IJCRR - 1(2), November, 2009
Pages: 23-37
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
ASSESSMENT OF THE TREATMENT PATTERN, CLINICAL OUTCOME, AND QUALITY OF LIFE IN PATIENTS WITH BLADDER OUTLET OBSTRUCTION IN A TERTIARY CARE TEACHING HOSPITAL
Author: R.Rajesh, Nitha.V, Sureshwar Pandey, Arun chawla
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Aim: This study provides an insight into the assessment of the treatment pattern, clinical outcome and quality of life in patients with Bladder outlet obstruction and to assess the safety and efficacy of (0.2 mg) and (0.4 mg) tamsulosin in female patients with Bladder outlet obstruction in a tertiary care teachinghospital. Method: Institutional ethics committee approval was obtained from kasturba hospital, Manipal for conducting this study.This was a randomised controlled study conducted for eight months at Dept. of Urology, Kasturba Hospital, Manipal. Inclusion criteria were all male bpatients in age group greater than 45years with bladder outlet obstruction symptoms due to BPH and all the female patients aged greater than 35 years with bladder outlet obstruction were included for the study. Exclusion criteria were allMale patients with Stricture urethra, acute cystitis, Carcinoma of prostate, Neurogenic voiding dysfunction and all female patients with Pelvic masses, previous pelvic surgery, and acute cystitis were excluded from the study. The American Urological Association Symptom Score (AUASS) was adopted to assess the severity of urinary symptoms and to check the effectiveness of the treatment. The percentage of improvement of treatment was also assessed in terms of both objective and subjective parameters like Maximum Flow Rate (MFR), Post Voidal Residual Volume (PVR) and bladder thickness. Female patients were randomised into two groups? first group of patients receiving (0.2 mg of tamsulosin) while second group of patients receiving (0.4 mg of tamsulosin) daily for a period of months with periodic follow up at 2nd , 4 th and 8 th week, assessed with IPSS (International Prostate Symptom Score) and uroflowmetry andultrasonography at 8 th week. The quality of life in patients with bladder outlet obstruction was evaluated by using the quality of life questionnaire.
Results: A total number of 177 patients diagnosed with bladder outletobstruction were aged between 55 to 65 years and males (n=152) predominated over females (n=25). Weak stream urinary symptoms were found to be the highest complained symptom. The co morbidities associated with bladder outlet obstruction was Hypertension. Surgery was the main line of treatment in patients with bladder outlet obstruction. The drug tamsulosin was the most implicated drug in the medical group. The most common surgical procedure performed was transurethral resection of the prostate. The safety and efficacy of tamsulosin in female patients showed that patients were having AUASS score between 8-19 (moderate) before treatment and most of them showed an improvement in the score from moderate to mild (1-7) aftertreatment. The subjective parameters showed that the female patients had an MFR value of < 15ml/s before treatment and have improved after treatment from < 15ml/s to >15ml/s. The PVR values were >50ml in all patients before treatment and < 50ml after treatment. The bladder thickness showed a reduction from > 5mm to < 2.5mm. Our results show tamsulosin to be very effective in the management of bladder outlet obstruction in female patient if detected early. Conclusions: In female patients? use of tamsulosin was found to be a very safe, well tolerated showing significant improvement in urinary outflow symptoms, reducing post void urinevolume and decreasing IPSS with minimal tolerable adverse events. The correct and timely diagnosis of bladder outlet obstruction in women was difficult, since clinical features are similar to those of other voidingdisorders and diagnostic modalities are often inconclusive or even misleading.
Keywords: bladder outlet obstruction, Medical management, tamsulosin, urodynamics.
