IJCRR - 4(2), January, 2012
Pages: 154-160
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
EVALUATION OF EFFECT OF COTTON DUST ON PULMONARY FUNCTIONS AND INCIDENCE OF
BYSSINOSIS IN COTTON MILL WORKERS
Author: Sujatha V Patil, Praveenkumar Inamadar, Vijayakumar B. Jatti, Shobha, Prabhawati P. Inamadar, VinodKumar C.S
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Byssinosis is an important occupational hazard and a type of pneumoconiosis, often observed among workers exposed to cotton, flax, and Hump dust in the cotton mills. The severity and extent of the problem are well recognized in the developed countries and control measures have been implemented to prevent the disease. This is not true, however, for the developing countries like India, where the severity and extent of the problem are not well studied and preventive measures are virtually non-existent. A review of the earlier studies on Byssinosis suggests a low prevalence of the disease in most of the Indian Textile mills. In this retrospective, epidemiological study carried out on workers in cotton mill / ginning factory of Bijapur district North Karnataka, 110 subjects were examined for different pulmonary function tests to study the prevalence of Byssinosis among the workers exposed to cotton fibers. However, our study showed a high prevalence of the disease, especially in the blow and card sections of the mill. The prevalence of byssinosis was found to be 8.95% among workers directly exposed to cotton dust. Prevalence of their respiratory symptoms among these workers is as follows: chronic cough (19.40%), chronic phlegm (7.46%), and chronic bronchitis (11.94%). The prevalence of byssinosis and other respiratory symptoms increased with increase in duration of exposure and advancement of age and are more prevalent among smokers compared to non-smokers. It can be concluded from the present study
that, the exposure to cotton dust results in decreases in pulmonary function parameters in worker at both dusty and non-dusty section of mill, which may result in onset of various respiratory disorders. The overall findings of the study of three textile mills are presented in the present paper.
Keywords: Byssinosis, Pulmonary function tests, Industrial exposure, spirometry, cotton
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
In the industrial work environment, inhalation is the commonest route of entry for most hazardous substances. Lungs, by virtue of their large surface area and direct contact with atmospheric air, are naturally the most commonly affected organs of the body in industrial situations. The cotton industry is one of the major components of the industrial network in India. One estimate has revealed that there are around 1,0.27 mills which are actively involved in processes involving cotton, flax and hemp and around 8,11,822 workers work in these mills. Occupational exposure to cotton, flax and hemp dust, leads to a disabling lung disease known as ?Byssinosis? (Meaning white thread in Greek). Byssinosis has been shows to develop in response to dust exposure in cotton processing. It is especially prevalent among cotton workers in the initial, very dusty operations where flakes are broken open, blown and carded to arrange the fibers in to parallel threads. Byssinosis has also described in other than textile sectors where cotton is processed, such as cottonseed oil mills, the cotton waste utilization industry, and the garneting, or bedding and batting industry. Byssinosis is characterized by shortness of breath and chest tightness. Symptoms are often associated with changes in pulmonary function. Most characteristic of acute pulmonary response to cotton dust exposure is a drop in FEV1 on the first day back at work after at least a 2 days layoff. Extensive studies in United States led to correlations between respirable dust, measured with a vertical elutriator and symptoms of byssinosis on one hand and cross shift reductions in flow in exposed workers which led to adoption of a threshold limit value for respirable cotton dust of 0.2mg/m3 by the occupational safety and Health Administration (NIOSH, 1994) Much research has been done on possible etiological mechanisms and effects of byssinosis. It seems likely that the mechanism of byssinosis involves stimulation of the some inflammatory receptors by endotoxin and by cotton dust. Gram-negative bacterial endotoxin contaminates cotton fiber and aqueous extract of endotoxin have produced acute symptom and lung function declines.
