IJCRR - 2(12), December, 2010
Pages: 25-31
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
METHOD VALIDATION FOR ULTRAVIOLET SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC DETERMINATION OF DICLOFENAC
SODIUM IN HUMAN STRATUM CORNEUM BY SKIN STRIPPING METHOD USING MARKETED DICLOFENAC SODIUM TOPICAL FORMULATIONS
Author: S. S. Rawat, R. V. Mayee, V. A. Arsul
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:The Diclofenac sodium containing marketed gel, an emugel formulation and a spray formulation were applied on the skin. The release of Diclofenac sodium from transdermal gels and spray formulations was studied using the Tape stripping method. Diclofenac sodium exhibited distinct λmax in methanol at 285nm. A good linear relationship (r2=0.9787) was observed between the concentration ranges of 5-25 pg/mL. The relative standard deviation (RSD) and assay values obtained by two analysts were 0.36 and 99.50, 0.31 and 99.60, for D1 formulation, 0.53 and 98.21, 0.45and 98.23 for D2 formulation and 0.54 and 97.76, 0.30 and 97.83 for D3 formulation respectively. The percutaneous absorption of D1 formulation was found to be more than other two formulations. The percentage recovery values indicates that there no interference from the excipients present in the formulation. This demonstrates that the developed spectroscopic method is simple, accurate and reproducible and can be easily used for the routine quality control of Diclofenac sodium in human stratum corneum by tape stripping method.
Keywords: Diclofenac gel formulations, Diclofenac spray formulations, Tape stripping method, Validation
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Diclofenac Sodium is sodium 2-[(2, 6- dichlorophenyl)- amino]phenylacetate. It is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug applied to reduce inflammation and as an analgesic reducing pain in conditions such as arthritis or acute injury1 . It is freely soluble in methanol; soluble in ethanol (95%); sparingly soluble in water and in glacial acetic acid; practically insoluble in ether, in chloroform and in toluene2 . Literature survey revealed the availability of method of estimation of drug by Tape stripping method3 . But a quantitative determination method of diclofenac sodium in various gel formulations and spray formulation and their comparison was not validated. The aim of present investigation is to validate UV Spectrophotometric method for diclofenac sodium topical formulations and to develop a quality control tool for diclofenac sodium gel and spray formulation.
Experimental
Instruments
A UV Spectrophotometer (UV-1700): Chemito-Spectroscan UV 2600, Double beam UV Visible Spectrophotometer with a matched pair of 10 mm quartz cells were used for experimental purpose.
Materials Diclofenac
sodium API was procured as gift sample from Wockhardt Research Centre, Aurangabad. The obtained Diclofenac sodium was dissolve in methanol for experimental purpose. In present study, three commercial products of diclofenac, a commercially available marketed gel formulation (D1) containing diclofenac diethylamine 1% w/w which is equivalent amount of 1.6% w/w Diclofenac sodium, an emugel formulation (D2) containing 1% w/w diclofenac diethylamine which is equivalent amount of 1.6% w/w Diclofenac sodium and a spray formulation (D3) containing 1% w/w diclofenac diethylamine which is equivalent amount of 1.6% w/w Diclofenac sodium has been used for estimation. We compared their percutaneous absorption through skin from one of the topical preparations. The samples were procured from local market, Aurangabad.
Preparation of Standard Stock
Solution
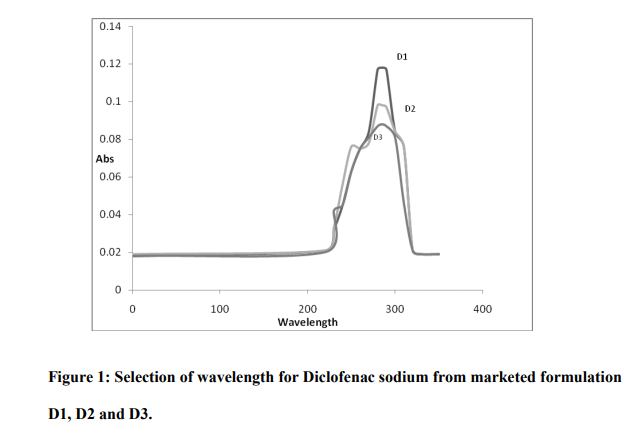
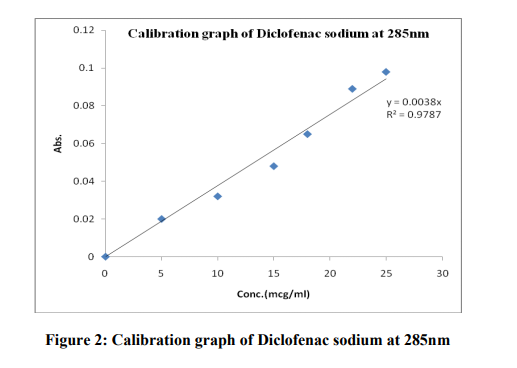
The standard stock solution was prepared by dissolving 0.2gm Diclofenac sodium in 200ml methanol to make final concentration of 100μg/ml. Different aliquots were taken from stock solution and diluted with methanol separately to prepare series of concentrations from 2-24 μg/ml. The λ max for Diclofenac sodium in methanol was found to be 285 nm. The calibration curve was prepared by plotting absorbance versus concentration of Diclofenac sodium4, 6 .
