IJCRR - 12(18), September, 2020
Pages: 14-19
Date of Publication: 22-Sep-2020
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Plasma Homocysteine Concentration in Acute Coronary Syndromes
Author: A. T. Pardesi, Dilip P. Patil, Nitin B. Jadav, Pramod Kulkarni, Dany John
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: The high plasma or serum concentrations of total homocysteine are associated with an increased risk of atherothrombotic disease. Aim- a study to assess Plasma Homocysteine Concentration in Acute Coronary Syndromes. Methods: Total 60 patients with the diagnosis of coronary artery disease and non-hemorrhagic stroke are included in this study. Results: In the present study, the plasma homocysteine level is significantly elevated in patients with CAD and non-hemorrhagic stroke. The elevated plasma homocysteine level is an independent and traditional risk factor for CAD. This is turn may revolutionise the development of new strategies of treatment for primary prevention of CAD and non-hemorrhagic stroke in those individuals who do not have traditional risk factors. In absence of the established major atherogenic risk factors like hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia and smoking, atherosclerotic occlusive vascular events are known to occur. This indicates that there may be an additional independent risk factor such as elevated plasma homocysteine. There is increasing evidence that, linked hyperhomocysteinaemia as a risk factor for the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. To confirm this concept, 60 cases of occlusive atherosclerotic vascular events (45 coronary artery disease and 15 non-haemorrhagic cerebrovascular diseases), without other risk factors are studied, for plasma homocysteine levels. Conclusion: Homocysteine levels are studied in control subjects without clinical vascular diseases. The data is analysed to demonstrate the correlation of homocysteine levels with vascular events.
Keywords: Homocysteine, Acute coronary syndromes, Non-Haemorrhagic stroke
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
The first to hypothesise that hyperhomocysteinaemia is a risk factor for atherothrombosis. More recently, many but not all cross-sectional and prospective studies have shown that high plasma or serum concentrations of total homocysteine are associated with an increased risk of atherothrombotic disease. High total homocysteine concentrations can be lowered by treatment with folic acid and vitamin B12. So assessment of whether such treatment lowers the risk of atherothrombosis is important.1,2
Hyperhomocysteinaemia as a Risk Factor:
Hyperhomocysteinaemia is an independent risk factor for Coronary Artery Disease (CAD).3 Elevated plasma homocysteine concentration is found in almost one-third of all patients with atherosclerosis. Elevation by 12% above the upper limit of normal (15 micromoles per litre) is associated with a three-fold increase in the risk of acute myocardial infarction (AMI). Homocysteine concentration is determined by genetic and nutritional factors.4 vitamin B12 and folic acid are essential co-factors for the remethylation of homocysteine to methionine and dietary supplementation with these vitamins lowers plasma homocysteine by up to 30 %. These observations have formed the basis of large scale intervention trials that are seeking to determine whether lowering homocysteine concentration through vitamin-B supplementation can improve survival in patients with CAD.22 Increasing evidence suggests that adverse vascular effects of elevated homocysteine are mediated through endothelial dysfunction which is an early manifestation of atherosclerosis.4
So, far studies investigating the effects of lowering homocysteine concentrations on vascular endothelial function have yielded conflicting results.5 In primates, folate supplementation is reported to reduce plasma homocysteine concentration but not to affect vascular function.34 In healthy human subjects, folate supplementation is associated with reduced homocysteine concentration and improved vascular endothelial function. Though in these studies there was no relation between homocysteine concentration and endothelial function implying that the effects of B vitamins on endothelial function may not be mediated through homocysteine lowering.6
India is on the threshold of an epidemic of cardiovascular disease (CVD). The country is going through an epidemiological transition. Infectious and nutritional diseases are receding as the cause of adult mortality, while non-communicable diseases assume more menacing proportions.7
MATERIALS & METHODS
All cases of acute coronary syndromes including acute myocardial infarction and non-hemorrhagic stroke admitted in the Intensive Care Unit, Dept. of Medicine, Krishna Hospital, Karad.
A total of 60 patients with the diagnosis of coronary artery disease and non-hemorrhagic stroke are included in this study.
Exclusion Criteria:-
The following patients were excluded from the study
-
Diabetes mellitus
-
Hypertension
-
Renal Disease
-
Chronic Smokers
-
Hyperlipidemia
Inclusion Criteria:-
-
Acute coronary syndromes including acute myocardial
Infraction (STEMI, NSTEMI), unstable angina, and cardiac enzyme abnormalities.