The severity and extent of the problem of byssinosis are well recognized in developed countries and control measures have been implemented to prevent the disease. However, this is not true for developing countries where the severity and extent of the problems are not well studied and preventive measures are virtually non-existent (Schilling Approximately 250,000workers are exposed to byssinosis in United States and over 1,000,000 worldwide (Kaye, 2004). In India several studies on byssinosis were undertaken in the past (Murlidhar, 1995, Gupta, 1969). A review of these studies provides contradictory view – some suggests a low prevalence of the disease in most of Indian textile mills (Gupta, 1969), others suggest a high prevalence of the disease (Parikh, 1989). In Northern part of Karnataka, there are many Ginning factories associated with processing of cotton. However there is no systematic evaluation of pulmonary function status of the workers working with these mills. Thus the present study was planned to measure the quantitative changes in lung functions in workers of ginning factory of Bijapur District, North Karnataka. This study is done to assess pulmonary function status of the workers of ginning factory is by measuring FVC, FEV1, FEV1% and PEFR and to find out incidence of byssinosis among the workers. This study suggests that the prevalence of byssinosis is not low in cotton mill workers.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The study is conducted on workers of a ginning factory, situated in Bijapur District, North Karnataka.
Experimental group: Consisting of workers of the cotton mill. Total number of subject: 110, which were divided in to two sub groups.
Group I: Workers who actually work with cotton and directly exposed to the cotton dust. All these workers work in the dustiest section of mill like spinning, Frame, Ring and Winding (Total No -67). Group II: Workers who does not actually work with cotton but work in other Departments of the mill, like, office workers and watchmen (Total No -43).
Control group: Control subjects were selected from among the male non-teaching staff members of BLDEA‘S Sri. B.M.Patil Medical College ?who represent same socioeconomic group as that of mill workers (Total No-50).
Methods of collection of Data: At the beginning of the study list of workers working in different section of the mill was obtained. The purpose of the study and content of the consent from was explained to them in their mother tongue. All the demographic data were obtained which are related the study.
Exclusion criteria: Workers with history of tuberculosis, in whom tuberculosis was strongly suspected on clinical grounds, with bronchial asthma, with positive family history of asthma and with deformities like gross kyphoscoliosis.
The clinical assessment of the subject for Byssinosis, Pulmonary function tests. Assessment of the workers for Byssinosis:
This was done for the study of only the experimental group. We used a questionnaire designed by Muralidhar, et. al in their Bombay study. Similar questionnaire was used by Parikh and National Institute of occupational Health, Ahmedabad (NIOSH, 1994).
Lung function tests: Spirometeric (FVC, FEV1, FEV1/FVC and PEFR) measurements (best of 3 readings) were carried out in the field using portable spirometer.
RESULTS
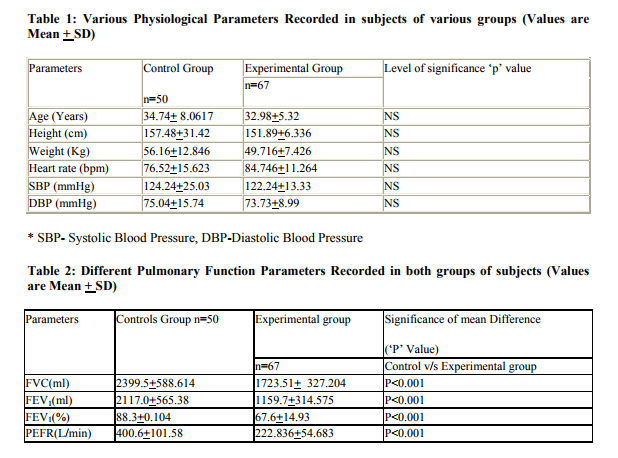
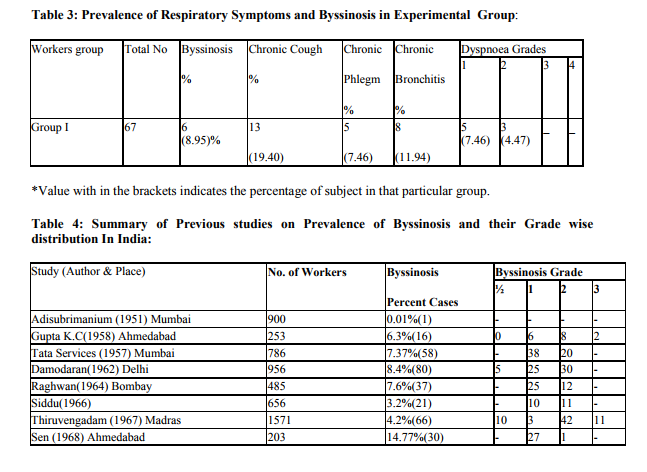
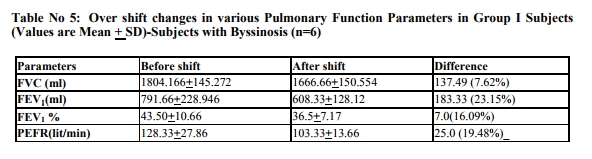
DISCUSSION
