IJCRR - 12(18), September, 2020
Pages: 05-08
Date of Publication: 22-Sep-2020
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Knowledge, Attitude and Practice of Mothers for Administration of Medicaments to Their Children and its Correlation with Dental Caries
Author: Nilima Ramdas Thosar, Sphurti Pramod Bane, Nandinee Hake, Suruchi Gupta, Sudhindra Baliga M., Nilesh Rathi
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Aim: The study was conducted to assess the awareness among parents especially the mothers regarding liquid medication among children and its relation to caries progression. Materials and Method: Around 230 mothers were included in the study. The mothers were asked to fill a validated questionnaire and her offspring were assessed for presence or absence of dental caries. Results: The data revealed that 80.4% of mothers preferred medication in syrup form, 63.5%administered medication twice daily while none of the mothers performed oral hygiene measures post medication. Around 78.7% of mothers were unaware of the relation between liquid medication and caries. Conclusion: The Pediatric dentists should create awareness among the mothers regarding liquid drug administration and oral hygiene measures.
Keywords: Liquid medication, Pediatric drugs, Dental Caries, Parental Knowledge, Oral Hygiene Practices
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Oral health is considered to be an important factor in a child’s overall growth and development. Dental caries being one of the major threats to children is multifactorial. It leads to decalcification of the teeth due to acid production caused by oral bacteria. The reaction between sugars in drinks, foods and bacteria in the dental biofilm present on the tooth surface causes the production of acid which is responsible for the initiation of dental caries.1,2
Analgesics and antibiotics along with various multivitamin supplements are commonly prescribed to children. These medications are widely available in syrup or suspension form and sweetened to increase patient compliance. Along with acceptance by the pediatric age group, medication in syrup form has good absorbability and flexibility with dosage.3 However, long term usage of sweetened oral medication can cause amplification of risks by making patients more susceptible to dentinal caries.4
High sucrose, fructose and glucose content in these medications along with other contributing factors like low pH, the duration and frequency and time of administration leads to an increase in caries in children. The incidence of caries can be reduced if proper precautionary and preventive measures are taken by the child’s parent or guardian. Poor attitude of parents towards the oral health of children is one of the reasons for the increase in caries prevalence.
Thus, this study is scheduled to assess the knowledge and awareness of mothers about cariogenicity of pediatric syrup medications and its correlation to dental caries.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The study was a prospective study conducted in the Department of Pediatrics and Preventive Dentistry, Sharad Pawar Dental College and Department of Pediatrics, Acharya VinobaBhave Rural Hospital, Sawangi(Meghe), Wardha. Institutional Ethical Approval (DMIMS (DU)/IEC/2018-19/7172) was obtained from Datta Meghe Institute of Medical Sciences ethical committee.
The study included 230 mothers of children aged between 4 to 8 years of age and mothers of immunocompromised children or those having systemic medical history were excluded from the study. A validated short questionnaire consisting of 4 multiple choice questions were used for the study. (Table 1) The questionnaire was framed in local language about awareness regarding the administration of medication to their children.
The oral cavity of children of participated mothers was examined for dental caries and recorded in the study.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
The data obtained was calculated using descriptive statistics employing absolute distribution, percentage of measures and techniques of interferential statistics. Frequency analysis was done using SPSS software version 22.0.
RESULTS
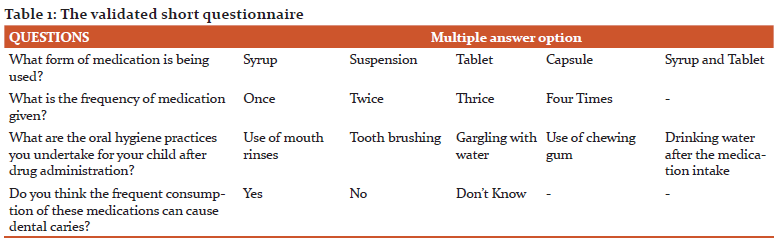
Amongst the 230 mothers who participated in the study, 80.4% mothers preferred syrup and 1.7% mothers preferred tablets for their child while 17.8% mothers preferred medication in both forms for their children (Graph 1). 63.5% of mothers revealed that they administered medication twice daily while 34.8% of mothers used to administer medication thrice for their children (Graph 2). None of the participated mothers made their child brush post medication, however, 93.9% mentioned that their child drinks water after intake of medication and 6.1% mothers took oral hygiene measures and made their child gargle with water post medication intake (Graph 3).