Non-hemorrhagic stroke.
Diagnostic Criteria:
The diagnosis of coronary artery disease was based on clinical history, ECG change(ST-elevation according to nomenclature, ST depression with enzyme abnormalities), cardiac enzyme estimation, and two Dimensional Echocardiography.
The diagnosis of non-hemorrhagic stroke patients was based on clinical history, clinical findings, and CT scan of the head.
OBSERVATIONS AND RESULTS
In the Department of Medicine, Krishna Hospital, Karad 133 patients were diagnosed as CAD.
Total of 358 patients presented with stroke out of which 263 patients were diagnosed as non-hemorrhagic stroke patients.
A total of 45 patients of CAD and 15 patients of non-hemorrhagic stroke fulfilled the criteria for the present study.
Randomly selected, age-matched 25 patients of other medical problems were taken as a control for this study.
SEX DISTRIBUTION
Out of a total of 60 patients with coronary artery disease and cerebrovascular disease, 34 (56.67%) are male and 26 (43.33%) are female shown in table 1
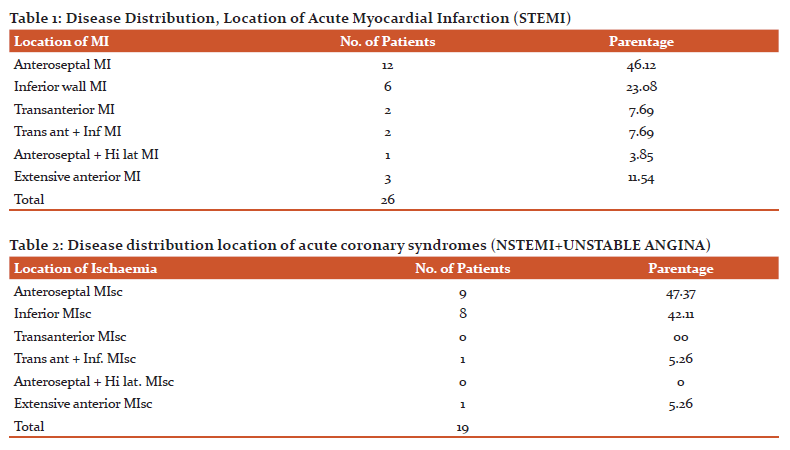
Out of 26 patients with acute myocardial infarction,12 (46.12%) have anteroseptal MI, 6 (23.08%) have inferior wall MI,2 (7.69%) have transaction MI, 2 (7.69%) have trans ant + inf MI,1 (3.85%) has anteroseptal + Hi lat MI and 3 (11.54%) have extensive anterior MI.
Out of total 19 patients with the acute coronary syndrome, 9 (47.37%) have anteroseptal MIsc, 8 (42.11%) have inferior MIsc, 1 (5.26%) has trans ant + inf MIsc, 1 (5.26%) has extensive anterior MIsc and none in trans ant MIsc as well as in anteroseptal + hi lat MIsc. (Table 2)
Disease distribution location of non-hemorrhagic infarctions
Out of a total of 15 patients with non-hemorrhagic stroke 7 (46.67%) have RMCA area infarction and 8 (53.33%) have LMCA area infarction.
Plasma homocysteine levels in the study group
Out of a total of 60 patients of the study group 2 (3.3%) have normal Hcy level, 13 (21.66%) have moderate Hcy level, 16 (26.66%) have intermediate Hcy level and 29 (48.33%) have severe Hcy level.
Plasma homocysteine levels in different MI groups.
Out of a total of 12 patients with anteroseptal MI 1 (8.33%) has a normal Hcy level, 1 (8.33%) has a moderate Hcy level, 6 (50.00%) have intermediate Hcy level and 4 (33.33%) have severe Hcy level.
Plasma homocysteine levels in different MI groups.
Out of a total of 6 patients with an inferior wall, MI 2(33.33%) have moderate Hcy level, 2 (33.33%) have intermediate Hcy level, 2 (33.33%) have severe Hcy level and none has normal Hcy level.
Plasma homocysteine levels in different MI groups.
Out of 2 patients with transanterior MI 2 (100%) have severe Hcy level and none has normal, moderate, and intermediate Hcy level.
