IJCRR - 8(5), March, 2016
Pages: 13-21
Date of Publication: 13-Mar-2016
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
ACCURACY OF SERUM URIC ACID IN PREDICTING COMPLICATIONS OF PRE-ECLAMPSIA
Author: A. Ramana Priya, K. Jeyapriya, N. S. Kannan
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Pre-eclampsia, is a pregnancy-specific syndrome that occurs after mid gestation comprising of gestational hypertension with significant proteinuria. If not treated properly will lead to maternal and foetal complications. Aims: To study the accuracy of serum uric acid in predicting complications of pre-eclampsia and its effect on pregnancy outcome. Methods: Sixty pregnant women at term gestation with diagnosis of pre-eclampsia were included in our study after informed consent. For all patients included in the study all routine investigations including serum uric acid were done and recorded. All the patients were followed up until delivery and all maternal and foetal events were recorded. All complications of pre-eclampsia both maternal and foetal were statistically analysed to prove the predictive value of serum uric acid levels. Results: 18.3% of mothers were between the age group 18-21 years, 26.7% were between 22-25 years, 28.3% were between 26-29 years, and 26.7% were above 30 years. 83.4% of 60 mothers were primi para, 8.3% were para 2, and 8.3% were para 3. The difference in the first minute APGAR in the high risk and no risk category was not statistically significant at p value of 0.1798. The difference in the 5th minute APGAR in the high risk and no risk category was statistically significant at p value of 0.001. 4 out of 42 women (9.52%) with serum uric acid ≥6mg/dl had maternal complications and 7 out of 18 women with serum uric acid < 6mg/dl had maternal complications (p value = 0.01) which is statistically significant. Considering less than 2.5 Kg as low birth weight, serum uric acid levels of more than 5.5 are associated with significant low birth weight (p value of 0.01) which is statistically significant. Conclusion: Our study with a sample size of 60 has proved that serum uric acid is statistically significant predictor (p value 0.01) of foetal complications of pre-eclampsia even though not of maternal complications (p value 0.42).
Keywords: Gestational hypertension, Eclampsia, HELLP syndrome, Maternal death, Intrauterine growth restriction, Foetal distress, Perinatal death
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Pre-eclampsia, a pregnancy-specific syndrome that occurs after mid gestation, is defined by the de novo appearance of hypertension (systolic blood pressure of ≥140 mm Hg or diastolic blood pressure of ≥90 mm Hg), accompanied by new-onset proteinuria, defined as ≥300 mg per 24 hours1 . Previous definitions included oedema, but this sign is nonspecific and is observed in many normotensive pregnant women. Thus, oedema is no longer considered part of the diagnostic criteria for preeclampsia.
The incidence of preeclampsia is 2-10%, depending on the population studied and definitions of Pre-eclampsia2 . It can result in many maternal complications3,4 such as severe hypertension, eclampsia and HELLP syndrome (Haemolysis, Elevated Liver enzymes and Low platelet count), or foetal complications5 such as growth restriction, foetal distress and even perinatal death. Early prediction of these complications might help to decide whether termination of pregnancy might be a better option than expectant monitoring.
AIMS AND OBJECTIVES:
Aims: To study the accuracy of serum uric acid in predicting complications of pre-eclampsia and its effect on pregnancy outcome. Objectives: 1. To estimate the serum uric acid levels in term gestation with pre-eclampsia. 2. To evaluate the relationship between serum uric acid and foetal outcome. 3. To know the association between the level of serum uric acid and severity of hypertension. 4. To correlate serum uric acid levels with maternal morbidity and mortality.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A prospective study to estimate serum uric acid was carried out in 60 pregnant women at term gestation ( > 37 weeks of gestation) admitted in Raja Muthiah Medical College Hospital during the period October 2011 - September 2013 with diagnosis of pre-eclampsia (pregnancy induced hypertension and proteinuria with or without pathological oedema). These patients were included in the study after due informed consent. The criteria adopted to diagnose pregnancy induced hypertension1 : Systolic blood pressure of ≥140 mm Hg or diastolic blood pressure of ≥90 mm Hg.
The criteria adopted to diagnose significant proteinuria3,17,18: One 24-hour urine collection with a total protein excretion of 300 mg / 24 hours. The criteria adopted with reference to oedema1,2: Previous definitions included oedema, but this sign is nonspecific and is observed in many normotensive pregnant women. Thus, oedema is no longer considered part of the diagnostic criteria for preeclampsia. Pre-eclampsia patients may or may not have pathological oedema. The criteria adopted to diagnose high-risk serum uric acid level19: Values ≥6 mg/dl (360 µmol/l) was cut off level for high risk in our study.