Full Text:
Introduction
Bladder outlet obstruction (BOO) is a blockage at the base of the bladder that reduces or prevents the flow of urine into the urethra, the tube that carries urine out of the body1 . Numerous gender-specific etiologies are responsible for bladder outlet obstruction. BOO may be induced by specific functional and anatomic causes. The resulting obstruction frequently produces lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), although the degree of bother by LUTS is highly variable and not predictable on the basis of the specific inciting etiology2 . Induced LUTS symptoms may be predominantly obstructive, irritative, or often a combination of both. Typically, obstructive symptoms include hesitancy, sensation of incomplete bladder emptying, diminished urinary stream, and post voiding urinary dribbling.Irritative complaints include urinary urgency, frequency of urination, occasional dysuria, and nocturia. Rarely are symptoms related to BOO isolated; often the individual experiencing LUTS presents with a variety of mixed symptoms of obstruction and irritation. BOO may also occur in the complete absence of symptoms and be first identified in the scenario of urinary retention or decompensation of the upper urinary tracts. BOO often occur in both male and females; it is more common in aging men. urodynamic evaluation and pressure flow evaluation is the gold standard diagnostic tool, other modalities may also be used, including post void residual analysis, urinary flow rates, cystoscopy, and selected radiologic ones. Patient self-appraisal of symptoms using various inventories such as the American Urologic Association Symptom Index3 or the International Prostate Symptom Score is relevant to the initial assessment and subsequent follow up. Analysis of secondary symptoms of obstruction in women is often performed using a subjective symptom appraisal and is determined urodynamically, assessing the pressureflow relation during voiding. The complete assessment of LUTS arising from BOO often includes several of these modalities to fully define the obstructive impact on the individual's urinary function and quality of life4 . There are a number of treatment options in both male and female patients with bladder outlet obstruction. The treatment options in male patients includes watchful waiting5 (A strategy of management in which the patient is monitored but receives no active treatment), medical treatment which includes alpha blocker therapy which inhibit contraction of prostatic smooth muscle and finasteride therapy, an enzyme inhibitor that lowers prostatic androgen levels and decreases prostate size, surgical treatment which includes balloon dilation (A catheter with a balloon at the end is inserted through the urethra and into the prostatic urethra. The balloon is then inflated to stretch the urethra narrowed by the prostate), Transurethral Incision of the Prostate (TUIP) an endoscopic surgical procedure in which patients with smaller prostates (<30 g) is inserted through the urethra to make one or two cuts in the prostate and reduce the constriction on the urethra, Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) is an surgical removal of the prostate's inner portion by endoscopic approach through the urethra. This is the most common and the gold standard of treatment and open prostatectomy is a surgical removal of the prostate via an incision in the lower abdomen. The main treatment options in females are urethral dilatation under local or regional anaesthesia. Alpha blockers is currently considered the preferred treatment alternative for those individuals who lack absolute indications for surgery. Although alpha blockers have proved to be very efficacious in males6, 7 but very few studies are done to prove the efficacy of alpha blocker in females.8 This observational, cross sectional descriptive study provides an insight into the assessment of the treatment pattern, clinical outcome and quality of life in patients with Bladder outlet obstruction in a tertiary care teaching hospital.
Material and Methods
The study was approved by the Institutional ethics committee at kasturba hospital, manipal. A suitably designed Informed Consent Form (ICF) in different languages namely English, Kannada and Malayalam was prepared and used for the purpose of the study. In order to record the data for the study, a separate Case Record Form (CRF) was designed and used, which contains the details of the patients demographics, medical history, medication history, final diagnosis, laboratory investigations, study specific investigations, patient outcome analysis chart, adverse event reporting card, discharge medication and details of follow up visits. The American Urological Association Symptom Score3 (AUASS) was used to assess the severity of urinary symptoms and to check the effectiveness of the treatment. The AUA symptom index questionnaire consists of 7 questions. For the purpose of this study questions 2, 4 and 7 were assigned to irritative symptoms, while questions 1, 3, 5 and 6 were assigned to obstructive symptom sub scores. Total scores were classified as mild 0 to 7, moderate 8 to 19 and severe 20 to 35 symptoms, as recommended by the AUA measurement committee3 . This questionnaire has been adopted worldwide and it is also known as the International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS). The