Welcome to IJCRR
Indexed and Abstracted in: Crossref, CAS Abstracts, Publons, Google Scholar, Open J-Gate, ROAD, Indian Citation Index (ICI), ResearchGATE, Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, WorldCat (World's largest network of library content and services)
|
|
Diagnosis of FNAC |
No of cases |
Percentage |
|
A |
Neoplastic lesion |
292 |
99.32% |
|
1 |
Primary malignancy |
66 |
22.44% |
|
a |
Hepatoblastoma |
07 |
2.38% |
|
b |
Hepatocellular carcinoma |
59 |
20.06% |
|
2 |
Secondary malignancy |
226 |
76.88% |
|
a |
Adenocarcinoma |
185 |
62.93% |
|
b |
Small cell carcinoma |
21 |
7.15% |
|
c |
Squamous cell carcinoma |
04 |
1.36% |
|
d |
Melanoma |
04 |
1.36% |
|
e |
Neuroendocrine tumor |
05 |
1.70% |
|
f |
Spindle cell tumor |
03 |
1.02% |
|
g |
Round cell tumor |
03 |
1.02% |
|
h |
Medullary carcinoma |
01 |
0.34% |
|
B |
Non neoplastic lesion |
02 |
0.68% |
|
1 |
Abscess |
02 |
0.68% |
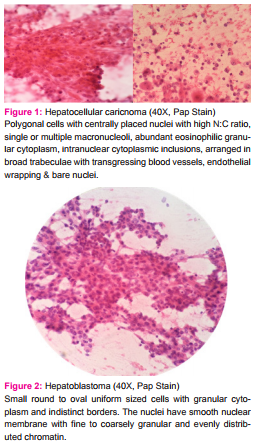
Out of 294 cases, 292 (99.32%) were malignant and 2 cases (0.68%) were of infective etiology – abscess formation. Of 292 malignant cases diagnosed, 66 (22.44%) were primary liver neoplasm and 226 (76.88%) were secondaries (metastasis). Benign hepatic lesions were not seen in our study. Out of 66 primary liver neoplasms, 7 cases were of hepatoblastoma and 59 cases were of Hepatocellular carcinoma. The most important cytomorphological features of primary tumors – HCC were cellularity, architectural patterns, cytological features of individual cell and background material. The main architectural pattern seen was broad trabeculae with transgressing blood vessels, cohesive clusters and endothelial wrapping and bare atypical nuclei in the background. The cytological features included were polygonal cells with centrally placed nuclei with high N:C ratio, single or multiple macronucleoli, abundant eosinophilic granular cytoplasm, intranuclear cytoplasmic inclusions and bile plugging (figure-1). Serum alphafetoprotein (S.AFP) level was raised in 41 cases and normal in 13 cases of HCC while in 5 cases S.AFP level was not done.
The hepatoblastoma is a primary liver tumor in pediatric age group, consisting of small round to oval uniform sized cells. The cytoplasm was granular with indistinct borders. The nuclei have smooth nuclear membrane, chromatin was fine to coarsely granular and evenly distributed. Few cells had single nucleolus. The background was dirty with fragments of capillaries and plump spindle shaped endothelial cells (figure - 2). S.AFP levels were elevated in all the cases of hepatoblastoma.
Metastatic tumor was the most common malignant hepatic lesion (226 cases- 76.88%). Metastatic adenocarcinoma was the commonest type (185 cases) followed by small cell carcinoma (21 cases), neuroendocrine tumor (5 cases), squamous cell carcinoma (4 cases), melanoma (4 cases), spindle cell tumor (3 cases), round cell tumor (3 cases) and medullary carcinoma (1 case). The commonest primary sites of adenocarcinoma were the lung, breast, GI tract, pancreas, ovary and gall bladder in decreasing order of frequency.
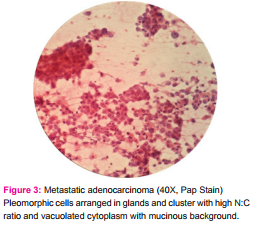
The common cytological features of adenocarcinoma were high cellularity, columnar or cuboidal tumor cells with nuclear pleomorphism, high nuclear to cytolplasmic (N:C) ratio with central to eccentrically placed nucleus, fine dispersed to coarse chromatin and scanty to moderate, vacuolated or pale cytoplasm. Cells were arranged in glands, acinar or palisade like patterns; three dimensional clusters; or singly. Inflammation, necrosis and fibrosis were seen in some cases. Most of them showed benign hepatocytes in the background (figure - 3). In 167 cases (73.89%) out of 226 cases, the commonest primary site of adenocarcinoma was the lung, breast, GI tract, pancreas, ovary, gall bladder in decreasing order of frequency. Rest 59 cases (26.11%) presented as metastasis of unknown origin to liver.