Inclusion criteria: All patients diagnosed as pre-eclampsia as per the above criteria subject to their willingness to participate in the study after informed consent. Exclusion criteria: 1. History of chronic hypertension 2. Family history of hypertension or diabetes mellitus 3. Pre existing medical illness like heart disease, diabetes mellitus, renal diseases or thyroid disorders. 4. Hypertension before 20 weeks of gestation 5. Patients who are not willing to participate in the study. Method of study Out of all cases admitted with the diagnosis of pre-eclampsia, 60 were selected based upon fulfilling inclusion and exclusion criteria.
A detailed history of each patient was taken and complete general and obstetric examination was done. All findings were recorded in pre-designed proforma. Hyperten- sion and Proteinuria were diagnosed as per the criteria already described. For all patients included in the study all routine investigations including serum uric acid were done and recorded. For determination of serum uric acid two methods have been described: 1. Calorimetric method (Caraway’s method) and 2.
Enzymatic method. Calorimetric method is influenced by many factors in the procedure as well as many contaminating substances in the glassware etc. In the enzymatic method, enzyme uricase has been widely used for uric acid determinations because of its improved specificity20-22. Therefore, we used enzymatic method. All the patients were followed up until delivery and all maternal and foetal events were recorded. All complications of pre-eclampsia both maternal and foetal were statistically analysed to prove the predictive value of serum uric acid levels.
RESULTS AND OBSERVATIONS
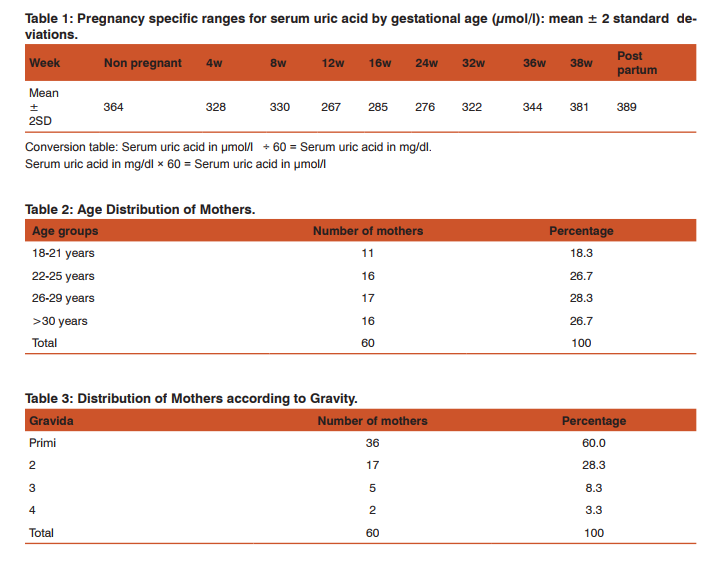
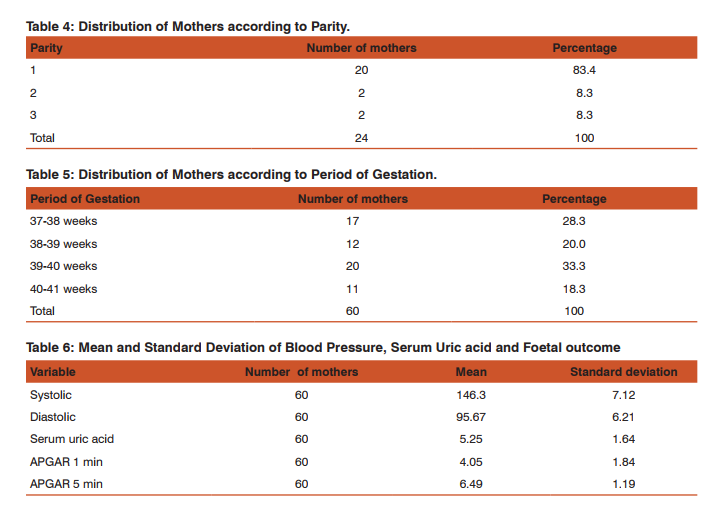
Distribution according to the age of mothers: 18.3% of mothers were between the age group 18-21 years, 26.7% were between 22-25 years, 28.3% were between 26-29 years, and 26.7% were above 30 years (Table/Fig 2). Distribution according to Gravida: 60.0% of mothers were primi, 28.3% were second gravid, 8.3% were third gravid and 3.3% were fourth gravid (Table/Fig 3). Distribution according to Parity: 83.4% of 60 mothers were primi para, 8.3% were para 2, and 8.3% were para 3 (Table/ Fig 4). Distribution according to period of gestation: 28.3% were 37-38 weeks, 2.0% were 38-39 weeks, 33.3% were 39-40 weeks, 18.3% were 40-41 weeks of gestation (Table/Fig 5).
