IJCRR - 10(4), February, 2018
Pages: 01-08
Date of Publication: 17-Feb-2018
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Mobile Health - An Effective Nutrition Communication Tool
Author: Sangna Raybardhan, Kalpana C.A.
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Information, education and communication approaches were used in this study to reach the target groups. Nutrition education was provided in the form of text messages integrated with mobile communication, an alternative choice of media already popular among college going girls instead of usual nutrition education practices. 284 college going girls were divided into cases and controls, with proportion of 1:1 ratio, from various institutions with English medium of instruction and using mobile phones were selected from Coimbatore city. A structured and reviewed questionnaire was used to collect background information and to assess the nutritional knowledge status of the target population. A total number of 28 messages were framed. The mHealth (mobile-health) messages were sent using broad band internet connection to the mobile numbers of 142 respondents using Microsoft Excel enabled plug-in for sending bulk SMS for a period of 14 days. The effect of mHealth on the nutritional knowledge of respondents was evaluated by administering a questionnaire. After imparting nutrition education by sending mHealth messages to their mobile phones, there was an increase in the general, therapeutic and adolescent and adult nutrition knowledge of the
experimental group when compared to the control group and statistically significant at 1% level. Mobile phones provided a new communication channel for health promotion and community mobilization. mHealth as a nutrition communication tool effectively increased nutritional knowledge among college going girls. mHealth and development of user friendly mobile apps for nutrition communication is very useful in imparting nutrition messages.
Keywords: mHealth, Healthcare, Mobile technology and applications, Wireless technology, Community mobilization
DOI: 10.7324/IJCRR.2018.1041
Full Text:
Introduction: Health and nutritional status of the population are recognized as the prime indicator of development at national and international levels. Indian women in the age group of 15 – 45 years comprise the vulnerable section of the population due to growth spurt when food and nutrient needs are higher and related risk of child bearing ability. Though nutrition interventions have been made in India, significant improvement in nutritional status has not occurred especially in women and girls. Nutritional disorders like anaemia, poor weight gain in pregnancy and poor caring practices in girls are still common in all socio-economic groups.[1] Nutrition education‘s main goal is to make people aware of what constitutes a healthy diet and ways to improve their diets and their lifestyles.[2] Use of mass media has become even more sophisticated as a tool for nutrition education. Mass media has expanded beyond broadcast and print media to include the range of opportunities available on the Internet and through other technology like cellular phones.[3] Cell phones are the most popular mobile device used in mHealth interventions. Distinct advantages offered by cell phones over other mobile tools include their relatively low cost, wide spread use, and onboard processing power to record, store, organize, and broadcast information in real time.[4]] Texting is the dominant mode of communication among teens.[5] With mobile technologies accessible to 95.5 percent of the world population, many believe that mHealth has the potential to transform the face of health service delivery across the globe by offering new means of when, where, how, and by whom health services are provided and accessed.[6] A systematic review of the literature on disease management and prevention services delivered through text messages found evidence to support text messaging as a tool for behaviour change in eight of nine studies with sufficient sample sizes.[7] In this study, the information, education and communication (IEC) approaches were being used to reach the target groups where nutrition education platform has been produced in the form of text messages integrated with mobile communication. The idea was to provide an alternative choice of media which is already popular among college students to impart nutrition education instead of usual nutrition education practices.
With this in view the study was conducted with the following objective:
- To assess the socio-economic background, dietary pattern and health status of college going girls.
- To study their physical activity and lifestyle pattern.
- To develop content for mHealth messages.
- To impart nutritional knowledge to the college going girls using mHealth as a tool for nutrition education.