quality of life questionnaires4 were classified as delighted with score (0), pleased with score (1), mostly satisfied with score (2), mixed with score (3), mostly dissatisfied with score (4), unhappy with score (5) and terrible with score (6) was used to assess the quality of life of the patient with bladder outlet obstruction.This was a randomised controlled study conducted in the Dept. of Urology of Kasturba Hospital, Manipal from September 2008 to April 2009. Our first step was to identify the female patients with bladder outlet obstruction and male patients with BPH during ward rounds or with the help of the physician. Once the patient was identified, they were enrolled according to the study criteria and subject information sheet was explained in detail to the patient or patient?s legally acceptable representatives and written inform consent was obtained from qualified patients prior to their enrolment. A detailed history, clinical examination, study specific investigations which includes Maximum Flow Rate (MFR), Post Voidal Residual Volume (PVR) and bladder thickness was done and the follow up details for all the patients was recorded in the CRF followed by assessment of American Urological Association symptom score (AUASS). The treatment patterns were analyzed with respect to medical treatment or surgical procedures adapted to the patient. Medical treatment includes the various drugs like alpha blockers, 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, and combination of both or sometimes anticholinergic and the surgical procedures include Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP), cystoscopy and dilatation, bladder neck resection etc. The incidence of bladder outlet obstruction was obtained in terms of gender and age group wise distribution. The occurrences of urinary symptoms were analyzed based on the number of patients presenting with each symptoms. The co morbidities most commonly associated with bladder outlet obstruction were assessed based on number of patients presented with co morbidities. The patterns of treatment the patient received such as medical or surgical treatment and drug class implicated, compliance, benefit and adverse effects of each therapy were analyzed. Outcome analysis of different treatment patterns were based on percentage of improvement in the AUAS score, MFR (>25ml/s), bladder wall thickness (<2.5mm) and PVR values (nil) after treatment. Female patients were randomised into two groups? first group of patients receiving (0.2 mg of tamsulosin) while second group of patients receiving (0.4 mg of tamsulosin) in order to assess the safety and efficacy of 0.2 mg and 0.4 mg of tamsulosin in female patients with bladder outlet obstruction. The clinical outcome of this therapy in terms of both subjective and objective improvement was evaluated by estimating the improvement in the AUASS, MFR, and ultrasound reports like bladder wall thickness and PVR values, before and after treatment in both groups and the quality of life in the female patients with bladder outlet obstruction was evaluated by using the quality of life questionnaire.
Results
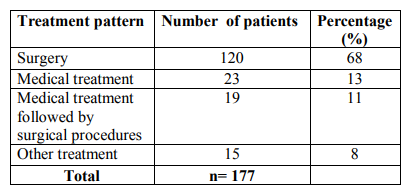
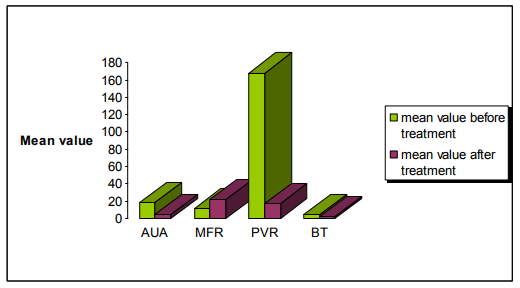
A total of 177 patients (n=152) males with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) as the risk factor for causing bladder outlet obstruction and (n=25) females with bladder outlet obstruction (BOO) were included in the study. Male predominance was observed over females. Only females? patients were studied to assess the safety and efficacy of 0.2 mg and 0.4 mg of tamsulosin with bladder outlet obstruction. There was difference in the mean age in years + standard deviation of patients with males (62.16 + 11.233) with that of females (53.76 + 9.418). Majority of bladder outlet obstruction patients were aged between 55 to 65 years. Results are summarized in Table 1. In the present study, the most severe obstructive urinary symptoms associated with bladder outlet obstruction were weak stream (72%) followed by irritative urinary symptoms nocturia (49%) and frequency (45%) as presented in Table 2. our study has detected a higher prevalence of hypertension (28%) as co morbidities associated with bladder outlet obstruction followed by diabetes (13%), respiratory diseases (6%), cardiac diseases other than hypertension (5%) and the least presented comorbidities associated with bladder outlet obstruction was parkinsonism as summarized in Table 3. Table 4 shows the various treatment pattern associated with bladder outlet obstruction in our study and results show that maximum number of patients were on surgical treatment (68%) followed by medical treatment (13%), medical treatment followed by surgical procedures (11%) and other treatment (8%) such as watchful waiting and life style modifications. The drug class most commonly prescribed in medical treatment was alpha blockers (55%) followed by anticholinergics (14%), combination treatment with alpha blocker and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors (14%), 5-alpha reductase inhibitor alone (5%) as summarized in Table 5. In our study tamsulosin followed by combination of Tamsulosin + dutasteride was the most implicated drug prescribed in the medical treatment; Table 6. A total of 139 patients underwent various surgical procedures, of which 110 patients had underwent transurethral resection of prostate, of which 28 patients had acute retention and had undergone catheterization for retention. 