IJCRR - 10(2), January, 2018
Pages: 25-30
Date of Publication: 19-Jan-2018
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
In Vitro Interaction Studies between Artemether \? Lumefantrine and Lamivudine/Metronidazole
Author: Awofisayo Sunday O., Arhewoh Matthew I., Okhamafe Augustine O.
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:This work assesses tablets of artemether and lumefantrine in vitro drug interaction with lamivudine or metronidazole. Spectra changes on artemether or lumefantrine vibration bands were evaluated using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and analyzed with essential FTIR (eFTIR) software. Instantaneous pH changes and acid buffering capacity in biorelevant media were also determined. USP type-2 dissolution apparatus (paddle) containing Fed State Simulated Intestinal Fluid Version 2 (FeSSIF-V2) was employed for dissolution test. Sample (5 mL) collected at various predetermined time intervals were analyzed simultaneously for artemether and lumefantrine with high performance liquid chromatographic (HPLC) reverse phase (RP) system, at 25oC. Artemether (O-H) stretching vibration was shifted to wavenumber 3387.0 and 3408.22 cm-1 by lamivudine and metronidazole, respectively. There was no significant shift in spectral bands corresponding to the endoperoxide linkage due to
both drugs. Lamivudine and metronidazole showed no significant change in the pH of biorelevant media (p > 0.05). The release kinetics in FeSSIF-V2 for artemether changed from Higuchi (R2 = 0.9124) to first order (R2 = 0.9422) due to presence of lamivudine while that of lumefantrine from first order (R2 = 0.9423) to Higuchi due to the metronidazole (R2 = 0.9871). There was no significant level of interaction between lamivudine and metronidazole with the actives of AL tablet in vitro. The drugs therefore can be co-administered without any biopharmaceutical implications.
Keywords: Release kinetics, Artemether-lumefantrine, Lamivudine, Metronidazole
DOI: 10.7324/IJCRR.2018.1026
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Co-prescribing and use of more than one drug at the same time is regular occurrence in clinical practice for the treatment of a single or multiple pathological conditions (Bennett and Brown, 2008). The concurrent use of multiple medicinal agents has been further necessitated by co-morbidities of pathologic conditions such as HIV/AIDS, diabetes, hypertension and malaria infection (Ahsan et al., 2012).
Malaria is one of the widely reported infectious diseases in the world that caused about one million deaths in the year 2006 (Rosenthal, 2014). The artemisinin derivatives have been co-formulated with other antimalarial agents and used with success in areas earlier reported with cases of multi-drug resistant Plasmodium falciparum infection (Adjei et al., 2008, Sagara et al., 2001). Some diseases of global interest along with malaria include intestinal parasitic infections such as amoebiasis or giardiasis and HIV/AIDS (Haque et al., 2003; CDC 2008, Cohen et al., 2008).
Artemether-lumefantrine (AL) is a fixed dose combination (FDC) antimalarial that is widely prescribed based on World Health Organization recommendation for uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria (WHO, 2015). This drug however may be co-prescribed with other drugs for which malaria has co-morbidities or share geographical distribution.
In the management of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, most clinicians prescribe fixed dose combinations of either tenofovir/emtricitabine or abacavir/lamivudine both of which can be given once daily. Zidovudine/lamivudine is commonly reserved for second or third line regimen due to toxicity and dosing schedule (Schooley, 2010; Thompson et al., 2010). Lamivudine as antiretroviral drug (ARD) and for hepatitis or metronidazole for intestinal and hepatic forms of amoebiasis/giardiasis may be co-administered with antimalarial AL. Antimalarial drug resistance has been of global concern with searchlight directed at avenues that predicate the bioavailability of the drugs.
