IJCRR - 3(11), November, 2011
Pages: 13-22
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A COMPARISON BETWEEN PERCEIVED STRESS IN PATIENT WITH PEPTIC ULCER AND CONTROL GROUP AND DETERMINING THE EFFICACY OF STRESS INOCULATION TRAINING AMONG PRIMARY SCHOOL TEACHERS IN AMOL CITY OF IRAN
Author: Shohreh GhorbanshiroudiJavad Khalatbari, Mohammad Ebrahim Maddahi, Mina Salimi , Mohammad Mojtaba Keikhayfarzaneh, Fariba Abolghasemi
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:The role of stress in gastrointestinal diseases including peptic ulcer has been known since long
time ago. Recently some (such as Lazuras) believe that person's assessment and coping skills
have more important role than stress itself .
This research was designed to make a comparison between rates of perceived stress in teachers
with peptic ulcer vs those without peptic ulcer and determination of effectiveness of « Stress
Inoculation Training » program, on perceived stress in patients with peptic ulcer.
This was a cross-sectional study. Among 724 primary school teachers of Amol city, a sample of
300 people through «Cluster Sampling »was selected and among 43 people that had peptic
ulcer, two groups each included 15 people was choose , one group as case and the other as
control . Case group went on the program of « Inoculation Training against Stress ».
All sampling stages were randomized and the research design was pretest- posttest with control
group type. Perceived Stress was scaled by Interview and «Perceived Stress Scale \? PSS » in
case and control groups before and after the execution of the procedure on the case group. PSS
is normalized in Iran, By Sepahvand and Guilani and Zamani. The results were analyzed by
ANCOVA and Independent.
The outcome of the study showed that:
- Rate of stress in patients with peptic ulcer was more than control group.
- Training of inoculation against stress was effective in reduction of perceived stress in patients
with peptic ulcer.
- There were no statistical meaningful differences between male vs female in mean perceived
stress scales.
This study showed that inoculation training program against stress in patients with peptic ulcer
can reduce perceived stress.
Keywords: perceived stress, stress inoculation training, peptic ulcer, stress in teachers
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Since long before, the importance and impact of stressful life events in the psychological description of disease and health, was on the focus of consideration [1]. The more stress may result the higher possibility of impairment [2]. However, the way and amplitude of this role is still on debate [3], [4], [5] recently, the objective A COMPARISON BETWEEN PERCEIVED STRESS IN PATIENT WITH PEPTIC ULCER AND CONTROL GROUP AND DETERMINING THE EFFICACY OF STRESS INOCULATION TRAINING AMONG PRIMARY SCHOOL TEACHERS IN AMOL CITY OF IRAN Shohreh Ghorbanshiroudi1 , Javad Khalatbari1 , Mohammad Ebrahim Maddahi2 , Mina Salimi 1 , Mohammad Mojtaba Keikhayfarzaneh3 , Fariba Abolghasemi1 1Department of Psychology, Tonekabon Branch, Islamic Azad University, Tonekabon, Iran 2 Shahed University, Department of Psychology, Tehran, Iran 3Department of Psychology, Zahedan Branch, Islamic Azad University, Zahedan, Iran E-mail of Corresponding Author: s.shiroudi@toniau.ac.ir 14 International Journal of Current Research and Review www.ijcrr.com Vol. 03 issue 11 November 2011 measures of this relation is more on the focus of attention. In the newer points of view [6] the role of threatening situations associated with lack of necessary resources to deal with the situation is more crucial. The severity of perceived stress is one of the core models of health belief that based on learning theory of psychology [7], [8], [9]. Severity of perceived stress refers to person‘s belief on the acuity of stress. How high the amount and severity of perceived stress is, the possibility of reaction is higher [7].
There are three approaches about psychogenic stress concept: In the first approach that focused on environment and stress described as an event or strains of specific situations .events and situations that are threatening or harmful and produce tension as result , are called stressor[10],[11],[12] . In the second approach stress is considered as response and focused on person‘s reaction to stressors. From this point of view the tension that people feels, are called stress. The psychogenic and physical response to a stressor is called strains. In the third approach stress is a process that included stressors and strains too [6], [13], [1], [12].
Stress is a condition that is a result of interaction between person and environment and may cause an incoordinance in the necessities of a situation and biological, psychological and social resources of the person[1], [14],[6] . Four component of this introduction includes:
1. Stress reduces bio psychosocial power of the person for coping with effects of events and problematic situations.
2. Necessities for a situation refer to resources that are needed to coping to a stressful situation. For example having a powerful volition to reduce weight.