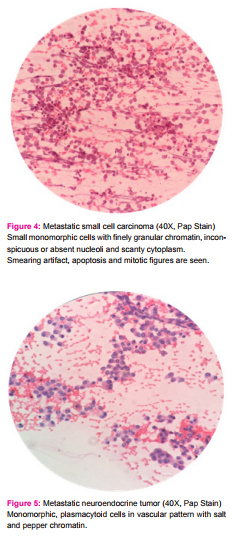
The small cell carcinoma showed small monomorphic cells with finely granular chromatin, inconspicuous or absent nucleoli and scanty cytoplasm. Nuclear moulding, smearing artifact along with apoptosis and mitosis were also seen (figure - 4).
Neuroendocrine tumor revealed monomorphic, plasmacytoid cells in vascular pattern with salt and pepper chromatin, small nucleoli and abundant cytoplasm. Mitotic activity and necrosis were not evident (figure - 5).
The squamous cell carcinoma showed squamoid tadpole like cells with irregular hyperchromatic nuclei and well defined, abundant, keratinized cytoplasm. The cells were present in the necrotic inflammatory background.
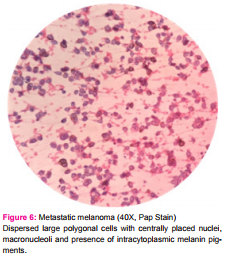
Metastatic Melanoma showed dispersed large polygonal cells with centrally placed nuclei, macronucleoli, intranuclear cytoplasmic inclusions with presence of intracytoplasmic melanin pigments (figure - 6).
Metastatic spindle cell tumor showed cohesive tissue fragments of spindle cells with mild atypia without necrosis and mitosis. These cases were known case of Gastro Intestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST) of small bowel.
Metastatic round cell tumor (3 cases) showed discrete small round cells with high N:C ratio with features suggestive of NHL, Wilm’s tumor and Ewing’s Sarcoma respectively.
One case of metastatic medullary carcinoma from thyroid was also seen during this study.
Two Non Neoplastic lesions were of infective etiology showing numerous polymorphs, necrosis and debris. ZN stain and PAS stain were performed to rule out tuberculosis and fungal infection respectively.
DISCUSSION
Lundquist et al in 1971 first showed the utility of FNAC in diagnosing hepatic lesions [1]. Guided FNAC is a very useful procedure for the diagnosis of various Neoplastic and Non Neoplastic hepatic lesions. It is a minimal intervening procedure at low cost and without major complication. The only contraindications are marked hemorrhagic diathesis and suspected vascular lesions [5,6]. No complications were seen during our study.
The diagnostic yield of our study was 73.5%; almost similar results were seen in the earlier studies [7,8,9].
For any SOL in liver the differential diagnosis includes inflammatory lesions, metastatic deposits and primary liver malignancy. The imaging techniques helps, but some overlap between the radiologic features of liver abscess, Hepatocellular carcinoma and metastasis are seen. Tumor either primary or secondary can undergo extreme necrosis and present radiologically as cavitary neoplasm mimicking abscess and similarly abscesses with accompanied proliferative reactive changes mimic neoplastic process radiologically. In this situation guided FNAC plays an important complementary role for the accurate cytological diagnosis of various liver lesions [10]. In focal liver lesions multiple aspirates can be done replacing core needle biopsy to a large extent [11]. It helps to categorize liver lesions into primary, metastatic or non neoplastic. With the use of cell blocks diagnostic accuracy is improved as it facilitates study of multiple sections, use of special stains and immunohistochemistry (IHC) [12].
Metastatic tumors were the most common (76.88%) among the malignant liver lesions. Our results are comparable with other studies such as, Dhameja et al [13], Rasania et al [9] and Ali SR et al [14] which showed 77.7%, 70.4% and 58% of metastatic tumors respectively among the total liver malignancies. However, study by Swamy et al [15] found primary malignancies more common than metastatic lesions.
We studied and evaluated the different features in HCC as described by Ali et al [16] and Tao et al [17]. The cytomorphological features were cellular arrangement, cell size, N:C ratio, cohesiveness of cells, nuclear shape and size, location, multinucleation, prominent nucleolus, amount of cytoplasm, vacuolation, bile production and hyaline bodies.
HCC was differentiated from other malignant and nonmalignant condition of liver by the different features collectively like cellularity, trabecular pattern, hyperchromasia, uniformly prominent nucleoli, multiple nucleoli and atypical naked nuclei. The most important and helpful cytological features were the trabecular pattern, irregular granular chromatin, prominent nucleoli and atypical striped nuclei [18]. The atypical naked nuclei were included as one of the important criteria for the diagnosis of HCC by Pedio et al [19] as these were rarely seen in benign and metastatic condition. Three criteria differentiate HCC from metastatic tumor; polygonal cells with centrally placed nuclei, malignant cells separated by sinusoidal capillaries and bile. Two additional criteria, namely endothelial cells surrounding tumor cell clusters and intranuclear inclusions were identified as being important secondary criteria for HCC [20].
