IJCRR - 12(20), October, 2020
Pages: 98-102
Date of Publication: 27-Oct-2020
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Depression in Teachers Due to Cyberbullying Who are Working in COVID-19 Pandemic: A CrossSectional Study
Author: Muzahid K Sheikh, Neha Chaudahry, Ajinkya Ghogare
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: During this Current pandemic situation, as we all know that the whole world is unfortunately forced to be indoor but, because of this pandemic various sectors have being affected, out of which the education sector has been affected greatly, as this corona pandemic has taken more than 6 months of the education, school, colleges and tuition teachers have started taking online classes thereby resuming the curriculum. The Educational platforms like google classroom, google meet, zoom etc. are being used more now than in the past as compared to the traditional teaching method in which teachers can interact one on one with the students. Method: Descriptive Study was conducted by providing E-Questionnaire and personal information sheet. 200 participants with the age group of 25 - 60 years both genders were selected according to the inclusion criteria. Results: Statistical analysis was done using a paired and unpaired t-test. The outcome was measured by using PHQ-9 Questionnaire and personal information form. Conclusion: The Above Conducted study Showed that there is a state of depression is present in the young teachers who are taking online lectures because of COVID-19 Pandemic situation.
Keywords: COVID-19, Depression in teachers, Work from Home, Online lectures.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
During this Current pandemic situation, as we all know that the whole world is unfortunately forced to be indoor but, because of this pandemic various sectors have being affected, out of which the education sector has been affected greatly, as this corona pandemic has taken more than 6 months of the education, school, colleges and tuition teachers have started taking online classes thereby resuming the curriculum. The Educational platforms like google classroom, google meet, zoom etc. are being used more now than in the past as compared to the traditional teaching method in which teachers can interact one on one with the students. Which is not permissible in online teaching as teachers have reported a lack of interaction in the class. Till now no such statistical data allied to cyberbullying on teachers has been cited since the onset of this pandemic.1
But, there have been multiple reviews by the teachers that, they are facing cyberbullying by the students. According to UNICEF cyberbullying is a type of harassment with the use of digital technologies which can take place via, any social media platform and education platform like google classroom, Google meet, Zoom ETC. It is a huge Disrespect to the teachers who are taking substantial efforts in teaching students even during this gloomy time of the pandemic.
Bullying by the students may have an adverse effect on the teachers which may include depression, anxiety, loss of self-esteem, lack of interest and associator health issues. the myriad of scenarios leading to the oblivious conditions are screen scratching, scribbling, students create anonymous IDs to make fun of the teachers, they pass comments while switching off the cameras, they create nuisance in the group chat as well by writing gratuitous comments or by sending memes, they also make needless sounds hereby distracting the class, as the lecture link can be shared with anyone so students add there anonymous friend and create mischief in the class.2,3
Since there isn’t a way to get holdoff the students violating the class decorum, therefore the teacher has to ignore, let go and continue teaching.