3. Whenever lack of balance between a situation necessities and the person resources is exist, the conflict comes up. This conflict can be due to lack of resources or lack of utilization of those resources.
4. Necessities, resources and conflicts are assessed in confrontation of environment. In Selye [15] definition stress is human general reaction to maladaptive and nonselective external events or in simple words disturbance in adaptive system and human body coping with external environment. He emphasized three phases in « General Adaptation Syndrome – G.A.S » [15] that include:
1. Alarm reaction
2. Resistance stage
3. Exhaustion stage Stress through nervous mechanisms mediated by neurotransmetters , endocrine reaction that mediated by hormones and also immune response that mediated by cellular and humeral immunity affect on the body[16]. Psychological and behavioral pattern of body reaction to stress refers to person reaction to stressor factors by utilizing of defense and confrontation mechanisms that finally make adaptation or maladaptation. Izeng (1988) and Oman(1993) relates the differences in the people sensitivity to stress to structural and cognitive processing differences . On the Oman opinion emotional fear is the subject that is response by flight or conscious avoidance. Prevention of these responses may result in anxiety.
Asadi Noghabi and colleagues divided stress symptoms to 5 groups: Physiological: dry mouth, sweating, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, obesity, dermatologic impairment, body pain [17].
Psychological: anger, fear, anxiety, depression, dysphasia, emotional instability, hopelessness Behavioral: insomnia , addiction to alcohol and substance , sexual problem Social: lack of communication Cognitive: decision making problem, memory and perception disturbance, concentration and judgment impairment Noghabi and colleagues (2007) have divided stressors to 2 groups: Biological: physiologic, pathologic, endocrine, hereditary and genetic, chemical Psychosocial: daily stressor factors, significant events, chronic stress [17]. Stress may affect the health directly (changing in physiology) or indirectly (by behavior). In the stressful situations people might behave so that the probability of making illness or being injured increases. Psychological factors by increasing secretion of acid may result in mucosal injury and finally ulcer in the stomach or duodenum.
Stress ulcers, are mucosal ulcers in the stomach and duodenum that follows some stressful events for instance burning, shock, septicemia, head trauma [18]. Digestive system ulcers may occur in the stomach or duodenum that is called peptic ulcer. Duodenal ulcer is more common than ulcer in the stomach [18]. Acute stress may cause physiological responses in some gastrointestinal organs. Stress can change the efficacy of superior esophageal sphincter and/or may reduce motility of anthrum of stomach that may result in nausea and vomiting [18]. Stress also in the small intestine may reduce functional motility and in the colon bioelectrical activity might increase under acute stress [18]. Affect of stress on small intestine and colon might be the responsible of intestinal symptoms of Irritable Bowel SyndromeIBS [19], [20]. Anxiety disorders may include physiological changes in the esophagus that can result in functional esophageal symptoms [21].Michenbaum have been proposed that modification of cognitive behavioral process may include three interwoven features:
1. Self – observation: observation of behavior by case him/herself
2. Beginning of new internal conversation
3. Learning of new skills Michnbaum have designed a three phase‘s model to training inoculation against stress: 1-Conceptual Phase : main focus is on the making a working relationship with the case. Establishing a therapeutic alliance between the case and therapist and training of problem solving routes is essential. Case will become alert of his/her role in the producing of stress. 2-Acquisition and rehearsal phase : emphases are on delivery of variety of behavioral and cognitive ways to execution in the stressful situations . As well as behavioral manner training (Relaxation, Social Skills, Time Management, Self Training), cognitive confrontation routs (survey on the adaptive and maladaptive behaviors and communication with internal conversation – self talking) are utilized. 3-application and follow through phase: focuses on transferring the modifications from therapeutic situation to real world. Emphases on self – talking and utilization of trained skills in the real life situations [22].