19 patients had undergone cystoscopy and dilatation and 10 patients had undergone bladder neck resection as there was reoccurrence of symptoms within few months or years as summarized in Table 7. In our study, the results of both objective and subjective parameters for all types of treatment in the bladder outlet obstruction showed that highest percentage of improvement in the surgical group i.e. 69% improvement in the (AUASS) American urological association symptom score, 70% improvement in the (MFR) Maximum flow rate values, 74% improvement in the (PVR) Post Void Residual Volume and 78% improvement in the (BT) bladder thickness as summarized in table 8. We analyzed the safety and efficacy of 0.2 mg and 0.4 mg of tamsulosin with bladder outlet obstruction. The results showed that patients were having AUA score between 8-19 (moderate) before treatment and all of them showed an improvement in the score from moderate to mild (1-7) after treatment. Similarly the subjective parameters showed that the female patients had an MFR value of < 15ml/s before treatment and have improved after treatment from < 15ml/s to >15ml/s. The PVR values were >50ml in all patients before treatment and < 50ml after treatment. The bladder thickness showed a reduction from > 5mm to < 2.5mm. No suspected adverse drug reactions were reported during the study period. The results of the quality of life questionnaire showed that most of the patients were unhappy by their disease state before treatment and mostly satisfied after treatment. There was a significant improvement in the urinary symptoms after treatment in both groups as shown in the figure 1.
Discussion
Bladder outlet obstruction (BOO) is becoming an increasingly recognized entity over the past several years. The goal of treatment of bladder outlet obstruction is primarily to provide a rapid and sustained improvement in lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and to reduce the long term complications. LUTS associated with BOO are a common disorder in urology. Surgical removal of prostate tissue or pharmacological prostate/bladder neck smooth muscle relaxation with alpha1AAR antagonists relieves outlet obstruction but does not improve irritative symptoms.9 Tamsulosin and nonselective subtype antagonists have the ability to relieve obstructive and irritative symptoms in men, while in women there is also some evidence for this. Although, recent studies suggest that it is an under diagnosed cause of female lower urinary tract symptoms.10 our study showed that the male patients were having Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) as the main risk factor for BOO. Symptomatic BPH is thought to be due to bladder outflow obstruction and is often referred to as lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of BOO11. This study systemically explored the treatment pattern and clinical outcome of treatment in patients with BOO in the Urology Department of Kasturba Hospital, Manipal. A total of 177 patients with BOO were evaluated during the eight month study period. On studying the overall gender wise distribution of the 177 patients with BOO, it was observed that there was male (n=152) predominance over female (n=25). This was because of under diagnosis and failure of the female patients to visit the Urology Department. In males, the occurrence of BOO was more common because gonadal androgens play a major role. The hormone testosterone is converted to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in males as the age progresses and this DHT has a pivotal role in the development of BPH. This observation was consistent with observation made by McConnell12 which revealed about a relationship between DHT and BPH. The male to female ratio was 63:1 with a mean age of 62.16 + 11.23 years for males and 53.76 + 9.41 years for females. A study by Nunzio et al5 showed similar results with males having mean age 64.5 + 7.6 years and a study by Pummangura and Kochakarn13showed that mean age of females affected by bladder outlet obstruction is 45.3 + 12.9. In this study, majority (42%) of the patients with BOO were in the age group of 55-65 years. This was because the chance of occurrence of this disease increases with the progression of age. Verhamme et al14 has observed that BPH is one of the most common condition associated with ageing men and approximately 40% of men are affected at the age fifties. The study patients were evaluated for the distribution of obstructive and irritative urinary symptoms with BOO. However, in our study these symptoms, which were mainly of the obstructive type (weak urinary stream), were reported. This finding is in accordance with the study carried out by Lee et al15 which showed a similar observation with weak stream as the most commonly observed obstructive urinary symptom. The result of our study further supports the co morbidity between Hypertension and bladder outlet obstruction. The prevalence of BPH and arterial Hypertension increases with age and hence both are frequent disease state in the elderly people with bladder outlet obstruction. This study result was consistent with a study carried out by Nicolas et al16 which confirms that there is a statistically significant relationship