IJCRR - 12(20), October, 2020
Pages: 75-80
Date of Publication: 27-Oct-2020
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Health Communication in Digital Era: A Study of Sub-Urban City of Jaipur
Author: Maninder Kumar Singh, Subhash Kumar
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Health communication generally deals with the process of communicating promotional health information on personal health and hygiene and educational campaigns on public health and sanitation. In this study on health, communication pursues target audience knowledge on health issues, demonstrate healthy practices, support health services and dispel the misconceptions about health. Materials and Methods: Keeping the study objectives in view an interview schedule was developed for data collection. The questionnaire was administered through a Google form. A random sample from the target audience group was selected for the study. Results: The total one hundred and thirty-three respondents from four villages were responded to the survey. In which majority of the respondents 52% are less than 40 years of age and 53% of the respondents are male, 47% of the respondents are female. A great majority (98 %) of the respondents are aware of health and hygiene. More than 90% of the respondent had a fairly good idea about various aspects of personal hygiene. Respondents reported that updated information on social media 68% and mobile apps 55% play a vital role. On self-protection from disease, more than 90% of respondents' state that they drink potable water, and keep the surroundings clean. In an analysis about media is creating awareness on personal health and hygiene, social media 87 % among them through awareness campaigns,television and radio 75% and mobile apps 52%. Government basic training on health and hygiene, 77 % of the respondents said such training was never given. Conclusion: The study reveals that the respondents have a fairly good knowledge of personal health and hygiene. The respondents have a very positive perception of health and hygiene and its importance to individual wellbeing.
Keywords: Communication, Development, Health, Media, Strategy, Information, Digital
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Development programme in any developing society like India has two major components. One is the development input, be it agriculture, health and hygiene or social development. The other is the media, be it mass media, traditional media, interpersonal channels and digital media that is employed to carry the development input. The use of media resources for ‘Development Support Communication’ is to ensure the development inputs reach the beneficiaries. Communication for development has three basic factors, Advocacy, Social Mobilization and Behavioural change. Health communication generally deals with the process of communicating promotional health information on personal health and hygiene and educational campaigns on public health and sanitation. Health communication pursues to increase target audience knowledge on health issues, demonstrate healthy practices, support health services and dispel the misconceptions about health and so on. To ensure that messages on health communication to reach target audiences accurately and quickly, health communication professionals must develop a health information package designed for the particular sections of the population in the society.Development Communication is the knowledge of social transformation carried out by the exploration, model, and skills in the communication to carry growth.
Development communication normally refers to communication policies and principles in the underdeveloped and developing countries. Development communication is resulting from social transformation to social growth and development theories that recognized the central issues of the post-world war era in terms of a lack of progress corresponding to first and second world countries.3
“The UN General Assembly in Article 25 wherein it was clearly stated that Health is both a public and merit good. Health cannot be forced by affordability, and cannot, therefore, be left to the market. It is an understanding in which primary health and hygiene care, like primary education, qualifies as a merit good for the provision of which the state has to bear special responsibility”.2
Brief Introduction of Four Villages of Sub-Urban city of Jaipur
Begas
Begas is a panchayat located in Sanganer tehsil of district Jaipur in Rajasthan, India. The entire terrestrial area of the village is 1752 hectares. Begas has an overall inhabitant of 5,149 peoples with male 2,617 and female 2,532. Agriculture and private service are the main occupations of Bega's villagers. The Total Literacy rate of the village is about 60% amongst the population of 5149 in which around 50% male and 18% female are literate.4
Dahmi Kalan
Dahmi Kalan is its-self gram panchayat situated under Sanganer Tehsil of Jaipur district in Rajasthan, India. The overall terrestrial land of the village is 914.16 hectares. Dahmi Kalan has approximate inhabitants of 5,850 peoples withthe males are 2950 and females are 2900 and in which around 919 houses in the village.Agriculture, business, daily wage labourer is the main occupation of the villager in the Dahmi Kalan. The Total Literacy rate of the village is about 52.6% amongst the population of 5,850 in which around 48.2% male and 17.4% female are literate.4
RamsinghPura
RamsinghPura is a village under the Fatehpura gram panchayat in Jaipur tehsil of Jaipur district in Rajasthan, India. The overall terrestrial area of the RamsinghPura village is 609 hectares with the population of 1,517 peoples in which 785 are male and 732 are female and approximately 217 houses. RamsinghPura’s people the main occupation are agriculture, business, government-private services. The Total Literacy rate of the village are about 50% amongst the population of 1517 in which around 50% male and 28% female are literate.4
Theekariya
Thikariya is itself a gram panchayat placed under the Sanganer Tehsil of Jaipur district in Rajasthan, India. The total terrestrial area of Thikariya village is 344.4 hectares. The village has an approximate population of 2,238 peoples in which 1137 are male and 1101 are female. With around 345 houses in Thikariya. Thikariya villager’s main occupation are business, government and private services, agriculture, daily wage labourers etc. The Total Literacy rate of the village is about 53.5% amongst the population of 2238 in which around 60.8% male and 19.7% female are literate.4
This study aims to know about knowledge, attitude, and practice regarding health and hygiene and role of media providing healthinformation among the people of four selected villages in the sub-urban area of Jaipur city in Rajasthan.