Method
Three Diclofenac sodium formulations (D1, D2 and D3) were applied on the skin. The diethylamine acts as penetration enhancer. The release of Diclofenac sodium from transdermal gels and spray formulations was studied using the skin stripping method. Tape stripping is a simple and efficient method for the assessment of quality and efficacy of cosmetical and dermatological formulations. The tape stripping method in its standardized form is well-suited to determine the dermatopharmacokinetics of topically applied substances. Before sampling the drug (D1) remaining on the site was removed by three cotton swabs to ensure complete removal of residual drug from the site. The pre-cut (1 sq. cm) adhesion tape was applied on site and mild force was applied to ensure the proper adhesion. The tape was removed and discarded.
Eight adhesion tape pieces were applied on the site area in same manner and each tape were removed using forceps so that complete removal of stratum corneum occurs. All 8 samples were collected in a single test tube with 60 ml of methanol in a 200-ml volumetric flask and dilute to volume with methanol. From this solution, suitable aliquots were prepared, then these dilutions were scanned in UV region and absorbances were noted at 285 nm and concentration was determined by linear regression equation. This method was repeated for D2 and D3 samples5, 8, and 9 .
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The tape stripping method for diclofenac sodium topical formulations was validated by studying the following parameters as ICH guide lines (ICH guide lines 1995) for method validation7 .
Linearity
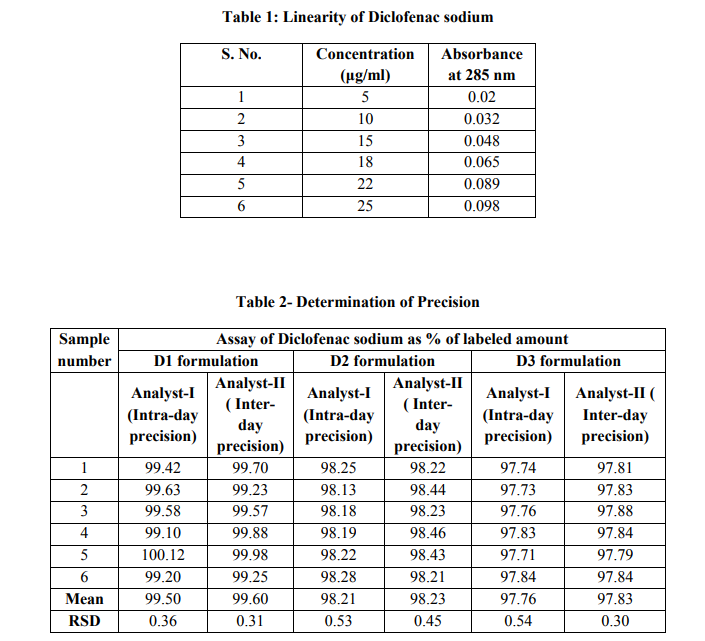
The linearity of the response of the drug was verified at 1 to 100 μg/ml concentrations, but linearity was found to be between 5-25 μg/ml concentrations. The equation of the calibration curve for Diclofenac sodium obtained y = 0.0038x, the calibration curve was found to be linear in the aforementioned concentrations. The correlation coefficient (r2 ) of determination was R = 0.9787(Table 1)
Precision
Assay of method precision (intraday precision) was evaluated by carrying out six independent assays of test samples of D1, D2 and D3 formulations. The intermediate precision (interday precision) of the method was also evaluated using two different analysts, systems and different days in the same laboratory. The relative standard deviation (RSD) and assay values obtained by two analysts were 0.36 and 99.50, 0.31 and 99.60, for D1 formulation, 0.53 and 98.21, 0.45and 98.23 for D2 formulation and 0.54 and 97.76, 0.30 and 97.83 for D3 formulation respectively. (Table 2)
Accuracy (Recovery test)
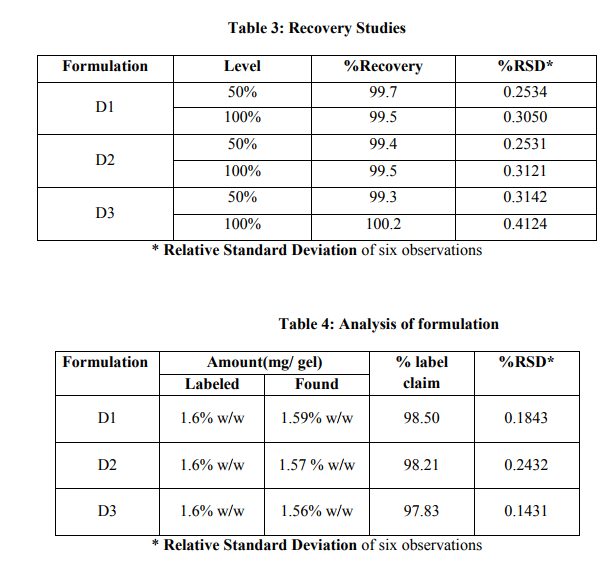