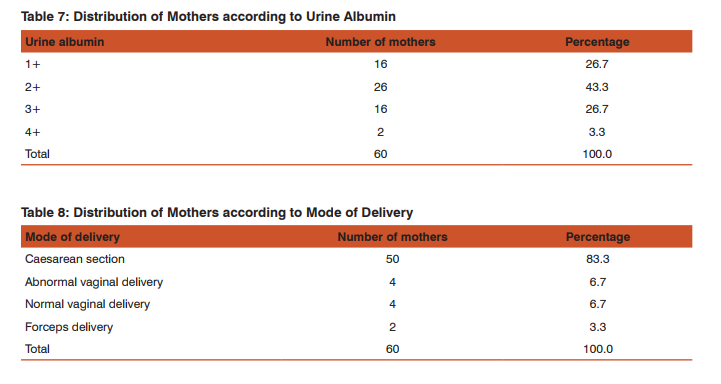
Mean and Standard Deviation of Blood Pressure, Serum Uric acid and Foetal outcome: The mean systolic was 146.33 and standard deviation 7.12. The mean diastolic was 95.67 and standard deviation 6.21. The mean uric acid was 5.25 and standard deviation 1.64. The mean foetal outcome of APGAR 1 minute was 4.05 and standard deviation 1.84. The mean foetal outcome of APGAR 5 minutes was 6.49 and standard deviation 1.19 (Table/Fig 6). Distribution of Mothers according to Urine Albumin: Urine albumin was 1+ in 26.7% of mothers, 2+ in 43.3% of mothers, 3+ in 26.7 % of mothers and 4+ in 3.3% of mothers (Table/Fig 7).
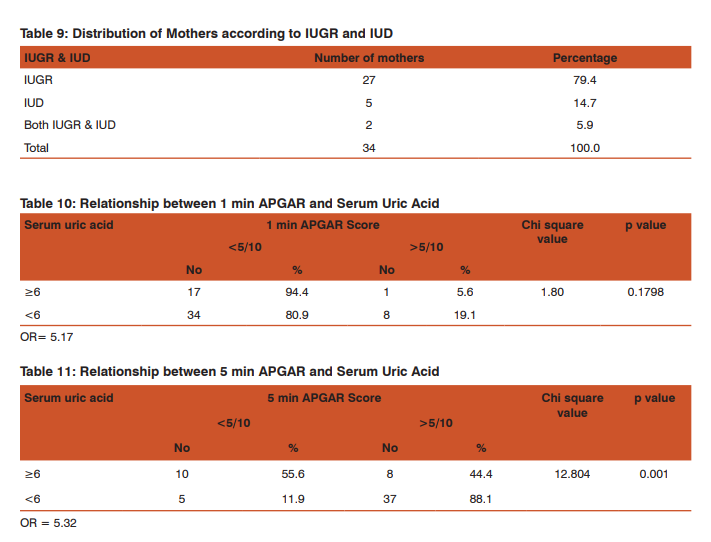
Distribution of Mothers according to Mode of Delivery: 83.3% of mothers had caesarean section, 6.7% of mothers had abnormal vaginal delivery, another 6.7% had normal vaginal delivery and 3.3% had forceps delivery (Table/Fig 8). Distribution of Mothers according to IUGR (intra uterine growth retardation) and IUD (intra uterine death): 79.4% of 60 mothers were admitted with IUGR, 14.7% of mothers were admitted with IUD and 5.9% of mothers were admitted with both IUGR and IUD (Table/Fig 9). Relationship between 1st min APGAR and Serum Uric Acid: 94.4% of babies under high-risk category had an APGAR of less than 5/10 in the 1st minute of their life, whereas 80.0% of the babies under no risk category had an APGAR of less than 5/10 in the 1st minute of their life. The difference in the first minute APGAR in the high risk and no risk category was not statistically significant at p value of 0.1798 (Table/Fig 10).