Drug - drug interactions (DDI) have been reported as consequent to treatment failure (Edwards and Aronson, 2000). A study on drug-drug interaction of pyronaridine/artesunate and ritonavir in healthy volunteers by Morris and co-workers concluded that co-administration of ritonavir and pyronaridine/artesunate interacts to alter exposure to artesunate, dihydroartemisinin and ritonavir itself (Morris et al., 2012). Several in vitro models have been developed for predicting in vivo drug interactions of co-administered dugs (Wienkers and Heath, 2005). Fourier transform infra-red spectroscopy (FTIR) utilizes the phenomenon of wave interference and a software Fourier transform of the interferogram, to produce an infra-red spectrum that is characteristic of molecules. This instrumental method has been exploited extensively as an in vitro approach to predicting possible in vivo DDI (Kumari and Balaji, 2013).
This study seeks to evaluate in vitro drug–drug interaction between AL and lamivudine or metronidazole.
MATERIALS AND METHOD
Materials
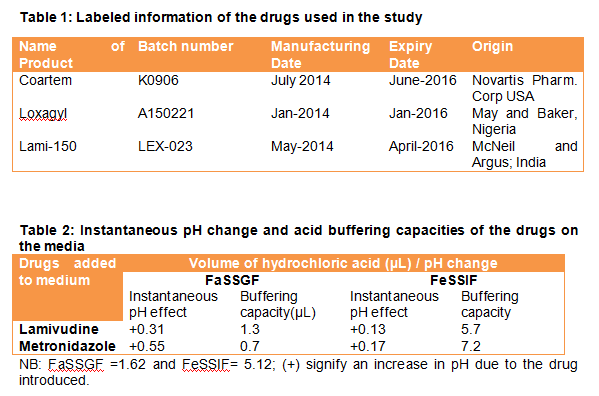
AL tablet (Coartem®) was bought from a registered drug outlet, in Uyo State, Southern Nigeria. Lamivudine and metronidazole tablets were purchased in Lagos State, Nigeria. The details of the drugs are presented in Table 1. Acetonitrile, methanol, tetrahydrofuran (THF), potassium dihydrogen phosphate were HPLC grade, products of Sigma Aldrich, Germany. FaSSIF/FeSSIF/FaSSGF and FeSSIF-V2 powder are products of Biorelevant.com, UK. Other reagents were of analytical grade, products of Sigma Aldrich, Germany.
Methods
Preparation of Standard solutions
The internal standard (IS) solution was prepared by accurately weighing 10 mg of halofantrine into 10 mL volumetric flask. A volume of 6 mL of methanol was added to dissolve and subsequently made to mark to produce a stock concentration of 1 mg/mL. A weight of 20mg and 120mg of reference standard artemether and lumefantrine, respectively were poured into different 10 mL volumetric flask. Artemether and lumefantrine were dissolved in acetonitrile and tetrahydrofuran (THF), to produce 2 mg/mL and 12 mg/mL stock solutions, respectively. Mixed standard solutions of artemether – lumefantrine and (IS) were prepared by adding equal aliquot volume of artemether and lumefantrine stock solutions (2 mL), dispensed into 5mL plain polypropylene sample bottles to produce 1 mg/mL and 6 mg/mL of the standards, respectively. Serial dilutions of the mixed standards and reference standard solutions were made to obtain graded concentrations of 0.01/10, 0.1/10.0, 0.5/20.0, 1.0/40.0, 5.0/60.0, 10.0/80.0 and 20.0/100.0 mg/mL. The mixed standard solutions were diluted with acetonitrile and THF (50:50 %, v/v). The obtained solutions were spiked with IS stock solution to give 5 µg/mL with micropipette (Huang et al., 2010).
Preparation of buffers and simulated intestinal solution
A weight of 1.0 g of sodium chloride was dissolved in 0.450 L of distilled water. The pH of the resulting solution was adjusted to 1.6 with hydrochloric acid solution and made up to 0.5 L with distilled water at room temperature. A weight of 2.020, 4.325 and 5.937 g of sodium hydroxide pellet, glacial acetic acid and sodium chloride, respectively, were dissolved in 0.450 L of distilled water and the resulting pH adjusted to 5.0 with either of 1N sodium hydroxide or hydrochloric acid. Fasted state simulated gastric fluid (FaSSGF) was prepared by dissolving 1.120 g of FaSSIF/FeSSIF/FaSSGF powder in 0.25 L of pH 1.6 buffer. This was stirred until the powder was completely dissolved. The solution was made up to 0.5L mark. The solution was allowed to stand for 2 hours before use and an unused portion was discarded after 48 h of preparation. Fed state simulated intestinal fluid was prepared by dissolving 5.60 g of FaSSIF/FeSSIF/FaSSGF powder in 0.25 L of buffer pH 5.0. The solution was made up to 0.5 L volume and allowed to stand for 2 h before use. Any unused solution was discarded after 48 h.Fed State Simulated Intestinal Fluid – Version 2 (FeSSIF – V2) was prepared by dissolving 5.0 g of FeSSIF – V2 powder in 5 L of distilled water (Galia et al., 1998).
