IJCRR - 10(14), July, 2018
Pages: 16-21
Date of Publication: 18-Jul-2018
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Larvicidal Activity of Crude Solanum Nigrum Leaf and Berries Extract Against Dengue Vector-Aedesaegypti
Author: Mithun Kumar Patel, Aishwarya Tiwari, Vijay Laxmi Saxena
Category: Life Sciences
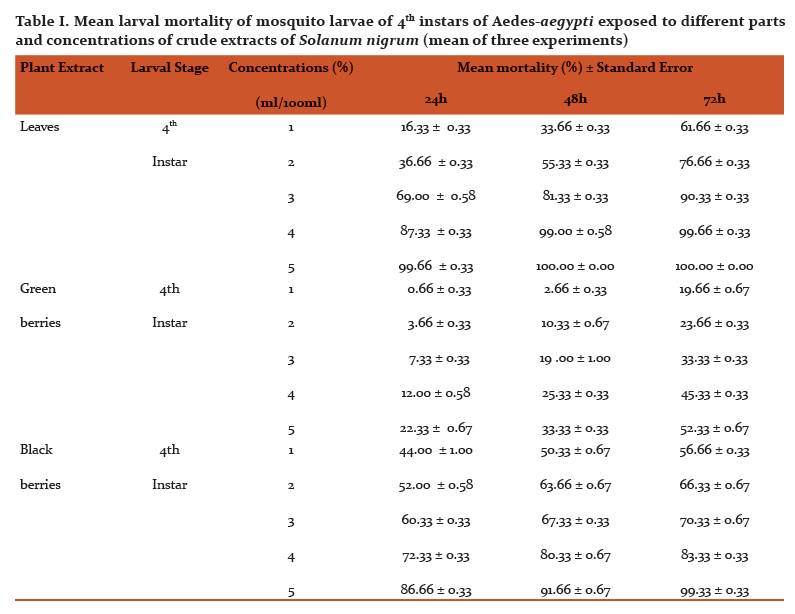
Abstract:Mosquitoes are the most vital single gathering of creepy crawlies as far as general wellbeing. They transmit various illnesses, for example, jungle fever, dengue fever, chikungunya, filariasis, Japanese encephalitis, West Nile infection and yellow fever and so on prompts a large number of passings consistently. The aim of this study is to investigate the impacts of various parts of Solanum nigrum unrefined concentrate tried against fourth instars hatchlings of dengue vector, Aedes-aegypti, under the research facility conditions. New Solanum nigrum plants were gathered from professional flower bed D.G.P.G College in Kanpur, U.P. India, and washed completely 2-3 times with running faucet water. 20 gm of new leaves and 10-10gm green and dark berries was gathered and quickly ground utilizing a pestle and mortar independently. All ground material was sifted through a Buchner pipe with What-man number 1 channel paper and independently put away in glass bottle till additionally utilize. Research centre raised fourth instars hatchlings of Aedes-aegypti were treated with various centralization of fluid arrangements all things considered. The tests were directed at room temperature (24\?C-29\?C). Fixations (1-5%) of the all concentrate were set up in de-chlorinated water. At each the given fixation, 100 hatchlings were uncovered. Mortality was watched for 24, 48 and 72 hours. Leaves and dark berries extricate displayed most noteworthy larvicidal movement with a LC50 estimation of 2.47, 1.67, 0.98 and 1.54, 1.14 0.99% following 24, 48 and 72 hours individually. No mortality was seen in the control gathering. This is another eco-accommodating methodology for the control of Aedes-aegypti mosquito as target species. The present outcomes propose that the viable rough leaf extricates can possibly be utilized as a perfect eco-accommodating methodology for the control of mosquito vectors.
Keywords: Aedes-aegypti, Solanum nigrum, Larval mortality, Dengue vector
Full Text:
Introduction:
There are many forms of mosquito living in the tropical and sub-tropical regions of the world, we can roughly them divide into two groups Culex and Aedes, but perhaps one of the most important is Aedes-aegypti. According to the World Health Organization, the virus for Dengue fever is the most important arbovirus to man in the world, and since Aedes has been found to transmit this virus, it has been widely studied and blamed as the vector. The males of all species of mosquitoes do not bite humans or animals of any species, they live on fruit. Only the female bites for blood because she requirements to mature her eggs. The eggs of most species are laid together in a raft form, but Aedes lays her eggs separately thus allowing them to spread over large surfaces of water if conditions permit, this way the eggs stand a better chance of survival. When freshly laid the eggs are white but soon turn black in color. The young larvae feed on bacteria in the water and soon cast their skins as they rapidly grow. Here, I must point out the fact that most species lay their eggs in any type of water, mainly dirty or even polluted. Not Aedes, she only lays her eggs in clean water which contains no other living species1.