Plasma homocysteine levels in different MI groups.
Out of a total of 2 patients with transanterior + inferior wall, MI 2 (100%) have severe Hcy level and none has normal, moderate, intermediate Hcy level.
Plasma homocysteine levels in different MI groups.
Out of a total of 1 patient with anteroseptal + high lateral MI 1 (100%) has a moderate Hcy level and none has normal, intermediate, severe Hcy level.
Plasma homocysteine levels in different MI groups.
Out of a total of 3 patients with extensive anterior MI 3 (100%) have severe Hcy level and none has normal, moderate, intermediate Hcy level.
Plasma homocysteine levels in different acute coronary syndrome groups.
None of the patients had transanterior myocardial ischemia.
Plasma homocysteine levels in different acute coronary syndrome groups.
Out of a total of 1 patient with transanterior + inferior MIsc 1 (100%) has an intermediate Hcy level and none has normal, moderate, severe Hcy level.
Plasma homocysteine levels in different acute coronary syndrome groups.
None of the patients had anteroseptal + high lateral myocardial ischemia. (Table 20)
Plasma homocysteine levels in different acute coronary syndrome groups.
Out of a total of 1 patient with extensive anterior Misc 1 (100%) has a severe Hcy level and none has a normal, moderate, intermediate Hcy level.
Cardiac Enzymes
Out of a total of 45 patients with coronary artery disease, 18 (40%) have CPK-MB elevated in the range of 20-40 IU/Iit and 27 (60%) have CPK-MB elevated by more than 40 IU/It.
Plasma homocysteine levels in different Non-hemorrhagic stroke groups.
Out of a total of 8 patients with LMCA area infarction, 2 (25%) have moderate Hcy level, 1 (12.50%) has intermediate Hcy level, 5 (62.50%) has a severe Hcy level and none has a normal Hcy level. (Table 23)
Plasma homocysteine levels in different Non-haemorrhagic stroke groups.
Out of a total of 7 patients with RMCA area infarction, 3 (42.86%) have moderate Hcy level, 1 (14.26%) has intermediate Hcy level, 3 (42.86%) have severe Hcy level and none has a normal Hcy level. (Table 24)
Plasma homocysteine levels in the control group.
Out of the total of 25 patients in the control group, 24 (96%) have normal Hcy level, 1 (4%) has moderate Hcy level and none has intermediate, severe Hcy level.
DISCUSSION
Out of total 45 patients are with CAD and 15 patients with non-hemorrhagic stroke are included in this study.
Age and sex distribution:
The age group of the male is 23-70 yrs. Age group of the female is 35-70 years. Male to female ratio in this study is 1.3:1After the age of 45 years, there is no significant gender difference in the prevalence of vascular events. In the younger (<45 years) patients, males appear to have a higher prevalence. Stamfer, Nygard, and Graham et al also noted similar male Predominance.8
In the present study, 1 person is in the age group 20-25 years (1.67%), 1 person is in the age group 26-35 years (1.67%), 10 people 36-45 years (16.67%). The majority are in the age group 46-55 years (35%) in the age group 56-65 (30%) and 66-70 years (15%).
In the study by Stamfer, the majority are in the age group of 40-45 years (41%).In the Perry study, 54% of the patients were in the age group of 60-70 years.9 Anterior (its variants) MI is the predominant in the present study (69.23%) followed by inferior MI (23.08%), combined (7.69%). Similar results are found in Graham and Nygard. Anterior (its variants) MIsc is predominant in the present study (52.63%) followed by inferior MI (42.11%) and combined (5.26%). Similar results are found in Graham and Nygard et al.
In the present study both right middle cerebral artery territory infarction (RMCA) and left middle cerebral artery territory infarction ( LMCA) are approximately equal in number. In this group there are no patients of vertebrobasilar territory infarction as the total number of non-hemorrhagic stroke in this study is small.
Homocysteine levels in anterior (and its variants) MI are normal in 5.56%, moderate in 11.11%, intermediate in 33.33%, and severe in 50.00% of patients. In inferior MI the Hcy levels are normal in None, moderate in 33.33%, intermediate in 33.33%, severe in 33.33%. In combined MI the Hcy levels are severe in 100%.