Assessment of tablet quality parameters
The weight uniformity, tablet friability, disintegration and hardness were performed based on established pharmacopeia protocols. The chemical content of artemether and lumefantrine were simultaneously determined using the chromatographic system.
FTIR Spectroscopic analysis
FTIR spectroscopy was performed using FTIR spectrophotometer (FTIR 84005,Schimadzu, Japan). One milligram of AL crushed powder and 200 mg of dried potassium bromide (KBr) powder were mixed in a mortar and compressed into a translucent disk. The scanning was carried out at a speed of 2 mm/s over a wavenumber region of 4000 to 500 cm-1. Similarly, the process was repeated with the addition of 1 mg of the co-administered drugs (i.e, lamivudine or metronidazole) to the AL before pellet formation with KBr. The resulting spectra were analyzed using essential FTIR (eFTIR) software.
Buffering capacity of drugs
A tablet of lamivudine (150 mg) or metronidazole (200 mg) was crushed and dispersed in 500 mL of FaSSGF and FeSSIF separately. The change in pH of the medium was observed as the instantaneous pH change due to the added drugs. The amount of hydrochloric acid that produced one unit pH change with continuous pH monitoring was also determined.
Dissolution studies
A tablet each of lamivudine or metronidazole was dissolved in 500 mL of FeSSIF-V2 in a dissolution apparatus (USP type 2, paddle method). A tablet of AL was placed in the apparatus with speed of agitation and temperature at 100 rpm and 37oC, respectively. A volume of 5 mL of the dissolution media was sampled at 5, 15, 30, 45, 60 and 90 min. The sampled volume was filtered using 0.45 µm syringe filter. The filtrate was analyzed for artemether and lumefantrine concentration simultaneously using HPLC system.
Statistical analysis
All experiments were performed in triplicates and the differences in the effects of lamivudine or metronidazole on artemether and lumefantrine profile were analyzed statistically using single factor analysis of variance and statistical significant difference was taken at p < 0.05.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
In this study, FeSSIF-V2 was employed for AL dissolution studies as this medium has been extensively used to predict in vivo drug release (Lakka and Goswami, 2012). The content of FeSSIF-V2 such as sodium taurocholate and lecithin makes the output of this biorelevant medium to closely mimic intestinal environment (Vertzoni et al., 2005).The use of this updated postprandial biorelevant media, FeSSIF-V2, presents a readily available dissolution testing tool for quick adjudging of in vivo performance of drugs.
In the model simulating the co-administration of lamivudine or metronidazole with AL, the result of instantaneous pH change due to lamivudine or metronidazole on FeSSIF produced a pH increase of 0.13 and 0.17 units, respectively (Table 2). The increases were however not significant as the pH were still within the range of physiological value for intestinal absorption of drugs. In the stomach-simulated media (FaSSGF), the instantaneous pH change result gave an increase of 0.31 and 0.55 units, respectively. Since a pH change of less than 1 unit was recorded in the gastrum, the ratio of unionized to ionized form of the dissolved drugs (i.e., artemether and lumefantrine) becomes insignificant.
