IJCRR - 6(10), May, 2014
Pages: 57-63
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A STUDY ON ATTEMPTED SUICIDE, ITS CLINICAL AND SOCIO-DEMOGRAPHIC VARIABLES IN A TERTIARY LEVEL HOSPITAL OF AHMEDABAD
Author: Nimesh Parikh, Prateek Sharma, Hitendra Gandhi, Girish Banwari
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background and Objective: Suicide attempt is one of the top five causes of acute admissions inhospitals and the area is scantily explored. This study aims to identify the socio-demographic and clinical variables in patients of attempted suicide in a tertiary level hospital of Ahmedabad. Method: After IRB approval, we approached the patientsof attempted suicide inpsychiatry OPD over a period of 3 months; demographic details were obtained from the consenting patients. They were then analyzed for presence ofmental illness in an interview based on DSM-IV TR andevident stressors. Beck`s Suicidal Intent Scale was applied on each study patient to know the severity of intent. The results were analyzed by spss v.20. Results: 78 out of 115 cases approached, consented to be a part of this study of which 56.4%werefemales.66.6%patients were less than 30 years of age, 84.6% were less than 12th standard educated, 74.3% were single and 87.5% of the unemployed patients, were housewives. In our study, 93.6% of suicide attempters had underlying psychiatric illnesses. 53.8% were diagnosed to have adjustment disorder. 65% of the patients having serious suicidal intent, were females. Conclusion: In our study, patients who are housewives (p=0.000); age < 30 years; < 12th standard education; nuclear family setup are variables that were clearly seen in majority of cases attempting suicide. Adjustment disorder was the most frequently observed diagnosis (p=0.028) in patients and female patients were found to have a more serious intent to die (p=0.025).
Keywords: Nimesh Parikh, Prateek Sharma, Hitendra Gandhi, Girish Banwari
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Suicide, also known as completed suicide, is the "act of taking one's own life"1 . Sigmund Freud explained suicide as “aggression turned inwards” and Karl Menninger conceived it as “inverted homicide”. Attempted suicide or non-fatal suicidal behavior is self-injury with the desire to end one's life that does not result in death2 . It is one of the top five causes of acute admission to general hospitals in both males and females3 . Depression, adjustment disorder, substance use (alcohol, cannabis), borderline personality disorder, conduct disorder, autism spectrum, anhedonia are associated with suicide attempts. Other risk factors include past history of attempted suicide4 , family history of suicide, hopelessness or the presence of traumatic brain injury.It is assumed to be linked to attention or help seeking behavior, which however is found to be of a false association in some studies5 . Globally, it is the 10th leading cause of death6 . There are an estimated 10 to 20 million non-fatal attempted suicides every year.7 According to American Association of Suicidology, for every 25 non fatal attempts, there is a case of successful suicide attempt8 . According to Synopsis of
Psychiatry by Kaplan and Saddock, 10% of suicide attempters subsequently suicide within 10 years. In Indian scenario, according to the recent nationwide compilation by NCRB (National Crimes Record Bureau) of The Ministry of Home Affairs, titled Accidental Deaths and Suicides in India 2010; last year there were about 15 suicides in India per hour, 23.9% growth in suicide rate was seen in last decade while the population growth rate was 18.3%. Gujarat ranked 17nth and witnessed about 6207 reported suicidal deaths. State`s suicidal rate was 10.7 as compared to the national average of 11.49 . The people who attempt suicide generally present to hospitals and small scale clinics with the medical complications. This makes a study of this group, an utmost priority as some of them might not even be able to avail adequate psychiatric care. The area is scantily explored in Gujarat, particularly Ahmedabad. Past suicide attempt is considered to be one of the best indicator of a future suicide. With this much to look at, the present study aims to identify the sociodemographic correlates, psychiatric morbidity and suicidal intent in patients of attempted suicide coming to Psychiatry OPD of a tertiary level hospital in Ahmedabad city.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
The study was carried out in the outpatient setting of Psychiatry Department of a tertiary level teaching hospital in Ahmedabad. IRB (Institutional Review Board) approval for the study was takenfrom the parent institute and the patients who had attempted suicide, coming to psychiatry OPD for management, were approached directly.Those who were willing to participate in form of giving written consent and ensuring confidentiality, were asked to fill a semi structured performa for demographic details. These patients were evaluated for the presence or absence of mental illnesses along with the reason of current event (according to patient). Then Beck`s Suicide Intent scale10(BSIS) was applied to
the study group as many previous studies have established reliability and validity of this instrument in the patients for screening of suicidal intent11. The complete scale is a 15-item survey: Items 1 to 8 cover objective circumstances of the attempt (e.g., isolation, precautions against discovery, suicide note); Items 9 to 15 report subjects intentions and expectations regarding the attempt. Allitems are scored on a 0-2 scale of severity and added. The total score range is 0 to 30 with scores above 28 indicating high suicidal intent, 20-28 indicating medium and 15-20 indicating low suicidal intent. All the patients of attempted suicide were explained regarding voluntary involvement in the study, and that their not taking part in the study will in no way interfere with the treatment decisions. The data thus obtained was analyzed by SPSS v. 20. Descriptive statistics were used to describe the data i.e. frequencies for categorical variables; chi square test to compare the socio-demographic details of patients, explanations for attempting self harm, final diagnosis (according to DSM-IV TR) and suicidal intent on BSIS, with the gender. Significance was set at p<0.05.