Training, practicing and application of trained subjects are essential contents of Michenbaum model . In a study on the married employees of Azad university of Tonekabon , « Inoculation Training Against Stress » was effective on reduction of marrietal conflics
on both men and women. In a research in China, there was a close association between fresh fruits and prepared foods intake with depression. They concluded that intervention through diet can be mixed with psychological preventive program among normal students of university [23]. In a study in Greece among telecommunication company employees, have been showed that negative affective states significantly can describe the association between stress and body pains [24] . In a research in the Austria, perceived stress and adaptation with it in adolescent was assessed and showed that there was a negative correlation between overcoming on stress with behavioral and affective problems. However, there were positive correlation between perceived stress and overcoming on it while utilizing maladaptive ways with coping problems, that in girls were stronger than in boys [25]. The correlation of perceived stress and function of the students are assessed on separate studies in Yazd,Iran [26], Tehran University [27], Amol, Iran [28] . All of them evaluate that its role was significant. The subject of a study in Medical Science University of Yasooj , Iran, was ways to confront to stress in patients with stomach and duodenal ulcer with the aim of determination and comparison of routs to confront to stress in these two diseases and control group was performed and concluded that people with disease utilizes the noneffective confrontation routs . Therefor , trying to modifying noneffective routs can be on the focus of attention to control the disease Relationship between life[29].
Stresses and digestive illness (peptic ulcer) was assessed in a study in Tabriz, Iran. In this study researchers have suggested the reduction of life stresses as a way to prevent the illness [30]. The efficacy of« Stress inhibition training – SIT» on decreasing of psychogenic pressure rate in female cancerous patients was assessed in a study in Razi Hospital in Rasht , Iran[31].In a study in Tehran ,Iran, Training the ways of confrontation to stress to parents of mental retarded children resulted in more satisfaction and less stress in them [32]. Training the strategies of confrontation to stress was effective on life satisfaction of spouses of Addicts. Assessed in a research in Kermanshah,Iran [33]. In the similar study it was effective on PTSD [34]. In a study in the Noor Hospital of Isfahan, Iran, application of confrontation routs to stress in patients that was under dialysis and had hypertension, affect on stress rate more than blood pressure[35].Training of problem solving skills and communication skill was effective on self steam of second level of high school girls in Lahijan,Iran[36]. Training of inoculation against stress had positive effect on quality of life of infertile women in Rasht,Iran [28]. Cognitive – Behavioral Therapy was effective on reduction of their depression and Anxiety [37]. Muscular relaxation and problem solving skills were effective on anxiety rate of high school girls students [38]. Perceived stress was effective on health quality of life in pregnant women in Makao,China. Sims , Gordon,Garcia, Mani, Campbell [23] ,in a study have showen a correlation between perceived stress and overeating. Nosek , Kennedy, Beyene , Taylor , Gilliss and Lee[39]in a study in North California found that severe perceived stress affect on the negative attitude to elderly and positive attitude to menopause was effective on menopausal symptoms . In a study on teachers there was an correlation between perceived stress and heart rate and gender differences was meaningful.
Burns,Carroll,Drayson,Whitham, and Ring[16]in a research found that there was a positive correlation between perceived stress and influenza incidence . In Taiwan , Chou, Avant,Kou, and Fetzer[40] showed that there was a correlation between severe nausea and vomiting in pregnancy and perceived stress that can be reduced by social support . In a survey in Midwest University, Reilly, Fitzpatrick and Faan[41], showed that there was a negative correlation between perceived stress and the sensation of belonging . In a study, Alfven,Ostberg,andHjern[42]the existence of a correlation between perceived stress and pain incidence in Sweden students was Shawn. In a study in Babol , Iran , an increase in salivary amylase enzyme in the condition of examination stress compared with post exam , was shown, [43] In a study in three hospital in the Babol and Sari , Iran , showed that Stressor events in patients with myocardial infarction was more than control group, [44].
METHOD
Sampling was cluster and randomized. Among all primary school teachers, 300 people, were selected as cluster sampling, among these people 73 people had perceived stress test higher than mean (26/605). From these, 43 people had peptic ulcer with approval of physician. Among them 30 people selected as random and divided in two equal groups each include 15 people. In order to make a comparison between patients with peptic ulcer and control group , among 43 people with peptic ulcer , 20 people was selected as random and among 257 people without peptic ulcer, 120 was selected as random, too. To compare perceived stress in men and women, among 178 female teachers, 90 people, and among 122 men teachers, 60 people all in random were selected. As sampling tool , Interview and «Perceived Stress Scale – PSS » that assesses perceived general stress during the last month and risk factors in behavioral disturbances , was applicator . This inventory have been already approved by Sepahvand,Guilani,Zamani [27]. This inventory has a questionnaire with 14 questions that each can receive scales of 0- 1-2-3-4, therefore final score may vary in the range of 0 to 56.