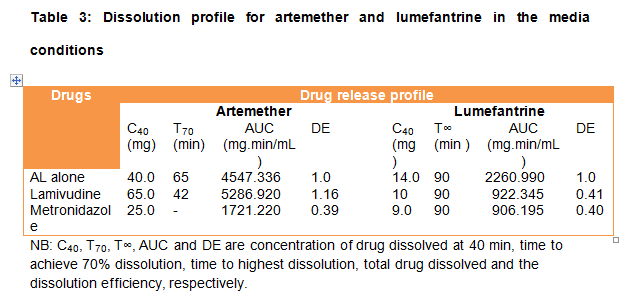
The R2 value for the determination of artemether and lumefantrine were 0.9920 and 0.9930, respectively. The dissolution curve for artemether and lumefantrine are presented in Figure 1a and 1b, respectively. It was observed that artemether had significantly higher drug release in the presence of lamivudine (p < 0.05).but there was no significant difference in the drug release profile for lumefantrine in the presence of either lamivudine or metronidazole.
An ideal formulation releases the exact amount of the active ingredient at the right time thereby optimizing the therapeutic action of the active ingredient (Dey et al, 2012). Drug release and other effects of co-administration of AL with other drugs have not been extensively evaluated. The dissolution profile for artemether and lumefantrine are expressed in Table 3. The C40 value for artemether in the medium containing metronidazole was significantly lower than that with lamivudine (25 versus 65 mg; p < 0.05). Media with metronidazole did not achieve 70% artemether release throughout the dissolution period. There was no difference in the dissolution profile for lumefantrine with respect to the additives (9.0 versus 10.0 mg). Lumefantrine did not achieve 70% release for the additives throughout the dissolution period.
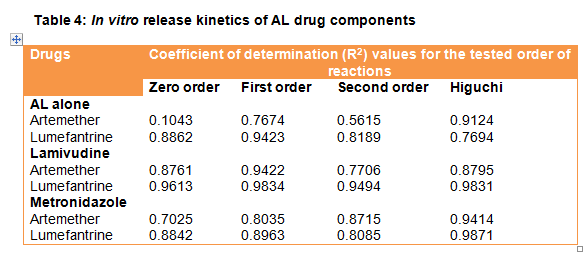
The R2 values of the media conditions describing the kinetic model that best describes the dissolution curves for artemether and lumefantrine drug release from AL tablet were Higuchi (R2 = 0.9124) and first-order (R2 = 0.9423), respectively. Table 4 presents the output for the coefficient of determination for the various tested models.
The basic information provided by the FTIR spectra analyses of drugs and their possible changes due to chemical interactions with the medium or chemical substances therein were compared for AL. The FTIR spectra analyses for AL and the mix (i.e., with the investigated drugs - lamivudine and metronidazole) are presented in Figure 3. The observed peaks for AL alone were compared with the characteristic spectra features of pure artemether and lumefantrine from the literature. This confirms the identity and the co-formulation status without interaction between actives or the excipients in the tablet as the spectra peaks for both artemether and lumefantrine were evident (Musibau et al., 2016).
In this study, the AL spectra in Figure 2a presented broad peaks at 3462.54 cm-1 due to the artemether component attributed to the aliphatic (O-H) bending. It also featured peak at 2937.48 cm-1 due to the aliphatic (C-H) stretching vibrations. The values here were found to be consistent with values for pure artemether spectra from the literature and the eFTIR software library. The AL sample exhibited broad peaks at 3419.79 cm-1due to aliphatic (C-H) stretching vibration and 2951.09 due to aliphatic (C-H) bending vibrations due to the lumefantrine entity. Previous study by Musibau and co-workers also confirmed the co-formulated status of the actives in AL (Musibau et al., 2016).This formed the baseline for the investigation of the effect of the co-pelletized studied drugs. A similar study conducted by Balaji and Kumari evaluating the formulation of immediate release pellets containing artemether and lumefantrine revealed artemether and lumefantrine spectral bands that were consistent with the literature values also indicating that artemether and lumefantrine in their product were co-formulated without any form of interactions (Balaji and Kumari, 2013). The inference therefore was that there was no breakdown in the structure of artemether in the co-formulation of the AL products. Similarly, the literature values for pure lumefantrine and the software library were in agreement with the characteristic spectra presentation of lumefantrine in the AL sampled in this study.
