions of the muscle spindles which in turn increases muscle tonus. [2] Stress can also influence the sympathetic activity. Prolonged sympathetic activity increases the tonicity of the muscle leading to painful muscle condition. This accustomed sympathetic response to stress play a crucial role converting the acute condition to a different phase. [2] So continued experience of emotional stress to a significant level becomes a perpetuating factor that can progress the condition to a more chronic pain disorder. Emotional stress not only increases the muscle activity but also the non-functional activities like bruxism and tooth clenching.
People who experience stress due to hectic family life or busy work schedule unknowingly clench their jaws. These Para functional activities can fatigue facial muscles, lead to pain around the temporomandibular joint and jaw bones, damage the teeth, and finally displacement or dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint to have far reaching effects. [8] Genetic factors like gene variability, biological factors like diet, hormones, sleep, age, sex can influence the adaptability. [9] [10] When there comes a situation of imbalance between the etiological factor and the adaptability there will be manifestation of temporomandibular symptoms. In such cases of decreased adaptability, even less significant etiology can become more influential, which makes the patient less responsive to treatments taking the condition from the acute state to a chronic state.[11]
Because of chronicity, changes can be elicited in the Central nervous system which can perpetuate the condition and can lead to different treatment plan. [2] Various studies in the past have also supported this relationship between stress and temporomandibular disorders in different ways. Manfredino et al conducted a study to find out the major contributing etiology for temporomandibular disorders. They used stress measurement questionnaire and on comparison with other etiological conditions, concluded that stress was significantly higher in patients with temporomandibular disorder.[12]
Madani et al also proved that stress has an important role in the prevalence of temporomandibular disorder.[13] Uhac et al conducted a study that evaluated temporomandibular disorder symptoms in patients diagnosed with PTSD and patients without Post Traumatic Stress disorder (PTSD) and found that war veterans with PTSD displayed significantly high levels of symptoms. [4] Other similar studies targeted at individual groups that are known to be going through stressful conditions have also proven that the group did have higher symptoms of temporomandibular disorder than their control groups.
Some such examples are the study by Ahmad Mottaghi et al that did the study on female students before university exams [14] and Leonordo et al did a study based on age group and concluded that young individuals are affected the most and the main reason for temporomandibular symptoms was identified as anxiety.[15] Digging deep into the literature shows that there are not enough evidences to assess the influence of stress on the adaptability of patients with temporomandibular disorders. In this case, pain score is treated as a direct measurement of the patient’s adaptability. So we took this task to assess adaptability by calculating the pain score in patients with stress and without stress to ascertain the association between stress, adaptability and temporomandibular disorders. What we found is that in patients with stress as the only cause for their disorder and patients where stress was one among the many cases for their disorder, the mean pain score were 3.33 (standard deviation 0.577) and 3.19 (standard deviation 0.821) respectively, which are significantly higher when compared with patients whose disorder is not caused by stress but by other factors with mean pain score of 1.79 (standard deviation 1.128).
Significant difference exists in the pain threshold i.e. pain perception between patients with stress (either alone or in combination with other etiological factors) and without stress. This leads to the conclusion that stress has a major individual role in affecting the adaptability of the body and is a front runner for various deleterious effects. The bottom line is that an eye should be kept on stress levels of patients with temporomandibular joint problems, so that proper treatment for the disease can be provided at the early stage.
CONCLUSION The chief findings of this study are that there is a definite relationship between stressful life events and adaptability i.e. pain tolerance and with onset and progression of temporomandibular disorders. Cognitive therapy should be a part of management decorum of temporomandibular disorder. Further studies should be conducted with a larger sample size along with assessment of cortisol level in patients with temporomandibular disorder, with or without stress as a major factor as ascertained by the stress questionnaire. This would help to reinforce the result regarding the role of stress in temporomandibular disorders. This may be followed by studies on role of stress management therapies in temporomandibular disorders.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: We acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. J. Durham Temporomandibular disorder (TMD): An over view .Oral Surgery. May 2008:60-68. DOI: 10.1111/j.1752- 248X.2008.00020.x
2. Jeffery P. Okeson. Management of temporomandibular disorder and occlusion. 7th ed. Elsevier Mosby; 2013.
3. G. Butler Definitions of stress Occas Pap R Coll Gen Pract. 1993; (61): 1–5.
4. Schneiderman N, Ironson G, Siegel SD .Stress and Health: Psychological, Behavioural, and Biological Annu Rev Clin Psychol.2005;1: 607–628. doi:10.1146/annurev. clinpsy.1.102803.144141.
5. Uhac I, Kovac Z, Valentic M, Juretic M . The influence of war stress on the prevalence of signs and symptoms of temporomandibular disorders Journal of Oral Rehabilitation .February 2003: 211–217. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2842.2003.01030.x.
6. Sayal D, Dodwad V, Vaish S, Sood R. Effects of Academic Stress on Gingival and Periodontal Health - A Questionnaire Study Journal of Dental Specialities, September 2014:32-38.
7. Ganesh Pradhan, Nishitha Linet Mendinca, Manisha Kar. Evaluation of Examination Stress and Its Effect on Cognitive Function among First Year Medical Students Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research. 2014 Aug, Vol-8(8): BC05-BC07 DOI:10.7860/JCDR/2014/9014.4680.
8. Schiffman EL, Fricton JR, Haley D. The relationship of occlusion, parafunctional habits and recent life events to mandibular dysfunction in a non-patient population. J Oral Rehabil 1992; 19:201-223.
9. Markland S, Wänman A.Risk factors associated with incidence and persistence of signs and symptoms of temporomandibular disorders.Acta Odontol Scand. 2010 Sep;68(5):289-99. doi:
10.3109/00016357.2010.494621. 10. Holliday KL, Nicholl BI, Macfarlane GJ, Thomson W, and Davies KA, Macbeth Genetic variation in the hypothalamicpituitary-adrenal stress axis influences susceptibility to musculoskeletal pain: results from the EPIFUND study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010 Mar; 69(3):556-60. doi: 10.1136/ard.2009.116137.
11. McBeth J, Chiu YH, Silman AJ, Ray D, Morriss R, Dickens C, Gupta A, Macfarlane GJ. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal stress axis function and the relationship with chronic widespread pain and its antecedents. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005; 7(5):R992-R1000. Epub 2005 Jun 17.
12. Manfredino D, Bandethini AB, Cantini E. Mood and anxiety Psychopathology and temporomandibular disorder. J Oral Rehabil. 2009; 4 1 :933–7.
13. Madani A, Mehdizade F. Investigating the prevalence of TMD risk factors in 100 patients referred to dental faculty of Mashhad University. J Shahid Beheshti Univ. 2003; 2: 229–37.
14. Ahmad Mottaghi, S. Mohammad Razavi, Elham Zamani Pozveh, and Milad Jahangirmoghaddam Assessment of the relationship between stress and temporomandibular joint disorder in female students before university entrance exam (Konkour exam). Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2011 Dec; 8 (Suppl1): S76–S79.
15. Leonardo R Bonjardim, Ricardo J Lopes-Filho1, Guilherme Amado, Ricardo LC Albuquerque Jr, Suzane R J Gonçalves. Association between symptoms of temporomandibulardisorders and gender, morphological occlusion, and psychological factors in a group of university students Indian J Dent Res, 2009 AprJun;20 (2):190-4 20(2) . DOI: 10.4103/0970-9290.52901.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License