This mosquito is small in comparison to others, usually between 4-5mm in length discounting leg length. It is totally black apart from white 'spots' on the body and head regions and white rings on the legs. The thorax is decorated with a white 'Lyre' shape of which the 'chords' are two dull yellow lines (Fig 1-E). Its wings are translucent and bordered with scales2. Aedes-aegypti bites primarily during the day. This species is most active for approximately two hours after sunrise and several hours before sunset, but it can bite at night as well. This mosquito can bite people without being observed because it approaches from behind and bites on the ankles and elbows. Aedes aegypti prefers biting people but it also bites dogs and other domestic animals, mostly mammals3. To find a host, Aedes-aegypti is fascinated to chemical compounds that are discharged by mammals. These compounds include ammonia, carbon, lactic acid, and octanol. Scientists at the Agricultural Research Service have studied the specific chemical structure of octenol in order to better understand why this chemical attracts the mosquito to its host4. One primary vector of yellow fever, chikungunya fever, dengue fever, dengue hemorrhagic fever (DHF) and dengue shock syndrome, is Aedes-aegypti5. However, Dengue fever has become an important public health problem as the number of reported cases continues to increase, especially with more severe forms of the disease, dengue hemorrhagic fever, and dengue shock syndrome, or with unusual manifestations such as central nervous system involvement6. Mosquito control, in view of their medical importance, assumes global importance. In the context of ever increasing trend to use more powerful synthetic insecticides to achieve immediate results in the control of mosquitoes, an alarming increase of physiological resistance in the vectors, its increased toxicity to non-target organism and high costs are noteworthy7. Most of synthetic chemicals are expensive and destructive to the environment and also toxic to humans, animals and other non-target organisms. Besides, they are no selective and harmful to other beneficial organisms. Some of the insecticides act as carcinogenic agents and are even carried through food chain which in turn affects the non-target organism. Therefore alternative vector control strategies, especially effective and low cost are extremely imperative8, 9, 10. The plant based herbal insecticides are found to more efficient, safe and best substitute for chemicalInsecticides11. Natural products of plant origin are safe to use than the synthetic insecticides12. Therefore biological and eco-friendly natural resources are broad search area for the control of vector of medical importance13. In recent years use of environment-friendly and easily biodegradable natural insecticides of plant origin has received renewed importance for disease vector control. Interest in this field has increased more so, as they are least phytotoxic and do not accumulate chemical residues in flora, fauna andsoil14. The present communication deals with the laboratory studies carried out to ascertain the larvicidal properties of different parts of Solanum nigrum (Figure 1) in Aedes-aegypti. This plant is widely distributed in the wild in many parts of India. Taxonomic position of this plant is as follows: Division – Embryophyta; Sub-division – Angiospermae; Class –Dicotyledoneae; Order – Tubeflorae; Sub-order – Solanales; Family – Solanaceae; Genera – Solanum. The local names in some important vernacular languages are: Hindi – Makoi15. S. nigrum L. subsp. Nigrum- glabrous to slightly hairy with appressed non-glandular hairs. This species is reported to have many medicinal properties and is used mainly as antidysenteric, diuretic, antipyretic, anti-in?ammatory, hepatoprotective, laxative and antispasmodic16.
Materials and Methods
Selection of Plant:
The whole plant of Solanum nigrum were collected from 2 months old mature plants growing in the Home garden of swarup nagar, Kanpur, India. The plants were identified as per method17 [S.K. Jain, A handbook of field and herbarium methods, New Delhi] and the plant was submitted to Department of Botany, D.G.P.G College, Kanpur, for taxonomic identification and confirmation of the species.