There are extensive reports of various Indian studies on cotton mill workers. Most of these studies suggested a low prevalence of byssinosis and other respiratory symptoms, among cotton mill workers in India (Kamal, 1981). By contrast with these findings, researchers in other countries have observed a high prevalence of the disease. For instance, E1 Batawi et al, observed a prevalence of 27% in card rooms (Butawi, 1964), whereas Molyneux and Tombleson found a prevalence of 24% in blow rooms and 36.8% in card rooms (Mlyxneux, 1963). In the present study, we have evaluated the prevalence of byssinosis and other respiratory disorders in cotton mill workers and compaired our findings with age group matched control subjects. The various physiological parameters studied, like, resting heart rate and resting blood pressure (both systolic and diastolic) were found to be within normal range among subjects of various groups. In the present study, we observed that 8.95% of workers directly exposed to cotton dust suffered from byssinosis. This finding is in agreement with the findings of other researcher‘s world over, which had shown that workers working in most dusty section of the mill are primarily effected by byssinosis. Schilling reported 60% incidence of byssinosis among card room workers in England and 27% incidence in Egypt (Butawi, 1964). Murlidhar et, al. also reported 30% prevalence of disease in dusty section comparable to the world statistics (Molyneux, 1963). One of the important causes of this low prevalence of byssinosis in our study is less exposure period of the subjects to cotton dust. In our study there are only three subjects who have an exposure duration more than 20 yrs. All these three subjects are suffering from byssinosis. Other three byssinotic subjects in our study has an exposure duration ranging from 15 to 20 years. Fox et al., have reported that with longer duration of exposure the prevalence of byssinosis increases (Fox, 1973). Parikh, et.al6 from their study reported that, the prevalence of byssinosis increased up to 25 years of exposure but thereafter it declines (Parikh, 1981). They proposed this might be due to the fact that some of the byssinotic workers prematurely retire owing to respiratory disability. This might be the cause why we encountered only three out of sixty seven workers with exposure duration of more than 20 years. However, 38.80% of workers in our study suffer from various other type of respiratory symptoms like chronic bronchitis, chronic phlegm and chronic cough in addition 8.95% workers suffering from byssinosis. This is consistent with the observations of Bouhuys (Bouhuys, 1967).
All these workers observed deterioration of lung function and appearance of various respiratory symptoms in workers who are exposed to cotton dust for 10 to 20 years. Analysis of age group wise distribution of workers with various respiratory disorders in our study revealed that all the byssinotic subjects belong to over 36 years age group. Most of the workers suffering from other form of respiratory symptoms belong to higher age group. Gerald J. Beck, et.al reported a gradual decline in respiratory function parameters and incidence of various respiratory symptoms in workers with both advancement of age and increase in duration of exposure (Gerald J Beck, 1982). In the course of interrogations during the study it was revealed that some of the colleagues of older employees had left the job due to health problems, notably due to shortness of breath. It is highly likely that at least few of those who left the job must have done so due to byssinosis or other respiratory disorder associated with exposure to cotton dust. Thus the prevalence of byssinosis in the present study may actually be higher than the estimated figure.
