IJCRR - 12(18), September, 2020
Pages: 42-47
Date of Publication: 22-Sep-2020
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Evaluation of Anxiogenic Effect of Pseudoephedrine in Albino mice
Author: Srinivasa Rao Konijeti, Kadiri Sunil Kumar, Sri Leela Movva, Muralikrishna K. S.
Category: Healthcare
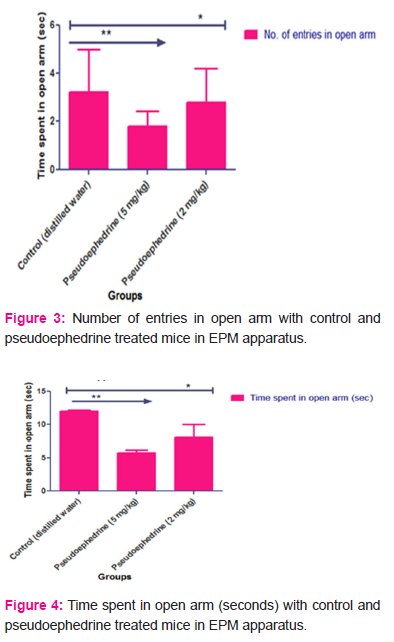
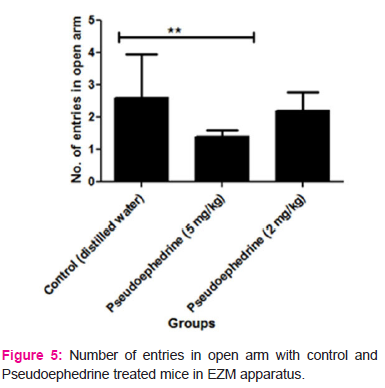
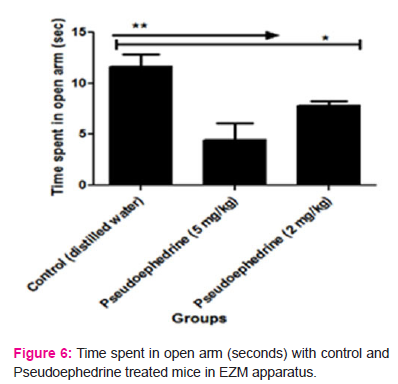
Abstract:Objectives: The study was designed with the rationale to investigate the anxiety-like behaviour with pseudoephedrine treatment in albino mice. Numerous reports of case studies suggest that pseudoephedrine treatment triggers anxiety symptoms in patients. Methods: Pseudoephedrine at doses 2 mg/kg and 5 mg/kg p.o was tested for its anxiogenic effect in albino mice by using elevated plus maze (EPM) and elevated zero mazes (EZM) models. Control and test group mice were treated with distilled water and pseudoephedrine for 15 days. The anxiogenic assessment was done on 15th day one hour after pretreatment with distilled water and pseudoephedrine. Results: In EPM study, there is a significant reduction in the number of entries (1.8 \? 0.63 with 5 mg/kg and 2.8 \? 1.39 with 2 mg/kg) and time spent in open arm (5.8 \? 0.47 seconds with 5mg/kg and 8.0 \? 1.98 seconds with 2mg/kg) with pseudoephedrine treatment at both doses when compared to control-treated mice (Number of entries=3.2 \?1.78 and time spent in open arm= 12 \? 0.14 seconds). In EZM there is a significant decrease in the number of entries in open arm (1.4 \? 0.21) and time spent in open arm (4.4 \? 1.72 seconds) with pseudoephedrine 5 mg/kg treatment when compared to control mice (Number of entries= 2.6 \? 1.35 and time spent in open arm= 11.6 \? 1.26 seconds). Conclusions: The reduction in the tendency of the mice to enter into the open arm after pseudoephedrine treatment indicates anxiety. This indicates that pseudoephedrine has an anxiety-inducing property.
