IJCRR - 5(24), December, 2013
Pages: 46-51
Date of Publication: 31-Dec-2013
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDY RELATED TO RISK FACTORS OF BREAST TUMOURS IN POPULATION OF SOUTHERN RAJASTHAN, INDIA
Author: Mukul Dixit, Jyoti Jain
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Objectives: This study was planned to identify different factors related to breast cancer with the intention that early detection and for better understanding of course and pathogenesis of benign and malignant breast cancer. Material and methods: The patients of breast tumours who attended surgical outdoor or breast clinic or patients admitted to the surgical wards of Maharana Bhopal Hospital, Udaipur from Jan'97 to Jun'97 were included in this study. Complete clinical examinations of the patients were done to see the symptoms, clinical manifestations, involvement of tissues etc. Results: There was an increased risk of benign breast tumour at a considerably younger age. Majority of the patients both in benign as well as in malignant were married, but this did not show any statistical significance in the present study. Occupational status of cases in the present study indicates that majority (63.82%) were housewives. The association of age at menarche and breast tumours was non-significant. Association observed between age at menopause and breast tumours was found to be statistically significant (P< 0.05). Conclusion: Women should be advised to self examines their breasts regularly so that they can find out any abnormality occurring in the breast so as to diagnose the tumours at earlier stages. Breast self examination strategy should be implemented at a community level so that more and more women can be benefitted. For this, Breast Clinic should be launched at every level of health system viz. District Hospital, Community Health Centre and Primary Health Centre.
Keywords: breast cancer, occupational status, menopause, breast self examination.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Tumours of the breast are the leading cause of the morbidity and mortality in females in the world. Benign as well as the malignant neoplasms are the commonest of all the neoplasms occurring in females. Despite the high incidence rates of benign neoplasms of the breast, their epidemiology has not been adequately described.
However, there are several studies about epidemiology about the breast cancer. Until recently benign disorders of the breast were regarded as relatively unimportant: far more attention was focused on breast cancer.
Duct Papilloma and fibroadenomas are common variant of benign breast tumours. The majority of Duct Papilloma tumours are single. In contrast, certain patients have multiple intraductal papillomas, which Haagensen believes are more likely to be peripherally located and associate an increased risk of cancer.(1) The majority of patients are found to have solitary Papilloma, which is benign, but identical symptoms are associated with multiple papillomatosis or rarely a papillary adenocarcinoma.
Fibroadenomas is the commonest tumour of the breast below the age of 35. Fibroadenomas usually presents as a solitary, firm, well defined, lobulated, extremely mobile lump, 1-3 cm in diameter. There is a well marked capsule. (2)
Although fibroadenomas are not considered to have a malignant potential, the epithelial elements appear to be at risk for neoplasia just as epithelium elsewhere in the breast. More than 100 invasive and non-invasive carcinomas have been reported in pre-existing fibroadenomas since l985. (3)
Breast cancer is the commonest malignant disease of women in England and Wales. It is estimated that 1 in 12 of all female children born will develop the disease during their lifetime.(4) Epidemiological data indicate well defined factors that indicate an increased liability to developing the disease. Such risk factors for breast cancer fall into three main groups: genetic, endocrine, and environmental
Previous attempts have been based on a number of different factors such as clinical symptoms, patients age, histological features, or that part of the secretary system in which the abnormality seen. This study were deigned to describe some other factor other than clinical symptom and related to breast cancer.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
For the present study 179 patients of breast tumours who attended surgical outdoor or breast clinic or patients admitted to the surgical wards of Maharana Bhopal Hospital, Udaipur from Jan’97 to Jun’97 were included. They were contacted in the outdoor or breast clinic or during their stay in the hospital and a complete clinical examination of the patients were done to see the symptoms, clinical manifestations, involvement of tissues etc.
All the patients whether newly admitted, operated for the malignant or benign lesions or who were receiving chemotherapy post-operatively and the patients attending breast clinic for advice were taken for study. The diagnostic criteria were based upon the histopathological examination.