The incidence of byssinosis reported previously by various Indian observers is summarized in table no: 4 for comparison. Results of present study, almost agrees with these figures. However, Parikh has reported a higher incidence of byssinosis in their Ahamedabad mill study (Parikh, 1969). Evidences provided by various researchers suggest that byssinosis and other respiratory symptoms are more prevalent among smokers compared to non smokers (NIOSH, 1994). In our study we have observed all the workers suffering from one or other type of respiratory disorders are smokers. There are reports that smoking habit does not determine the incidence of byssinosis or other respiratory symptoms in cotton mill workers. These workers suggested that cotton dust has more powerful independent effect that smoking (Fox, 1973). However in our study, numbers of non smokers among workers were very less. The various lung function parameters like FVC, FEV1, FEV1% and PEFR showed a significant decrease in workers in comparison to control. The decrease of these parameters was more pronounced in workers who are directly exposed to cotton dust than the workers who are not directly exposed. Various researchers all over the world have observed such decline in lung function due to exposure to cotton, hemp or other dust. Gandevia reported that there is a decline in FEV1 in workers at the beginning of the week and that continues through out the week (Gandevia, 1965). However, this decrease is more pronounced in exposed group which reveals the fact that age is not the only factor responsible for such decline. These findings are in agreement with the reports of other workers who have reported age related decline in lung functions in all individuals. In our study we have observed fall in PEFR along with FVC and FEV1. PEFR in our study showed a good correlation with FEV1 showing linear fall with age; more in the exposed group than the control group. The studies using PEFR alone as an index of bronchoconstrictor response have not been reported. The present study showed that the values of PEFR were significantly lower in byssinotics. This is in agreement with the reports at other centers (Mc Kerrow, 1958). In our study we have observed a decline in all the respiratory parameters at the end of the shift in comparison to that recorded at the beginning of the shift.a Ginning factory in Bijapur were screened for presence of cotton dust induced respiratory disorders. Various pulmonary function parameters (FVC, FEV1, FEV1% and PEFR) were recording in them before and after shift and compared with age matched control subjects of similar socioeconomic group. The prevalence of byssinosis was found to be 8.95% among workers directly exposed to cotton dust. Prevalence of their respiratory symptoms among these workers is as follows: chronic cough (19.40%), chronic phlegm (7.46%), and chronic bronchitis (11.94%). The prevalence of byssinosis and other respiratory symptoms increased with increase in duration of exposure and advancement of age. It can be concluded from the present study exposure to cotton dust results in decreases in pulmonary function parameters in worker at both dusty and non-dusty section of mill, which may result in onset of various respiratory disorders. These affects increase with time in duration of exposure and advancement of age. Smoking adds to the deleterious effect of cotton dust in causing respiratory disorders among workers in cotton mill.
References:
1. National Institute for Occupational Safty and Health Administration. NIOSH packet guide to chemical hazards DHHS (NIOSH) Publ.1994:Washington,D.C 94-116.
2. Schilling RSF. ?World wide problems of byssinosis?. Chest:1981:79: 3-55.
3. Kaye HK ?Byssinosis? Chapter 14 Occupational Respiratory Diseases Maxcy Rosenau Public Health and Preventive Medicine; 574-76.
4. Murlidhar V, Murlidhar VJ. Kahere V. ?Byssinosis in a Bombay textile mill?. Natl Med J India; 1995 Sep-Oct: 8(5): 204-7.
5. Gupta MN.?Review of byssinosis in India?. Indian J Med Res: 1969: 57:1776-89.
6. J R Parikh, L J Bhagia, P K Majumdar, A R Shah, and S K Kashyap. Prevalence of byssinosis in textile mills at Ahmedabad, India. Br J Ind Med. Nov-1989; 46(11): 787–790.
7. Kamat SR, Kamat GR, Salpekar VY, Lobo E. ?Distinguishing byssinosis from chronic obstructive Pulmonary disease? Am Rev Respir Dis; 1981:124:31-41.
8. El Batawi MA, Schilling RSF,Valic F, Warford J. ?Byssinosis in Egyptian cotton industry: Change in ventilatory capacity during the day?. Br J Ind Med:1964: 27:225- 234.
9. Molyneux MKB, Tombleson JBL. ?An epidemiological study of respiratory symptoms in Lancashire mills?. Br J Ind Med.: 1963- :27:225-34.
10. Fox AJ, Tombleson JBL, et al,.?A survey of respiratory disease in cotton operatives Part I?. Symptoms and ventilation test results. Br.J Ind Med: 1973:30:42-47.
11. Bouhuys A, Heaply LJ, Schilling RSF, et al: ?Byssinosis in the United States?. N Engl J med; 1967:277:170.
12. Gerald J. Beck, et al. ?A prospective study of chronic lung disease in cotton Textile workers?. Annals of Internal Medicine.1982: 97:(5). 645-651.
13. Gandevia B, Milne J. ?Ventilatory capacity changes on exposure to cotton dust and their relevance to byssinosis in Australia?. Br J Ind med; 1965: 22: 295-304.
14. Valic F, Zuskin E. ?Effects of different vegetable dust exposure?. Br J Ind Med; 1972: 29:293-7.
15. Mckerrow CB, Mcdermott M, Gilson JC, Schilling RSF : ?Respiratory function during the day in cotton workers. A study in byssinosis?. Br. J.Ind med; 1958: 15: 75- 83.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License