Keywords: Pseudoephedrine, Anxiogenic, Elevated plus maze, Elevated zero maze, Open arm, Number of entries.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Anxiety disorders are a group of conditions set apart by outrageous or obsessive uneasiness or dread.1 Anxiety disorders can meddle with an individual's work, family and public activity. They will in general be constant and can be impairing. Despite their across the board commonness, anxiety issues have not gotten a similar acknowledgement as other significant conditions, for example, mood and psychotic disorders, also, the primary care doctor is typically the central assessor and treatment provider.2,3 In any case, anxiety turns into an issue when it interferes with typical capacities, is irrelevant to a genuine danger, causes physical side effects and gets excruciating to the individual.4 Pseudoephedrine is a sympathomimetic drug beneficial and widely used in nasal congestion problems during the common cold.5 The psychotropic impact of pseudoephedrine is notable since their broad use by belligerents on all sides of the Second World War, is one of stimulation with increased aggression and higher fatigue threshold.6 There are several reports which indicate that continuous treatment with pseudoephedrine can lead to cardiovascular, neurological, anxiogenic and mood-related issues.7,8,9 However there are no preclinical studies till date regarding the anxiogenic effect of pseudoephedrine treatment. Therefore the present study was planned to explore the anxiety-like behaviour induced by pseudoephedrine treatment in albino mice by using widely accepted anxiety models such as elevated plus maze and elevated zero mazes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
For the present study, a pure sample of pseudoephedrine was purchased from Chandra Laboratories, Hyderabad. Pseudoephedrine was suspended in 0.5% w/v acacia and the suspension of pseudoephedrine was utilized for acute toxicity and in vivo anxiety study.
Experimental animals
Albino mice (20-25g) were used for the anxiogenic evaluation. They were procured from Sainath agencies, Musheerabad, Hyderabad (282/99/CPCSEA). After randomization into various groups and before initiation of the experiment, the rats were acclimatized for 10 days. Animals were housed in polypropylene cages and maintained under standard environmental conditions such as temperature (26±2°C), relative humidity (45-55%) and 12 hr. dark/light cycle. The animals were fed with mice/rodent pellet diet (Golden Mohur Lipton India Ltd) and water ad libtum. The research was carried out in the experimentation room of animal husbandry of Marri Laxman Reddy Institute of Pharmacy, Dundigal, Hyderabad. The study protocol was approved from the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee (IAEC) before the commencement of the experiment (1567/PO/Re/S/11/ CPCSEA)
Determination of Acute Toxicity (OECD Guidelines 423)10
Pseudoephedrine was studied for single-dose oral acute toxicity study at a dose of 5 mg/kg, 50 mg/kg, 300 mg/kg and 2000 mg/kg p.o in albino mice (6 mice in each group) by following the guidelines of OECD 423. All the mice were observed for toxicity signs for 24 hrs followed by 14 days. On 8th day and 14th-day body weights of mice were recorded.
Evaluation of Anxiogenic activity of Pseudoephedrine in albino mice11
Control and test mice were treated with 0.5% acacia and pseudoephedrine suspension 1 hour before the evaluation of anxiogenic effect.
Elevated Plus Maze
The EPM mechanical assembly comprises two crossing arms that frame the state of a '+'. Two contradicting shut arms are built with high dividers and are frequently named alleys. The converging open arms are a similar width and length as the closed arms, yet need sides to make a raised, thin strolling surface. Mazes can be built of the scope of materials, including wood or shaded Plexiglas, or metal. The size of the maze changes by species, research facility and producer. A common rodent maze raised roughly 70cm over the floor, with each arm estimating 10cm wide by 45cm long with the dividers of the encased arms around 30cm high. For mice, the device is downsized with arms that are around 5 cm wide by 30cm long, the side nooks 15cm high, and the whole contraption raised roughly 30cm over the floor. The walking surface might be secured with elastic or fixed with ledged on the external edges of the open arms to improve footing. All the animals were also subjected to elevated plus-maze assessment of anxiety levels. Every rodent was set separately in the focal point of the maze looking towards the open arm and coming up next were recorded a) time spent in open arm. b) Number of entries in the open arm during 5 minutes session.12
Elevated Zero Maze
All the animals were investigated for anxiety levels by employing elevated zero mazes set up. This test is the pharmacological validated assay of anxiety in animal models that is based on the natural aversion of mice to EZM. It is composed of a 6 cm wide range ring with outer diameter of 45cm containing four equal quadrants of alternating walled or installed sections. The entire ring is elevated to a height of 20 cm from the floor. Control and Pseudoephedrine treated mice were placed in the walled region at the start of 5 minutes session and the number of entries and time spent in the open arm by individual mice were recorded during these 5 minutes.13
Statistical Methods
The values are demonstrated as mean ± S.E.M and measurable noteworthiness among treated and control group was analyzed utilizing One way ANOVA, trailed by Dunnett's test where ***P<0.001, **P<0.01 and *P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Acute toxicity study
Pseudoephedrine was found to be toxic orally at 50 mg/kg which is evident by the death of all the mice at 50 mg/kg. At 5 mg/kg the mice were found to be healthy and exhibited no clinical signs and symptoms of toxicity even after 14 days. Hence 5 mg/kg (higher dose) and 2 mg/kg (lower dose) were considered as therapeutically safer doses for the Pharmacological studies.