RESULTS
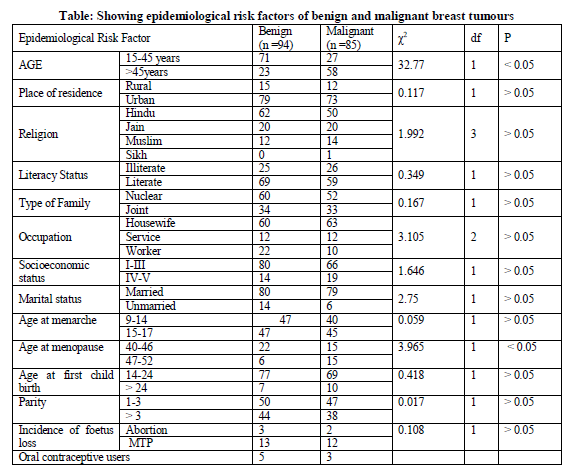
Most of patients of benign group young age group while in patients with malignant tumours most of them were from higher age group suggesting an increased risk of benign breast tumour at a considerably younger age.
Majority 65.95% of patients with benign tumours were Hindus. The association between Hindu and other religion which was however comes out to be non significant (> 0.05).
The association between type of family and the breast tumours was non-significant statistically. Majority of the patients in both groups were married, but this did not show any statistical significance in the present study.
Regarding the educational status, Association between literacy status and breast tumours was found to be non-significant. Occupational status of cases in the present study indicates that majority (63.82%) were housewives but no statistical association could be established.
The association of age at menarche and breast tumours was non-significant.
Association observed between age at menopause and breast tumours was found to be statistically significant (P<0.05).
There was non-significant association between age-groups (14-24 and >24) at first child birth and breast tumours.
As regards abortion status, the association was insignificant between abortion and MTP and breast tumours.
Only 5.32 percent patients in case of benign and 3.52 percent patients in case of malignant group used oral contraceptive and that too for a short period.
DISCUSSION
The present study was taken out in the patients attending surgical outdoor and Breast Clinic or admitted in Maharana Bhopal Hospital, Udaipur
from January to June, 1997. In this study, 94 patients with benign tumours and 85 patients with malignant tumours were studied.
Breast cancer is a major and important form of malignant disease in the western world and is becoming frequent in developing countries as well. In North America it was the most common malignancy among the women, accounting for 27 percent of all female cancers. Mortality rates from breast cancer have increased during the past 60 years in every country.
In any case the age-incidence pattern of benign strongly implies that the condition is highly dependent upon some hormonal correlate of the reproductive years.
The association between 15-45 and more than 46 age groups with the benign and malignant tumours as shown in table was statistically significant (P<0.05). Most of patients of benign group (75.53%) were under 26-45 age group while in patients with malignant tumours most of them (67.05%) were from 46-65 age group.
The age-incidence curve of benign breast disease in Boston (Cole P et al)(5) is thus clearly different from that of breast cancer, which shows a steady rise throughout life.(6)Breast cancer is uncommon below the age of 35, the incidence increasing rapidly between the ages of 35 and 50. A slight bimodal trend in the age distribution has been observed with a dip in incidence at the time of menopause.(7)
The age-incidence pattern of benign tumour is perplexing; one possible explanation is that the disease is due to anovular cycles which characterize the menstrual cycles of young women.
Hughes L.E. and Courtney, .S.P. observed that a secondary rise in frequency often occurs after the age of 65. Women who developed their first breast cancer under the age of 40, had three times the risk of developing a second breast cancer than did those who developed their first cancer after the age of 40.(8)
As regarding residential status of the patients (table 1), most of patients were belonged to urban area with benign tumours and malignant tumour. The association was however found to be statistically insignificant. Our results are well correlated some other studies from Delhi and south India. (9, 10) Urban dominance in breast tumour could be attributed to the changing life style; breast feeding practices and possibly some environmental factors influence its occurrence.