The inoculation against stress course for reduction of stress in patients with peptic ulcer performed through two and half month, based on weekly interval, each session 45 minutes, total 9 sessions. Order and amount of sessions and training subjects were included: 1st session: Rapport and Alliance and introduction to the rules of work 2nd session: Interactive component of stress and Reconceptualization 3rd session: Stress outcomes and relaxation training 4th and 5th session: Cognitive reconstruction
6th session: Problem Solving Training
7th session: Self - Direction Skills Training
8th session: Lack of Distractibility Training
9th session: Summation and providing systematized exposure to reality In this research inoculation training was independent variable, perceived stress is dependent variable and education , gender and age were control variables.
Findings (Data analysis )
For testing of first hypothesis, the effectiveness of inoculation against perceived stress on reduction of perceived stress in patients with peptic ulcer, at the beginning data of analysis of co – variance (ANCOVA) was assessed.
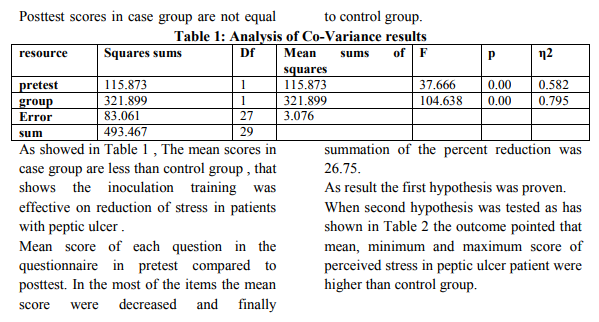
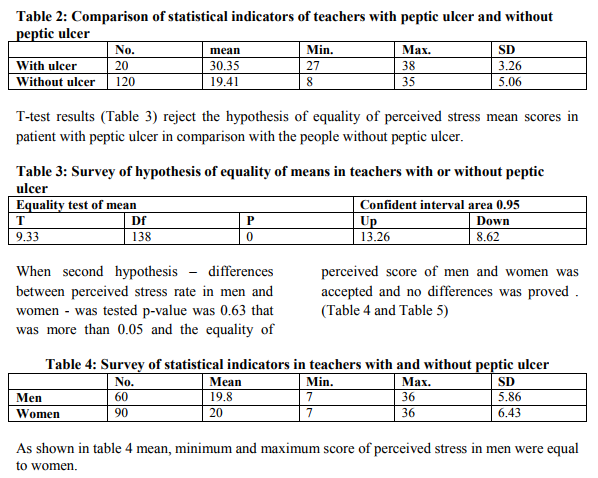
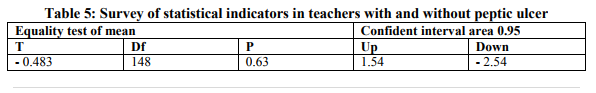
As shown in table 5 the equality of perceived stress score of men and women was accepted (p=0.63 > 0.05). Data gathered from completed inventories before and after inoculation training procedures against perceived stress for reduction it, were used to analysis by SPSS [45] from many different features. The Accuracy of three designed hypothesis were tested.
DISCUSSION
This research performed with three hypotheses: First, inoculation against perceived stress training is effective on diagnostic symptoms of peptic ulcer disease. Survey and analysis of hypothesis showed that the mean crude scores in stress inventory in case group after execution of training inoculation against perceived stress (posttest results) , in comparison with pretest , were decreased . This finding had similarity to other researches in literature. Second, perceived stress in teachers with peptic ulcer is different from those without peptic ulcer. Findings showed that mean perceived stress in teachers with peptic ulcer was statistically meaningful higher than those without peptic ulcer. This finding had similarity to findings of other researchers in the most studies in the world. Third, perceived stress in men vs women teachers are different. Considering the equality of means in two independent groups in perceived stress test, was not approved. This finding was different from the findings of other researchers. Limitations: Absence of follow up of cases was among limitations. Considering that acceptance and application of new skills need time, probably data from follow up could approve the research findings [22]. Another limitation was cases falling down; however researcher had her best struggle to conserve them. RESEARCH SUGGESTIONS - In the future researches consider the time to follow up the findings. - Training of these skills on community is considered as a necessity. - The role of financial problems as a stressor in teachers, in the future researches, could be considered. - In the future researches pay more attention to behavioral assessments and by using the behavioral lists that measure correlation of negative and positive interactions evaluation during therapy performs.