Work environment stressors are a leading health and safety issue for schoolteachers.1 Stress is an evitable part of an individual’s working life. Over the last decades, teaching has been widely conceded as a profession considering full of stress and anxiety.2 The number of teachers suffering from stress-related disorders- specifically depression and anxiety appear to be increasing. Such painful symptoms are brought about by the teacher’s recent working state and the pressure under which they find themselves.3 According to Kyriacou, the teaching profession is one of the high-stress occupation parallels to other stressful jobs such as police, the prison service, air traffic controllers, nurses and doctors. All type of stressors are denoted as barriers appraised by the teachers that interfere with the instructional process carried out to accomplish learning principles and that would explain a high level of burn out. Schwarzer and Greenglass, 1999, Blasé, 1982).4,5.6
Stressors are not limited to a particular school, city, or state and can influence teachers in public and private elementary, middle, and high schools (Grayson and Alvarez, 2008; Jarvis, 2002; Rieg, Paquette, and Chen, 2007).4 The 2003-2004 U.S. Department of Education’s School Survey on Crime and Safety reports that the schools have unsafe work environments with probably dangerous students. The prevalence of violence has not increased significantly during the past two decades, but violent and aggressive students are now considered as a problem in U.S. public school systems. Urban school teachers are more likely to be victims of violent crime at school than rural teachers. One or more violent crimes, such as sexual assault, aggravated assault, robbery, or rape, were described to have raised in 20% of U.S. public schools (DeVoe et al., 2004; Guerino et al., 2006).8,9
A challenging workload (Class size, paperwork, lack of planning time) was a habitual stressor mentioned in the veteran and novice teachers’ work environments (Liu and Ramsey, 2008; McCann and Johannessen, 2004; O’Donnell and Lambert, 2008; Pearson and Moomaw, 2005; Plash and Piotrowski, 2006; Rieg et al., 2007). Schonfeld (1990, 1996) postulated that social support may also have a direct effect on health outcomes among teachers.10
Anxiety is one of the aspects of stress that affects the teacher’s quality of teaching, which ultimately affects the learning process and fulfilment of the course objectives. It is a personalized state of internal discomfort.3 Anxiety is a normal emotion with adaptive value in which it acts as a warning system alerting a person to nearing the danger. It usually occurs without any conscious or apparent stimulus, which differentiates it from fears. It can be focused on a particular object, event or activity or it can be unfocused and demonstrated or indicated as a more general dread.3
There are five major types which are as follows: Panic disorder, Obsessive-Compulsive disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder, Generalized anxiety disorder and Phobic disorder. (Anxiety Disorders of America, 2005).3
Depression is one of the most likely unfavourable psychological consequence. The variety of other feasible psychological problems include, “burn out”, alcohol abuse, uncleaned physical symptoms including “absenteeism”, chronic fatigue and accidents, sick building syndrome and repetitive strain injury. (Hotopt, Wessely, 1997).11 Rejection and sadness are the most likely and silent emotional symptoms of depression. The individual feels hopeless and unhappy. Activities that used to bring self- satisfaction becomes dull and joyless. The depressed individual slowly starts losing interest in hobbies, recreation and family activities. It is correlated with psychological, behavioural and physical symptoms too. (Cassano and Fara, 2002).12,13 The depressed individual has negative thoughts, low self- esteem and low motivation for progress. A few studies specified anxiety occurred due to fear of immediate or future threat (e.g., robbery), and depression occurred due to a loss event (e.g., the death of a significant other) (Eysenck, Payne, and Santos, 2006; Sandin, Chorot, Santed, and Valiente, 2004). Jurado, Gurpegui, Moreno, and de Dios Luna (1998) announced depression increased with years of teaching experience and teacher age.14
In a study, Daniel Veronica (2011), stated that gender produces evident differences in the level of experienced anxiety. In comparison with their male counterparts, female suffered more from higher levels of anxiety and depression. It was found that female teachers suffer more from stress as compared to male teachers.15 The level of anxiety or stress is not the only difference between the two different genders. The type of stressors can also be marked between them. For example, Green glass and Burke (2003) suggested that the raised job stress of females might stock from gender differences in non-working domains, with the higher total workload and higher role conflict between work and family.16 The present study investigates the anxiety, depression and stress among the secondary school teachers working in residential and non-residential schools.
Method
Research Design
The research is conducted in cross-sectional study design with compliance of the survey model.
Samples of study
The study is composed of teachers who are working from home and taking lectures via the internet the teachers are from higher school, tuition teachers and higher studies lecturers. The sample size of this study is 200 teachers from various institutes.
Data Collection and Questionnaire.
Personal Information form and PHQ-9 (Patient Health Questionnaire) is made by the researcher with the help of google form and send it to the teachers via the link, who are willing to share the personal information with the doctor. In the PHQ-9 questionnaire, there is 9 question which grades individuals depression and anxiety. We have typed those questions in the google form and made an E-questionnaire because in this pandemic it is not possible to meet the teachers personally and fill the form.