RESULTS
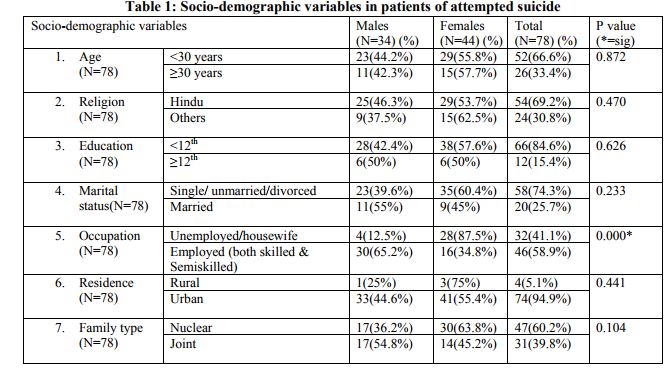
The sample obtained comprised of 78 cases (34 (43.58%) males, 44 (56.41%) females) from a total of 115 patients approachedover a period of 3 months, to be a part of the study. Table1 comprises of gender wise sociodemographic correlates of patients of attempted suicide. 66% (52 out of 78) cases were less than 30 years of age and 84% (66) patients had less than 12th standard of schooling. 54% (54 out of 78) were Hindu. 58 patients (74%) were single / unmarried / divorced as compared to 20 married ones. Although suicide attempted by employed patients were more as compared to unemployed patients (59%) but in the unemployed ones 87.5% i.e. a majority, were housewives. 74 (95%) were from urban areas and 47 (60%) cases had nuclear family setup. Nimesh Parikh et. al. A STUDY ON
Table 2 consists of reasons given by patients under study for the suicide attempt and their psychiatric diagnosis. Family problems, marital disharmony, financial crisis and other reasons (exams, illness related, alcohol) reported by males in descending order.While in females the reasons remain the same except financial crisis being cited by a single case only. 16.6% patients did not come out with a reason for attempt. No correlation was however found statistically significant in this case. 53.8% patients (42 out of 78) were diagnosed as having adjustment disorder with depressed mood followed by Major depressive disorder (27%), alcohol dependence (75% males out of total 8 cases), 5 patients (6.4%) with no major axis 1 diagnosiswhich means that 93.6% of suicide attempters have underlying psychiatric illnesses. The results obtained were found statistically significant (p=0.028). Figure 1 depicts the number of male and female cases having low (15-19) and medium (20-28) intent of suicide on the BSIS. There were however no subjects in the study group having high suicidal intent (score ≥29). Thus, in our study group more patients had serious suicidal intent in form of having medium suicide intent score on BSIS amongst whom females were having a significantly more number (35 out of 56 patients having medium suicidal intent score) (p=0.025) as compared to 24 patients having low suicidal inten
DISCUSSION
Our study demonstrates a slight female preponderance in cases of attempted suicide i.e. 56.4%. This however is in contradiction with the previous studiesby Venkoba Rao12 andBadrinarayan13 where male predilection for suicides was observed but in cohesion with study by Lal and Sethi14where females were observed to attempt more number of suicides. They reported that the age group of 15-25 years is the most vulnerable group attempting self harm. Same results were also obtained in studiesby Vijaykumar15 and Conwell16 that adolescents tend
o have more number of suicide attempts. Sureshkumar17, Shukla18 and Nandi19 have shown that men are more likely to commit suicide as compared to females by a factor of 2.3. These observations, however can be explained in a way that the studies previously referred to, are works done on completed suicides and it is already known that rate of attempted suicide is higher in females but the rates of completed suicide and severity of the attempt, are higher in males, hence probably a higher number of observed female cases. 66 (84.61%) cases (28 males and 38 females) were found to be less than 12thstandard pass as compared to 12 cases who were more than 12thstandard educated but the difference was not significant indicating that education has nothing to do with suicide if we take gender into account. Independently, although it may be deciphered that more number of patients who attempted suicide were less educated. Clearly more single / divorced patients attempted suicide (58 (74.35%) out of 78) as compared to 20 who were married suggesting that probably marriage is a protective factor but the difference between male and female patients, in this regard was not significant. More females (87.5%) who had attempted suicide were housewives as compared to more proportion of males who were not working, (in conjunction to a study by Vijaykumar15) however an overall more number of attempts were made by people who were employed (58.9%). This was probably due to overall more number of working class patients coming to our hospital setup. 