References:
1. Cox, T. (1978).Stress, Baltimore University Park press.
2. Abramson, L.Y., Selligman , M.E.P and Teasdale, J. D. (1978) , learned helplessness in humans : critique and information, journal of abnormal psychology, 87,49-74.
3. Averill, J.R. (1973), personal control over aversive stimuli and its relationship to stress. Psychological bulletin, 80,286-303.
4. Baer, P.E., Garmezy, L.B. , McLauchlin, R.J., Pokorny, A.D., and Wernick ,M.J.(1987) Stress, coping , family conflict , and adolescent alcohol use . Journal of behavioral medicine, 10, 449-446.
5. Banduran , A. (1986) , Social foundations of thought and action: a social cognitive theory , Englewood Cliffs , NJ : Prentice-Hall.
6. Lazarus , R. (1987) , Stress related transactions between person and environment, Perspective in 20 International Journal of Current Research and Review www.ijcrr.com Vol. 03 issue 11 November 2011 interactional psychology , New York : Plenum.
7. Rosenstock, I. M. (1990) , The health belief model : explaining health behavior trough expectancies , Health behavior and education : theory , research , and practice ,39-62.
8. Becker , M.H. and colleagues (1997), the health belief model and prediction of dietary compliance : A field experiment , journal of Health and Social Behavior , 18 , 348-366.
9. Sheeran, P. , and Abraham , C. (1995) , the health beliet model .In m. Conner, and P.Norman (Eds). Predicting health behavior. 121-162.
10. Baum, A. (1990), stress, intrusive imagery, and chronical distress , journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 40 , 1078-1089.
11. Coyne, L.C., and Houroyd , K. (1981) , Stress coping and illness , a transactional perspective , handbook of clinical health psychology , New York : Plenum.
12. Hobfoll, S.E. (1989), Consevation of resource: a new attempt at conceptualizing stress. American Psychologist, 44, 513-524.
13. Folkman , S. , and Lazarus (1980) , an analysis of coping in a middle – aged community sample . journal of health and social behavior, 21,219-239.
14. Singer , J. E., and Davidson , L.M. (1986) , Specificity and stress research . In M.H. appley and R. trumball (Eds). Dynamics of stress : physiological , psychological , and social perspectives , New York : plenum.
15. Selye , H. (1985), History and present status of the stress concept. In A. Monat and R. S. Lazarus (Eds), stress and coping ( 2nd edition) , New York : Colombia university Press.
16. Burns , V.E. and colleagues (2003) , Life events , perceived stress , and antibody response to influenza vaccination in young , healthy adults , jounal of psychosomatic research, www.sciencedirect.com.
17. Asadi Noghabi, Ahmad Ali (1997) , Psychonersary and psychic health, Tehran,Iran , Tablighe Bashari publication.
18. Asadi, Hamzeh Ali (1998), Causes of upper gastrointestina bleeding in outpatients in the emergency unit of Shahid Yahyanejad Hospital of Babol , Iran, thesis of MD, Babol Medical University.
19. Smeltzer, Susan S. colleagues (2008), Internal-surgery nursery, Translated to Persian by: Alikhani,maryam ,(2009) Jameh Negar publication.
20. Pinto , C. and colleagues (2000) , Stressful life events , anxiety, depression and coping in patients of irritable bowel syndrome. Journal of associated physicians India, 48, 589- 593.
21. Sadock,B.J.(2009), Kaplan and Sadock‘s comprehensive textbook of psychiatry, ninth edition,chapter24, psychosomatic medicine, 2263- 2273.
22. Michenbaum, D.H. (1986) , stress inoculation training , New York : McMillan
. 23. Sims , R. , and colleagues (2007) , perceived stress , and eating behaviors in a commumity based sample af African-americans . scienceDirect – Eating behaviors : www.sciencedirect.com.
24. Lazarus , L . and colleagues (2009) , Perceived occupational , stress , affective and physical well – being among telecommunication employees in Greece. Social Science and Medicine, www.sciencedirect.com. 21 International Journal of Current Research and Review www.ijcrr.com Vol. 03 issue 11 November 2011
25. Hampel,P. and Patermann, F (2006) , perceived stress , coping , and adjustment in adolescents ,journal of Adolesxent Health:ScienceDirect:, www.sciencedirect.com.
26. Masoodnia, Ebrahim (2009) , acuity of perceived stress and approaches to challenge with it , Ravanshenasi Moaser journal, 4th circulation, No. 2 , pages : 71-80.