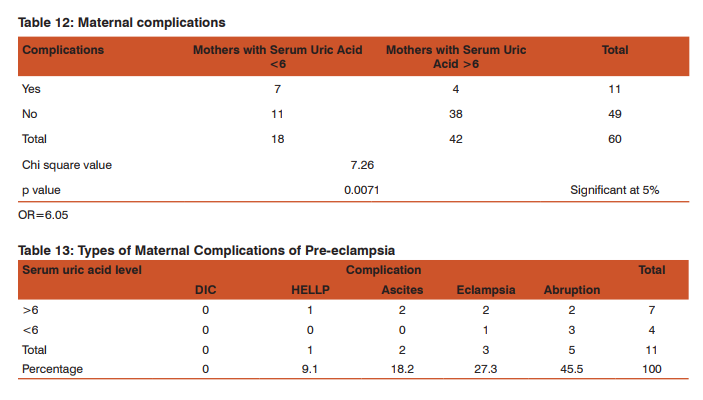
Relationship between 5th min APGAR and Serum Uric Acid: 55.6% of babies under high-risk category had an APGAR of less than 5/10 in the 5th minute of their life, whereas 11.9% of the babies under no risk category had an APGAR of less than 5/10 in the 5th minute of their life (Table/Fig 11). The difference in the 5th minute APGAR in the high risk and no risk category was statistically significant at p value of 0.001. From this table infers that the mothers whose serum uric acid was more than 6 mg/dl had 4-5 times increased risk of having APGAR of less than 5/10 at 5th min when compared to mothers with serum uric acid less than 6mg/dl. Maternal complications: 4 out of 42 women (9.52%) with serum uric acid ≥ 6mg/dl had maternal complications and 7 out of 18 women with serum uric acid <6mg/dl had maternal complications with a statistically significant p value of 0.01 (Table/Fig 12).
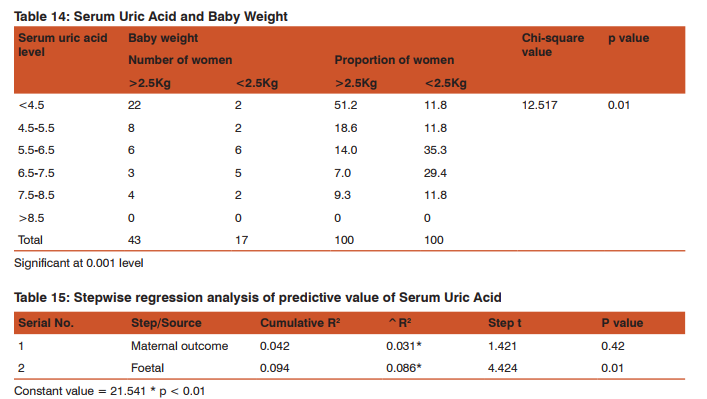
Types of Maternal Complications of Pre-eclampsia: 9.1% of mothers developed HELLP, 18.2% of mothers developed Ascites, 27.3% of mothers developed Eclampsia and 45.5% of mothers developed Abruption (Table/Fig 13). Serum Uric Acid and Baby Weight: Considering less than 2.5 Kg as low birth weight serum uric acid levels of more than 5.5 are associated with significant low birth weight (p value of 0.01) which is statistically significant (Table/Fig 14). Stepwise regression analysis of predictive value of Serum Uric Acid: Serum uric acid has significantly contributed for predicting the foetal outcome compared to maternal outcome. The predictive value of the variable separately is 0.01. Altogether, the above computations clearly state that serum uric acid will be highly predictive of foetal complications as compared to maternal complications (Table/Fig 15).
DISCUSSION Total number of patients fulfilling all inclusion criteria and having given consent for the study were 60 (n=60). Age and gravida/para status: According to Mac Gillvary23 the relationship of the maternal age and pre-eclampsia incidence gives a ’J’ shaped curve with increased incidence among young primi gravida and markedly increased among older primi gravid.