The objective of this study:
-
To ascertain the knowledge, attitude and practices on health and hygiene in rural areas
-
To examine the use of conventional mass media by the target audience for information on health
-
To assess the role and use of digital media on delivering health information
-
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The study is being conducted under Ex-Post-Facto conditions in four selected villages in the sub-urban area of Jaipur city in Rajasthan. Keeping the study objectives in view an interview schedule was developed for data collection. The questionnaire was administered through a Google form. Where ever respondents were not able to use the Google Form, the form was filled on their behalf through personal interviews. A random sample from the target audience group was selected for the study. A total number of 133 respondents from four villages were responded to the survey. All these responses were calculated with the help of SPSS software.
ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION
The data collected through the survey in Google form. Tables present the demography of the respondents. Majority of the respondents (52%) are less than 40 years of age. (24%) of the respondents are of 40 to 50 years of age. (12 %) of the respondents are of the age group from 51 to 62 years. Rest 12% respondent are more than 65 years of age. On the other hand, a majority (53%) of the respondents are male, (47%) of the respondents are female.

The (Table 1)above shows that a great majority (98 %) of the respondents are aware of health and hygiene. This a remarkable fete in rural areas, wherein the awareness about health and hygiene always remained low. This may be because there is a greater amount of information available today and better exposure as well.
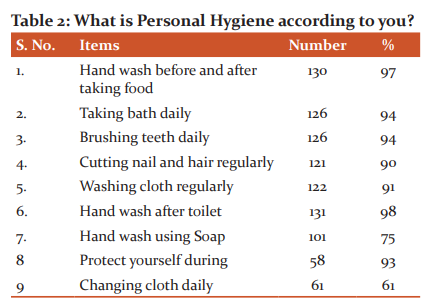
To a question enquiry about the knowledge of personal hygiene, (Table 2) the data has revealed that more than 90% of the respondent had a fairly good idea about various aspects of personal hygiene. As the awareness was very high, further proving to show that personal hygiene factor-like washing hand before the food had an awareness of more than 97%. Other hygiene had its like bath daily, brushing teeth, hand washing after toilet, washing cloth had a high score of more than 90% among respondent. Even washing cloth regularly (90%) was attributed to hygiene practice. However, changing clothes daily as a hygiene practice was poor with 45%. Washing hands with soap scores a fairly good awareness of 75% among the respondent. Among the 62 women respondent, 93% of them consider protection during menstrual period as good hygiene habit.

A question was asked regarding the understanding of personal health, the data has revealed that rise in body temperature (fever) and viral fever is known to more than 90% respondents. Knowledge about Blood pressure among the respondent is also high (75%) in comparison to Sugar level (54%) and Diabetic (38%). One of the reasons for better awareness about viral fever and a health condition called diabetes is due to better availability of information through mass media. However, blood pressure and increased sugar level information which are slightly more technical have not been perceived by the rural community(Table 3).
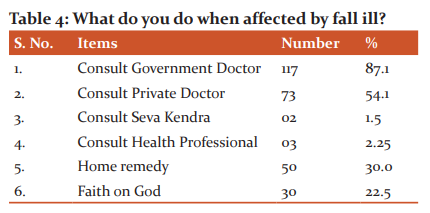
In response to a question regarding falling ill more than 85% among the respondent beliefs in visiting Government Doctors in comparison to Private Doctors only 54%. The data has also revealed that more than 50% of the respondents believe in home remedy and 22% believe in God. However, visiting Seva Kendra in their village scores poorly 2.5% among respondent. The data shows that there is a need to strengthen the health facilities under the Government (Table 4).
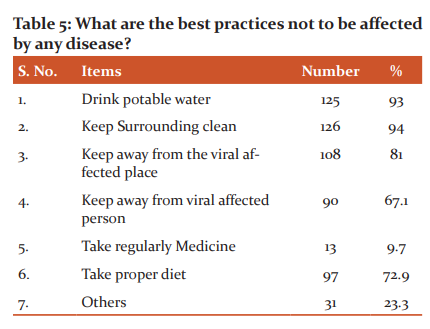
To a question on self-protection from any disease, more than 90% of respondents’ state that they drink potable water, and keep the surroundings clean. During the viral affection, more than 80% respondent had a fair idea of not to visit the affected place and person both. More than 70% of the respondent belief in taking proper diet during viral infection. Taking medicine as a precaution during by viral disease was poorly rated only 9%. This indicates that there is a greater awareness among the rural community about issues related to health and precautions need to be taken (Table 5).