As observed in Figure 2, the spectra of artemether in the AL drug showed a broad peak at the wavenumber 3462.54 cm-1 and 2937.48 cm-1 due to (O-H and (C-H) stretching vibrations, respectively. The corresponding (O-H) stretching vibrations due to lamivudine and metronidazole were shifted downwards to 3387.0 and 3408.22 cm-1, respectively with respect to the plain AL spectral bands. The reference artemether band had 3379 and 2947 cm-1, respectively. Comparing the wavenumber difference for the effect of lamivudine and metronidazole with respect to the reference artemether band, they had values of 8 and 9 cm -1, respectively. The same arguments hold for the difference in wavenumber of peak expression for (C-H) stretching as approximately 18 and 9 cm-1, respectively. The endoperoxide bridge (C-O-O) demonstrated a broad IR stretching at 890 - 820 cm-1, adjudging by the reference artemether band. The co-pelletization with lamivudine and metronidazole did not affect the (C-O-O) stretching of artemether as they revealed IR spectra band within that range (i.e., 871.82 and 881.47 cm-1, respectively).
Similarly, the spectra for pure lumefantrine revealed a broad peak at 3394.72, 2951.82 and 1462.04 cm-1for (O-H) and (C-H) stretchings and for (C-H) bending, respectively (Figure 2). Comparing the spectra bands for AL alone revealed a co-formulated product of artemether and lumefantrine along with excipients with no complexation with respect to the lumefantrine component. Comparing the spectra bands for lamivudine and metronidazole when co-pelletized, shift in spectral wavenumber downwards of values 7 and 14 cm-1 were observed for (O-H) stretching due to the investigated drugs, respectively. Considering (C-H) stretching, the differences in band wavenumber values were 22 and 12 cm-1, respectively. The software adjudged the spectra on Figure 2B and 2C corresponding to lamivudine and metronidazole, respectively, as not having a significant shift in the spectral features of artemether or lumefantrine as presented in Figure 2A.
CONCLUSION
In this study, the presence of metronidazole or lamivudine in the admixture with AL has not significantly affected the FTIR spectra presentation of AL. There was no complex formed with AL by either lamivudine or metronidazole. AL tablet can be co-administered with either lamivudine or metronidazole, based on the in vitro assessments.
Furthermore, the release profile of AL drug components was affected by the presence of metronidazole but unaffected by lamivudine. The release of artemether from AL matrix in the presence of lamivudine and metronidazole were first order kinetics and Higuchi respectively. The release kinetics for lumefantrine for both drugs was Higuchi.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors are grateful to the Management of Central Research Laboratory of University of Lagos for the use of their equipments and Mr. PD Ojobor for his technical assistance.
AUTHOR’S STATEMENT
The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.


References:
- Adjei GO, Kurtzhal JA, Rodrigues OP, Alifrangis M, Hoegberg LC, Kitche ED, Badoe EV, Klamptey R, Coka BD. 2008. Amodiaquine – artesunate vs Artemether – lumefantrine Efficacy and Safety Trial with One Year Follow up. Mal J, 7:127.
- Ahsan MR, Sultan MZ, Amjad FM, Sultana S, Baki MM. 2012. Ofloxacin with Paracetamol and Zinc in Aqueous Medium. J Sci Res, 4:201 – 708.
- Bennett PN, Brown MJ 2008. Clinical Pharmacology (10thedn) Church Hill Livingstone Elsevier, Edinburgh London, New York Oxford, Philadelphia, St. Louis, Syndney, Toronto Pp. 74 – 114.
- Bercu TE. 2007. Amoebic Colitis: New Insights into Pathogenesis and Treatment. Curr Gastroenterol Rep, 9(5): 429-33.
- CDC. 2008. HIV Transmission through Transfusion- Missouri and Colorado, 2008. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 59 (41):1335-9. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20966896. (Accessed 12 January, 2015)
- Cohen MS, Hellmann N, Levy JA, DeCock K, Lange J. 2008. The Spread, Treatment, and Prevention of HIV-1: Evolution of a Global Pandemic. The J Clin Invest, 18 (4): 1244–54.