Elevated plus Maze apparatus (EPM)
The results obtained from EPM indicates the anxiety-inducing potential of Pseudoephedrine (Anxiogenic effect) when treated in albino mice with both higher and lower doses for 15 days. In Pseudoephedrine treated group it was found that Number of entries in open arm (higher dose= 1.8±0.63, Lower dose= 2.8±1.39) is significantly less when compared to control-treated mice (Number of entries in open arm= 3.2±1.78). The time spent in open arm in Pseudoephedrine treated mice (higher dose= 5.8 ± 0.47sec, Lower dose= 8.0±1.98 sec) is significantly less when compared to Control mice (time spent in open arm = 12±0.14 sec). This reduction in the number of entries in open arm and time spent in open arm in Pseudoephedrine treated mice when compared to control mice indicates induction of anxiety with Pseudoephedrine. The results are shown in tables 1, 2 and 3 and displayed in Figure 3 and 4.
Elevated zero Maze apparatus (EZM)
In EZM apparatus, it was found that Pseudoephedrine treated mice exhibited a significant reduction in the number of entries in open arm (higher dose= 1.4±0.21 and lower dose = 2.2±0.59) and time spent in open arm (higher dose= 4.4±1.72 seconds and lower dose = 7.8±0.43 seconds) when compared to the control group mice (number of entries in open arm = 2.6±1.35 and time spent in open arm = 11.6±1.25 seconds). This indicates that the Pseudoephedrine treated mice have a fear for the open areas and have more tendencies towards the closed arm. Hence Pseudoephedrine at both doses has produced anxiety in albino mice on treatment for 15 days. The results are depicted in Table 5, 6 7 and 8 and figure 5 and 6.

DISCUSSION
Cough and cold remedies comprise a major portion of the OTC market. An excessive dose of a nasal decongestant Sympathomimetic is reported to cause bipolar disorder in a 13-year-old girl.14 Several case reports are describing the anxiogenic symptoms with Pseudoephedrine such as restlessness, irritability and insomnia.15,16 The participation of 9 of 74 children in a clinical trial of Pseudoephedrine has to be terminated because of severe side effects such as dizziness, irritability, nightmares and general malaise.17 Few countries have banned Pseudoephedrine due to its undesirable effects on CNS. However, it is widely used in India as an effective nasal decongestant. There are no preclinical or clinical reports to substantiate the anxiogenic potentials of Pseudoephedrine. Therefore the current study was planned to evaluate the anxiogenic effect of Pseudoephedrine in mice by using EPM and EZM models. Pretreatment with Pseudoephedrine for 15 days has shown a significant decrease in the number of entries in open arm and time spent in the open arm when compared to control mice. This shows that Pseudoephedrine can induce anxiety in albino mice. There is no precise mechanism to correlate Pseudoephedrine with anxiety but it can be hypothesized that Pseudoephedrine as a mixed acting sympathomimetic can trigger anxiety symptoms by directly acting on adrenergic receptors or by increasing the availability of norepinephrine or epinephrine to stimulate adrenergic receptors. Pseudoephedrine may also enhance glutamate levels which result in anxiety-like symptoms.
CONCLUSIONS:
Neuropsychiatric adverse effects such as sedation, bipolar disorder, psychosis, disturbed sleep and memory impairment have been linked to medications used in the treatment of asthma and allergic rhinitis. One such OTC marketed drug which on long term use is reported to cause anxiety-like behaviour is Pseudoephedrine. Therefore by employing standard anxiety-based animal models such as EPM and EZM in the present study to evaluate the effect of Pseudoephedrine on anxiety in albino mice. Based on the results of the present study we conclude that Pseudoephedrine (5 mg/kg and 2 mg/kg) treatment for 15 days exhibited significant anxiety in albino mice in EPM and EZM models. There is a significant reduction in the number of entries in open arm and time spent in open arm with Pseudoephedrine treatment at both doses. However further biochemical and histopathological studies are required to establish the exact neurochemical mechanism behind the induction of anxiety with Pseudoephedrine.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors are grateful to the management of Marri Laxman Reddy Institute of Pharmacy, Hyderabad for providing the facilities for our research.