between Hypertension and LUTS secondary to BPH and correlation between mean blood pressure and prostate size. In our study majority of the patients had undergone surgery for bladder outlet obstruction because their urinary symptoms were moderate to severe in AUA index score and also patients presented with reoccurrence of urinary symptoms which suggestive of clear indication for surgery. This may be due to the fact that the treatment pattern followed was similar to the AUA guidelines in the management of Bladder outlet obstruction and also the European Urology guidelines on BPH. As per the guidelines, watchful waiting is recommended for patients with mild symptoms, medical treatment for patients with mild to moderate symptoms and surgery for patients who failed medication or conservative management and who have moderate to severe symptoms and/or complications of BPH. Although in our study men with LUTS due to BPH are generally managed with watchful waiting or medical therapy, some of the patients presented with progressive disease that can result in symptom deterioration, acute urinary retention, urinary tract infection, renal failure, and thereby indicated for surgery. Our study results showed that majority of the patients were prescribed with Tamsulosin, in the treatment of BOO and several studies have shown its superiority for treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms associated with Bladder outlet obstruction. Recently tamsulosin was found to be effective in patients with neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction; the drug decreased the maximal urethral pressure significantly in the long term follow up and improves cystometric parameters related to bladder storage and emptying17 . Interestingly, in our study it is preferred by the physicians because of the propensity to cause adverse drug reaction with alpha blocker is comparatively less with that of other classes of drugs. Transurethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) is the gold standard of treatment for BPH. In our study most of the patients with BOO in whom BPH was the risk factor had bothersome BPH symptoms refractory to medical treatment and because of the symptom severity and reoccurrence of symptoms there was a clear indication for transurethral Resection of Prostate surgery. This finding is consistent with the European Urology guidelines where it is clearly indicated that TURP is the most frequently performed surgical procedure for those patients who have bothersome symptoms.18 Most of the female patients in our study were presented with urethral and meatal narrowing, which causes obstruction in them and in these patients cystoscopy and urethral dilatation has been preferred as an empirical treatment. Bladder neck resection surgery has been preferred because of reoccurrence of symptoms. Critical analysis of our result data very clearly illustrates the safety and efficacy of tamsulosin in medical management of bladder outlet obstruction. Being an uroselective antagonist it controls both irritative and obstructive symptoms thereby giving a total therapeutic effect in relieving urinary symptoms. The result of our study in comparable to many international studies conducted. Abrams et al 19 in their randomized placebo control clinical trial on 296 patients found tamsulosin to be well tolerated drug showing significant improvement in UFR and symptoms score. Lee et al 20 from Korea found tamsulosin to be a safe drug showing statistically significant improvement in urine flow and symptom score as compared to placebo. The Japanese study conducted by Kawabe et al21 and the Chinese study conducted by Yan Jun et al22 showed results similar to our result. Our study showed that AUA score decreased from 23.9 to 16.1 after treatment with tamsulosin, mean MFR was 11 ml/s before treatment and 22 ml/s after treatment with tamsulosin. Similarly, there was an improvement in PVR and bladder thickness as early as 2 nd week and improvement was maintained throughout the treatment period. The improvement was seen both in 0.2 mg and 0.4 mg tamsulosin after treatment. The improvement was seen both in IPSS and urodynamic parameters. Tamsulosin was found to be very effective, safe and well tolerated drug with no significant differences with 0.2 mg and 0.4 mg as far as the vital signs and adverse events were concerned. Quality of life improved among the patient prescribed with tamsulosin due to improved flow rate and decreased symptom score. Many of the patients in our hospital were prescribed tamsulosin for management of their features of prostatism. In our study about 70% of patients taking Tamsulosin showed significant overall improvement in both objective and subjective parameters.
Conclusions
The AUA symptom index score may be useful as a bothersomeness index in women with bladder outlet obstruction. A complete urodynamic evaluation is essential for making the diagnosis, although standard urodynamic definitions are still lacking. Further epidemiological and pathophysiological investigations are needed to evaluate the causes and risk factors for bladder outlet obstruction in women. Better understanding the pathophysiological mechanisms associated with bladder outlet obstruction in women may provide the possibility of using appropriate diagnostic and treatment modalities, thus, avoiding any unnecessary intervention.