Preparation of leaf extract of Solanum nigrum:
50gm fresh leaves were washed with tap water and cleaned thoroughly with a cloth. The leaves were cut into small pieces and immediately ground using a pestle and mortar. The ground material was filtered by cloth and then passing the filtered material through What-man No. 1 filter paper and filtrate of the crude leaf extract was stored in a clean brown bottle till further use.
Preparation of berries extract of Solanum nigrum:
Collect 40gm berries, 20gm black and 20gm green colour washed with tap water and dried on a paper towel. Both berries extract was prepared separately by grinding in a mortar and pestle and ground material was filtered by cloth and then passing the filtered material through Buchner funnel (Borosil, Mumbai, India) with What-man No. 1 filter paper.
Selection of mosquito species:
The eggs of Aedes-aegypti(Fig. 1-A)were procured from stagnant water of pools with the help of hand net from an around area of civil lines, Kanpur city, UP, India. The egg rafts of Aedes-aegypti were kept in the tray containing tap water (culture medium) and maintained at 24 ± 20C temperature, 70 ± 30C relative humidity under 14 h light (L): 10 h dark (D) photo period cycle. After 24-36 hrs of incubation, the eggs were observed to hatch out into first instar larvae. Appropriate amount of nutrient (sterilized yeast powder and dog biscuit in 1:1 ratio) were added to enhance the growth of larvae. The 4th instar larvae(Fig. 1-B) were used in the study. The treated larva was mounted on a slide and examined under a microscope (Zoomstar III, Trinocular Stereozoom microscope-Dewinter Technologies, Italy) for image capture on a Dewinter digital Microscope camera (Dewinter Technologies, Italy). All stages of Aedes-aegypti were identified and take the pictures of main characters: Larval abdomen have pitch fork shaped comb scale with distinct larger median spine(Fig. 1-C), strong black hooks on side of larval thorax (Fig. 1-D), adult- scutum black or brown with a pair of submedian-longitudinal white stripes and lyre-shaped silvery-white scales (Fig. 1-E), mesepimeron with two well separated white scale patches(Fig. 1-F), clypeus has white scales (Fig. 1-G).

Larvicidal bioassay
A laboratory reared colony of Aedes-aegypti larvae was used for the larvicidal activity. Each of the previously made concentration of 1,2,3,4 and 5% each crude extracts of Solanum nigrum(leaf and berries extract) was transferred into a sterilized glass beakers (250 ml capacity). Hundred larvae of 4th instar per concentration were used for all larvae experiment with 100ml of tap water (8pH, checked by indicator papers-S D fine chem. Ltd., Mumbai). Larval food (sterilized yeast powder and dog biscuit in 1:1 ratio) was added in each beaker. The treatments were replicated three times, and each replicate set contained one control. Mortalities were reported after 24hr, 48hr, and 72hr of the exposure period. Laboratory room temperature was maintained at 24-+20C during the experiment period. The dead larvae in three replicates were combined and expressed as percentage mortality for each concentration. Dead larvae were acknowledged when they failed to move after probing with a needle and brush.
Result
Larvicidal properties of extracts from different part of Solanum nigrum:
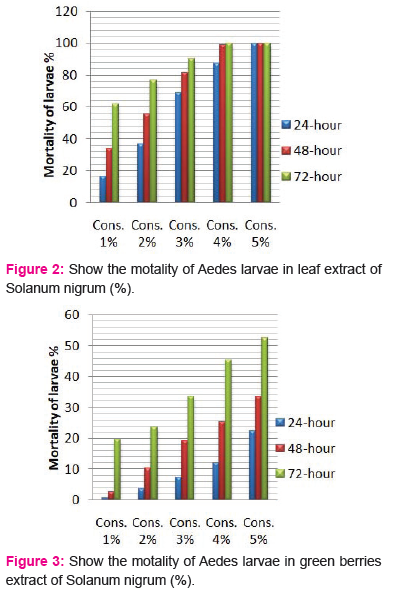
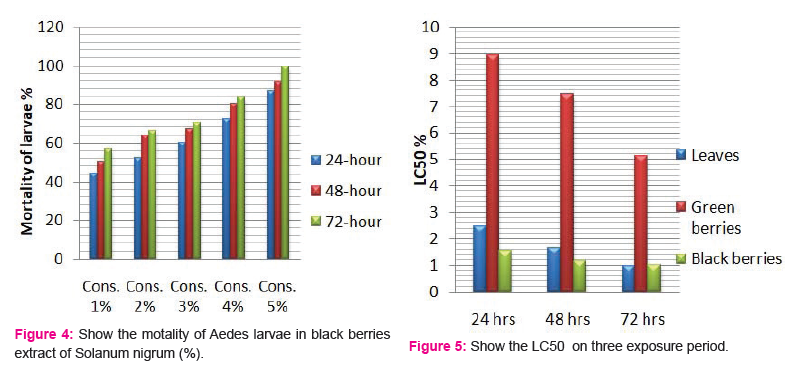
The crude extracts from different parts of Solanum nigrum were respectively prepared into five different concentrations of each part; and the mortality of the Aedes-aegypti larvae was observed. All extracts showed considerable larvicidal activity when tested against Aedes-aegypti. The effects of the leaf and berries extracts of Solanum nigrum were tested at 1,2,3,4 and 5% each extract and showed activity against the fourth instar larvae of Aedes-aegypti (Table 1). All plant extracts showed moderate larvicidal effects after 24 h; however, the highest larval mortality was found in leaf and black berries extract of 5% concentration.