- To evaluate the impact of mHealth on the nutritional knowledge of college going girls
Methodology: A total of 284 girls between the age group of 18 – 21 years from various institutions of Coimbatore city with English medium of instruction and using mobile phones were selected as samples. The sample was divided into cases and controls, with the proportion of 1:1 ratio. In this study mHealth was selected as tool for imparting nutrition education. Thus, a total of 142 respondents were included in the cases and the same number of controls was taken. The samples for the study was selected by non-random sampling method called convenience sampling. Convenience sampling is the cheapest and simplest and does not require a list of population. Hence, the investigator selected samples with the inclusion criteria as college going girls of 18 – 21 years, girls using mobile phones, able to understand, read and write in English and exclusion criteria as girls less than 18 yrs and more than 21 yrs, not using mobile phones, unable to understand, read and write in English. A well structured close ended questionnaire was formulated and the details on socio-economic status, lifestyle pattern, physical activity pattern and knowledge on nutrition were collected from them. The section for assessing nutrition knowledge status consisted of 25 questions on general, therapeutic and, adolescent and adult nutrition. Each question had four options and respondents were instructed to choose appropriate answer by tick mark. Data was collected in two phases namely pre-awareness and post awareness phase by administering questionnaire personally to the individual respondent by the investigator herself. Framed the content of mHealth messages and imparted nutritional knowledge to the selected respondents of the experimental group by sending mHealth messages to their mobile phones. Nutrition education was imparted to 142 girls using Microsoft Excel enabled plug-in for sending bulk Short Messaging System (SMS) for a period of 14 days. The basic package of 5000 SMS credits were purchased from Outsourced Marketing, New Delhi. The nutrition education was imparted using the basic mobile phone service of SMS. Each day two text messages were sent, consisting of 160 characters including special characters and spaces. Strictly adhering to the Telecommunication Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) Regulations, one message between 6:00 – 6:15 PM and the other one between 8:30 – 8:45 PM were sent, keeping in mind the time preference of the respondents as well. The impact of mHealth on the nutritional knowledge of respondents was evaluated by administering questionnaire pertaining to nutrition education. Each question answered correctly was attributed as 1 point. Wrong answers did not receive any score. The total score of the respondents varied from 1 to 25. The collected data were consolidated, tabulated and analyzed statistically using the software SPSS of version 16.0 to assess the effectiveness of mHealth and impact of nutrition education on the selected respondents.
Results: Socio-economic status - Among 284 selected samples, 12.7 per cent belonged to the age group of 18 years; 18 per cent were 19 years, 27.8 per cent were 20 years and 41.5 per cent were 21 years. About 70 per cent stayed in hostels, 37 per cent resided in their homes, 0.4 per cent was paying guests and 1.8 per cent lived in rented houses. It was evident that 2.1 per cent of the respondents belonged to low income group, 15.5 per cent belonged to low middle income group, 26.8 per cent of them belonged to middle income group and 55.6 per cent of them were from high income group.
Health status - Majority (90.8%) were not allergic towards any type of food and the remaining 9.2 per cent were allergic towards a specific kind of food; About 2.8 per cent of them suffered from anaemia, 0.4 per cent was affected by diabetes, 2.5 per cent were hypertensive, 8.0 per cent were suffering from obesity, 6.0 per cent were affected by overweight and the remaining 80.3 per cent were not affected by any kind of diseases. Approximately 87 per cent were not having menstrual problems and the remaining 13 per cent were having menstrual problems with 7 girls having problems related to reproductive health in spite of having regular periods. Only 78.4 per cent of the respondents consulted doctors regarding menstrual problems, and the remaining 21.6 per cent did not consult doctors.
mHealth - Among 142 selected cases, 100 per cent received two text messages daily for a period of 14 days in their mobile phones and 63.4 per cent shared messages while 36.6 per cent did not share the messages. The messages were shared via mobile was 53.3 per cent and messages shared personally was 46.7 per cent. Messages shared by the recipients to less than 5 persons were 77.8 per cent and between 5 to 10 persons were 22.2 per cent. All the respondents understood the meaning of the messages. About 2.8 per cent received messages only at the time between 6 – 6:15 pm, 2.8 per cent received between 8:30 – 8:45 pm, and the remaining 94.4 per cent received at both timings. All the respondents are willing to receive similar kind of mHealth messages in future also. Topic suggested for sending further messages was 2.8 per cent for anaemia, 2.1 per cent wished information on anticancer diet, anticancer foods (2.8 %), antioxidants (4.9 %), arthritis reduction diet (2.1%), balanced diet (7.7 %), cholesterol reduction diet (2.8 %), diet during menstruation (2.1 %), disease prevention (2.8 %), diet for gout (2.1 %), healthy diet (7 %), healthy foods (12.8 %), metabolic syndrome (1.4 %), PCOS (11.9 %), pregnancy (2.8 %), reproductive health (2.8 %), diet for weight gain (7 %), weight loss diet (16.1 %), yoga (7.7%), and no suggestion was 2.8 per cent. Preference to receive messages once a week was 2.8 per cent, thrice a week preferred by 2.8 per cent, 17.6 per cent preferred to receive messages for 10 days, 19.7 per cent preferred 14 days, 14.1 per cent preferred 15 days, 2.8 per cent preferred 20 days, 34.5 per cent preferred 30 days and 5.6 per cent preferred 60 days for receiving messages. Also 85.2 per cent preferred to receive messages at the same given time while 7.1 per cent preferred in the morning and 7.7 per cent preferred at the evening. Majority (95.1 %) opined that message size was sufficient and 4.9 per cent felt that message size was not sufficient. Nearly one-third (31%) preferred to receive increased number of messages while 69 per cent did not wish to receive increased number of messages. Local language was preferred by 33.8 per cent to receive the messages and 66.2 per cent did not wish to receive messages in local languages and 49.3 per cent preferred to receive messages with images and 50.7 per cent preferred to receive messages without images.