- Dey S, Dutta S, Mazumder B. 2012. Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Matrix Tablet of Atenolol for Gastroretentive Drug Delivery. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci, 3: 433-437.
- Edwards IR, Aronson JK. 2000. Adverse Drug Reactions: Definitions, Diagnosis and Management. Lancet, 356:1255 – 1259.
- Galia E, Nicolaides E, Horter D, Lobenberg R, Reppas C, Dressman JB. 1998 Evaluation of Various Dissolution Media for Predicting In Vivo Performance of Class I and II Drugs. Pharm Res, 15(5): 698-705.
- Gonzales ML. 2009. Antiamoebic Drugs for Treating Amoebic Colitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 15(2): CD0060085.
- Huang L, Lizak PS, Javewardene AL, Marzan F, Lee MN, Aweeka FT. 2010. A modified method for determination of lumefantrine in human plasma by HPLC-UV and combination of Protein Precipitation by solid Phase Extraction: application to a Pharmacokinetic Study. Anal Chem Insight, 29(5): 15-23.
- Haque R, Huston CD, Hughes M, Houpt E, Petri WA. 2003. Current Concepts in Amoebiasis. N Engl J Med, 348: 1565-73.
- Kumari MH, Balaji A. 2013. Formulation and Evaluation of Immediate Release Pellets Containing Artemether and Lumefantrine. Int J Pharm Ind Res, 03(04): 335-345.
- Kumari MH. 2013. Recent Novel Advancements in Pellet Formulation: A Review. Int J Pharm Sci Res, 4(10): 3803-382.
- Lakka NS, Goswami N. 2012. Solubility and Dissolution Profile Studies of Gliclazide in Pharmaceutical Formulation by RP-HPLC. Int J Pharm, 3 (6): 126-129.
- Morris CA, Lopez-Lazaro L, Jung D, Methareethorn J, Duparc C, Borghini-Fuhrer I, Pokorny R, Shin CS, Fleckenstein L. 2012. A Study of Drug-Drug Interaction of Pyroaridine/artesunate and ritonavir in healthy volunteer. Am J Trop Med Hyg, 86(3):489-495.
- Mustapha MA, Iwuagwu MA, Uhumwangho MI. 2016. Comparison of Performance Indices of Artemether-lumefantrine Fixed Dose Combination Tablets using Quality by Design Approach 1: Physico-technical Metrics Evaluation. J Pharm Sci Tech, 5(2):105-108.
- Rosenthal PJ. 2014. Protozoal and Helminthic Infection. In: Current Medical Diagnosis and treatment. Papadakis MA, McPhee SJ, Rabow MW (Eds), McGraw Hill Education, 53rd Ed. 1442-1477.
- Schooley RT. 2010. Antiretroviral Treatment of Adult HIV Infection. JAMA, 304 (3):321-333. doi 10,1001/jama.2010.1004.
- Sunesen VH, Pedersen BL, Kristensen HG, Mullertz A. 2005. In vivo / in vitro correlation for a poorly soluble drug, danazol using the flow through dissolution method with biorelevant dissolution media. Eur J Pharm Sci, 24: 305-313.
- Thompson MA, Aberg JA, Cahn P, Montaner SG, Rizzmadini G, Telenti A, Gatel JM, Gunthard HR, Hammer SM, Hirsch MS, Jacobsen DM, Reiss P, Richmann DD, Volberding PA, Yeni P, Vertzoni M, Dressman J, Buffer J, Thempenstall J, Reppas C. 2005. Simulating of Fasting Gastric Conditions and its Importance for the In-vivo Dissolution of Lipophilic Compounds. Eur J Pharm Biopharm, 60 (3): 413 – 417).
- Wienka LC, Heath TG. 2005. Predicting In vivo Drug Interaction from In Vitro Drug Discovery Data. Nature, 4: 825-833.
- World Health Organization. 2015. Guidelines for the treatment of malaria, 3rd ed., WHO, Geneva 2015. http://www.who.int/malaria/publications/atoz/9789241549127/en/ (Accessed on September 10, 2015).
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License