Larvicidal activity of crude Leaf extracts:
The effects of the plant leaf crude extracts of
Different concentrations (1, 2, 3, 4 and 5%) were shown in Fig. 2, respectively. At concentration of 5%showed highest mortality (100%) after 48 h, followed by extract 1, 2, 3 and 4%. The LC50 values2.47, 1.67, 0.98% and LC90 values 4.15, 3.49 and 2.64% after 24, 48 and 72h, respectively.
Larvicidal activity of crude berries extracts:
The larvicidal activity of different concentrations of green and black berries extracts were shown in Fig. 3 and 4, respectively. After 24 h and concentration of 5%, black berries extracts showed 86.66 % mortality and green berries extracts showed 22.33% mortality of larvae. The LC50 value in green berries extract, 8.92, 7.47, 5.14 %, LC90 values 23.21, 26.96, 45.98% and LC50 value in black berries extract, 1.54, 1.14, 0.99%, LC90 values 11.64, 7.67, 5.61% after 24, 48 and 72h, respectively.

Statistical analysis:
The percentage mean mortality (%) was calculated by statistic calculator and probit analysis (calculating LC50 and LC90 values) calculated by StatsDirect3 software using logit model.
Discussion
The transmission of mosquito-borne diseases can be interrupted by the potential insecticides of herbal origin at the individual as well as at the communitylevel18. Recently the natural insecticides of plant origin have been given importance due to their eco-friendly nature and biodegradability as a substitute of synthetic. Insecticides for the control of vectors of public health importance19. Many approaches have been developed to control the mosquito menace. One such approach to prevent mosquito-borne disease is by killing mosquito at the larval stage. The current mosquito control approach is based on synthetic insecticides. Even though they are effective, they created many problems, such as insecticide resistance20, pollution, and toxic side effects on humans21. The present study evaluatebio-control efficacy of crude extract of Solanum nigrum (different part) against Aedes-aegypti. Highest mortality was recorded after 24h in5% concentration of crude leaves extract against 4th instar larvae. In the present study, at a very low concentration of 1%, extract of leaves and black berries of S. nigrum resulted in 61.66and 55.66 per cent mortality of 4thinstar larvae after 72 h of exposure which indicates its bio-control potentiality.
Conclusion:
In the present study, Solanum nigrum crude extract showed larvicidal activities against mosquito probably due to the presence of active compounds such as eugenol and (E)-6-hydroxy-4,6-dimethyl-3-heptene-2-one (Kelm and Nair, 1998) which either in single form or in combination with other responsible compounds for larval death. There is no any abnormal behaviour of non-target organisms when they exposed to LC50 value so it is safe to use in natural condition. The present investigation revealed that the leaves of Solanum nigrum have a potential source of useful drugs due to the presence of phytochemicals and can be utilized in the treatment of many diseases. However further studies required to isolate the active principle from the crude extract for proper drug development.
Acknowledgements: Authors thanks Ankita Sethia, Swati Srivastava, Khushboo Arya, Dolly Chauhan, Mohit Kashyap and Anjali Katiyar for their critical inputs in this manuscript.