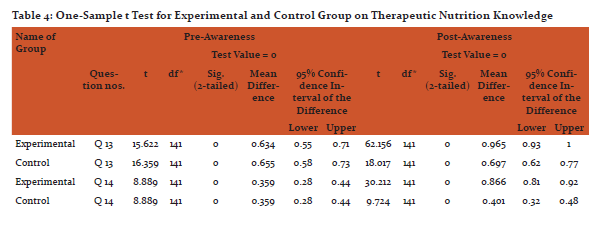
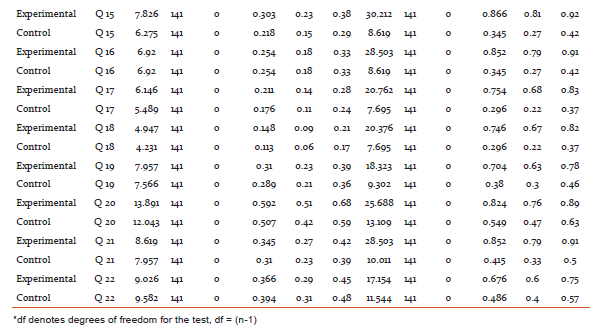
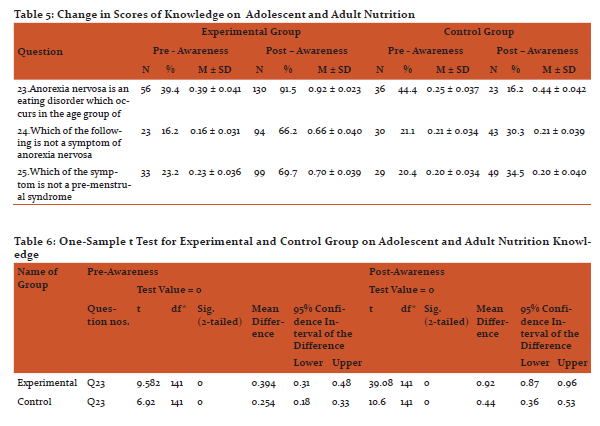
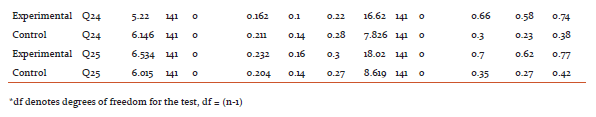
After imparting nutrition education by sending mHealth messages to their mobile phones, there was an increase in the knowledge on general nutrition, therapeutic nutrition, adolescent and adult nutrition of the experimental group when compared to the control group, except question number 9 on better way of cooking method, which college going girls were already aware about. The findings are statistically significant at 1% level.