Hepatoblastoma usually affects 3 years old or younger children and has markedly elevated S.AFP level as seen in our study. Hepatoblastoma is not associated with cirrhosis. On FNAC, a hepatoblastoma can resemble a normal liver if it exhibits a predominantly fetal type differentiation with trabecular pattern. If other epithelial components such as embryonal, small cell or macrotrabecular patterns are present, the tumor shows a more heterogenous population of variably sized cells with or without trabecular groups, suggesting diagnosis of hepatoblastoma. On cytology smears alone, abundant embryonal or small cell components may resemble other small-cell tumors of childhood, such as embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma, neuroblastoma, Ewing’s sarcoma, Wilm’s tumor and Lymphoma [4]. The macrotrabecular component can be more cytologically pleomorphic, mimicking HCC [1].
Metastatic Adenocarcinoma show variable differentiation. The cytoplasm differs markedly from that of hepatocytes. Necrosis, inflammation, mucin and columnar or cuboidal differentiation favours metastatic adenocarcinoma [9,10,15].
Metastatic Squamous cell carcinoma, usually from the lung, may not pose any diagnostic difficulty except for poorly differentiated tumors, in the absence of keratin and in the presence of marked necrosis and inflammation [9,10,15].
Metastatic Melanoma may present diagnostic difficulty with HCC, especially when the primary has not been discovered. Melanoma has several features in common with HCC, including polygonal cells with centrally placed nuclei, prominent nucleoli and intra nuclear cytoplasmic inclusions. Presence of coarse brown pigment of melanin has been considered an important diagnostic feature of melanoma. Even melanin pigment may resemble various liver cell pigments. Melanin may not be found in metastatic lesions. In such cases Immunohistochemistry for HMB-45, S-100 and cytokeratin is recommended [11].
Small/Intermediate round cell malignancies include neuroendocrine tumor, small cell carcinoma, lymphoma and round cell tumors. Most neuroendocrine tumors are from the gastrointestinal tract, pancreatico-biliary tract or lung. A primary hepatic neuroendocrine tumor is unusual. Small cell carcinoma usually arises from the lung. Lymphoma seldom present as primary neoplasm, although hepatic involvement is common in advanced disease. It can be mistaken for poorly differentiated carcinoma or HCC [10].
Hence, this study shows different neoplastic and non neoplastic lesions can be accurately diagnosed by guided FNAC as shown by other studies.
CONCLUSION
In the present setup from this study it is felt that USG guided FNAC is very useful in a diagnosis of different liver SOLs lesions as the procedure is simple, safe, quick, economical and accurate. It can segregate benign and malignant lesions and primary and secondary malignancies with accuracy. Early diagnosis decreases the length of stay in hospital and minimizes further ancillary investigations. Accurately sampled, well prepared and well stained cytological samples along with clinical and radiological correlation yield the best results.
So, FNAC is a simple and effective tool in our hand.
DECLARATION
Prior Publication - NIL
Support - NIL
Ethical Clearance- Approved.
Source of Funding – NA
Conflict of Interest – NIL
ABBREVIATION
FNAC - Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology
PAP - Papanicolau
MGG - May-Grunwald-Giemsa
SOL - Space Occupying Lesions
USG - Ultrasonography
CT - Computed Tomography
S.AFP - Serum alphafetoprotein
GIST - Gastro Intestinal Stromal Tumor
NHL – Non Hodgkin Lymphoma
ZN - Ziehl–Neelsen
PAS - Periodic acid–Schiff
IHC - ImmunoHistoChemistry
HCC – HepatoCellular Carcinoma
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose article cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Note: The present study was undertaken at tertiary care hospital of Gujarat to know the etiology of the various liver space occupying lesions by FNAC. In the present study, FNAC performed on the patient as routine diagnostic procedure which was with prior consent of the patients. Ethical committee clearance has not been required as confidentiality of patients’ details has not been published.
References:
Indexed and Abstracted in






Antiplagiarism Policy: IJCRR strongly condemn and discourage practice of plagiarism. All received manuscripts have to pass through "Plagiarism Detection Software" test before forwarding for peer review. We consider "Plagiarism is a crime"
IJCRR Code of Conduct: To achieve a high standard of publication, we adopt Good Publishing Practices (updated in 2022) which are inspired by guidelines provided by Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE), Open Access Scholarly Publishers Association (OASPA) and International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE)
Disclaimer: International Journal of Current Research and Review (IJCRR) provides platform for researchers to publish and discuss their original research and review work. IJCRR can not be held responsible for views, opinions and written statements of researchers published in this journal.
International Journal of Current Research and Review (IJCRR) provides platform for researchers to publish and discuss their original research and review work. IJCRR can not be held responsible for views, opinions and written statements of researchers published in this journal
148, IMSR Building, Ayurvedic Layout,
Near NIT Complex, Sakkardara,
Nagpur-24, Maharashtra State, India
editor@ijcrr.com
editor.ijcrr@gmail.com
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
Copyright © 2026 IJCRR. Specialized online journals by ubijournal