Acknowledgements
The author?s wishing to thank staff of urology department and administrative staff of Kasturba Medical College, Manipal University, Manipal for their technical support and encouragement.
Table.1.Age group and gender wise distribution of Bladder outlet obstruction.
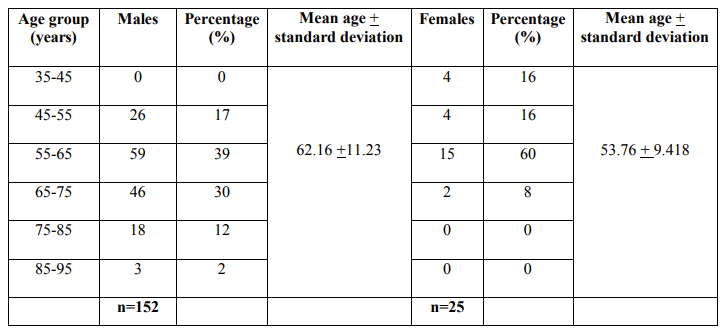
Table.2.The distribution of obstructive and irritative urinary symptoms associated with bladder outlet obstruction.
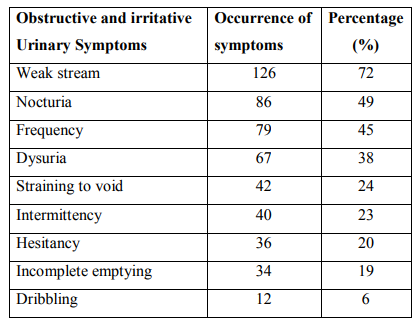
Table.3.Co morbidities associated with bladder outlet obstruction.

Table.4.Treatment pattern associated with bladder outlet obstruction.
.5. Drug Class most commonly prescribed in patients with bladder outlet
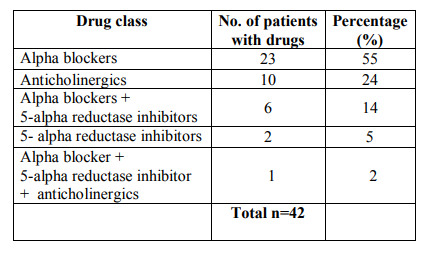
Table.6.Drugs implicated in the medical treatment with bladder outlet obstruction.

Table.7.Surgical procedures performed in bladder outlet obstruction.
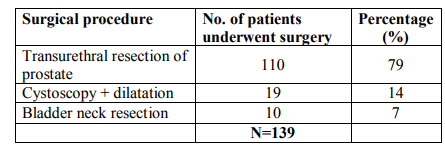
Table.8. Objective and subjective improvement for all types of treatment in bladder outlet obstruction.
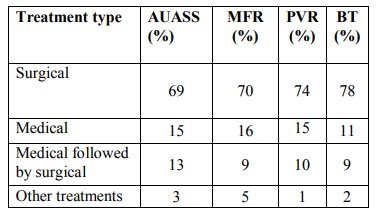
Figure 1 Safety and efficacy of tamsulosin in female patients with bladder outlet obstruction.
? AUA - American Urological Association symptom score
? MFR – Maximum Flow Rate
? PVR – Post Void Residual Volume
? BT – Bladder Thickness
References:
1. Bladder outlet obstruction. Medline plus Medical Encyclopaedia. [Online]. 2008 [cited 2009 Jun 2]; Available from: http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/en cy/article/002238.htm
2. Zderic, S. A., Chacko, S., DiSanto, M. and Wein, A. J.: Voiding function: relevant anatomy, physiology, pharmacology, and molecular aspects. In: Adult and Edited by J. Gillenwater, J. Grayhack, S. Howard and M. Mitchell. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkin. Pediatric Urology, 4th ed. 1061– 1114, 2002
3. Barry, M. J., Fowler, F. J., Jr., O?Leary, M. P. et al: The AmericanUrological Association symptom index for benign prostatic hyperplasia. Measurement Committee of the American Urological Association. J Urol, 148: 1549, 1992
4. Kupelian V, Wei JT, O?Leary MP, Kusek JW, McKinley JB. Prevalence of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms and effect on quality of life in a racially and ethnically diverse random sample: The Boston Area Community Health Survey. Archieves of Internal Medicine 2006; 166 (21): 2381- 2387.