60% of our cases belonged to a nuclear family setup which is considered to be a non protective factor for attempted suicide in contrast to being in a joint family, but in our study this distinction was not found significant (p=0.104). Majority of the patients were Hindu (69.2%) but this was probably due to the more frequency of Hindu patients coming to our hospital. On analyzing the patients explanation for suicide attempt, adjustment issues with family was the major factor (31 (39.7%) cases) followed by
marital disharmony (29 (37.2%) cases). Similar results were obtained in a study by Das et al.2013 patients out of the total study sample (16.6%) did not give any reason for the current attempt. It may be due to guardedness on part of patients. 4 out of the total 5 cases (75%) who had attempted suicide due to financial reasons, were males. This may be due to the more patriarchal nature of Indian society where the monitory matters have to be taken care by the male only and females are majorly involved in household work. Statistically the result, however was found non significant. In a study by Srivastava21, 94% prevalence of mental illnesses was found in patients who attempted suicide. Kessing22, Barraclough23 and Baxter24 also have reported the prevalence of psychiatric morbidity between 80-100%. In our study more than 3/4th of the patients were having common mental conditions that are usually associated with suicide like adjustment disorder and depression (63 out of total 78 cases),the rest were suffering from psychosis (mania, schizophrenia), were not having any major axis 1 disorder or were having alcohol dependence (6 males out of total 8). This makes the prevalence of major axis 1 psychiatric disorders in our study group 93.6%. Adjustment disorder with depressed mood followed by MDD were the 2 leading diagnosis in our study. In all, depression emerged as the forerunner, co-morbid with suicide attempt with a rate of 80.76%, this is also in conjugation with studies by Srivastava21and Vijaykumar15 . However it was unanimously agreed that depression and hopelessness are potential risk factors for attempting suicide25.Sarkaret. al26 found that those attempting suicide were more impulsive in nature, our results in form of some imminent dispute being the most common reason given by patients that led them to attempt suicide, points in the same direction. 10.2% of our patients had diagnosis of alcohol dependence as compared to a study by Ponnuduraiet al.27 where 10% prevalence of alcohol alone was found. Identical results were obtained despite of Gujarat being a dry state.
Other diagnosis like mania and schizophrenia were also found (2 out of 78), but considering the low prevalence of such cases, they were grouped together under the name of psychosis. The male and female distinctions in diagnosis, 71% females having adjustment disorder, 75% males having alcohol dependence (Acc. to DSM-IV TR) was statistically significant (p=0.028). We obtained 54 (69.2%) patients having medium intent (scores 20-28) from the total 78 patients, 35 (65.81%) amongst which were females. There were 15 males as compared to 9 females having low suicide intent score. Mean suicide intent score of both males and females were almost identical (20.06±3.67 in males and 20.36±2.85 in females). This indicates that probably the intent to die was same in our subjects irrespective of their gender but more females had serious intent to die as compared tomales having similar intent.