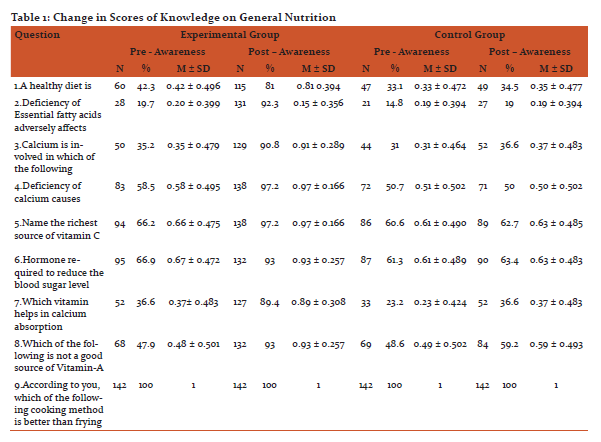
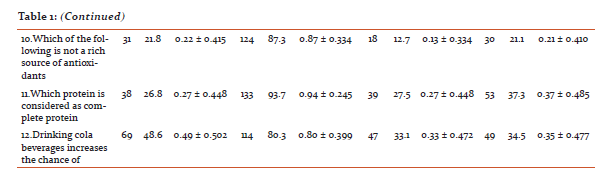
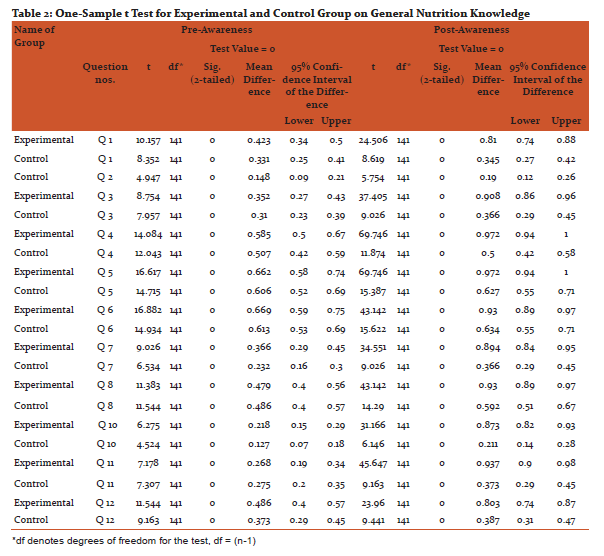
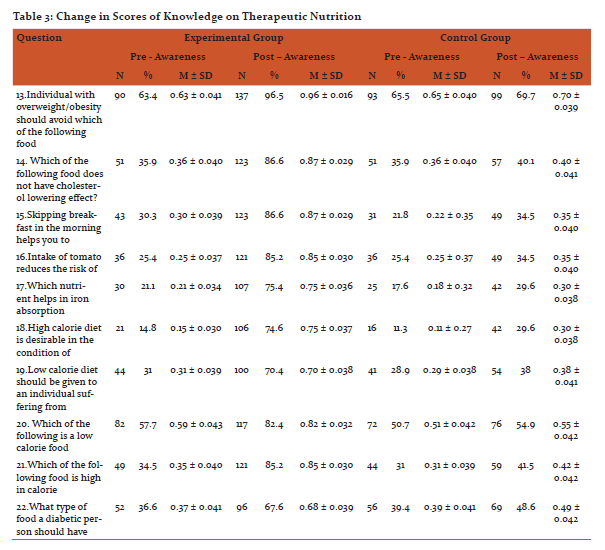
Discussion: Adolescents require the knowledge and support to develop a healthy lifelong relationship with food.[8] Nearly 50 per cent of adolescent girls aged 15–19 in India are underweight, with a body mass index of less than 18.5, and more than one quarter are underweight in 10 other countries. Such under-nutrition renders adolescents vulnerable to disease and early death and has lifelong health consequences.[9] The onset of over three fourths of eating disorders (76%) occurs between the ages of eleven and twenty.[10] In a study conducted among adolescents in Pune, reported prevalence of anaemia in 51% of girls which was statistically highly significant compared to boys (13%).[11] Overall, information and communication technologies have a potentially major role to play in health information systems. Technology in healthcare can improve access for geographically isolated communities; aid in data sharing; provide visual tools linking population and environmental information with disease outbreaks; and is an electronic means for data capture, storage, interpretation and management.[12] mHealth (mobile-health) is the use of mobile and wireless technologies to support the achievement of health objectives. mHealth can be utilized for a wide variety of purposes, including health promotion and disease prevention, health care delivery, training and supervision, electronic payments, and information systems.[13] One of the most promising aspects of mHealth is its potential for enhancing the smart integration of health services and the continuity of care across provider, place, and time by making information available at the right place and at the right time. Vast majority of mHealth interventions are currently implemented in either pilot programs or at limited scale, a growing number of mHealth systems are reaching significant scale and/or being adopted by national governments, including ministries of health (MOH) in countries like Rwanda, South Africa, Uganda, Ghana, Kenya, Tanzania, Malawi, Bangladesh and India.[14] Cole-Lewis and Kershaw (2010) found evidence to support text messaging as a tool for changing behaviour or improving clinical care outcomes in eight of the nine sufficiently powered studies they reviewed. The authors noted that these changes were found across different ages, ethnicities, and nationalities. Health promotion campaigns using mHealth technologies most frequently make use of text messaging technology to send information on pertinent health issues to target populations.[15] Health-related functions of text messaging interventions can include health behaviour reminders, prompts to schedule or confirm an appointment, notification of a laboratory result or health status report, requests for data, encouragement to engage in positive behaviours, or information and resources to improve self-efficacy. The goal of these interventions is to promote efficiencies in care management practices and, ultimately, improve individual and population health outcomes.[16] Overall, recent research on the use of text messages related to sexual health suggests that text messaging offers promise for reaching teens about health information, referrals, and testing reminders.[17]
Conclusion: Information, education and communication approaches were used in this study to reach the target groups. An intervention of mHealth as tool was used for imparting nutrition education by sending messages on general, therapeutic and, adolescent and adult nutrition to their mobile phones, an alternative choice of media already popular among college going girls instead of usual nutrition education practices. After imparting nutrition education, there was an increase in the general, therapeutic and, adolescent and adult nutrition knowledge of the experimental group when compared to the control group and statistically significant at 1% level. Mobile phones provided a new communication channel for health promotion and community mobilization. mHealth as a nutrition communication tool effectively increased nutritional knowledge among college going girls. mHealth and development of user friendly mobile apps for nutrition communication is very useful in imparting nutrition messages .