5. Nunzio C, Franco G, Rocchegiani A, Iori F, Leonardo C, Laurenti C. The evolution of detrusor over activity after watchful waiting, medical therapy and surgery in patients with bladder outlet obstruction. The Journal of Urology 2003; 169: 535-39.
6. Dunn, Christopher J, Matheson, Anna, Diana M. Tamsulosin: a review of pharmacology and therapeutic efficacy in the management of lower urinary tract symptoms: Drug evaluation. Drugs and aging 2002; 19(2):135-161.
7. Arnold EP. Tamsulosin in men with confirmed Bladder Outlet Obstructive Syndrome: A clinical and urodynamic analysis from a single centre in New Zealand. BJU International 2001; 87(1): 24-30.
8. Rahardjo D, Soebadi DM, Sugandi S, Birowo P, Djati W, Wahyudi I. Efficacy and safety of Tamsulosin hydrochloride compared wiyh doxazozin in the treatment of Indonesian patients with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms due to Benign Prostrate Hyperplasia. International Journal of Urology 2006; 13(11): 1405-9.
9. Blue, D., Zinner, N., Grino, P., Crager, M. and Ford, A.:RO700004, a selective alpha1A-adrenoceptor antagonist, does not improve lower urinary tract symptoms in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol, suppl., 167: 265, abstract 1044, 2002
10. Athanasopaulose A, Gyftopaulose K, Giannitsas K, Fisfis J, Perimenis P. Combination treatment with an alpha blocker plus an anticholinergic for bladder outlet obstruction: A prospective, randomized controlled study. Journal of Urology 2008; 169: 2253 - 56.
11. Speakman MJ. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. European Urology 2001; 39 (3): 13-19.
12. McConnell JD. Prostatic growth: new insights into hormonal regulations. British Journal of Urology 1995; 76 (1): 5-10.
13. Pummangura N and Kochakarn W. Efficacy of Tamsulosin in the Treatment of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) in Women. Asian Journal of Surgery (2007); 30 (2): 131-7.
14. Verhamme KMC, Dieleman JP, Bluemink GS, Sturkerboom MCJM. Incidence and prevalence of lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia in primary care-The triumph project. European Urology 2002; 42: 323-28.
15. Lee KS, Choo MS, Yoo TK, Park HJ, Jeong H. Efficacy and safety of tamsulosin for the treatment of nonneurogenic voiding dysfunction in female: an 8 week prospective study. Urotoday ICS 2006; 1: 379-380.
16. Nicolas TJ, Tornero RJ, Banon PV. Relation between hypertension and clinical cases of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Archivos Espanoles Urologia 2003; 56 (4): 355-8.
17. Morant SV, Reilly K, Bloomfield GA, Chappel C. Diagnosis and treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of overactive bladder and bladder outlet obstruction among men in general practice in the UK. International Journal of Clinical Practice 2008; 62: 668-9.
18. Jean JCMH, Alivizatos G, Maderbacher S, Perachino M. EAU Guidelines on Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. European Urology 2001; 40: 256-63.
19. Abrams P, Schulman CC. Vaage S and the European Tamsulosin Study Group. Tamsulosin, a selective α1c, - adrenoreceptor antagonist: a randomized, controlled trail in patients with benign prostatic `obstruction' (symptomatic BPH). Br J Urol 1995; 76; 325-36.
20. Lee E, Lee C. Clinical comparison of selective and nonselective α1A adrenoreceptor antagonists in benign prostatic hypetplasia. Studies on tamsulosin in a fixed dose and terazocin in an escalating doses in Korean patients. Br J Urol 1997: 32; 210-213.
21. Kawabe K, Nijima T, Ueno T, Takimoto Y, Aso Y, Kato H. Use of an α1 blocker, YN617 in the treatment of benign prostatic hypertrophy. J Urol 1990; 144: 908-911
22. Yan-Jun N, Ying Lu G, Fang Liu G et al. Clinical comparison of selective and non selective α1A adrenoreceptor antagonists for bladder outlet obstruction associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia. 3rd Asian Congress Urology 1996: 22: 301-7.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License