Accuracy of the method was studied by recovery experiments. The recovery experiments were performed by adding known amounts of the drug in the placebo. The recovery was performed at two levels, 50 and 100% of Diclofenac sodium standard concentration. The recovery samples were prepared in before mentioned procedure. Three samples of each marketed formulation (D1, D2 and D3) were prepared for each recovery level. The solutions were then analyzed, and the percentage recoveries were calculated from the calibration curve. The result of analysis the recovery studies presented in Table 3and 4. The percentage recovery values indicates that there no interference from the excipients present in the formulation that developed method is found to be sensitive, accurate, precise and most reproducible.
CONCLUSIONS
The equation of the calibration curve for Diclofenac sodium obtained y = 0.0038, the calibration curve was found to be linear in the aforementioned concentrations. The correlation coefficient (r2 ) of determination was R² = 0.9787. The relative standard deviation (RSD) and assay values obtained by two analysts? shows that there is no major variation in the results. The recovery was performed at two levels, 50 and 100% of Diclofenac sodium standard concentration. The percentage recovery values indicates that there no interference from the excipients present in the formulations. The percutaneous absorption of D1 formulation was found to be more than other two formulations. This demonstrates that the developed spectroscopic method is simple, accurate and reproducible, can be easily used as the routine quality control tool for Diclofenac sodium gel formulations.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors acknowledge Principal, Dr. Vedprakash Patil Pharmacy College Aurangabad, as well the Principal, Shri Bhagwan College of Pharmacy, N-6, Cidco, Aurangabad, India for providing facilities for conducting research. The authors also thanks to Wockhardt Research Centre, Aurangabad for providing the Diclofenac Sodium API.
References:
1. United States Pharmacopoeia, USP 24/NF 19, US Pharmacopoeial Convention Inc,2000, USA, pp.2149-2152. 2.
2. Indian Pharmacopoeia I (1996), Government of India Ministry of Human and Family Welfare Published by the Controller of Publication, Delhi. 3.
3. U.V.Sera, M.V.Ramana, In vitro skin absorption and drug release - a comparison of four commercial hydrophilic gel preparations for topical use. The Indian Pharmacist, 2006, 73, 356-360 4.
4. Agrawal, YK. and Shivramchandra K, Spectrophotometric determination of diclofenac sodium in tablets. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1991, 9: 97- 100.
5. Knudsen, EA. Isolation of dermatophytes from foot wear with adhesive tape strips. J, of Medical and veterinary Mycology 1986, 25; 59-61
. 6. Flynn, G.L., Shah, V.P., Tenjarla, S.N., et al., Assessment of value and applications of in vitro testing of topical dermatological drug products. Pharm. Res. 1999, 16, 1325-1330.
7. ICH-Q2R1, Validation of Analytical Procedures: Methodology International Conference on Harmonization of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use 1996, Geneva, Switzerland.
8. Pinkus H. Examination of the Epidermis by the strip method of removing horny layers. J Invest Dermatol 1951, 16; 383-386.
9. Mo, Z and Chen Z: UV spectrophotometric determination of compound diclofenac sodium injection. Yaowu Fenxi Zazhi., 1988, 8: 314-316.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License