CONCLUSION
Young age group (66% were less than 30 year of age) represents the most vulnerable group which is in need for urgent interventions. Results show that 93.6% of suicide attempters have underlying psychiatric illnesses. Demographically, occupational status and clinically, psychiatric diagnosis and suicide intent scores were the only 3 variables found to be statistically significant in context of the gender distribution of our sample.80% were diagnosed to have depression and were having some or the other adjustment issues at home. 65.8% of the patients having a serious intent to die, were females. This is a potentially workable area where if proceeded, than the suicide rates can surely be brought down in our state. However our study has some limitations that this data was not a complete representative of general population as all cases of suicide attempts or suicide practically don’t reach a psychiatrist. Hence our findings should be interpreted in keeping these limitations in mind. Moresoever a robust study having a large sample size and involving other specialties as well as a surveybased approach may prove to be of more efficacy in predicting population based statistics
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature of this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
REFERRENCES
1. Stedman's medical dictionary (28th ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins. 2006.
2. World Report on Violence and Health (Vol. 1). Genève: World Health Organization. p. 185.
3. Hawton K, Fagg J. Trends in deliberate selfpoisoning and self-injury in Oxford, 1976-90. Br Med J 1992;304:1409-11.
4. Chang B; Gitlin D; Patel R . "The depressed patient and suicidal patient in the emergency department: evidence-based management and treatment strategies". Emergency medicine practice 2011:13 (9); 1–23.
5. Suyemoto, K. L. "The functions of selfmutilation". Clinical Psychology Review 1998;18 (5): 531–554.
6. Hawton K, van Heeringen K. "Suicide". Lancet2009:373 (9672); 1372–81.
7. BertoloteJM, Fleischmann A. "Suicide and psychiatric diagnosis: a worldwide perspective". World Psychiatry2002:1 (3); 181–5.
8. JL McIntosh. USA suicide 2006 Official final data: for the American Association of Suicidology 2009.
9. Accidental Deaths and suicides in India. National Crime Records Bureau.Ministry of home affairs. Government of India; 2010.
10. BeckaT., Herman I and Schuyledr. Development of suicidal intent scales. In A. T. Beck, H. L. P. Resnik, and D. Lettieri (Eds.), Measurement of suicidal behauiors. New York: Charles Press, 1973, in press.
11. MinkoppK ., Bergmane., Beck A . T., and Beckr. Hopelessness, depression and attempted suicide. Am. j. Psychiatry.,1973: 130; 455- 459.
12. Rao VA. Attempted suicide. Indian J Psychiatry 1965;7:253-64.
13. Badrinarayana A. Suicidal attempt in Gulbharga. Indian J Psychiatry 1977;19:69-70.
14. Lal N, Sethi BB. Demographic and socio demographic variables in attempted suicide by poisoning. Indian J Psychiatry 1975;17:100-7.
15. Vijayakumar L, Rajkumar S. Are risk factors for suicide universal? A case?controlled study in India. ActaPsychiatrScand 1999;99:407?11.
16. Conwel Y, Duberstein PR, Cox C, Herrmann JH, Forbes NT, Caine ED.Relationship of age and axis I diagnosis in victims of completed suicide: A psychological autopsy study. Am J Psychiatry 1996;153:1001?8.
17. Sureshkumar. Kerela. Indian J Psychiatry 2004;46:144?9.
18. Shukla GD, Verma BL, Mishra DN. Suicide in Jhansi city. Indian J Psychiatry 1990;32:44?51.
19. Nandi DN, Mukherjee SP, Banerjee G, Ghosh A, Horal GC, Choudhary A, et al. Is suicide preventable by restricting the availability of lethal agents?A rural survey of West Bengal. Indian J Psychiatry 1979;21:251?5.
20. Das PP, Grover S, Avasthi A, Chakrabarthi S, Malhotra S, KumarS.Intentionalself harm seen in psychiatric referrals in a tertiary care hospital. Indian J Psychiatry 2008;50:187-91.
21. Srivastava A. Study of hundred completed suicides. Indian Journal of Psychiatry 2013;55(3):268-72.
22. Kessing LV. Severity of depressive episodes according to ICD?10:Prediction of risk of relapse and suicide. Br J Psychiatry 2004;184:153?6.
23. Harris EC, Barraclough BM. Suicide as an outcome for mental disorders: A meta?analysis. Br J Psychiatry 1997;170:205?28.
24. Baxter D, Appleby L. Case register study of suicide risk in mental disorders. Br J Psychiatry 1999;175:322?6.
25. Jain V, Singh H, Gupta SC, Kumar S. A study of hopelessness, suicidal intent and depression in cases of attempted suicide. Indian J Psychiatry1999;41:122-30.
26. Sarkar P, Sattar FA, Gode N, Basanar DR. Failed suicide and deliberate self harm: A need for specific nomenclature. Indian J Psychiatry 2006;48:78-83.
27. Ponnudurai R, Jeyakar J, Saraswathy M. Attempted suicides in Madras.Indian J Psychiatry 1986;28:59-62.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License