Homocysteine levels in anterior (and its variants) MIsc are normal in 10.00%, moderate in 40.00%, intermediate in 10.00%, severe in 40.00%. In inferior MIsc, the Hcy levels are normal in None, moderate in 12.50%, intermediate in 37.50%, severe in 50.00%. In combined MIsc the Hcy levels are moderate in 100.00%.
Homocysteine levels in LMCA area infarction are normal in None, moderate in 25.00%, intermediate in 12.50%, severe in 62.50%. In RMCA area infarction Hcy levels are normal in None, moderate in 42.86%, intermediate in 14.26%, severe in 42.86%.
Abnormal homocysteine levels are found in all categories of ACS and cerebral infarction.
The level of hyperhomocysteinemia does not seem to reflect the area of infarction in the brain.
It appears to be a linear, severity dependent correlation of the vascular episodes with plasma homocysteine levels.
More extensive myocardial infarctions such as transanterior or combined (anterior + inferior) reflect the severity of the disease and appear to have a significantly elevated level of homocysteine.
In our present study, the mean value of homocysteine from the study group is 78.7 micromol (SD ±40.94) and from the control group 9.5 micromol (SD ±3.10), which is statistically significant (P<0.05)
The evidence for the role of elevated homocysteine in the causation of CVD is still inconclusive. Even in the event of availability of such evidence from studies in the West, extrapolation to the Indian population will be precluded by the latter’s distinct risk factor profile which mandates a study of independent and interactive risk contributions. For new hazard components to be significant in infection avoidance in any populace, they should either be liable for a generous extent of the malady trouble, or their adjustment must tangibly affect sickness pervasiveness in that populace. The major known modifiable risk factors explain at least 75% of new cases of cardiovascular disease even in the western world. Doctors and their patients should hence not dismiss the way that way of life changes consolidating smoking end, a heart sound eating regimen, weight decrease, and ordinary physical movement along with sedate treatment for dyslipidemia, remain the foundations of CVD avoidance in our populace. The normal estimation of plasma homocysteine and the utilization of explicit treatments coordinated at diminishing raised levels aren't yet suggested.
On the other hand, Mc Culley hypothesized that elevated plasma homocysteine could cause atherosclerosis. Abundant epidemiologic evidence from more than 20 case-control and cross-sectional studies involving 2000 patients has validated this relation.
The Arnesen et al 9 study found that 26%, 26%, 2% of patients were in the moderate intermediate and severe category of Hcy respectively.9 In another study by Perry, the incidence was 23%, 6%, and 1% respectively.
Boers and colleagues screened 75 patients with the premature atherosclerotic vascular disease for hyperhomocysteinemia using methionine challenge and found that yearly 1/3rd of all patients with cerebrovascular and peripheral vascular disease had hyperhomocysetinaemia.10
Clark and colleagues subsequently measured homocysteine concentration after methionine loading in a cohort of men with premature vascular disease and demonstrated that 30% of patients with CAD, 42% with cerebrovascular disease, 28% with the peripheral vascular disease had hyperhomocysetinaemia.11
Two large prospective studies have assessed the risk of CAD in patients with hyperhomocysteinemia. In the physician's health study 14916 male physicians without known atherosclerosis had an initial homocysteine measurement and were prospectively followed for an average of 5 years. Men with plasma homocysteine concentrations that were 12% above the upper limit of normal had approximately a three-fold increase in the risk of myocardial infarction as compared with those with lower levels even after correction for other risk factors. They estimated that 7% of 271 observed myocardial infractions could be attributed by hyperhomocysetinamia.12
A prospective TROSMO study reported similar results and several other studies have consistently indicated that hyperhomocysteinemia is an independent risk factor for vascular disease.
Graham and coworkers recently measured plasma homocysteine concentration in 750 patients with atherosclerosis and 800 normal subjects. There was a statistically significant difference in plasma homocysteine concentration during fasting between patients and controls (11.25 micromoles / Ltr Vs 9.73 micromoles /Ltr.) and a methionine challenge revealed an additional 27% of patients had hyperhomocysteinemia. Elevated plasma homocysteine conferred an independent risk factor for vascular disease similar to that of smoking or hypercholesterolemia and also had a multiplicative effect as risk amongst smokers and patients with hypertension. The author suggested that controlling hypertension and smoking might be particularly important with hyperhomocysteinemia.