27. Sepahvand, tooraj, Guilani , Bijan and Zamani,Reza (2008),relation between perceived Stress and general health with regard of styles of considerations. Ravanshenasi va Oloome tarbiati journal, year 38 , No.4, 27-43.
28. Nazari , Roghayehand colleagues (2006) , assessment of stress inoculation training on life style of infertile women , thesis of MA, Islamic Azad University , Tonekabon Unit.
29. Kharamin, Shirali and colleagues(2008), comparison of challenging with stress styles in patients with ulcers in stomach and duodenum , irritable bowel syndrome and nonpatient people , Armahan Danesh Journal, No.2 , pages : 95-1049.
30. Vafayee, Bagher (2004) , assessment of relation between life stresses and digestive disease (gastric ulcer), Pajuhesh dar Pezeshki journal of Shahid Beheshti University of Medical sciences , 28th year , No.4, pages : 285-289.
31. Osoolian, Zahra (2010), An assessment of relationship between the rate of Psychotic pressure feeling with styles of confrontation to stress and effectiveness ov SIT on reduction of rate of psychotic pressure in female cancerous patients in the Razi Hospital of Rasht, Iran , thesis of MA , Islamic Azad University , Tonekabon Unit.
32. Salari, Arash (2008) , assessment of efficacy of Approaches to challenge with stress on rate of marrietal satisfaction and stress of parents of mental retarded children, thesis of MA, Islamic Azad University , Tonekabon Unit.
33. Roshani, Alireza (2010), assessment of efficacy of Approaches to challenge with stress on rate of marital satisfaction and pleasant of spouses of addicts in Behzisti in Kermanshah city , thesis of MA, Islamic Azad University , Tonekabon Unit.
34. Talebi, Moosarreza (2009), , assessment of efficacy of Approaches to challenge with stress on reduction of marrietal conflicts in the spouses of patients with PTSD from war , thesis of MA, Islamic Azad University , Tonekabon Unit.
35. Dehghan, Mehrnaz (2010), assessment of efficacy of group stress inoculation training on rate of psychic pressure and blood pressure in the patient under hemodialysis, thesis of MA, Islamic Azad University , Tonekabon Unit.
36. Moradidust, Hajar (2010) , comparison of efficacy of problem solving skill and communication skill on rate of selfsatisfaction and pleasure of girls of 2nd level of high school in Lahijan city, thesis of MA, Islamic Azad University , Tonekabon Unit.
37. Hamzehpour, Tahereh (2010) , determination of efficacy of cognitive behavioral therapy on reduction of rate of depression and anxiety in infertile women, thesis of MA , Islamic Azad University , Tonekabon Unit.
38. Asgarian , Fatemeh (2010), comparison of efficacy of relaxation training and problem solving skill on rate of anxiety in high school girls students , thesis of 22 International Journal of Current Research and Review www.ijcrr.com Vol. 03 issue 11 November 2011 MA, Islamic Azad University , Tonekabon Unit.
39. Nosek , M . and colleagues (2010), the effects of perceived stress and attitudes toward menopause and aging on symptoms of menopause .Journal of Midwifery and Women‘s Health, www.sciencedirect.com.
40. Chou, F.H. and colleagues (2007), the relationship between nausea, perceived stress, social support, planned pregnancy and psychological adaptation in sample of mothers: study of an inventory, journal of Psychophysiological research, www.sciencedirect.com.
41. Kharamin, Shirali and colleagues(2008), comparison of challenging with stress styles in patients with ulcers in stomach and duodenum , irritable bowel syndrome and nonpatient people , Armahan Danesh Journal, No.2 , pages : 95-1049.
42. Alfvan, G. , Ostberg, V. , and Hjern, A. (2008) . Stressor, perceived stress, and recurrent pain in Swedish school children, journal of psychosomatic research, www.sciencedirect.com
43. Zarei, Jalal (2008), determination of salivary amylase enzyme before and after preinterny examination stress among medical student of Medical Science University of Babol , thesis of MD, Babol Medical University.
44. Kamrani, Masoumeh (2007), assessment of tate of annual stresses on Myocardial Infarction, thesis of MD, Babol Medical University.
45. Brace, Nikola and colleagues, translated to farsi by Ali Abadi and Samadi(2009), 3rd edition, Analysis of psychological data with SPSS , Doran publication.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License