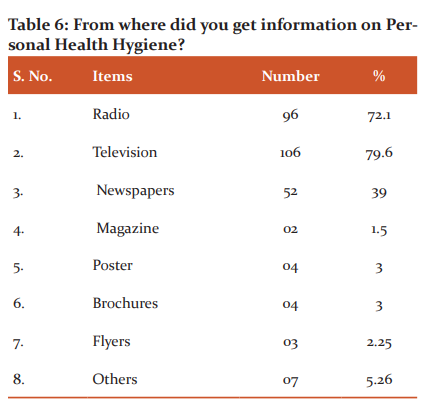
To a question on from where did you get information on Personal Health and Hygiene, radio and television score high more than 70% in comparison to newspaper, magazine, poster, and brochures are 30%, 1.5%, 3%, 3% respectively ( Table 6). The indication is that the audio-visual medium is more sought after for information on health and hygiene. The print media is not the sought source of information since it is a literate medium and also the coverage of information on health and hygiene is also pretty low. Surprisingly, even posters which are abundant in-display do not look atthe popular source of information.
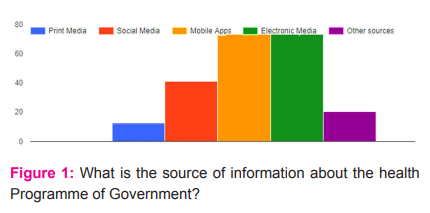
To a question about the sources of information on health programme of government, Social media including mobile apps score more than 70%. Electronic media information on health programme of the government was fairly good scores about 54% among the respondents. Print media only 12% among the respondent was the fairly poor medium of information regarding health awareness programme of government is a concern ( Fig. 1).
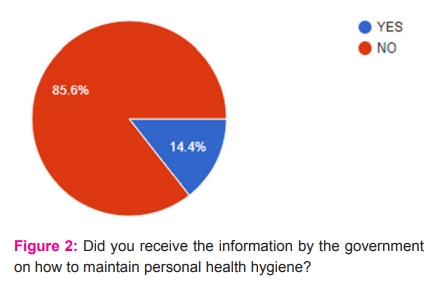
To a question analysis on receiving information by the government about maintaining personal health and hygiene. The respondent response to this particular question mostly in the negative way of more than 85% ( Fig. 2).
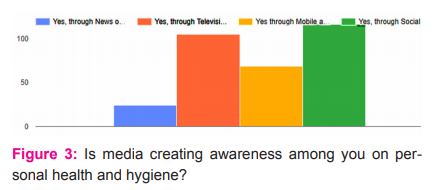
In an analysis about media is creating awareness on personal health and hygiene, it was found that social media is creating more awareness (87 %) among them through awareness campaigns. Through mobile apps, 52% of respondent had positively aware of health and hygiene. Information about health and hygiene awareness programme by Television and Radio scores more than 75%. Creating an awareness programme among respondents by newspaper and magazine was poorly about less than 19% ( fig 3).
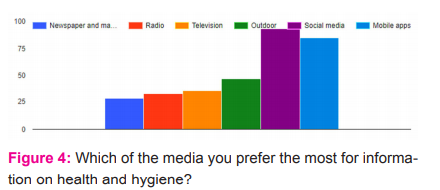
Keeping the consistency in the response, 69 % of the respondents said they depend on social media and 63 % of on mobile applications (Fig. 4). Traditional mass media like print, electronic and outdoor media has the very little role as the most preferred source of information.
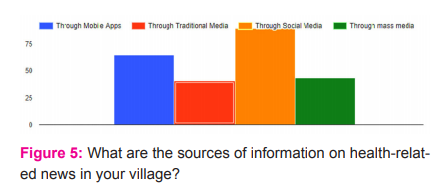
For any development message to be diffused in a community, the dispersion of the message through appropriate media is essential. The data has revealed that a host of social media platforms play a very important role in the diffusion of information. According to the study, social media platforms (66 %) have a major role, followed by mobile apps (48 %) ( Fig. No. 5). Traditional media and mass media also play an important role. The high dependency on social media platforms and mobiles apps even rural areas is because of the percolation of internet facilities. Besides, not so expensive and affordable mobile phone technology is also there.

To a question on the media supporting to maintain personal health and hygiene, the respondents reported that updated information on social media (68%) and mobile apps (55%) play a vital role. Besides, the latest information provided by radio and TV (63 %) also have an important in this regard (Fig. 6). The data also reveals that print media as a source has a limited role.