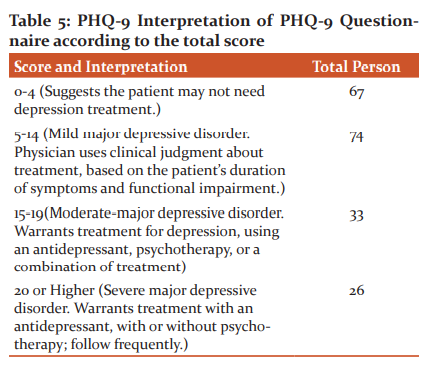
In PHQ-9 Questionnaire the scores and interpretation are 0-4 (Suggests the patient may not need depression treatment.), 5-14 (Mild major depressive disorder. Physician uses clinical judgment about treatment, based on patient’s duration of symptoms and functional impairment.), 15-19(Moderate-major depressive disorder. Warrants treatment for depression, using an antidepressant, psychotherapy, or a combination of treatment), 20 or Higher (Severe major depressive disorder. Warrants treatment with an antidepressant, with or without psychotherapy; follow frequently.) The diagnostic validity of scale having a sensitivity of 88% and a specificity of 88% for Major Depressive Disorder.16
The PHQ-9 Questionnaire is the instrument commonly used for measuring the depression. In this questionnaire, there are a total of 9 questions which composed of 4 gradings respectively by which the symptoms of depression is noticed. It takes about 10-15 to read and fill the form. This scale is the same PRIME-MD screening questions to detect depressive symptoms.
Procedure
The PHQ-9 Questionnaire and the personal information form are the data collection instrument, were implemented by the researcher in the teachers who are willing to share the information, the teachers are informed how to answer the questionnaire during the questionnaire session it will take approx., 10-15 minutes to complete the form for each teacher after completing the e-questionnaire the participant will send the form to the researcher, the special attention is given so that form will be restricted to only one entry per participant, by enabling the option in google form setting. The number of teachers that completed the questionnaire was observed to 200.instst software programme was used for statistical analysis t-test, Mann-Whitney test, and Statistician were used.
Findings
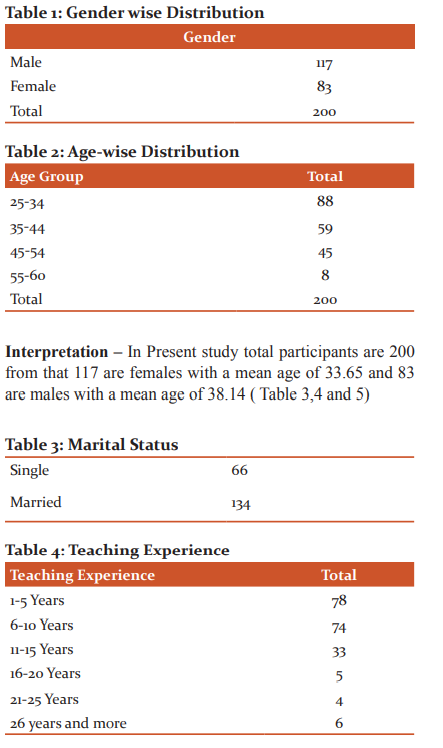
The Data Obtained from the research was given below ( Table 1, 2).
5. Discussion.
In this study, we have focused on the depression level on the teachers taking online Classes. The Outcome measure which we have taken is Personal Information form and PHQ-9 (Patient Health Questionnaire) taken 200 Samples in which there are 83 males and 117 females have been included who all are in the teaching profession and currently working and taking lectures via online method. according to statistical analysis,
We have 88 subjects of age group 25-34 which is 44% of total sample size, 59 subjects of age group 35-44 which is 29.5% of total sample .0size, 45 subjects of age group 45-54 which is 22.5% of total sample size, 8 subjects of age group 55-60 which is 4% of total sample size.
In the present study as there are both males and females has included their marital status has also been taken into consideration we have 134 subjects who are married Which 66% of the total sample and remaining 66 subjects are single which is 33% of the total sample. The marital status has considered because as subjects are working from home many problems encountered the profession that will lead to irritation and if this persists for longer duration it will affect the normal life and will lead to depression.