Nygard and colleagues recently reported a prospective study involving 587 patients with angiographically documented CAD. Baseline homocysteine measurements were obtained and patients were followed for a median of 4.6 years during which time 1.9% of them died. These investigators found a strong association between homocysteine concentrations and overall mortality.13
In a recent meta-analysis, Boushey and colleagues estimated that 10% of the risk of CAD in the general population was attributed to elevated homocysteine. They reported that an increase of 5 micromoles per ltr. in plasma homocysteine concentration, raises the risk of CAD by as much as an increase of 20 mg per deci ltr. in the cholesterol concentration.14
In the present study, in patients with CAD and cerebrovascular atherosclerotic disease, where the major risk factors were excluded, an elevated homocysteine level is obvious. Though the number of patients is small, it may be inferred as an independent risk factor, as only two of the cases had normal homocysteine levels.
CONCLUSIONS
Elevated plasma homocysteine levels are seen in 95.5% of patients with coronary artery disease and cerebrovascular disease in this study. There is a statistically significant association between the level of plasma homocysteine and occlusive atherosclerotic vascular disease in the present study and linear correlation of the number of cases with the severity of plasma homocysteine levels. The elevated plasma homocysteine appears to be an independent risk factor for occlusive atherosclerotic vascular disease.
Conflict of interest- nothing to report.
Source of funding- Kimsdu Karad
Acknowledgment- Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references to this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals, and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. McCully KS, Ragsdale BD. Production of arteriosclerosis by homocysteinemia. The American journal of pathology. 1970 Oct; 61(1):1.
2. Wilken, D.E.L., and Wilken, B. ().Pathogenesis of coronary artery disease. A possible role for methionine metabolism. J. Clin. Invest. 1976: 57, 1079-1082.
3. Boushey CJ, Beresford SA, Omenn GS, Motulsky AG. A quantitative assessment of plasma homocysteine as a risk factor for vascular disease: probable benefits of increasing folic acid intakes. Jama. 1995 Oct 4;274(13):1049-57.
4. Welch GN, Loscalzo J. Homocysteine, and atherothrombosis. New England journal of medicine. 1998 Apr 9;338(15):1042-50.
5. Lentz SR, Malinow MR, Piegors DJ, Bhopatkar-Teredesai M, Faraci FM, Heistad DD. Consequences of hyperhomocyst (e) anemia on vascular function in atherosclerotic monkeys. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology. 1997 Nov;17(11):2930-4.
6. Verhaar MC, Wever RM, Kastelein JJ, van Loon D, Milstien S, Koomans HA, Rabelink TJ. Effects of oral folic acid supplementation on endothelial function in familial hypercholesterolemia: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Circulation. 1999 Jul 27;100(4):335-8.
7. Mudd S.H. The natural history of homocysteinemia due to cystathionine beta-synthase deficiency. Am. J. Hum bent. 1985;37; 1-31.
8. Graham IM, Daly LE, Refsum HM, Robinson K, Brattström LE, Ueland PM, Palma-Reis RJ, Boers GH, Sheahan RG, Israelsson B, Uiterwaal CS. Plasma homocysteine as a risk factor for vascular disease: the European Concerted Action Project. Jama. 1997 Jun 11;277(22):1775-81.
9. Arnesen E, REFSUM H, BØNAA KH, UELAND PM, FØRDE OH, NORDREHAUG JE. Serum total homocysteine and coronary heart disease. International journal of epidemiology. 1995 Aug 1;24(4):704-9.
10. Boers GH, Smals AG, Trijbels FJ, Fowler B, Bakkeren JA, Schoonderwaldt HC, Kleijer WJ, Kloppenborg PW. Heterozygosity for homocystinuria in premature peripheral and cerebral occlusive arterial disease. New England Journal of Medicine. 1985 Sep 19;313(12):709-15..
11. Clarke R, Daly L, Robinson K, Naughten E, Cahalane S, Fowler B, Graham I. Hyperhomocysteinemia: an independent risk factor for vascular disease. New England journal of medicine. 1991 Apr 25;324(17):1149-55..
12. Farhadi D. Plasma homocysteine levels and mortality in patients with coronary artery disease. The New England journal of medicine. 1997 Nov;337(22):1632-author..
13. Boushey CJ, Beresford SA, Omenn GS, Motulsky AG. A quantitative assessment of plasma homocysteine as a risk factor for vascular disease: probable benefits of increasing folic acid intakes. Jama. 1995 Oct 4;274(13):1049-57.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License