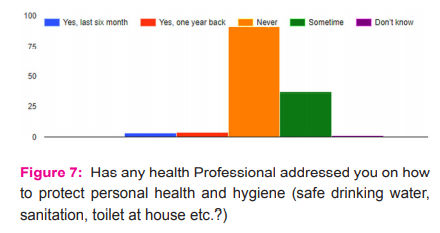
Considering the role and impotence of health worker in supporting health and hygiene in rural areas, a question was asked about the frequency of health worker visit or contact. A majority (68 %) of the respondents said it never happened and some 27 % said once in a way the health worker contacted for providing information on health and hygiene ( Fig. 7).
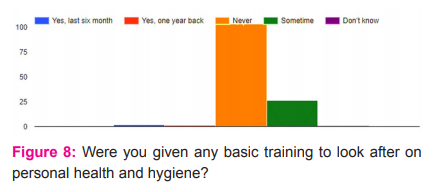
Also a question on providing some basic training on health and hygiene, 77 % of the respondents said such training was never given (Fig. 8). However, a bit surprisingly some 19 % said at some point in time some basic training on health and hygiene was given in the villages.
CONCLUSION
The study reveals that the respondents have a fairly good knowledge of personal health and hygiene. The respondents have a very positive perception of health and hygiene and its importance to individual wellbeing. In this study, ‘Development Support Communication’ revealed the technology has changed the present situation in the diffusion of information to mass regarding awareness on their health and hygiene. The study also supports the advancement of technology in the field of Communication in the form of mobile applications to avail of this benefit. Media is creating awareness on various aspects of health and hygiene but the medium is changed from traditional to digital. The study revealed the government official and intuition are hardly concerned about support and training of personal health and hygiene. Seva Kendra and government health professional is a failure in providing information among these four sub-urban villages of Jaipur on personal health and hygiene. Digital media extensively used to access the information, for their health and hygiene issues. The study also reveals the use of smartphones for easy access, with constantly updated on the news apps, to save their time and money.
Acknowledgement: Authors acknowledge the immense help received from villagers of Theekariya, Begas, Dahmi Kalan and RamsinghPura of Rajasthan for support to conduct the study.The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed in this manuscript.
Ethical clearance- not applicable.
Source of funding- self.
Conflict of Interest- not applicable.
References:
-
Everett Rogers M. Diffusion of Innovations,The Free Press, New York, 1983: 5-37, 64-68, 84-88.
-
Mefalopulos Paolo.DevelopmentCommunicationSourcebook:Broadening the Boundariesof Communication, The World Bank Washington, D.C., 2008: 3,5 6,7.
-
Genevey Remi, Pachauri Rajendra K. and Tubiana Laurence. Reducing Inequalities: A Sustainable Development Challenge, AFD IDDRI TERI, 2013, 124,157,189.
-
List of Districts in Rajasthan [Internet] Available from the site: https://villageinfo.in/rajasthan.html.
-
Minakshi, Joshi P.C., Kumar Rahul. “Mental Health Problems in Wake of Disaster: A Gendered Perspective.” Rupkatha Journal on Interdisciplinary Studies in Humanities.” Vol.12, No.1, 2020. pp. 1-12.
-
Gupta Rajeev Kumar, Raina Sunil Kumar, Shora N. Tajali, Sharma Renu, Hussain Shahid. “A household Survey to Assess Community knowledge, Attitude and practice on Malaria in a Rural Population of North India.”Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care, Vol. 1, No.3, 2016, pp. 101-107.
-
KadamSuhas, AdhavAmbadas, Mote Balu, KalaskarShrikant, M. Thirumugam, KurbudeRavindra, PatilSushil. “Knowledge, Attitude and Practices of People Towards Malaria in Tribal Communities of Jawhar, Maharashtra, India.” International Journal of Current Research and Review, Vol.7, Issue 18, 2015, pp. 25-30.
-
Nandha B., Srinivasan R., Jambulingam P. “Cutaneous Leishmaniasis: Knowledge, Attitude and Practices of the Inhabitants of the Kani Forest Tribal Settlements of Tiruvananthapuram District, Kerala, India.” Health Education Research, Vol. 29, No.6, 2014, pp.1049-1057.
-
Lie Rico. Rural HIV/AIDS Communication/Intervention: From Using Model to Using Frameworks and Common Principles, one chapter in edited book by Jan Servaes, Communication for Development and Social Change, Sage publications India, 2008: 280,283,284.
-
Schramm Wilbur. Mass Media and National Development, East-West Communication Institute Honolulu, Hawaii U.S.A 1979: 13,14, 16.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License