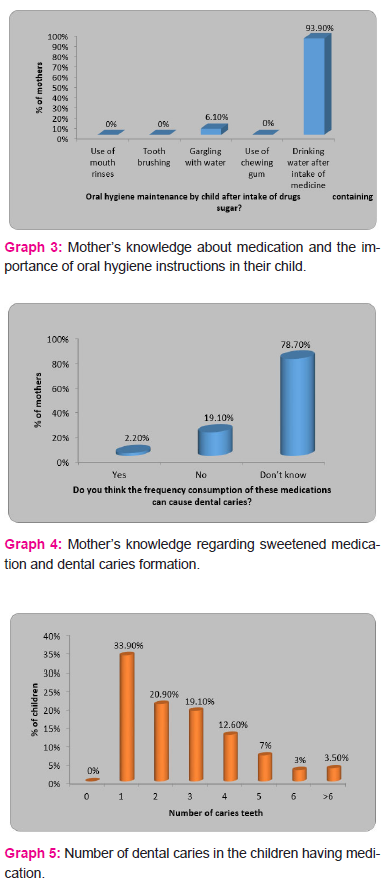
The relationship between frequent consumption of medications and dental caries was not known to 78.7% mothers while 19.1% of mothers thought that these medications could not cause dental caries (Graph 4). The dental caries status of children having one carious lesion is among 33.9% whereas only 3.5% of children had more than 6 carious teeth in the mouth (Graph 5).

DISCUSSION
Lokken et al. and Imfeld et al. mentioned the presence of sucrose in medicines having cariogenic potential. This sucrose amount varied from 0-67% in pediatric liquid medication.5 Agrawal et al.6 observed a range of 20.62 – 68.26% sucrose in Indian Pediatric liquid medication.6 Commercially available medications for pediatric age group are mainly in sucrose based syrup forms as the liquid preparation for drug delivery are popular and easily accepted by children.7
Historically, Roberts and Roberts first documented harmful effects on the oral health of a child due to oral medication in 1979.8 Physicians including the Pediatricians prescribe medications for cough, fever along with medications for overall growth and well-being. Pediatric dentists are well aware of the relationship between liquid medication and dental caries. However, due to parental preference and lesser knowledge about the of non-sweetened pediatric medications availability in the market, they tend to prescribe the medication in liquid syrup form.
Mothers are unaware of the hidden sugar components in liquid medicaments and their implication on the oral and dental health of the child. Liquid medications can lead to rampant dental decay and it can be considered as one of the major etiologic factors.9 Literature suggests an increase in caries incidence in children consuming liquid medication. It has been noted that in children consuming liquid medications, the incidence of dental caries is also increased.10,11,12 Also, low endogenous pH of these medications is responsible for erosive and cariogenic potential in children.13,14
Nowadays, it is seen that there is an increased usage of non-prescription and over the counter liquid medicaments for cough and cold in children. But many studies have shown that there are adverse effects associated with non-prescription drug administration.15 Walimbe et al.16 through his study stated that about 50% paediatrician prescribed medication in the form of syrup, whereas more than 80% parents stated that their children preferred medication in the liquid form as stated in the present study.
Mothers are often responsible for the administration and care related to the use of pediatric medicines. The medical practitioners should encourage the parents to restrict the intake of the medication to mealtimes and avoid administrating medication before sleeping.17 In the present study, around 63.5% of parents administered medications twice daily while only 0.4% administered it four times a day. The duration has a major impact on dental caries, as Girish Babu et al.5 stated that syrups given in 2-3 divided doses especially during the night have a deleterious effect on enamel. This can be attributed to the fact that the saliva rate decreases during the night and the oral muscular co-ordination is less leading to decrease in the oral clearance process and reduced ability to eliminated the retained particles from the mouth.
Pediatric dentists emphasize parents on seeking regular preventive oral care for their children along with a routine oral hygiene recommendation post medication administration.7 The frequency of consumption of sugar is proportional to the experience of caries. Consumption of these liquid medicines increases the number of sugar exposure in the child’s normal diet thereby increasing the risk of caries.18 About 33.9% of children had only one carious lesion while only 3.5% has carious lesion more than six carious teeth. This can be attributed to the fact that majorly 91% of mothers mentioned that they made the child drink water post medication. This was a major oral hygiene factor practised by the mothers unknowingly, flushing the liquid medication of the teeth surface and decreasing dental caries incidence.