References:
-
Centers for disease control. (2007). Chikungunya fever fact sheet. Division for Vector-borne infectious disease: Centers for disease control.
-
Roland Mortimer, Rio de Janeiro. Aedes-aegypti and Dengue fever.Onview.net Ltd, Microscopy-UK. Retrieved 2010-08-27.
-
"Travelers' Health Outbreak Notice". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. June 2002, 2010. Archived from the original on 26 August 2010. Retrieved 2010-08-27.
-
Dennis O'Brien (March 9, 2010). "ARS Study Provides a Better Understanding of How Mosquitoes Find a Host". U.S. Department of Agriculture. Archived from the original on 8 October 2010.Retrieved 2010-08-27.
-
Grantz, G.N. (1993) .What must we do to effectively control Aedes aegypti. Journal of Tropical Medicine, 35, 243-251.
-
Pancharoen, C., Kulwichit, et al., 2002. Dengue infection: a global concern. J. Med. Assoc. Thai. 85, 25–33.
-
World Health Organization, 1975. Manual on Practical Entomology in Malaria Part I. Who division of malaria and other parasitic diseases, pp. 160.
-
Piyarat, S.W.K., Freed, M., Roy, S., 1974. Biologically active plant extract for the control of mosquito larvae. Mosq. News 34, 398.
-
Kalyanasundaram, M., Das, P.K., 1985. Larvicidal and synergistic activity of plant extracts for mosquito control. Indian J. Med. Res. 82, 19–23.
-
Jayapal Subramaniam, Kalimuthu Kovendan, et.al.(2012). Mosquito larvicidal activity of Aloe vera (Family:Liliaceae) leaf extract and Bacillus sphaericus, against Chikungunya vector, Aedes aegypti. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences,
-
Ghosh A., Chowdhury N., Chandra G., 2012, Plant extracts as potential mosquito larvicide, Indian J. Med. Res, 135: 581-598.
-
Kishore N., Mishra B.B., Tiwari V.K. and Tripathi V., 2011, A review on natural products with mosquitosidal potentials, In: Tiwari VK, editor, Opportunity, Challenge and Scope of Natural Products in Medicinal Chemistry, Kerala: Research Signpost, pp.335-65.
-
Singha S., Adhikari U., Ghosh A., Chandra G., 2012, Mosquito larvicidal potentiality of Holoptelea integrifolia leaf extract against Japanese encephalitis vector, Culex vishuni group, Journal of Mosquito Research, 2(4): 25-31.
-
Thomas, T. G., Sharma, S. K., Jalees, S. and Rahman, S. J., J. Basic Appl. Biomed., 1994, 2, 53–55.)
-
Chopra, R. N., Nayar, S. L. and Chopra, I. C., Glossary of Indian Medicinal Plants, PID, New Delhi, 1956, p. 229.
-
Jain, R, Sharma, A, Gupta, S, Sarethy, I.P., Gabrani, R., "Solanum nigrum: current perspectives on therapeutic properties." Altern Med Rev. 2011 Mar;16(1):78-85.
-
S.K. Jain and R.R Rao, A handbook of field and herbarium methods, (New Delhi: Today and Tomorrow Printers and Publishers-1976).
-
Campbell F.L., Sullivan W.W. and Smith L.N., 1993, The relative toxicity of nicotine, nabasine, methylanaba sine and lupinine for Culicine mosquito larvae, J. Econo. Entomol., 26: 505-509.
-
Mousumi Kundu ; Anjali Rawani ; Goutam Chandra 2013, Evaluation of Mosquito Larvicidal Activities of Seed Coat Extract of Cassia sophera L. Journal of Mosquito Research, Vol.3, No.11, 76-81.
-
Liu H., Xu Q., Zhang L., Liu N., 2005 -Chlorpyrifos resistance in Mosquito Culex aegypti and Culex pipiens pallens. - J.Med. Ent. 42: 815-820.
-
Lixin S., Huiquin D., Chongxia G., et al., 2006 Larvicidal activity of extracts of Ginko biloba Exocarp for three different strains of Culex pipiens pallens. - J.Med. Ent. 43: 258-261.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License