Acknowledgement: Authors expresses their gratitude and thanks to all the respondents of various academic institutions for their rendered cooperation and support in the successful completion of the study.Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
- Patil, R.S. (2011). “Impact of IEC activity on women’s knowledge through health exhibition arranged on women’s day”, National Journal of Community Medicine, Vol2 Issue 2 July-Sept, pp-260,261.
- Eat Well. (2011). “Review of policy actions, data available for their analysis and existing evaluations throughout Europe”. Deliverable 1.1 of Eat Well for the European Commission.
- McNulty Judiann. (2013). “Challenges and Issues in Nutrition Education”,
- Riley, Pamela. (2010). “mHealth: The Tool You Can’t Afford to Do Without.” Presentation from SHOPS and mHealth Alliance Hold Online Conference: Using Mobile Technologies to Improve Family Planning, Maternal Health and Newborn Services in the Developing World.
- Lenhart, Amanda. (2012). “Teens, Smartphones & Texting.” Washington, DC: Pew Internet and American Life Project.
- Rebecca Levine, Alison Corbacio, Sarah Konopka, Uzaib Saya, Colin Gilmartin, JoAnn Paradis, and Sherri Haas.(2015). “mHealth Compendium”, Volume Five. Arlington, VA: African Strategies for Health, Management Sciences for Health.
- Cole-Lewis, H., and T. Kershaw. (2010). “Text Messaging as a Tool for Behaviour Change in Disease Prevention and Management.” Epidemiologic Reviews, vol. 32, no. 1, pp. 56–69
- www.sportsdietitians.com
- UNICEF. ( 2012). “Progress for Children: A report card on college going s”, pg-6, 20
- National Association of Anorexia Nervosa and Associated Disorders. (2008). “Facts About Eating Disorders”. Retrieved on May 31, 2008 from National Association of Anorexia Nervosa and Associated Disorders website: www.anad.org/22385/index.html (www.californiateenhealth.com)
- Mane, S.V. S.R. Agarkhedkar, D.S. Karwa, V. Pande, S.S. Singhania, G.R. Karambelkar. (2012). “Study of risk factors for lifestyle diseases among adolescents in Western India,” Intl Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Sciences 3(4): 224–228.
- Don Lewis, Health Informatics Consulting , Nicola Hodge Health Information Systems Knowledge Hub, School of Population Health, University of Queensland, Duminda Gamage Research Assistant Professor Maxine Whittaker Health Information Systems Knowledge Hub, School of Population Health, University of Queensland. (2011). “Understanding the role of technology in health information systems”, Health Information Systems Knowledge Hub, Working Paper series, Number 17, June 2011.
- World Health Organization, (2011): mHealth New horizons for health through mobile technologies, Global Observatory for eHealth series - Volume 3.
- mHealth Compendium. (2015). Vol5, USAID/AFR.
- Cole-Lewis, H., and T. Kershaw. (2010). “Text Messaging as a Tool for Behaviour Change in Disease Prevention and Management.” Epidemiologic Reviews, vol. 32, no. 1, pp. 56–69
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. (2014). “Health Resources and Services Administration. Using Health Text Messages to Improve Consumer Health Knowledge, Behaviors, and Outcomes: An Environmental Scan”, Rockville, Maryland: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
- Gard, Jennifer C., and Robert D. Furberg. (2012). “Texting, Sexual Health, and Teens: A Systematic Review of SMS-Based Health Behavior Change Interventions.” Poster presented at Sex::Tech 2012—5th Annual ISIS Conference on New Media, Youth & Sexual Health, San Francisco, CA. Available at http://www.rti.org/files/sextech-gard_poster.pdf
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License