It is important to spread awareness amongst parents about the potential risk of inadvertent and injudicious use of these medications in which Pediatricians and Pedodontists play an important role. They should inform the parents about the sugar content of these medications, recommend limited use whenever possible, use of tablets be encouraged, advice brushing after administration, medication to be given at mealtimes rather than between meals and avoid administration at bedtime.19Pediatricians, Pediatric dentists and Physicians should prescribe non-sucrose medicaments and advice adequate preventive and oral hygiene measures for children on the long term use of liquid medicines.20
Conclusion
The Pediatric dentist and Pediatricians should create awareness among the parents regarding caries incidence due to liquid medication. They should be encouraged to take adequate post medication measures in their children.
Financial support
Nil
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References:
1. Gaidhane, A.M., M. Patil, N. Khatib, S. Zodpey, and Q.S. Zahiruddin. “Prevalence and Determinant of Early Childhood Caries among the Children Attending the Anganwadis of Wardha District, India.” Indian Journal of Dental Research 24, no. 2 (2013): 199–205. https://doi.org/10.4103/0970-9290.116677.
2. Kriplani, R., R. Bahadure, and N. Thosar. “Full Mouth Rehabilitation of Early Childhood Caries: A Case Report.” Journal of Datta Meghe Institute of Medical Sciences University 7, no. 1 (2012): 51–53.
3. Nunn T, Williams J. Formulation of medicines for children. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2005 Jun;59(6):674–6.
4. Roberts IF, Roberts GJ. The relation between medicines sweetened with sucrose and dental disease. Br Med J. 1979 Jul 7;2(6181):14–6.
5. K. L. Girish Babu, Geeta Maruti Doddamani, L. R. Kumaraswamy Naik, K. N. Jagadeesh J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2014 May-Aug; 4(2): 108–112.
6. Agrawal N, Shashikiran ND, Vanka A, Thakur R, Sandhu SS. Cariogenic potential of most commonly prescribed liquid oral medicines for children. Peo J Sci Res. 2010;3:7–10.
7. Jehan Al Humaid. Sweetener content and cariogenic potential of pediatric oral medications: A literature. Int J Health Sci Qassim. 2018 Jun;12(3):75–82.
8. Bhandary S, M. R P, Shetty UA. Paediatricians Perceptions towards the Use of Sweetened Liquid Medications and its Relationship to Oral Health of Children. J Evol Med Dent Sci. 2019 Oct 14;8(41):3070–3.
9. Feigal RJ, Jensen ME, Mensing CA. Dental caries potential of liquid medications. Paediatrics. 1981 Sep;68(3):416–9.
10. Roberts IF, Roberts GJ. The relation between medicines sweetened with sucrose and dental disease. Br Med J. 1979 Jul 7;2(6181):14–6.
11. Bigeard L. The role of medication and sugars in pediatric dental patients. Dent Clin North Am. 2000 Jul;44(3):443–56.
12. Shaw L, Glenwright HD. The role of medications in dental caries formation: need for sugar-free medication for children. Pediatrician. 1989;16(3–4):153–5.
13. Passos IA, Sampaio FC, Martínez CR, Freitas CHS de M. Sucrose concentration and pH in liquid oral pediatric medicines of long-term use for children. Rev Panam Salud Publica Pan Am J Public Health. 2010 Feb;27(2):132–7.
14. Lökken P, Birkeland JM, Sannes E. pH changes in dental plaque caused by sweetened, iron-containing liquid medicine. Scand J Dent Res. 1975 Sep;83(5):279–83.
15. Yang M, So T-Y. Revisiting the safety of over-the-counter cough and cold medications in the pediatric population. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2014 Apr;53(4):326–30.
16. Walimbe H, Bijle MNA, Nankar M, Kontham U, Bendgude V, Kamath A. Knowledge, Attitude and Practice of Paediatricians toward Long-Term Liquid Medicaments Associated Oral Health. J Int Oral Health. :4.
17. Nirmala SV, Popuri VD, Chilamakuri S, Nuvvula S, Veluru S, Minor Babu MS, et al. Oral health concerns with sweetened medicaments: Pediatricians’acuity. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2015;5:35–9.
18. Girish Babu KL, Doddamani GM, L.R KN. Knowledge, attitude, and practice of paediatricians regarding pediatric liquid medicaments. Eur J Dent. 2017 Jan;11(01):106–10.
19. Durward C, Thou T. Dental caries and sugar-containing liquid medicines for children in New Zealand. N Z Dent J. 1997 Dec;93(414):124–9.
20. Bradley MB, Kinirons MJ. Choice of sugar-free medicines by a sample of dentists, doctors and pharmacists in Northern Ireland: the views of parents and health professionals. Community Dent Health. 1998 Jun;15(2):105–8.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License