According to Duckitt K et al24, about 60% of the patients in pre-eclampsia group were primigravdae. This correlates well with our present study. In our present study 17 women were between 26-39 years (28.3%) and 16 women were between 22-25 and less than 30 years (26.7%) and only 11women were between 18-21 years (18.3%). 36 (60%) were primigravidae and 24 (40%) were multi gravidae; 83.4% were primi para, 8.3% were second para and 8.3 were third para. Maternal outcome and serum uric acid: According to Disha Sahijuani et al25 10 out of 50 women (20%) with uric acid 6mg/dl and only 11.9% of them with APGAR less than 5/10 at fifth minute were under low risk category.
The difference in fifth minute APGAR in the high risk and no risk group was statistically significant at p value of 0.001. It is inferred that mothers whose serum uric acid was high had 4-5 times increased chances of delivering baby with less than 5/10 APGAR at fifth minute when compared to mothers whose serum uric acid was normal. Even though the above inferences in our study are, in favour serum uric acid levels ≥6mg/dl is predictive of both maternal and foetal complications at p value of 0.001 and 0.01 respectively, the step wise regression analysis infers that serum uric acid will be highly predictive of foetal complications (p value of 0.01) as compared to maternal complications (p value of 0.42).
In systematic review conducted by Thangaratinam et al27, on 17 studies26,24-43 with sample size ranging from 14-504 pre-eclampsia women, it was concluded that serum uric acid is a poor predictor of maternal and foetal complications in women with pre-eclampsia. Several other studies (six studies) have reported a positive correlation between elevated maternal serum uric acid and adverse maternal and foetal outcomes9-15.
CONCLUSION In the past 17 studies with sample sizes ranging from 14 to 504 have concluded that serum uric acid is poor predictor of foetal and maternal complications of pre-eclampsia. Six other studies have reported a positive correlation between elevated maternal serum uric acid and adverse maternal and foetal outcomes. However, our study with a sample size of 60 has proved that serum uric acid is statistically significant predictor (p value 0.01) of foetal complications of pre-eclampsia even though not of maternal complications (p value 0.42). Further studies with bigger sample size may substantiate our conclusion.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT Authors duly thank Dr. S. Viswanathan, Professor and Head, department of obstetrics and gynaecology, and Dr. S. Balasubramaniyan, Dean, Raja Muthiah Medical College and Hospital, Annamalai University, Annamalai Nagar, Chidabmbaram, India, for permitting us to publish the contents of PG Dissertation of Dr. A. Ramana priya, as an article in IJCRR. Authors also acknowledge Dr. K. Lalitha Professor obstetrics & gynaecology, Raja Muthiah Medical College and Hospital, Annamalai University, Annamalai Nagar, Chidabmbaram, India, for her immense help as Guide to Dr. A. Ramana priya, in accomplishing her dissertation work. Authors also acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. Authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Source of funding: Nil Conflict of interest: All authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
References:
1. Roberts JM, Pearson G, Cutler J, Lindheimer M. Summary of the NHLBI Working Group on Research on Hypertension During Pregnancy. Hypertension 2003;41:437-45.
2. Carelton H, F.A., Flores R. Remote prognosis of pre-eclampsia in women 25 years old and younger. Am J Obstet Gynecol, 1988; 159:156-60.
3. ACOG. ACOG Practice Bulletin: Diagnosis and Management of Preeclampsia and Eclampsia: The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Number 33. Jan 2002.
4. von Dadelszen P, Payne B, Li J, et al. Prediction of adverse maternal outcomes in pre-eclampsia: development and validation of the full PIERS model. Lancet. 2011 Jan 15. 377(9761):219- 27.
5. Gabbe. Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. Hypertension. 5th ed. Churchill Livingstone, An Imprint of Elsevier; 2007.
6. Hughes EC (ed): Obstetric-gynecologic terminology. Philadelphia, Davis, 1972, pp 422-3
7. MacGillivray, I. Pre-Eclampsia. The Hypertensive Disease of Pregnancy. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, PA; 1983 p17
8. Davey DA, MacGillivray I. The classification and definition of the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1988 Apr 30;158(4):892-8.
9. Redman CW, Beilin LJ, Bonnar J, Wilkinson RH. Plasma-urate measurements in predicting fetal death in hypertensive pregnancy. Lancet. 1976;1:1370-1373
10. Stone JL, Lockwood CJ, Berkowitz GS, Alvarez M, Lapinski R, Berkowitz RL. Risk factors for severe preeclampsia. Obstet Gynecol. 1994;83:357-361
11. Roberts JM, Bodnar LB, Lain KY, Hubel CA, Markovic N, Ness RB, Powers RW. Uric acid is as important as proteinuria in identifying fetal risk in women with gestational hypertension. Hypertension. 2005;46:1263-1269.