In case of benign group, 65.95 percent patients were from Hindu religion.21.27 percent patients were from Jam community and 12.76 percent patients belonged to Muslim community. In case of malignant group, 58.82 percent patients of Hindu religion, further, 23.52 percent patients were from Jam community, 16.47 percent were Muslims and only 1.17 percent patient was Sikh. Difference in distribution according to religion in breast cancer is related to resident population in that area like another study from Mumbai showed that the highest incidence reported at 48.3 per 100,000 women in the Parsi community of Mumbai.(11)
Majority of the patients both in benign as well as in malignant 63.82 percent and 61.17 percent were from single (nuclear) family. As regards the marital status of the patients, 85.10 percent patients were married in case of benign tumours. In Malignant group, 92.94 percent cases were married. Showing higher incidence of breast cancer in married women but other studies showed that nulliparous women had a 2.2-fold higher risk than parous women.(12)
Regarding the educational status, majority of breast cancer patients were literate. Other studies also are also shown that higher education level and income may be an important risk factor for breast cancer. (13)These two provide economic independence, which further may promote women to stay single or late marriage thereby increasing their danger of the disease (15.9%). (14)
An attempt made to see the impact of occupation of patients and occurrences of breast tumours show that majority (63.82%) were housewives, similarly in malignant group, 74.11 percent were housewives. Three groups were taken for association-Housewife, Service and Worker (agriculture and labourer) which was found out to be non-significant. Occupation explains the physical activity. The observation of a case - control study does not show any difference with reference to physical activity. Both case and control groups, a high numbers of subject were in occupied in rigorous household activity. This suggests that rigorous house work to be a form of physical activity. (15)
High socioeconomic status has been shown to be related to an increased risk of benign disease by Nomura et al, Vessey MP et al.(16,17,)
Cole P et al found that fibrocystic disease incidence is directly but only weakly, related to social class, while no consistent relationship was found for fibroadenoma. (5) Similar relationships were also shown by Nomura et al with respect to educational level, but not to family income. (16) Vessey et al showed a weak direct relationship of benign breast lesions and social class. (17) While McMahon B et al found that breast cancer is weakly directly related to social class. (18)
In our study, most of the patients were from lower socioeconomic class.85.10 percent patients in benign and 77.64 percent patients of malignant group were in I-III socioeconomic class. 14.89 percent patients of benign and 22.32 percent patients of malignant were in socioeconomic class IV-V.
Fasal and Parfenbarger found no association between social class and breast tumours. Despite the socioeconomic status as an established factor in the causation of breast tumours, the association between socioeconomic status and breast tumours was found to be non-significant. Our findings were in consistent with the findings of Fasal and Parfenbarger. (19)
Most of the patients both in benign as well as malignant groups were having their age at menarche at higher age group. 50.00 percent were in 15- 17 years age group in the patients with benign tumours. Whereas, in case of malignant group, 52.94 percent patients were in 15-17 age group.Kelsey et al and Soini I et al found that early menarche and lactation history had no effect. (20, 21)
Cole P et al and Sartwell PE et al observed in their studies that late menopause was an indication of an increased risk of benign disease. (5, 22) Our findings were in consistent with the findings of Cole P et al regarding the age at menopause. There were 28 women in benign group and 48 women in malignant group who attained the age at menopause. Among them, in benign group 78.57 percent patients were in 40-46age group, 21.4 percent patients were in 47-52age group. In case of patients suffering from malignant disease, 50 percent were in 40-46 age group, 50 percent in 47-52 age group, Statistical association observed between age at menopause and breast tumours was significant (P<0.05).
Some previous workers have reported indirect association of risk of developing breast tumours with parity, but no association of risk with age at first child birth was reported. In case of patients with benign lesions, 81.91 percent patients were under 14-24 age group, 7.44 percent patients were under > 24 age group. Only 2 patients experienced sterility. In case of patients with malignant tumours, 81.91 percent and 11.76 percent patients were under 14-24 age group and more than 24 age groups respectively.
In case of benign group, 53.19 percent patients were having 1-3 children, 46.80 had >3 children. 47 (55.29%) patients had 1-3 children, 38 (44.7%) patients had > 3 children in case of malignant group. The association between parity of the patient and breast tumours was found to be non-significant (P>0.05).