SOURCE OF FUNDING
No Funding
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
This is to inform you that the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest regarding this article.
References:
Frye CA, Walf AA, Rhodes ME, Harney JP. Progesterone enhances motor, anxiolytic, analgesic, and anti-depressive behaviour of wild-type mice, but not those deficient in type 1 5α-reductase. Brain research. 2004 Apr 9;1004(1-2):116-24.
2. Roy-Byrne PP, Craske MG, Stein MB, et al. A randomized effectiveness trial of cognitive-behavioural therapy and medication for primary care panic disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62(3):290–298.
3. Stein MB, Sherbourne MG, Craske MG, et al. Quality of care for primary care patients with anxiety disorders. Am J Psychiatry. 2004;161(12):2230–2237.
4. Qiu A, Tuan TA, Ong ML, Li Y, Chen H, Rifkin-Graboi A, Broekman BF, Kwek K, Saw SM, Chong YS, Gluckman PD. COMT haplotypes modulate associations of antenatal maternal anxiety and neonatal cortical morphology. American Journal of Psychiatry. 2015 Feb 1;172(2):163-72.
5. Lockey RF. Rhinitis medicamentosa and the stuffy nose. Journal of allergy and clinical immunology. 2006 Nov 1;118(5):1017-8.
6. Mortuaire G, De Gabory L, François M, Massé G, Bloch F, Brion N, Jankowski R, Serrano E. Rebound congestion and rhinitis medicamentosa: nasal decongestants in clinical practice. A critical review of the literature by a medical panel. European annals of otorhinolaryngology, head and neck diseases. 2013 Jun 1;130(3):137-44.
7. Laccourreye O, Werner A, Giroud JP, Couloigner V, Bonfils P, Bondon-Guitton E. Benefits, limits and danger of ephedrine and pseudoephedrine as nasal decongestants. European Annals of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Diseases. 2015 Feb 1;132(1):31-4.
8. Mucha SM, Detineo M, Naclerio RM, Baroody FM. Comparison of montelukast and pseudoephedrine in the treatment of allergic rhinitis. Archives of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery. 2006 Feb 1;132(2):164-72.
9. Kanfer I, Dowse R, Vuma V. Pharmacokinetics of oral decongestants. Pharmacotherapy: The Journal of Human Pharmacology and Drug Therapy. 1993 Nov 12;13(6P2):116S-28S.
10. P'ng XW, Akowuah GA, Chin JH. Acute oral toxicity study of Clinacanthus nutans in mice. International journal of pharmaceutical sciences and research. 2012 Nov 1;3(11):4202.
11. Kulkarni, Shrinivas K., Kulwinder Singh, and Mahendra Bishnoi. "Comparative behavioural profile of newer antianxiety drugs on different mazes." September 2008 Vol. 46 (4): 633-638.
12. Emamghoreishi M, Khasaki M, Aazam MF. Coriandrum sativum: evaluation of its anxiolytic effect in the elevated plus-maze. Journal of ethnopharmacology. 2005 Jan 15;96(3):365-70.
13. Matto V, Harro J, Allikmets L. The effects of cholecystokinin A and B receptor antagonists on exploratory behaviour in the elevated zero-maze in the rat. Neuropharmacology. 1997 Mar 1;36(3):389-96.
14. Dalton R. Mixed bipolar disorder precipitated by pseudoephedrine hydrochloride. South Med J 1990;83:64-5.
15. Erickson CH, McLeod RL, Mingo GG, Egan RW, Pedersen OF, Hey JA. Comparative oral and topical decongestant effects of phenylpropanolamine and d-pseudoephedrine. American journal of rhinology. 2001 Mar;15(2):83-90.
16. Bender B, Milgrom H. Neuropsychiatric effects of medications for allergic diseases. Journal of allergy and clinical immunology. 1995 Feb 1;95(2):523-8.
17. Bain D. Can the clinical course of acute otitis media be modified by systemic decongestant or antihistamine treatment? Br Med J 1983;287:654-6.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License