12. Parrish M, Griffin M, Morris R, Darby M, Owens MY, Martin JN. Hyperuricemia facilitates the prediction of maternal and perinatal adverse outcome in patients with severe/superimposed preeclampsia. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2010;23:1541-1545.
13. Laughon SK, Catov J, Powers RW, Roberts JM, Gandley RE. First trimester uric acid and adverse pregnancy outcomes. Am J Hypertens. 2011;24:489-495.
14. Paula LG, da Costa BE, Poli de Figuereido GE, Antonello IC. Does uric acid provide information about maternal condition and fetal outcome in pregnant women with hypertension Hypertens Pregnancy. 2008;27:413-420
15. Yalamati P, Bhongir AV, Betha K, Verma R, Dandge S. Relationship of serum uric acid, serum creatinine and serum cystatin C with maternal and fetal outcomes in rural Indian pregnant women. International journal of reproduction, contraception, obstetrics and gynecology. 2015;4(5):1505-1510. doi:10.18203/2320- 1770.ijrcog20150737.
16. Lind T, Godfrey KA, Otun H, Philips PR. Changes in serum uric acid concentrations during normal pregnancy. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1984 Feb;91(2):128-32.
17. Lopez-Espinoza, I, Dhar, H, Humphreys, S, Redman, CWG. Urinary albumin excretion in pregnancy. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1986;93:176-181.
18. Sibai, BM, Rodriguez, JJ. Preeclampsia: diagnosis and management. in: Principles and Practice of Medical Therapy in Pregnancy. 2nd ed. Appleton and Lange, Norwalk; 1992:871-879.
19. O’sullivan JB, Francis JO, Kantor N. Comparison of a colorimetric (automated) with an enzymatic (manual) uric acid procedure. Clin Chem. 1965 Mar;11:427-35.
20. www.pointescientific.com/uploads/inserts/OU982-01-2150.pdf
21. Klackar, H.M., J. Biol Chem. 167:429 (1947).
22. Praetorius, E., Poulson, H., Scand. J. Clin. Invest. 5:273 (1953).
23. Macgillivray I, Some observations on the incidence of pre-eclampsia. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Emp. 1958 Aug;65(4):536-9
24. Duckitt K, Harrington D. Risk factors for pre-eclampsia at antenatal booking: systematic review of controlled studies. Bmj. 2005 Mar 10;330(7491):565.
25. Sahijwani D, Desai A, Oza H, Kansara V, Ninama P, Maheshwari K, Soni C, Padhiyar B. Serum Uric Acid as a Prognostic Marker of Pregnancy induced Hypertension. Journal of South Asian Federation of Obstetrics and Gynaecology JSAFOG. 2012 Sep;4(3):130-3.
26. Liedholm H, Montan S, Åberg A. Risk grouping of 113 patients with hypertensive disorders during pregnancy, with respect to serum urate, proteinuria and time of onset of hypertension. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1984;63(S118):43-8.
27. Thangaratinam S, Ismail KM, Sharp S, Coomarasamy A, Khan KS. Accuracy of serum uric acid in predicting complications of pre-eclampsia: a systematic review. Br J Obstet Gynaecol: An International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology. 2006 Apr 1;113(4):369-78.
28. Yassaee F. Hyperuricemia and perinatal outcomes in patients with severe preeclampsia. Iran J Med Sci 2003;28:198-9.
29. Williams KP, Galerneau F. The role of serum uric acid as a prognostic indicator of the severity of maternal and fetal complications in hypertensive pregnancies. J Obstet Gynaecol Can 2002;24:628–32.
30. D’Anna R, Baviera G, Scilipoti A, Leonardi I, Leo R. The clinical utility of serum uric acid measurements in pre-eclampsia and transient hypertension in pregnancy. Panminerva Med 2000;42:101–3.
31. Martin JN Jr, May WL, Magann EF, Terrone DA, Rinehart BK, Blake P-G. Early risk assessment of severe preeclampsia: admission battery of symptoms and laboratory tests to predict likelihood of subsequent significant maternal morbidity. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;180:1407-14.
32. Odendaal HJ, Pienaar ME. Are high uric acid levels in patients with early pre-eclampsia an indication for delivery S Afr Med J 1997;87:213-18.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License