Concerning teaching experience 78 subjects are in teaching field from 1-5 years, 74 subjects who are in teaching field from 6-10 years, 33 subjects who are in teaching field from 11-15 years, 5 subjects who are in teaching field from 16-20 years, 4 subjects who are in teaching field from 21-25 years, 6 subjects who are in teaching field from 26 years and more. As a larger number of subjects are from 1-10 years of experiences i.e total 76% of total subjects. According to this personal information form record, it is calculated that most of the teachers out there in the teaching field are the young population with many responsibilities so while handling this online classes along with responsibilities it can lead to irritation and further depression.
Lastly, According to PHQ-9 Questionnaire Interpretation, 67 Subjects fall under 0-4 (Suggests the patient may not need depression treatment.) i.e. 33.5 % of total subjects,
74 subjects who fall under 5-14 (Mild major depressive disorder. Physician uses clinical judgment about treatment, based on patient’s duration of symptoms and functional impairment.) i.e. 37% of the total population
33 subjects who fall under15-19(Moderate-major depressive disorder. Warrants treatment for depression, using an antidepressant, psychotherapy, or a combination of treatment) i.e. 16.5% of total subjects.
26 subjects who fall under 20 or Higher (Severe major depressive disorder. Warrants treatment with an antidepressant, with or without psychotherapy; follow frequently.) i.e. 13% of the total population.
Because in this situation teachers are facing many problems such as students doesn’t respond to the command, students are making fun of teachers as their identity has not reveled or they can easily change their name while joining the class, making inappropriate Soundsas this kind of students disturb the whole class
Conclusion.
In this study, we have found out that during this present Covid pandemic the teachers who are taking online lecture are suffering from depression or some are on the verge of depression. Because the teachers who are of young age group and are married they are having high chances of getting depressed because of family responsibilities and job responsibilities as well.
Recommendation
Further Study should be conducted with larger sample size.
References:
-
Barnes L et al. Reliability generalization of scores on the Spielberger state-trait inventory. Educational and Psychological Measurements, 2002; 62(4): 603-618.
-
American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th edition text revision, DSM-IV-TR. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association, 2000.
-
Anxiety Disorders of America (2005). Anxiety disorders. Retrieved October 15, 2005 from http://www.adaa.org.
-
Borg M, et al. Stress in teaching: A study of occupational stress and its determinants, job satisfaction and career commitment among primary school teachers. Educational Psychology, 1991; 11: 59-75.
-
Fontana D. Stress levels, gender and personality factors in teachers. Br J Educ Psychol. 1993; 63: 261–270.
-
Beehr T, et al. Work stressors and coworker support as predictors of individual strain and job performance. Journal of Organizational Behaviour, 2000; 21, 391-405.
-
Beehr T. Social support and occupational stress: Talking to supervisors. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 1990; 36: 61-81.
-
Betoret F. Stressors, self-efficacy, coping resources, and burnout among secondary school teachers in Spain [Electronic version]. Educational Psychology, 2006; 26(4), 519-539.
-
Brewer, E et al. Job stress and burnout among industrial and technical teacher educators. Journal of Vocational Education Research, 2003; 28: 125-140.
-
Cassano P, et al. Depression and public health. An overview. Journal of Psychosom Research, 2002; 53: 849.
-
Cooper CL, ed (1996) Handbook of stress, medicine and health. (CRC Press, USA).
-
Hotopf M, Wessely S. Stress in the workplace: unfinished business. J Psychosom Res; 1997; 43(1): 1–6.
-
Gurian BS, and Miner JH, Clinical presentation of anxiety in the elderly. In C. Salzman and B.D. Lebowitz (Eds), Anxiety in the elderly; Treatment and research. 1991: 31-44. New York: Springer.
-
Daniela Veronica, Stress and Job Satisfaction among University Teachers; International Conference of Scientific Paper AFASES, Brasov,1996: 26-28.
-
Green glass ER, and Burke RJ. Teacher stress. In M. F. Dollard, A. H. Wine field, and H. R. Wine field (Eds.), Occupational stress in the service professions 2003;213–236. New York:
-
Kroenke K, et al. The PHQ-9: validity of a brief depression severity measure. Journal of General Internal Medicine, 2001; 16(9): 606-613.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License