Cole P et al found no meaningful association of risk of benign breast disease with parity or with age at first birth either in crude data or after controlling the social class. Their findings are thus not consistent with those of some previous workers who have reported indirect association of risk with parity. In previous studies dealing with the risk factors of benign breast lesions, nulliparous women were found to have a high risk of benign breast disease and the risk was inversely associated with increasing number of pregnancies whereas late first pregnancy had no effect on risk or was associated with an increased risk.(5)
3.19 percent patients in case of benign group and 2.12 percent patients in case of malignant group gave a history of abortions. As regards MTP, in case of benign 15.29 percent patients underwent MTP and 14.11 percent patients in case of malignant group had undergone MTP.()
Several studies have demonstrated a protective effect of oral contraceptives while Nomura A and Comstock GW have shown no association. In our study, only 5.32 percent patients in case of benign and 3.52 percent patients in case of malignant group used oral contraceptive and that too for a short period. Since the number of oral contraceptive users as too small, association could not be established. (22)
CONCLUSION
Women should be advised to self examines their breasts regularly so that they can find out any abnormality occurring in the breast so as to diagnose the tumours at earlier stages.
Breast self examination strategy should be implemented at a community level so that more and more women can be benefitted. For this, Breast Clinic should be launched at every level of health system viz. District Hospital, Community Health Centre and Primary Health Centre.
References:
- Yuasa S, McMahon B. Lactation and reproductive histories of breast cancer patients in Tokyo, Japan. Bull WHO 1970; 42:195
- Love and Belly. A Short Practice of Surgery. 4th edition. P 802-805
- Pathak DR, Whittemore AS. Combined effects of body size, parity, and menstrual events on breast cancer incidence in seven countries. Am J Epidemiol 1992; 135:153-68.
- Hughes LE, Mansel RE, Webster DJT. Benign disorders and diseases of the breast: concepts and clinical management. London, England: Bailliere Tindall, 1989;27-39
- Cole P, Elwood JM, Kaplan SD. Incidence rates and risk factors of benign breast neoplasms. Am J Epidemiol 1978;108:1 12-20
- Salber EJ, Trichopoulos D, MacMahon B. Lactation and reproductive histories of breast cancer patients in Boston, 1965-66. J Natl Cancer Inst 1969; 43:1013-1024
- Clemmesen, J. (1979). In: Measurement of Levels of Health, WHO Reg. Pubi. EURO. Ser. No.7, p.
- Hughes L.E. and Courtney, S.P. (1985). Brit. Med. J. 290: 1229 (editorial)
- Somdatta P, Baridalyne N . Awareness of breast cancer in women of an urban resettlement colony of Delhi. Indian J Cancer. 2005; 42: 149.
- Prince AH, Kavitha S, Binu VS, MS Vidyasagar, Suma N Risk factors for breast cancer among women attending a tertiary care hospital in southern. J Collaborative Res Int Med and Public Hlth.2010; 2:109-16.
- National Cancer Registry Programme: Consolidated report of the population based cancer registries 1990-1996. Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi, 2001
- Rao DN, Ganesh B, Desai PB (1994). Role of reproductive factors in breast cancer in a low-risk area: acase-control study. Br J Cancer, 70, 129-32.
- Singh MM, Devi R, Walia I, Kumar R (1999). Breast self examination for early detection of breast cancer. Indian J Med Sci, 53, 120-6.
- Tavani A, Gallus S, La Vecchia C, et al (1999). Risk factors for breast cancer in women under 40 years. Eur J Cancer, 35, 1361-7.
- Mathew A, Gajalakshmi V, Rajan B, et al (2008). Anthropometric factors and breast cancer risk among urban and rural women in South India: a multicentric case–control study. Br J Cancer, 8, 207-13.
- Nomura A, Comstock GW, Tonascia JA Epidemiologic characteristics of benign breast disease. Am J Epidemiol 1977;105:505-12
- Vessey MP, Doll R, Sutton PM. Oral contraceptives and breast neoplasia: A retrospective study. Br Med J 1972;3:719-24.
- MacMahon B, Cole P, Brown J. Etiology of human breast cancer: A review. J Natl Cancer Inst 1973 ;50:21-42.
- Fasal E, Paffenbarger RS. Oral contraceptives as related to cancer and benign lesions of the breast. J Nati Cancer Inst 1975;55:767-773.
- Kelsey JL, Gammon MD. Epidemiology of breast cancer. Epidemiol Rev 1990;12:228-40.
- Soini I, Aine R, Lauslahti K, et al. Independent risk factors of benign and malignant breast lesions. Am J Epidemiol 1981; 114:507-14.
- Nomura A, Comstock GW. Benign breast tumours and estrogenic hormones: A population based retrospective study. Am J Epidemiol 1976;103:439-444
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License